#include <stdio.h>#include <stdlib.h>#include <string.h>#include <math.h>#include "misc/util/util_hack.h"#include "epd.h"
Go to the source code of this file.
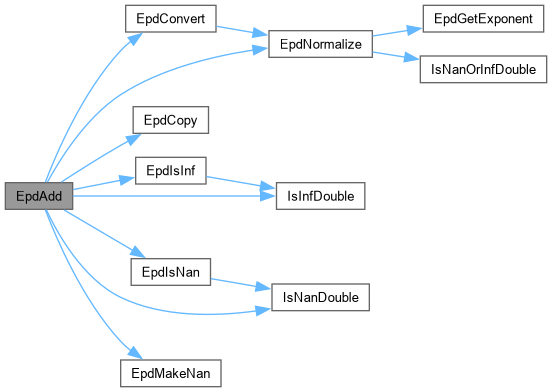
| void EpdAdd | ( | EpDouble * | epd1, |
| double | value ) |
Function********************************************************************
Synopsis [Adds two arbitrary precision double values.]
Description [Adds two arbitrary precision double values.]
SideEffects []
SeeAlso []
Definition at line 536 of file epd.c.
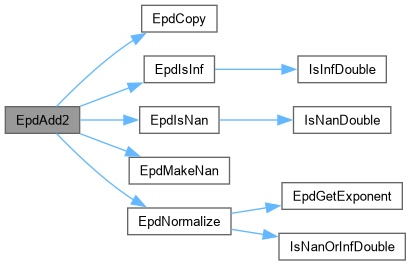
Function********************************************************************
Synopsis [Adds two arbitrary precision double values.]
Description [Adds two arbitrary precision double values.]
SideEffects []
SeeAlso []
Definition at line 598 of file epd.c.
Function********************************************************************
Synopsis [Adds two arbitrary precision double values.]
Description [Adds two arbitrary precision double values.]
SideEffects []
SeeAlso []
Definition at line 660 of file epd.c.
| ABC_NAMESPACE_IMPL_START EpDouble * EpdAlloc | ( | void | ) |
CFile***********************************************************************
FileName [epd.c]
PackageName [epd]
Synopsis [Arithmetic functions with extended double precision.]
Description []
SeeAlso []
Author [In-Ho Moon]
Copyright [Copyright (c) 1995-2004, Regents of the University of Colorado
All rights reserved.
Redistribution and use in source and binary forms, with or without modification, are permitted provided that the following conditions are met:
Redistributions of source code must retain the above copyright notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer.
Redistributions in binary form must reproduce the above copyright notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer in the documentation and/or other materials provided with the distribution.
Neither the name of the University of Colorado nor the names of its contributors may be used to endorse or promote products derived from this software without specific prior written permission.
THIS SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED BY THE COPYRIGHT HOLDERS AND CONTRIBUTORS "AS IS" AND ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTIES, INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE ARE DISCLAIMED. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE COPYRIGHT OWNER OR CONTRIBUTORS BE LIABLE FOR ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT, INCIDENTAL, SPECIAL, EXEMPLARY, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES (INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, PROCUREMENT OF SUBSTITUTE GOODS OR SERVICES; LOSS OF USE, DATA, OR PROFITS; OR BUSINESS INTERRUPTION) HOWEVER CAUSED AND ON ANY THEORY OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT LIABILITY, OR TORT (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE OF THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE.]
Revision [
] Function********************************************************************
Synopsis [Allocates an EpDouble struct.]
Description [Allocates an EpDouble struct.]
SideEffects []
SeeAlso []
| void EpdConvert | ( | double | value, |
| EpDouble * | epd ) |
Function********************************************************************
Synopsis [Converts double to EpDouble struct.]
Description [Converts double to EpDouble struct.]
SideEffects []
SeeAlso []
Definition at line 185 of file epd.c.
| void EpdDivide | ( | EpDouble * | epd1, |
| double | value ) |
Function********************************************************************
Synopsis [Divides two arbitrary precision double values.]
Description [Divides two arbitrary precision double values.]
SideEffects []
SeeAlso []
Definition at line 386 of file epd.c.
Function********************************************************************
Synopsis [Divides two arbitrary precision double values.]
Description [Divides two arbitrary precision double values.]
SideEffects []
SeeAlso []
Definition at line 439 of file epd.c.
Function********************************************************************
Synopsis [Divides two arbitrary precision double values.]
Description [Divides two arbitrary precision double values.]
SideEffects []
SeeAlso []
Definition at line 490 of file epd.c.
| void EpdFree | ( | EpDouble * | epd | ) |
| int EpdGetExponent | ( | double | value | ) |
Function********************************************************************
Synopsis [Returns the exponent value of a double.]
Description [Returns the exponent value of a double.]
SideEffects []
SeeAlso []
Definition at line 1068 of file epd.c.
| int EpdGetExponentDecimal | ( | double | value | ) |
Function********************************************************************
Synopsis [Returns the decimal exponent value of a double.]
Description [Returns the decimal exponent value of a double.]
SideEffects []
SeeAlso []
Definition at line 1091 of file epd.c.


| void EpdGetString | ( | EpDouble * | epd, |
| char * | str ) |
Function********************************************************************
Synopsis [Converts an arbitrary precision double value to a string.]
Description [Converts an arbitrary precision double value to a string.]
SideEffects []
SeeAlso []
Definition at line 135 of file epd.c.
| void EpdGetValueAndDecimalExponent | ( | EpDouble * | epd, |
| double * | value, | ||
| int * | exponent ) |
Function********************************************************************
Synopsis [Returns value and decimal exponent of EpDouble.]
Description [Returns value and decimal exponent of EpDouble.]
SideEffects []
SeeAlso []
Definition at line 1034 of file epd.c.

| int EpdIsInf | ( | EpDouble * | epd | ) |
Function********************************************************************
Synopsis [Checks whether the value is Inf.]
Description [Checks whether the value is Inf.]
SideEffects []
SeeAlso []
Definition at line 1201 of file epd.c.
| int EpdIsNan | ( | EpDouble * | epd | ) |
Function********************************************************************
Synopsis [Checks whether the value is NaN.]
Description [Checks whether the value is NaN.]
SideEffects []
SeeAlso []
Definition at line 1240 of file epd.c.
| int EpdIsNanOrInf | ( | EpDouble * | epd | ) |
Function********************************************************************
Synopsis [Checks whether the value is NaN or Inf.]
Description [Checks whether the value is NaN or Inf.]
SideEffects []
SeeAlso []
Definition at line 1258 of file epd.c.

| int EpdIsZero | ( | EpDouble * | epd | ) |
| void EpdMakeInf | ( | EpDouble * | epd, |
| int | sign ) |
| void EpdMakeNan | ( | EpDouble * | epd | ) |
| void EpdMakeZero | ( | EpDouble * | epd, |
| int | sign ) |
| void EpdMultiply | ( | EpDouble * | epd1, |
| double | value ) |
Function********************************************************************
Synopsis [Multiplies two arbitrary precision double values.]
Description [Multiplies two arbitrary precision double values.]
SideEffects []
SeeAlso []
Definition at line 205 of file epd.c.
Function********************************************************************
Synopsis [Multiplies two arbitrary precision double values.]
Description [Multiplies two arbitrary precision double values.]
SideEffects []
SeeAlso []
Definition at line 246 of file epd.c.
Function********************************************************************
Synopsis [Multiplies two arbitrary precision double values.]
Description [Multiplies two arbitrary precision double values.]
SideEffects []
SeeAlso []
Definition at line 285 of file epd.c.

Function********************************************************************
Synopsis [Multiplies two arbitrary precision double values.]
Description [Multiplies two arbitrary precision double values.]
SideEffects []
SeeAlso []
Definition at line 321 of file epd.c.
Function********************************************************************
Synopsis [Multiplies two arbitrary precision double values.]
Description [Multiplies two arbitrary precision double values.]
SideEffects []
SeeAlso []
Definition at line 355 of file epd.c.


| void EpdNormalize | ( | EpDouble * | epd | ) |
Function********************************************************************
Synopsis [Normalize an arbitrary precision double value.]
Description [Normalize an arbitrary precision double value.]
SideEffects []
SeeAlso []
Definition at line 977 of file epd.c.
| void EpdNormalizeDecimal | ( | EpDouble * | epd | ) |
Function********************************************************************
Synopsis [Normalize an arbitrary precision double value.]
Description [Normalize an arbitrary precision double value.]
SideEffects []
SeeAlso []
Definition at line 1007 of file epd.c.
| void EpdPow2 | ( | int | n, |
| EpDouble * | epd ) |
Function********************************************************************
Synopsis [Computes arbitrary precision pow of base 2.]
Description [Computes arbitrary precision pow of base 2.]
SideEffects []
SeeAlso []
Definition at line 917 of file epd.c.

| void EpdPow2Decimal | ( | int | n, |
| EpDouble * | epd ) |
Function********************************************************************
Synopsis [Computes arbitrary precision pow of base 2.]
Description [Computes arbitrary precision pow of base 2.]
SideEffects []
SeeAlso []
Definition at line 946 of file epd.c.

| void EpdSubtract | ( | EpDouble * | epd1, |
| double | value ) |
Function********************************************************************
Synopsis [Subtracts two arbitrary precision double values.]
Description [Subtracts two arbitrary precision double values.]
SideEffects []
SeeAlso []
Definition at line 726 of file epd.c.

Function********************************************************************
Synopsis [Subtracts two arbitrary precision double values.]
Description [Subtracts two arbitrary precision double values.]
SideEffects []
SeeAlso []
Definition at line 788 of file epd.c.
Function********************************************************************
Synopsis [Subtracts two arbitrary precision double values.]
Description [Subtracts two arbitrary precision double values.]
SideEffects []
SeeAlso []
Definition at line 850 of file epd.c.
| int IsInfDouble | ( | double | value | ) |
Function********************************************************************
Synopsis [Checks whether the value is Inf.]
Description [Checks whether the value is Inf.]
SideEffects []
SeeAlso []
Definition at line 1276 of file epd.c.
| int IsNanDouble | ( | double | value | ) |
Function********************************************************************
Synopsis [Checks whether the value is NaN.]
Description [Checks whether the value is NaN.]
SideEffects []
SeeAlso []
Definition at line 1305 of file epd.c.
| int IsNanOrInfDouble | ( | double | value | ) |
Function********************************************************************
Synopsis [Checks whether the value is NaN or Inf.]
Description [Checks whether the value is NaN or Inf.]
SideEffects []
SeeAlso []
Definition at line 1333 of file epd.c.