#include <stdio.h>#include <stdlib.h>#include <string.h>#include <assert.h>#include "satStore.h"
Go to the source code of this file.
Classes | |
| struct | Int_Man_t_ |
Functions | |
| Int_Man_t * | Int_ManAlloc () |
| FUNCTION DEFINITIONS ///. | |
| int * | Int_ManSetGlobalVars (Int_Man_t *p, int nGloVars) |
| int | Int_ManGlobalVars (Int_Man_t *p) |
| void | Int_ManResize (Int_Man_t *p) |
| void | Int_ManFree (Int_Man_t *p) |
| void | Int_ManPrintClause (Int_Man_t *p, Sto_Cls_t *pClause) |
| void | Int_ManPrintResolvent (lit *pResLits, int nResLits) |
| void | Extra_PrintBinary__ (FILE *pFile, unsigned Sign[], int nBits) |
| void | Int_ManPrintInterOne (Int_Man_t *p, Sto_Cls_t *pClause) |
| Sto_Cls_t * | Int_ManPropagate (Int_Man_t *p, int Start) |
| void | Int_ManProofWriteOne (Int_Man_t *p, Sto_Cls_t *pClause) |
| int | Int_ManProofTraceOne (Int_Man_t *p, Sto_Cls_t *pConflict, Sto_Cls_t *pFinal) |
| int | Int_ManProofRecordOne (Int_Man_t *p, Sto_Cls_t *pClause) |
| int | Int_ManProcessRoots (Int_Man_t *p) |
| void | Int_ManPrepareInter (Int_Man_t *p) |
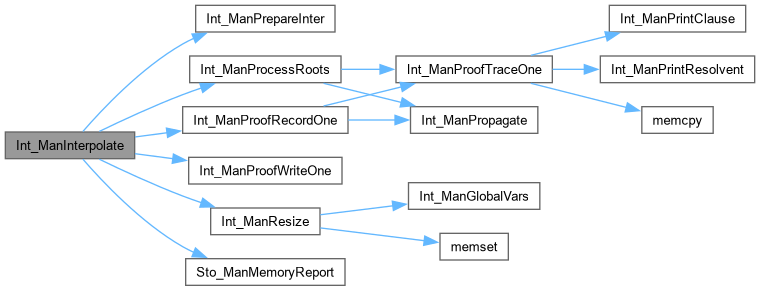
| int | Int_ManInterpolate (Int_Man_t *p, Sto_Man_t *pCnf, int fVerbose, unsigned **ppResult) |
| void Extra_PrintBinary__ | ( | FILE * | pFile, |
| unsigned | Sign[], | ||
| int | nBits ) |
Function*************************************************************
Synopsis [Records the proof.]
Description []
SideEffects []
SeeAlso []
Definition at line 347 of file satInter.c.
| Int_Man_t * Int_ManAlloc | ( | ) |
FUNCTION DEFINITIONS ///.
Function*************************************************************
Synopsis [Allocate proof manager.]
Description []
SideEffects []
SeeAlso []
Definition at line 107 of file satInter.c.
| void Int_ManFree | ( | Int_Man_t * | p | ) |
Function*************************************************************
Synopsis [Deallocate proof manager.]
Description []
SideEffects []
SeeAlso []
Definition at line 273 of file satInter.c.
| int Int_ManGlobalVars | ( | Int_Man_t * | p | ) |
Function*************************************************************
Synopsis [Count common variables in the clauses of A and B.]
Description []
SideEffects []
SeeAlso []
Definition at line 150 of file satInter.c.
Function*************************************************************
Synopsis [Computes interpolant for the given CNF.]
Description [Returns the number of common variable found and interpolant. Returns 0, if something did not work.]
SideEffects []
SeeAlso []
Definition at line 1005 of file satInter.c.
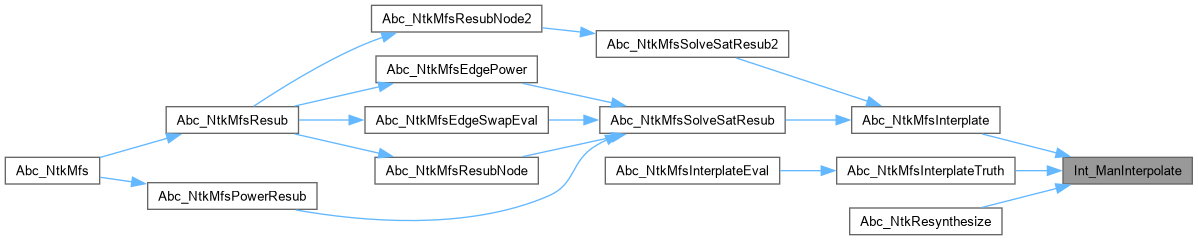
| void Int_ManPrepareInter | ( | Int_Man_t * | p | ) |
Function*************************************************************
Synopsis [Records the proof.]
Description []
SideEffects []
SeeAlso []
Definition at line 948 of file satInter.c.
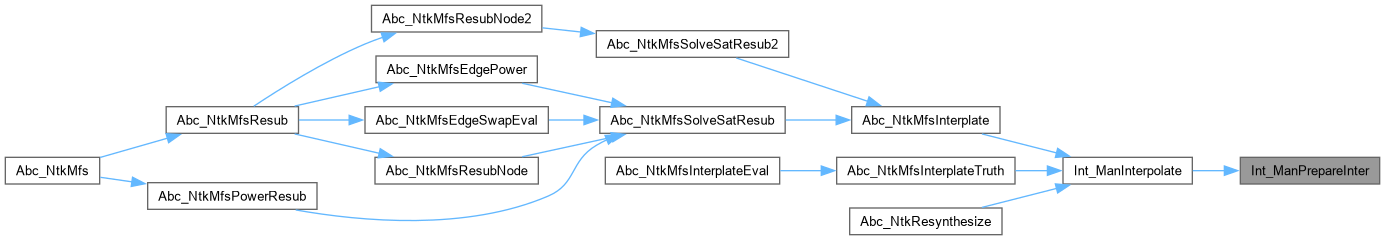
Function*************************************************************
Synopsis [Prints the clause.]
Description []
SideEffects []
SeeAlso []
Definition at line 307 of file satInter.c.
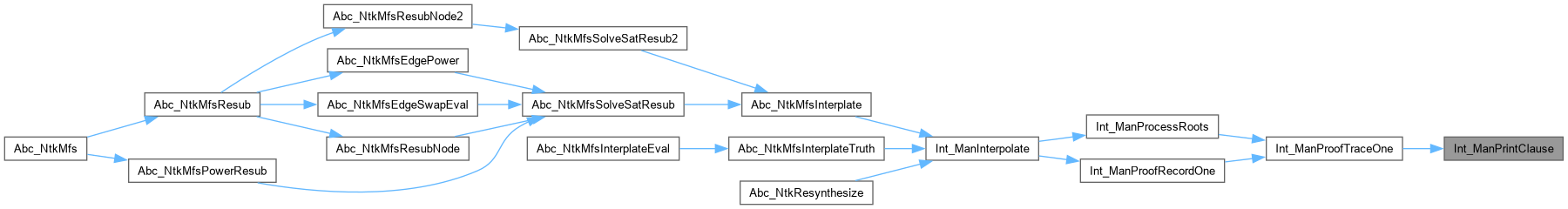
Function*************************************************************
Synopsis [Prints the interpolant for one clause.]
Description []
SideEffects []
SeeAlso []
Definition at line 371 of file satInter.c.
| void Int_ManPrintResolvent | ( | lit * | pResLits, |
| int | nResLits ) |
Function*************************************************************
Synopsis [Prints the resolvent.]
Description []
SideEffects []
SeeAlso []
Definition at line 327 of file satInter.c.
| int Int_ManProcessRoots | ( | Int_Man_t * | p | ) |
Function*************************************************************
Synopsis [Propagate the root clauses.]
Description []
SideEffects []
SeeAlso []
Definition at line 875 of file satInter.c.

Function*************************************************************
Synopsis [Records the proof for one clause.]
Description []
SideEffects []
SeeAlso []
Definition at line 770 of file satInter.c.
Function*************************************************************
Synopsis [Traces the proof for one clause.]
Description []
SideEffects []
SeeAlso []
Definition at line 589 of file satInter.c.
Function*************************************************************
Synopsis [Writes one root clause into a file.]
Description []
SideEffects []
SeeAlso []
Definition at line 564 of file satInter.c.
Function*************************************************************
Synopsis [Propagate the current assignments.]
Description []
SideEffects []
SeeAlso []
Definition at line 534 of file satInter.c.
| void Int_ManResize | ( | Int_Man_t * | p | ) |
Function*************************************************************
Synopsis [Resize proof manager.]
Description []
SideEffects []
SeeAlso []
Definition at line 209 of file satInter.c.
| int * Int_ManSetGlobalVars | ( | Int_Man_t * | p, |
| int | nGloVars ) |
Function*************************************************************
Synopsis [Allocate proof manager.]
Description []
SideEffects []
SeeAlso []
Definition at line 133 of file satInter.c.