#include <internal.hpp>
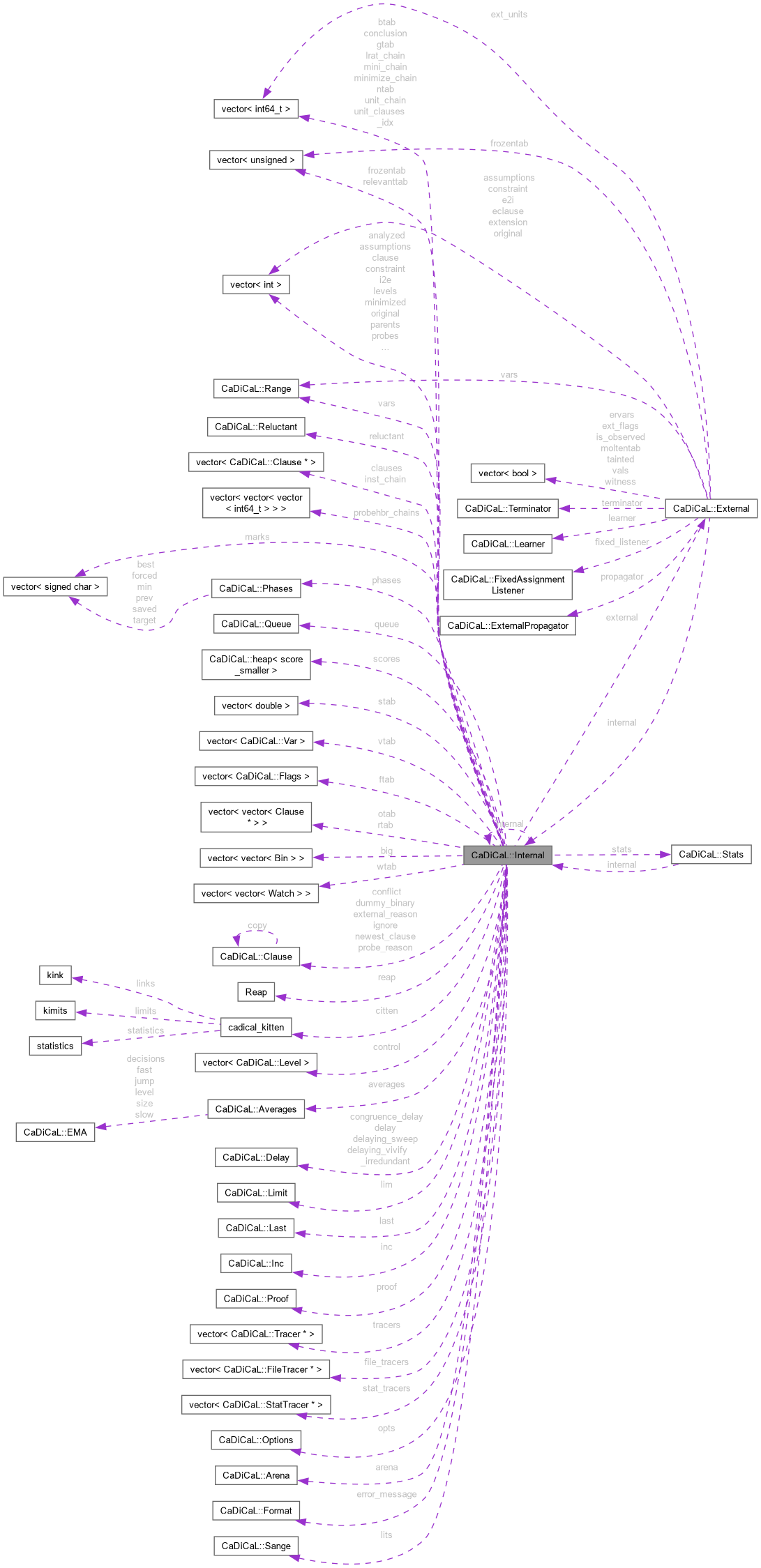
Public Types | |
| enum | Mode { BLOCK = (1 << 0) , CONDITION = (1 << 1) , CONGRUENCE = (1 << 2) , COVER = (1 << 3) , DECOMP = (1 << 4) , DEDUP = (1 << 5) , ELIM = (1 << 6) , FACTOR = (1 << 7) , LUCKY = (1 << 8) , PROBE = (1 << 9) , SEARCH = (1 << 10) , SIMPLIFY = (1 << 11) , SUBSUME = (1 << 12) , SWEEP = (1 << 13) , TERNARY = (1 << 14) , TRANSRED = (1 << 15) , VIVIFY = (1 << 16) , WALK = (1 << 17) } |
Static Public Member Functions | |
| static bool | is_valid_limit (const char *name) |
Definition at line 136 of file internal.hpp.
| Enumerator | |
|---|---|
| BLOCK | |
| CONDITION | |
| CONGRUENCE | |
| COVER | |
| DECOMP | |
| DEDUP | |
| ELIM | |
| FACTOR | |
| LUCKY | |
| PROBE | |
| SEARCH | |
| SIMPLIFY | |
| SUBSUME | |
| SWEEP | |
| TERNARY | |
| TRANSRED | |
| VIVIFY | |
| WALK | |
Definition at line 143 of file internal.hpp.
| CaDiCaL::Internal::Internal | ( | ) |
Definition at line 12 of file cadical_internal.cpp.
| CaDiCaL::Internal::~Internal | ( | ) |
Definition at line 56 of file cadical_internal.cpp.
|
inline |
Definition at line 362 of file internal.hpp.
|
inline |
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::add_core | ( | Sweeper & | sweeper, |
| unsigned | core_idx ) |
Definition at line 494 of file cadical_sweep.cpp.
Definition at line 478 of file cadical_external_propagate.cpp.
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::add_factored_divider | ( | Quotient * | q, |
| int | fresh ) |
Definition at line 599 of file cadical_factor.cpp.
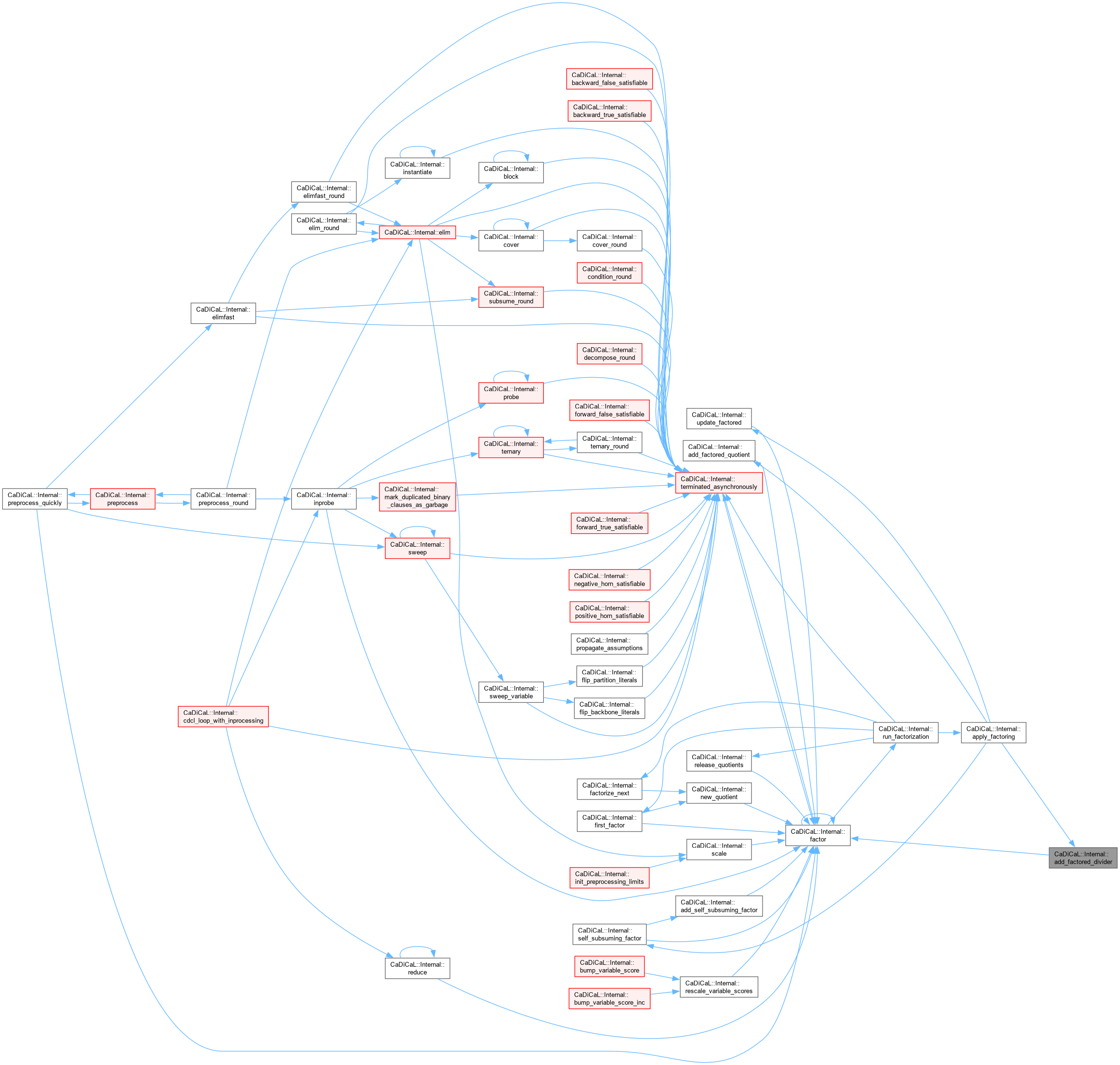
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::add_factored_quotient | ( | Quotient * | q, |
| int | not_fresh ) |
Definition at line 631 of file cadical_factor.cpp.
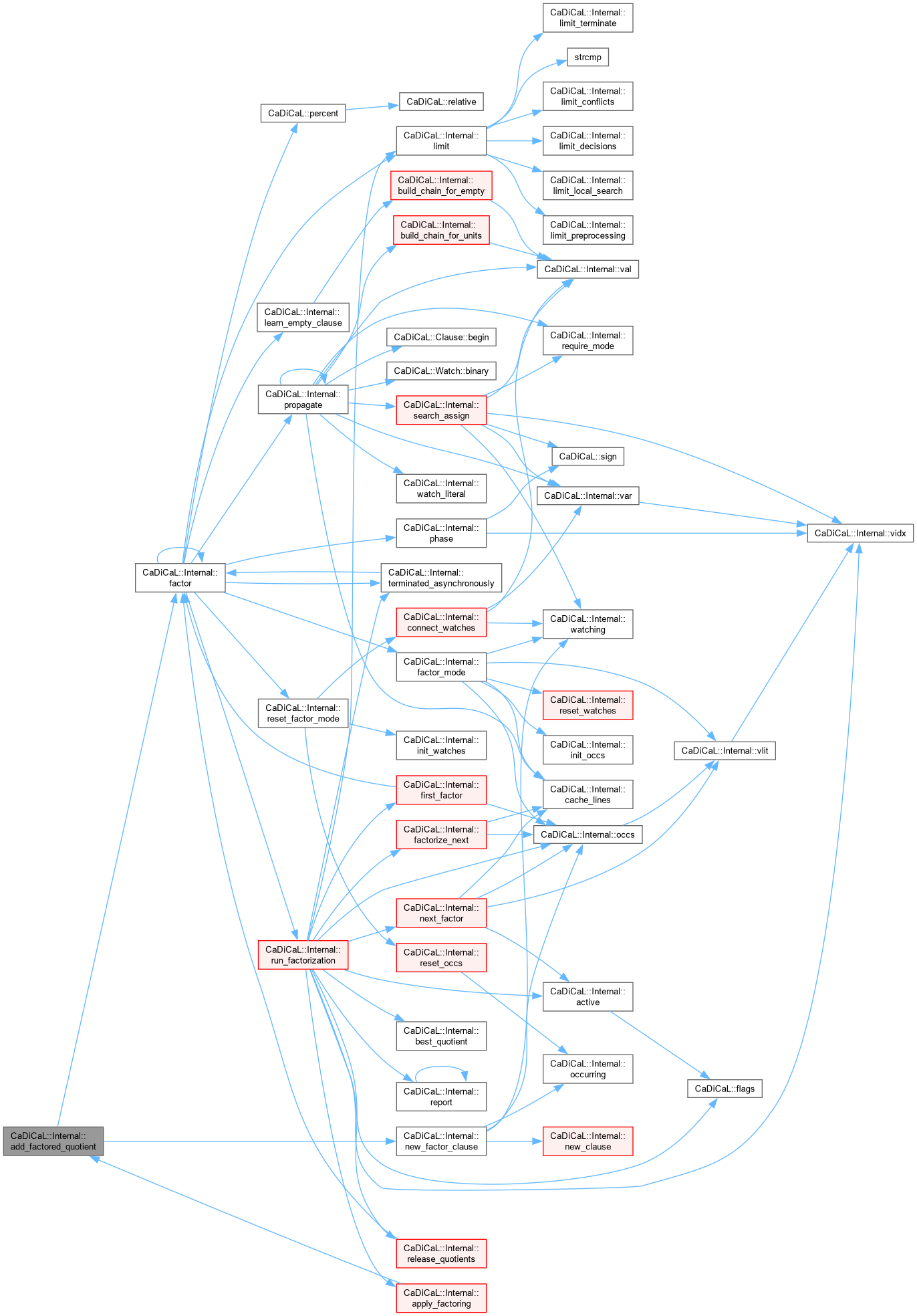
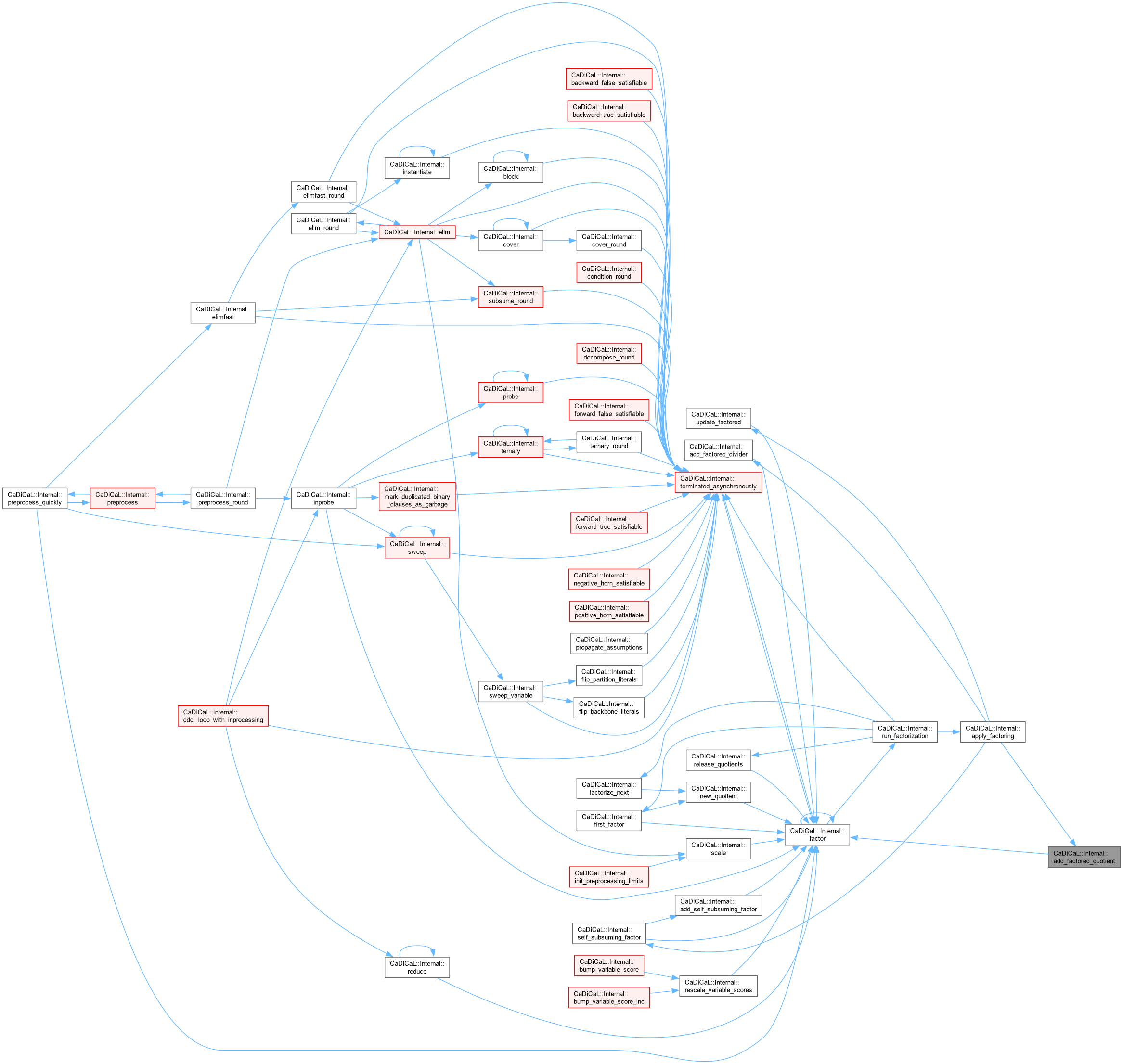
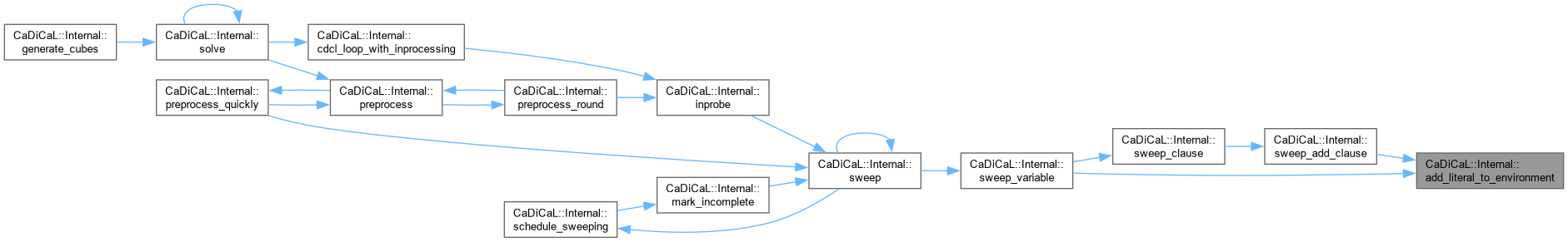
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::add_literal_to_environment | ( | Sweeper & | sweeper, |
| unsigned | depth, | ||
| int | lit ) |
Definition at line 343 of file cadical_sweep.cpp.
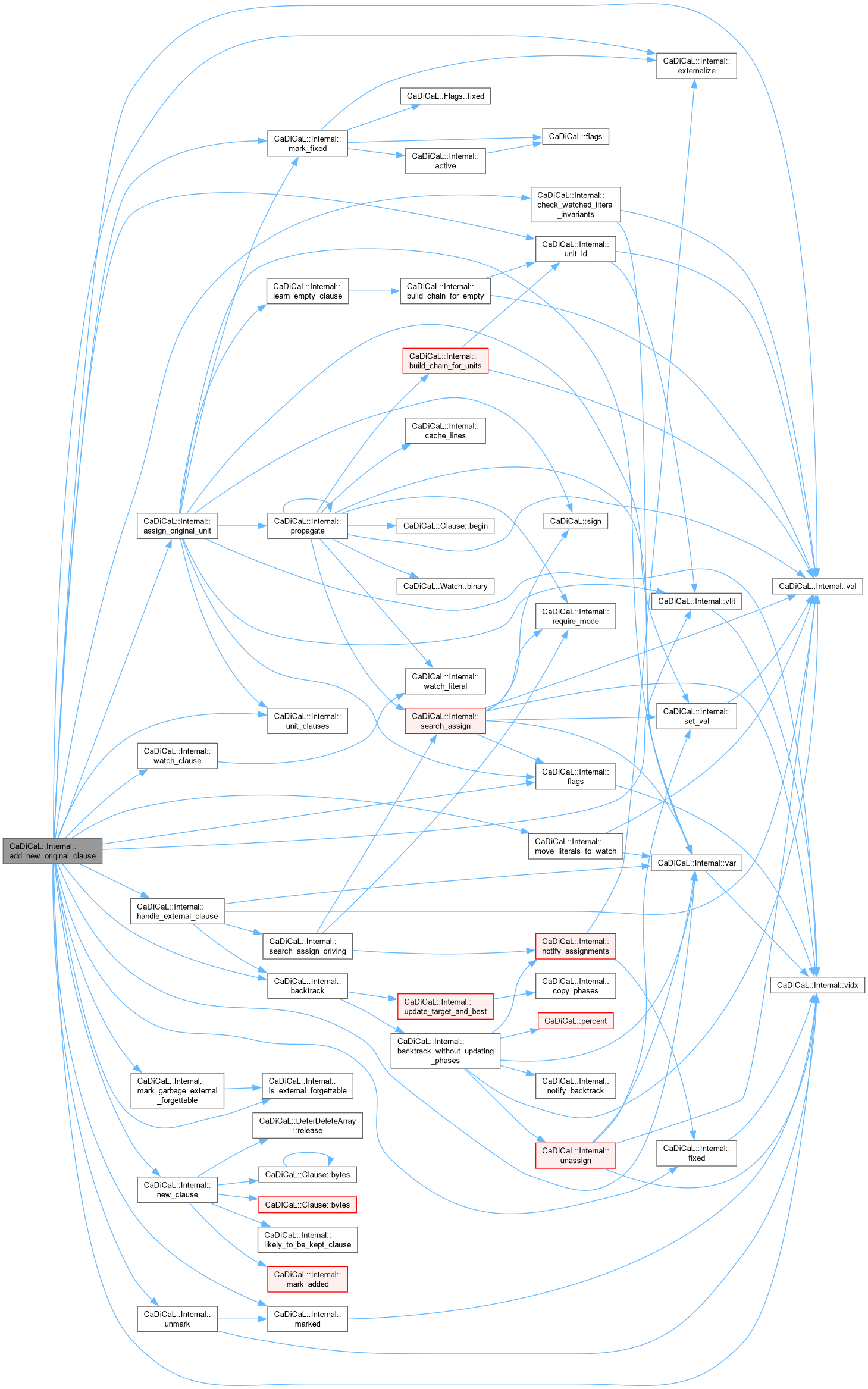
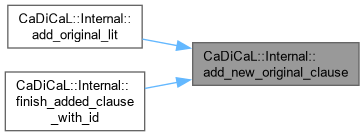
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::add_new_original_clause | ( | int64_t | id | ) |
Definition at line 385 of file cadical_clause.cpp.
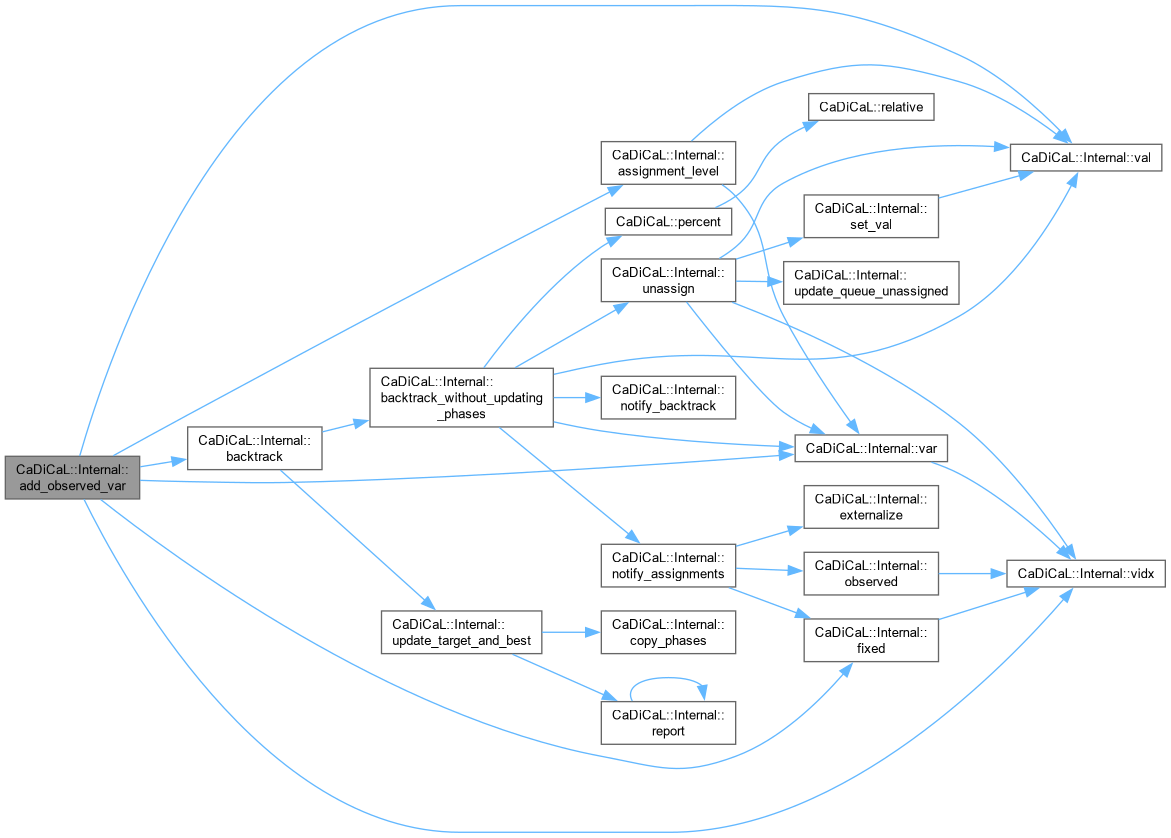
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::add_observed_var | ( | int | ilit | ) |
Definition at line 14 of file cadical_external_propagate.cpp.
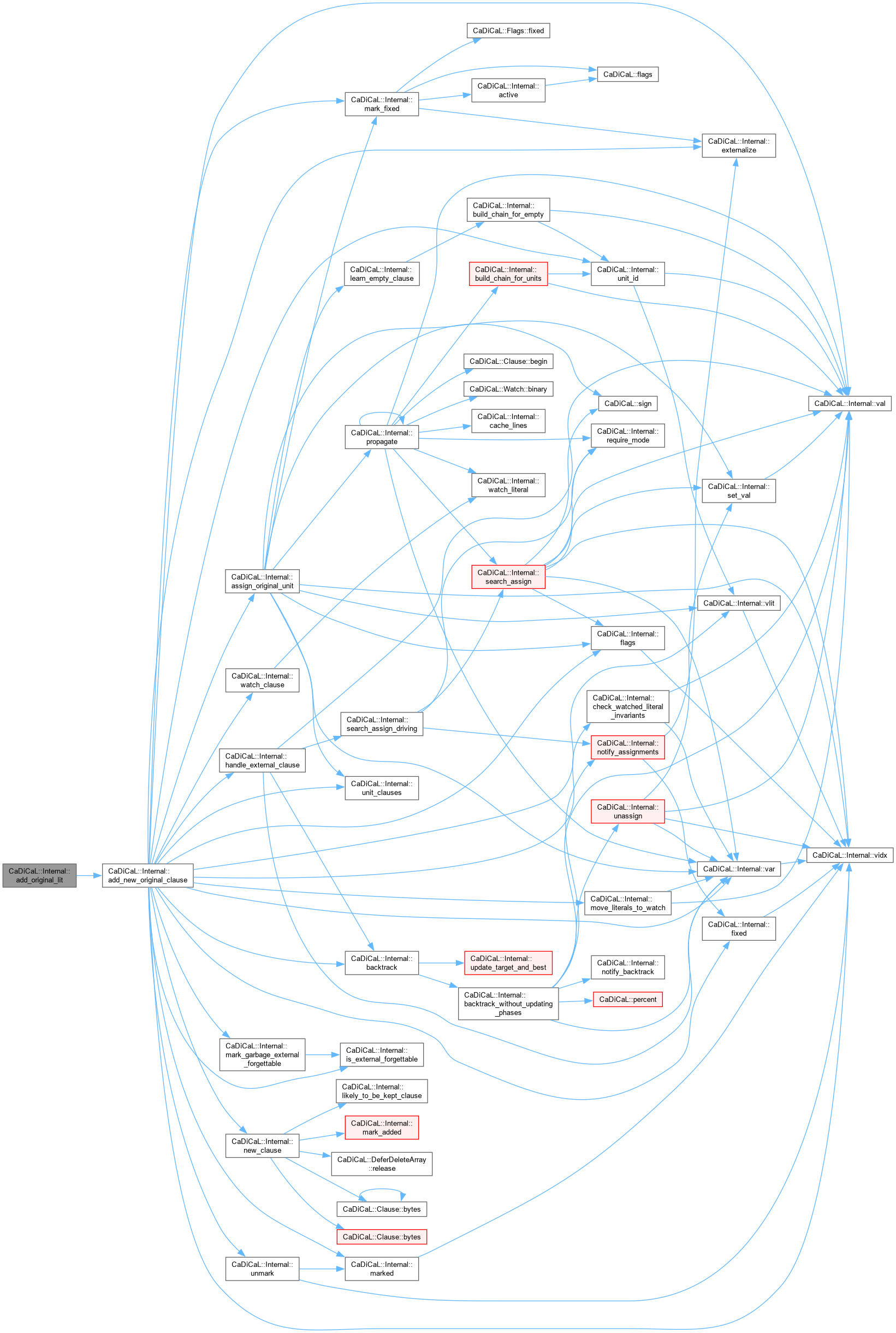
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::add_original_lit | ( | int | lit | ) |
Definition at line 184 of file cadical_internal.cpp.
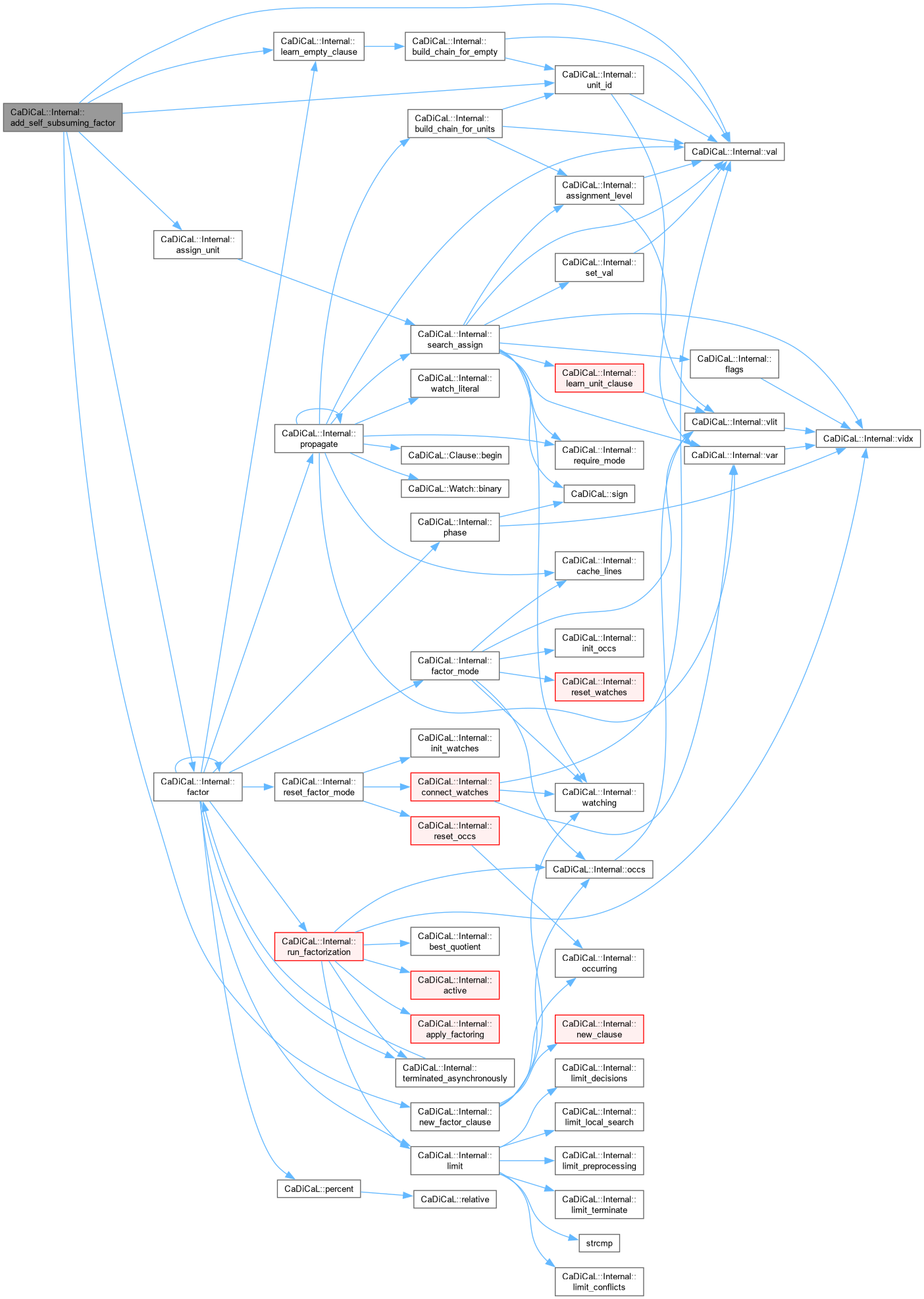
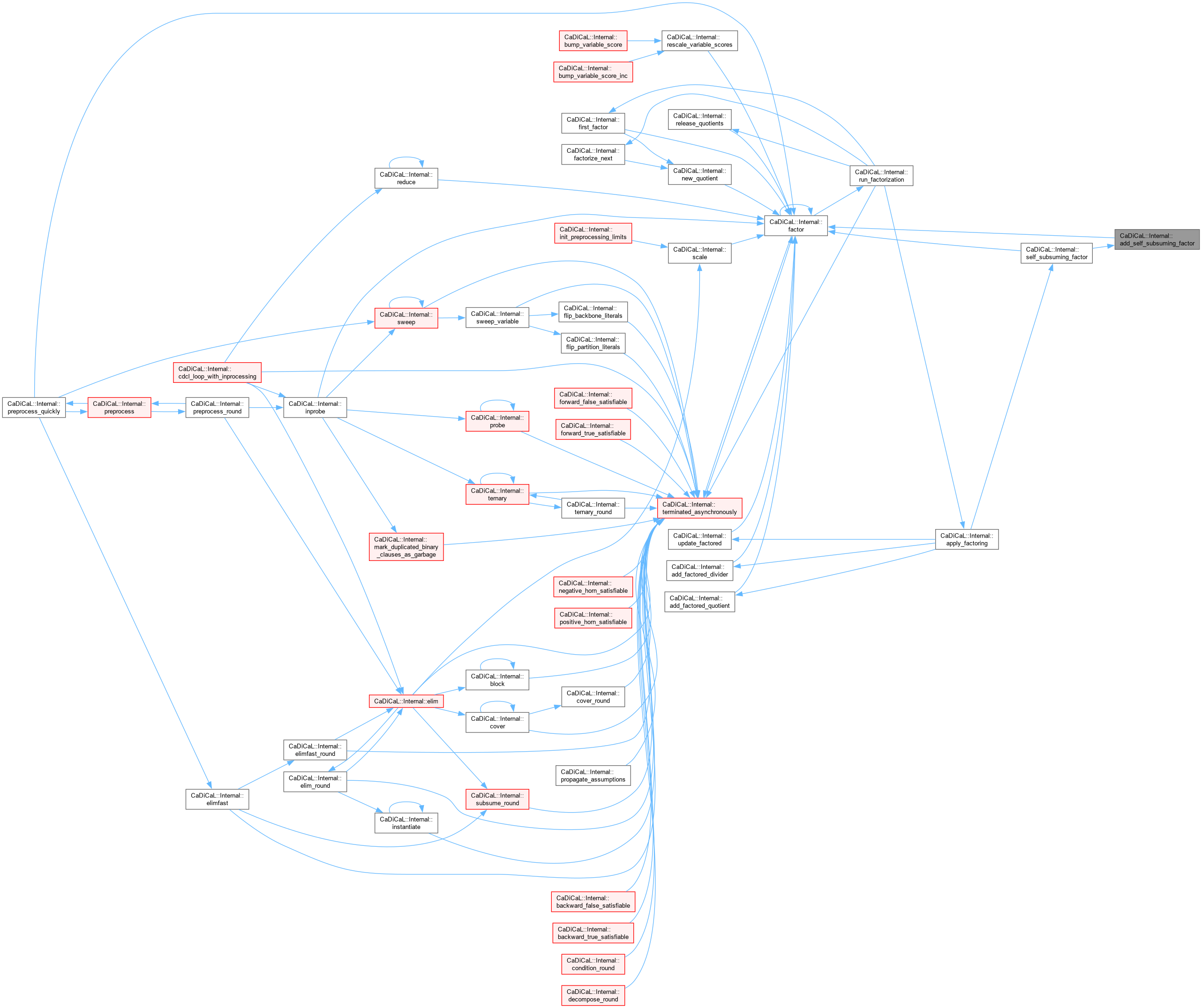
Definition at line 510 of file cadical_factor.cpp.
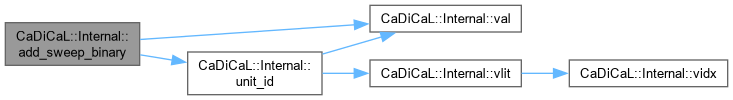
| int64_t CaDiCaL::Internal::add_sweep_binary | ( | sweep_proof_clause | pc, |
| int | lit, | ||
| int | other ) |
Definition at line 899 of file cadical_sweep.cpp.
| int CaDiCaL::Internal::already_solved | ( | ) |
Definition at line 941 of file cadical_internal.cpp.
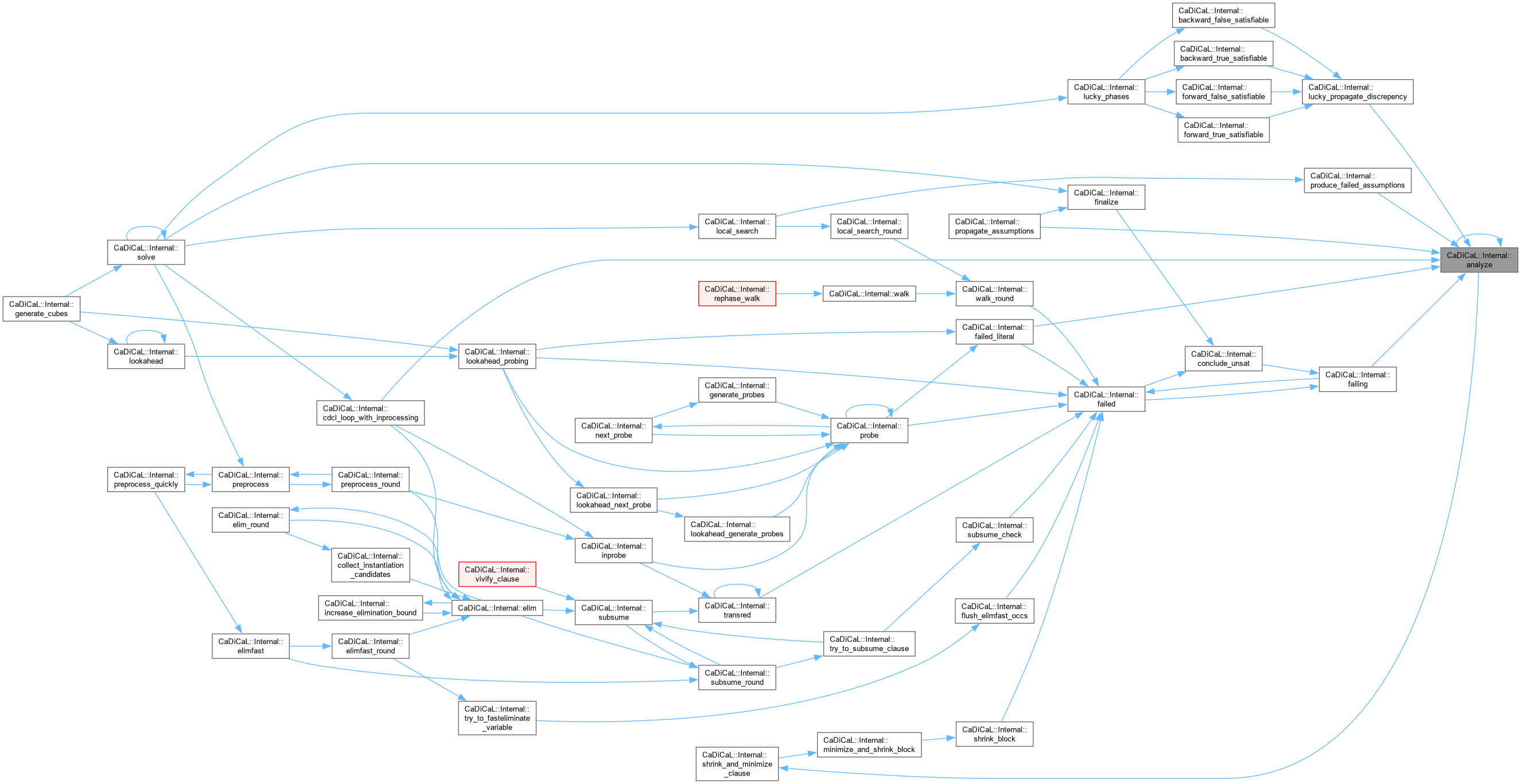
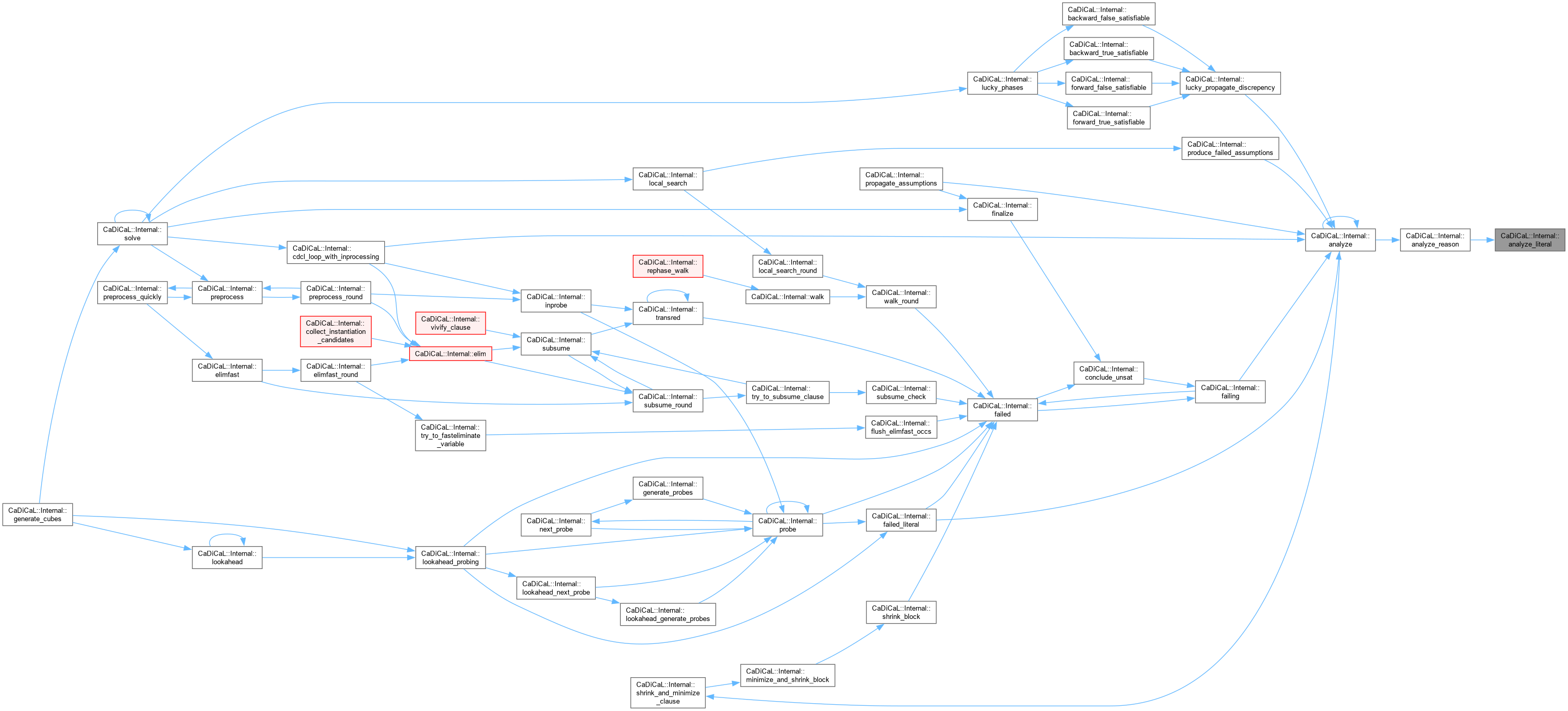
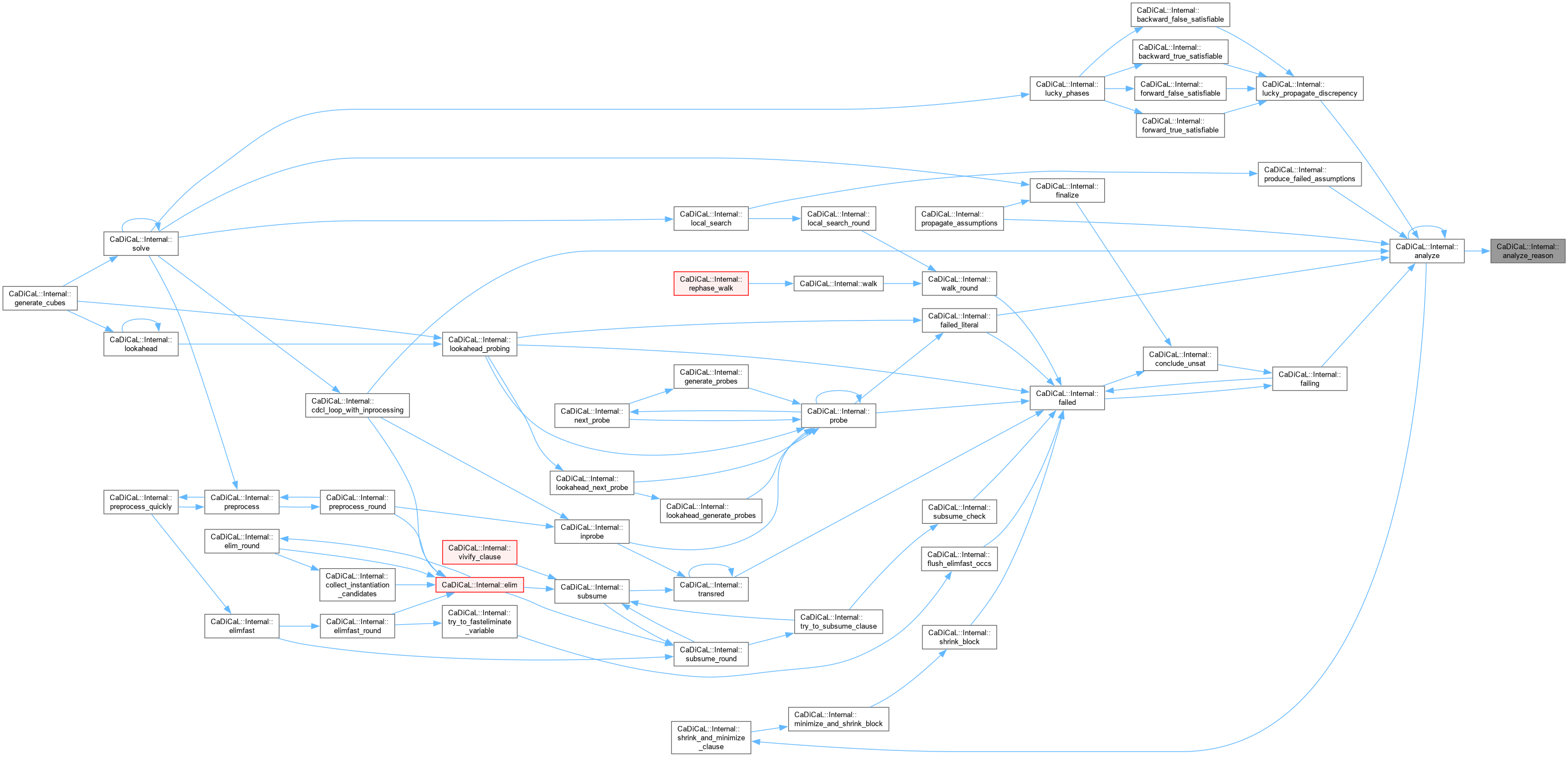
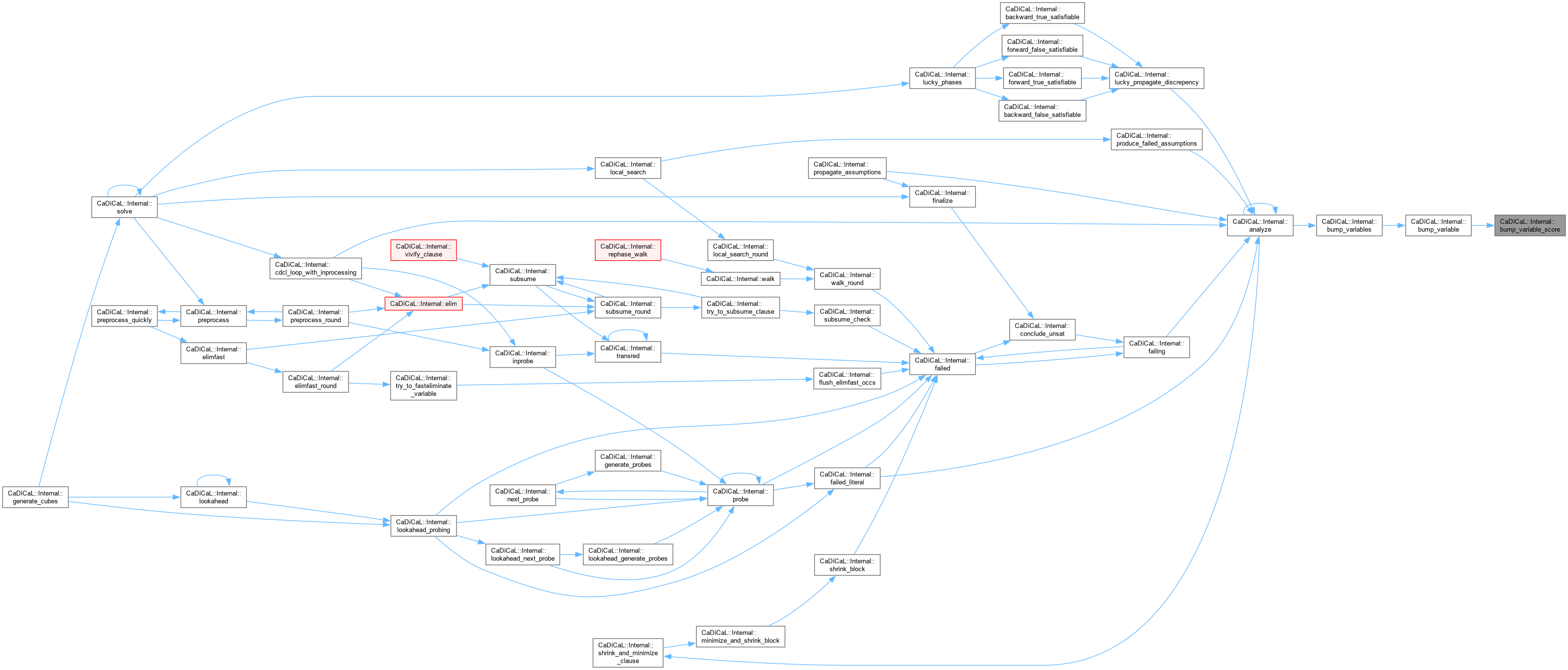
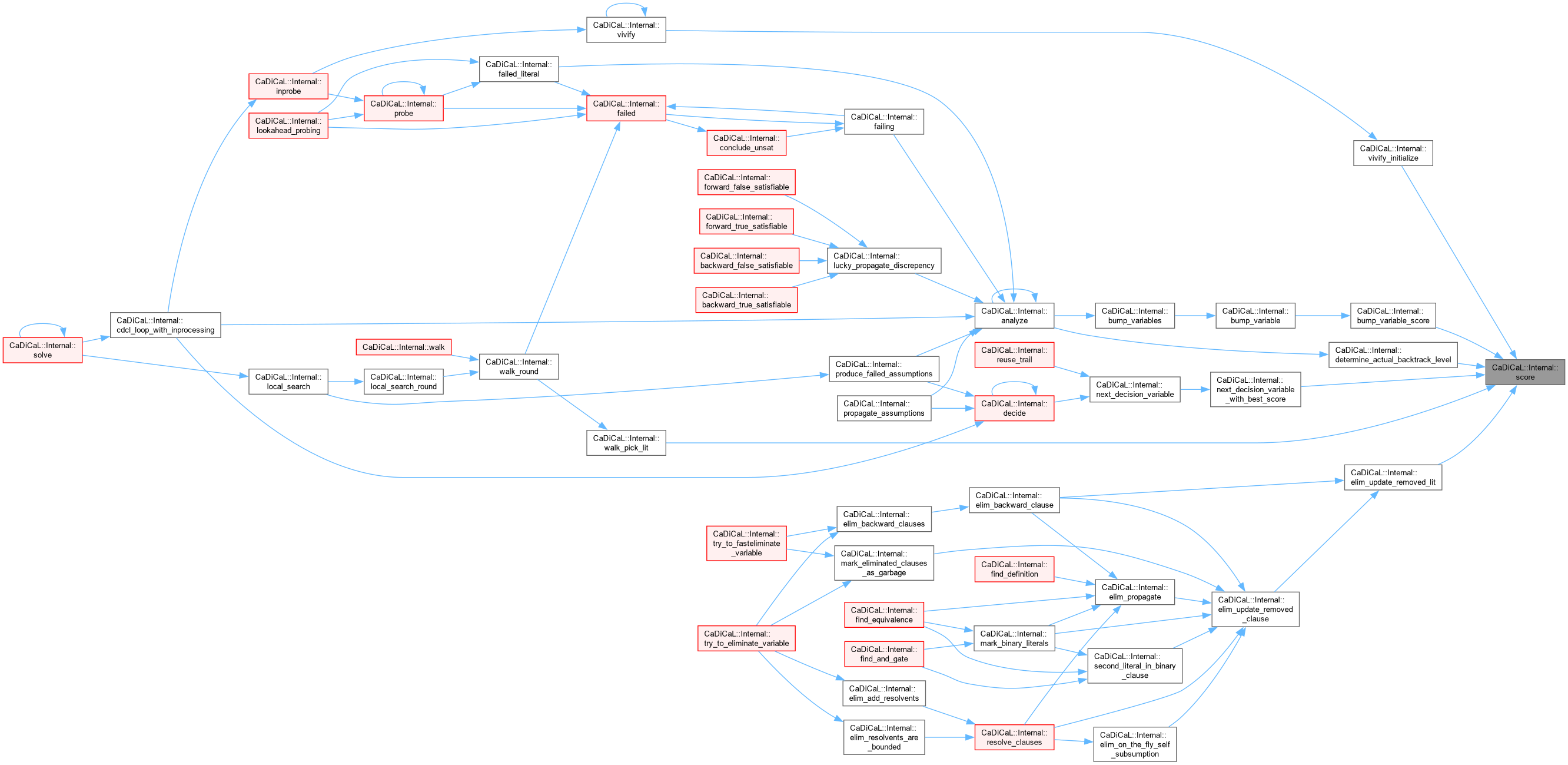
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::analyze | ( | ) |
Definition at line 943 of file cadical_analyze.cpp.
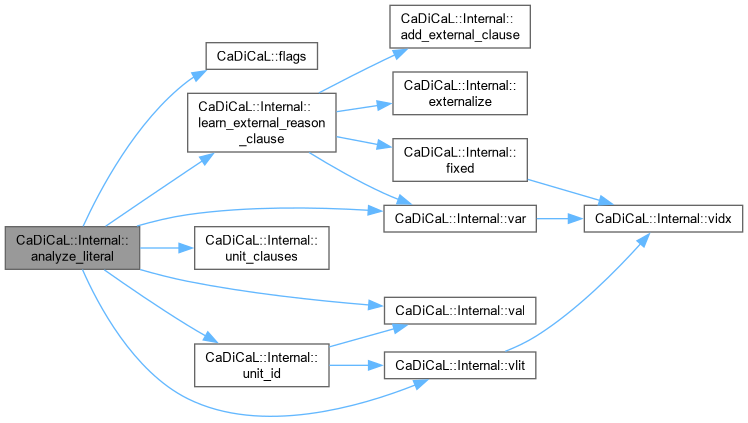
|
inline |
Definition at line 256 of file cadical_analyze.cpp.
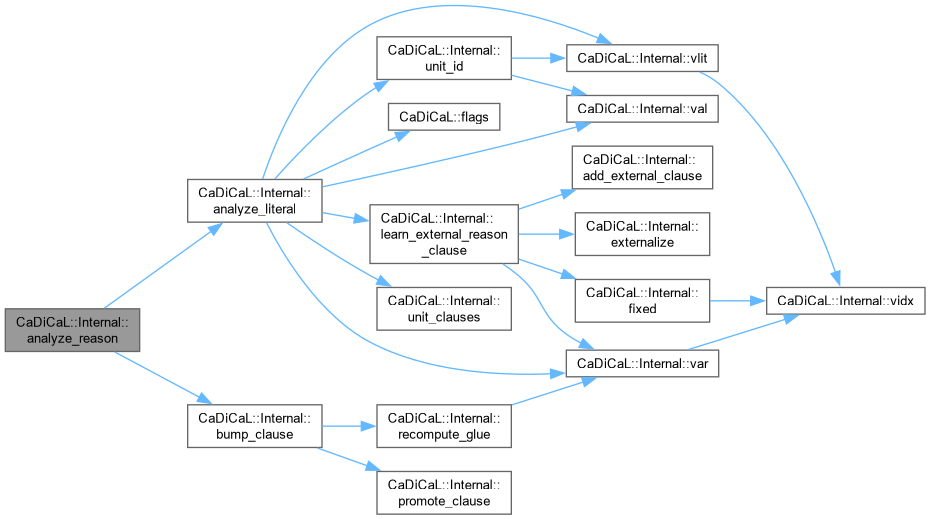
|
inline |
Definition at line 319 of file cadical_analyze.cpp.
Definition at line 713 of file cadical_factor.cpp.
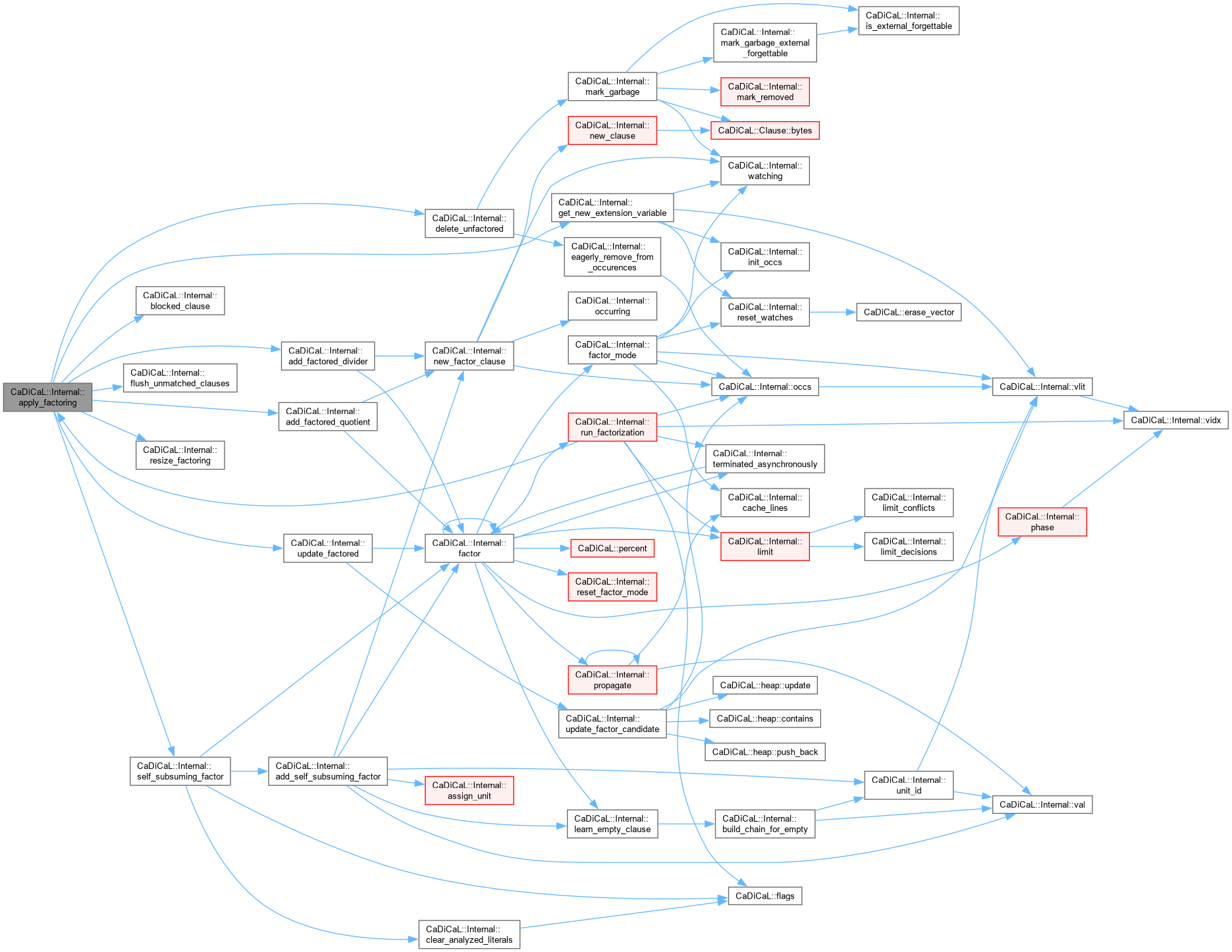
| bool CaDiCaL::Internal::arenaing | ( | ) |
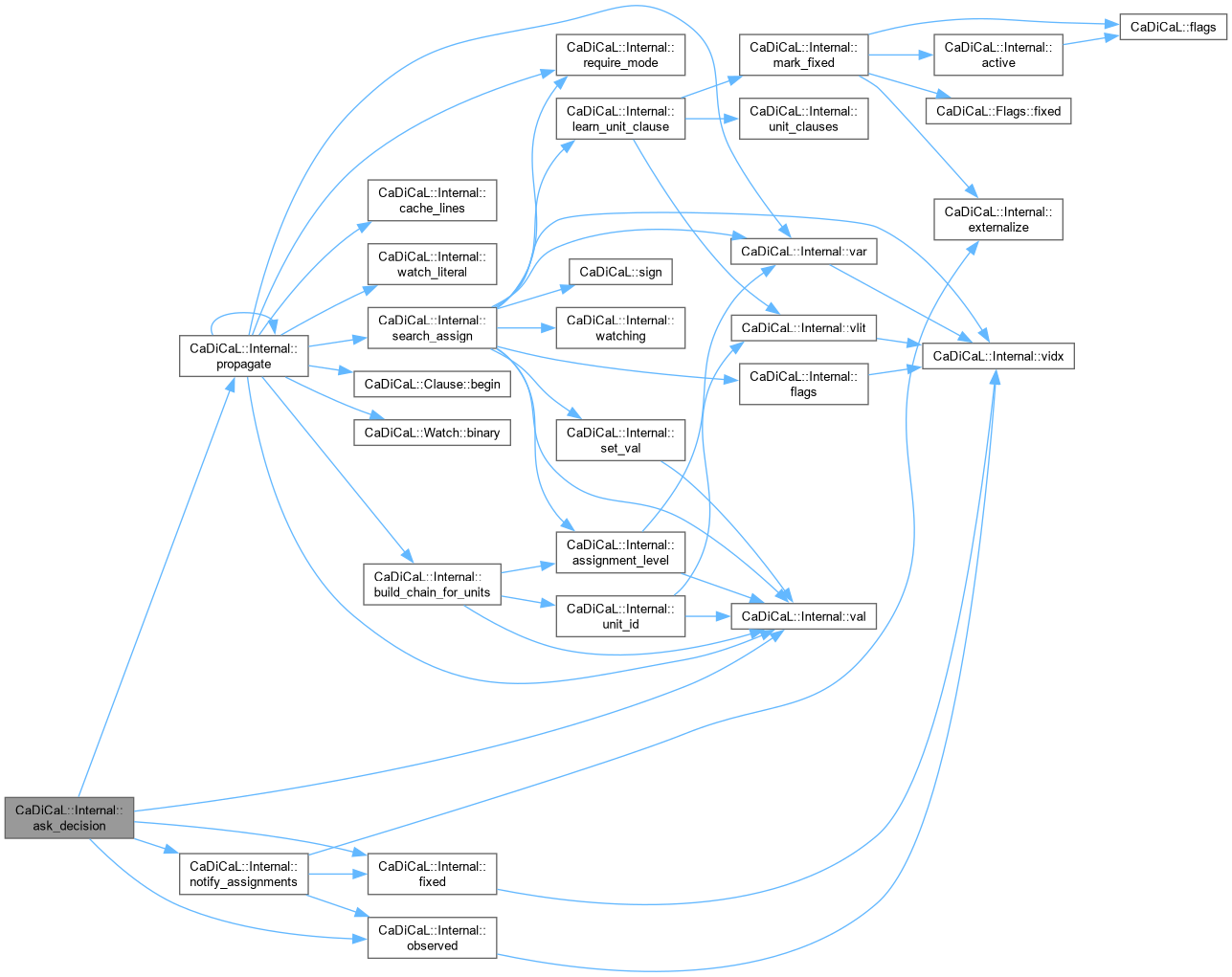
| int CaDiCaL::Internal::ask_decision | ( | ) |
Definition at line 998 of file cadical_external_propagate.cpp.
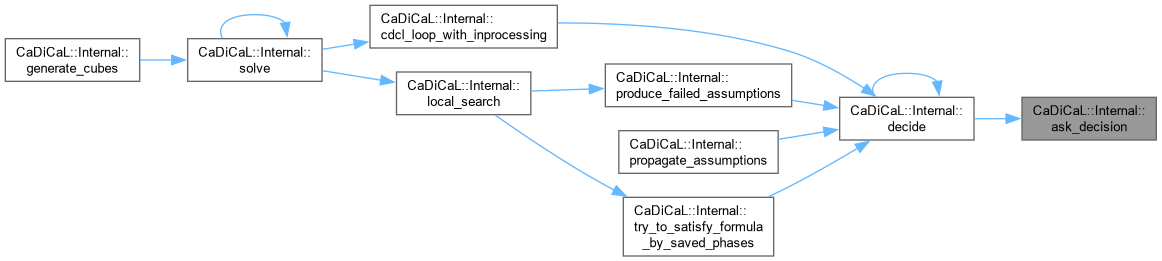
| bool CaDiCaL::Internal::ask_external_clause | ( | ) |
Definition at line 392 of file cadical_external_propagate.cpp.

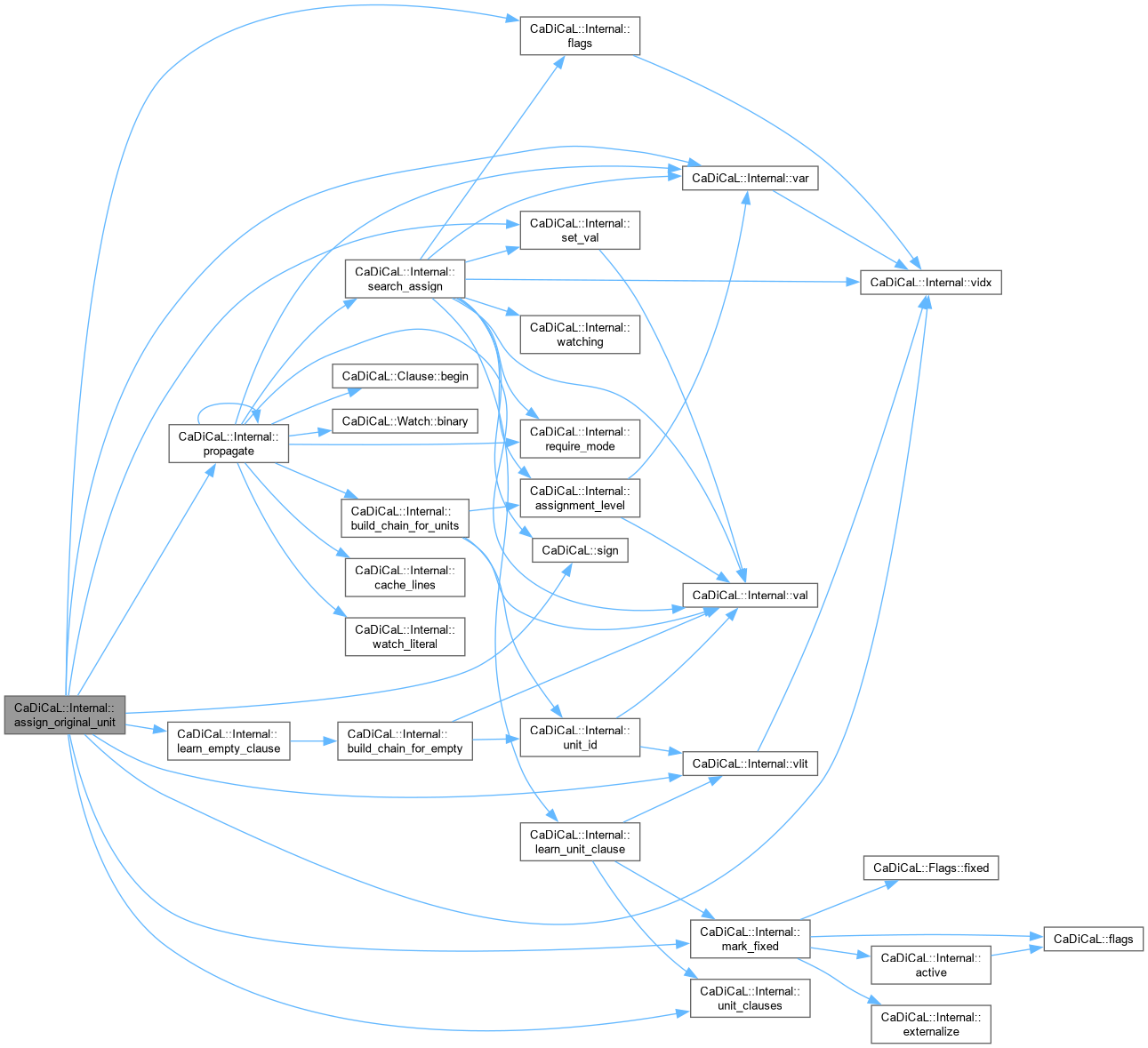
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::assign_original_unit | ( | int64_t | id, |
| int | lit ) |
Definition at line 347 of file cadical_clause.cpp.

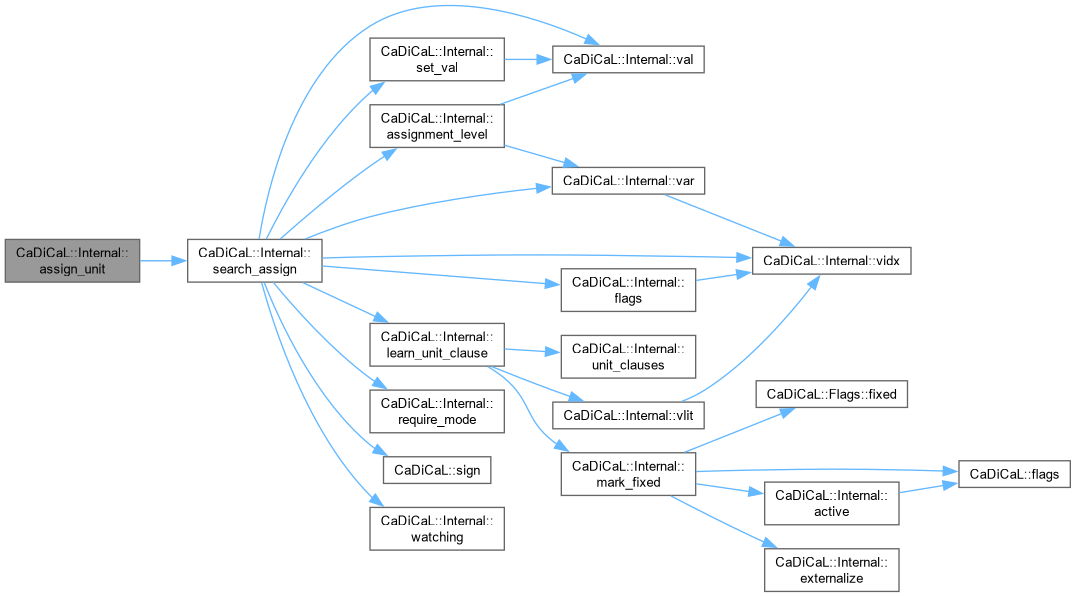
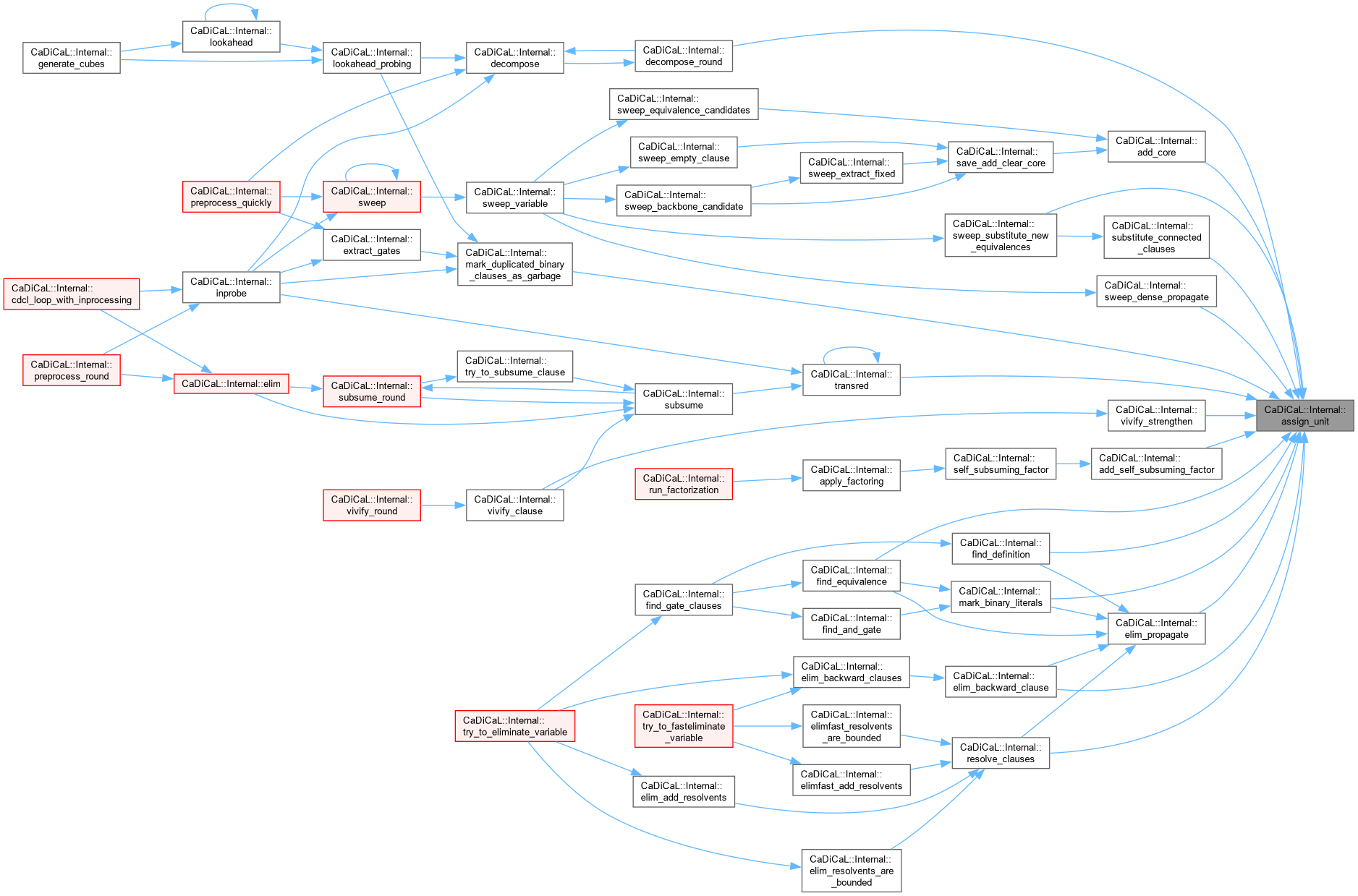
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::assign_unit | ( | int | lit | ) |
Definition at line 184 of file cadical_propagate.cpp.
|
inline |
Definition at line 42 of file cadical_propagate.cpp.

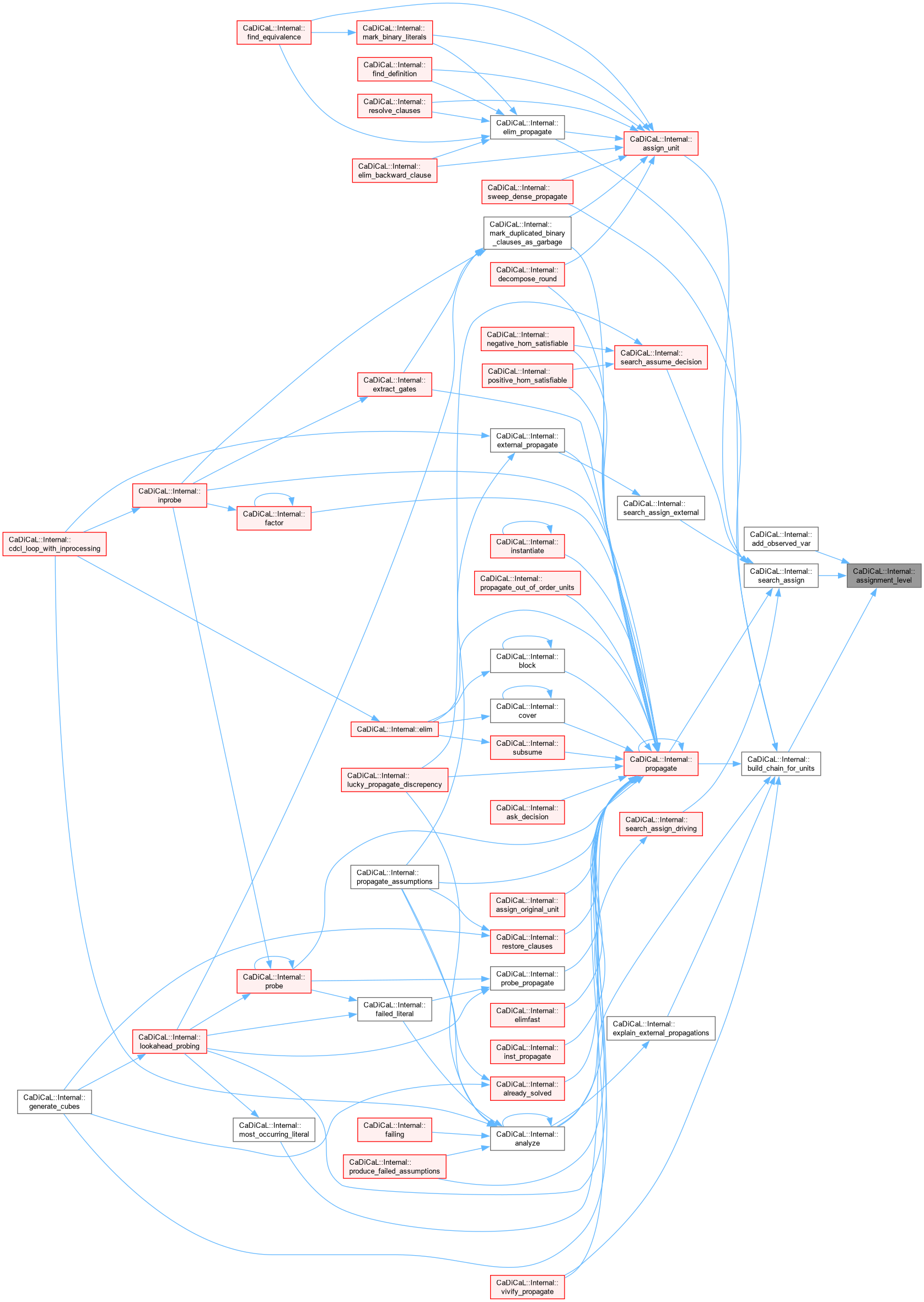
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::assume | ( | int | lit | ) |
Definition at line 13 of file cadical_assume.cpp.

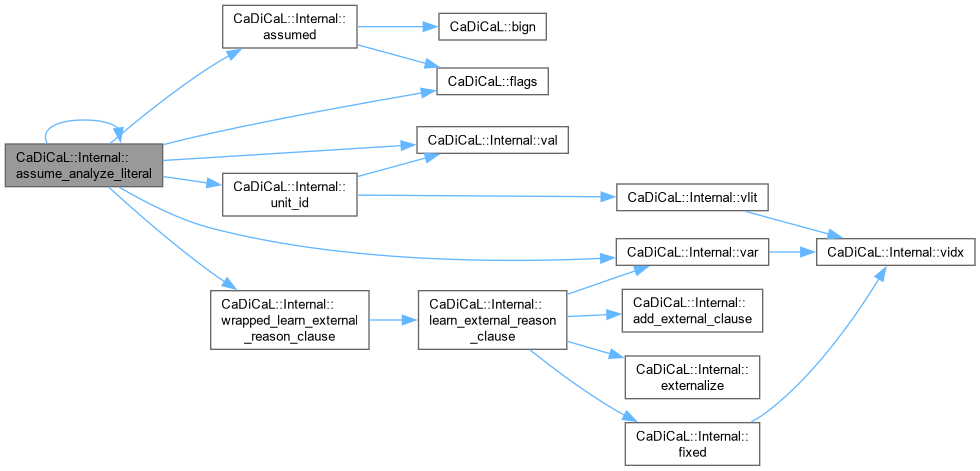
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::assume_analyze_literal | ( | int | lit | ) |
Definition at line 33 of file cadical_assume.cpp.
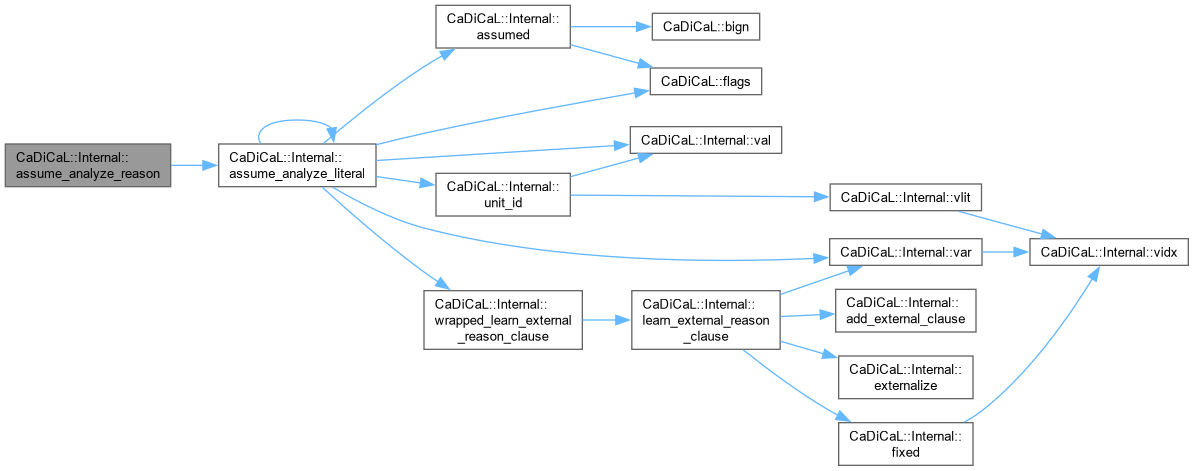
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::assume_analyze_reason | ( | int | lit, |
| Clause * | reason ) |
Definition at line 66 of file cadical_assume.cpp.
|
inline |
|
inline |
Definition at line 85 of file cadical_cover.cpp.
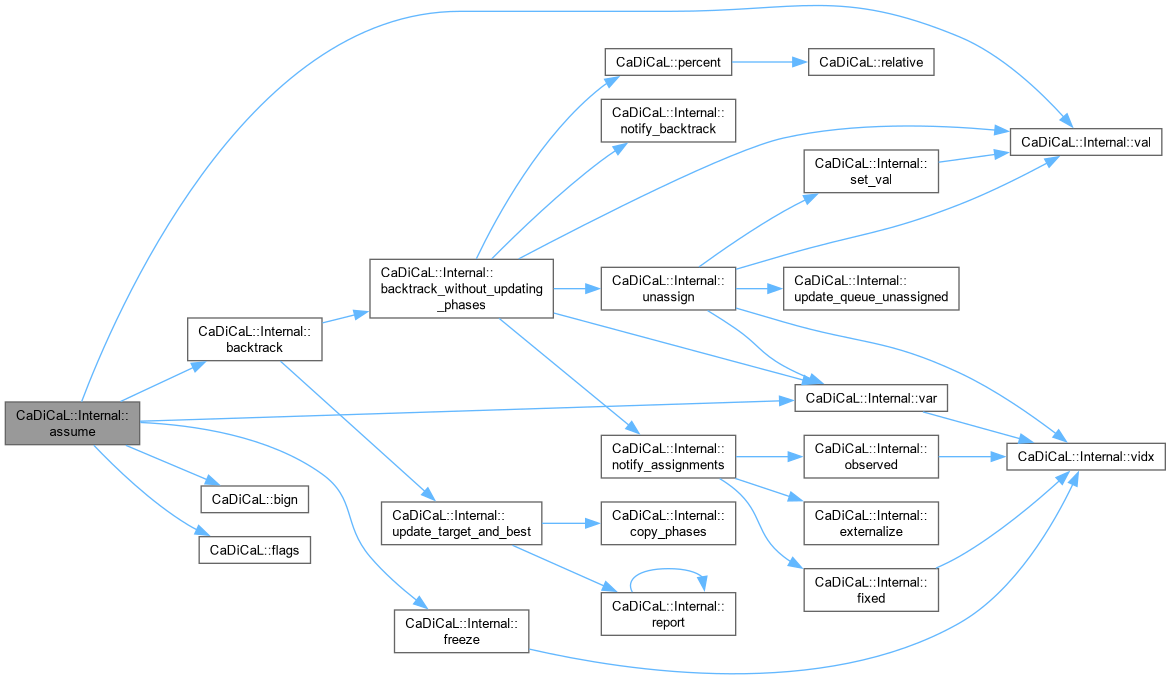
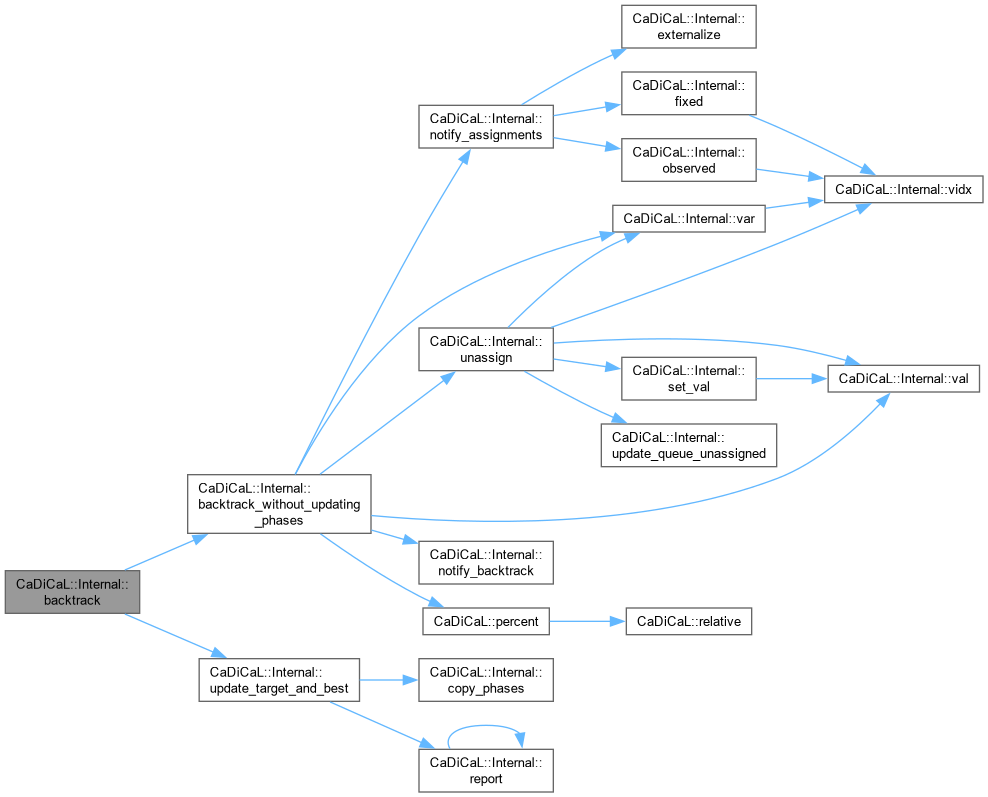
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::backtrack | ( | int | target_level = 0 | ) |
Definition at line 80 of file cadical_backtrack.cpp.
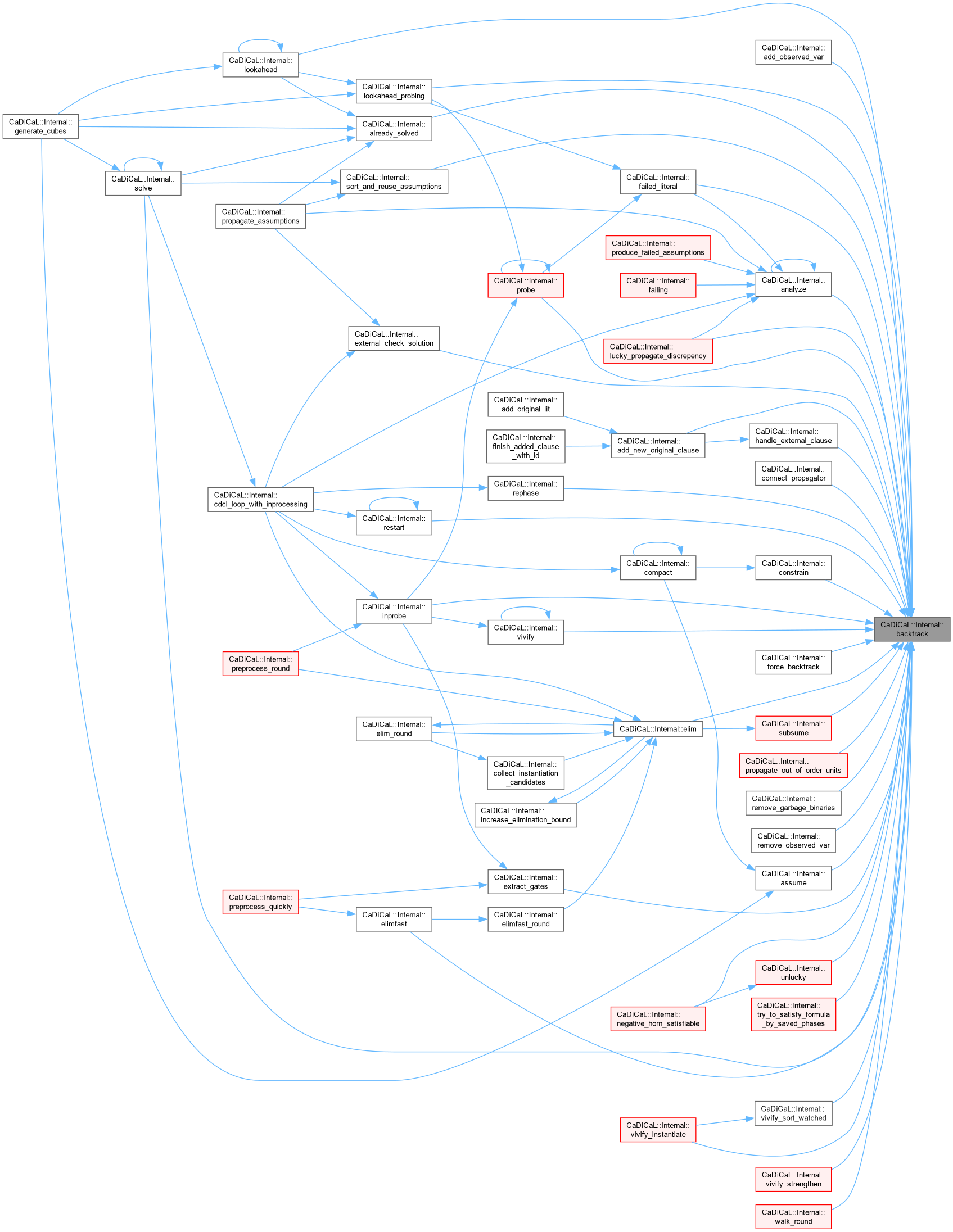
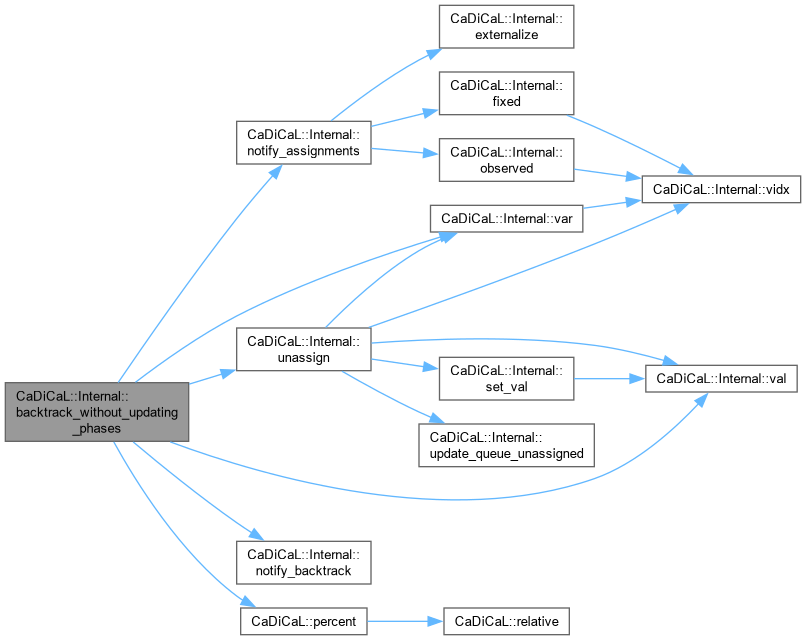
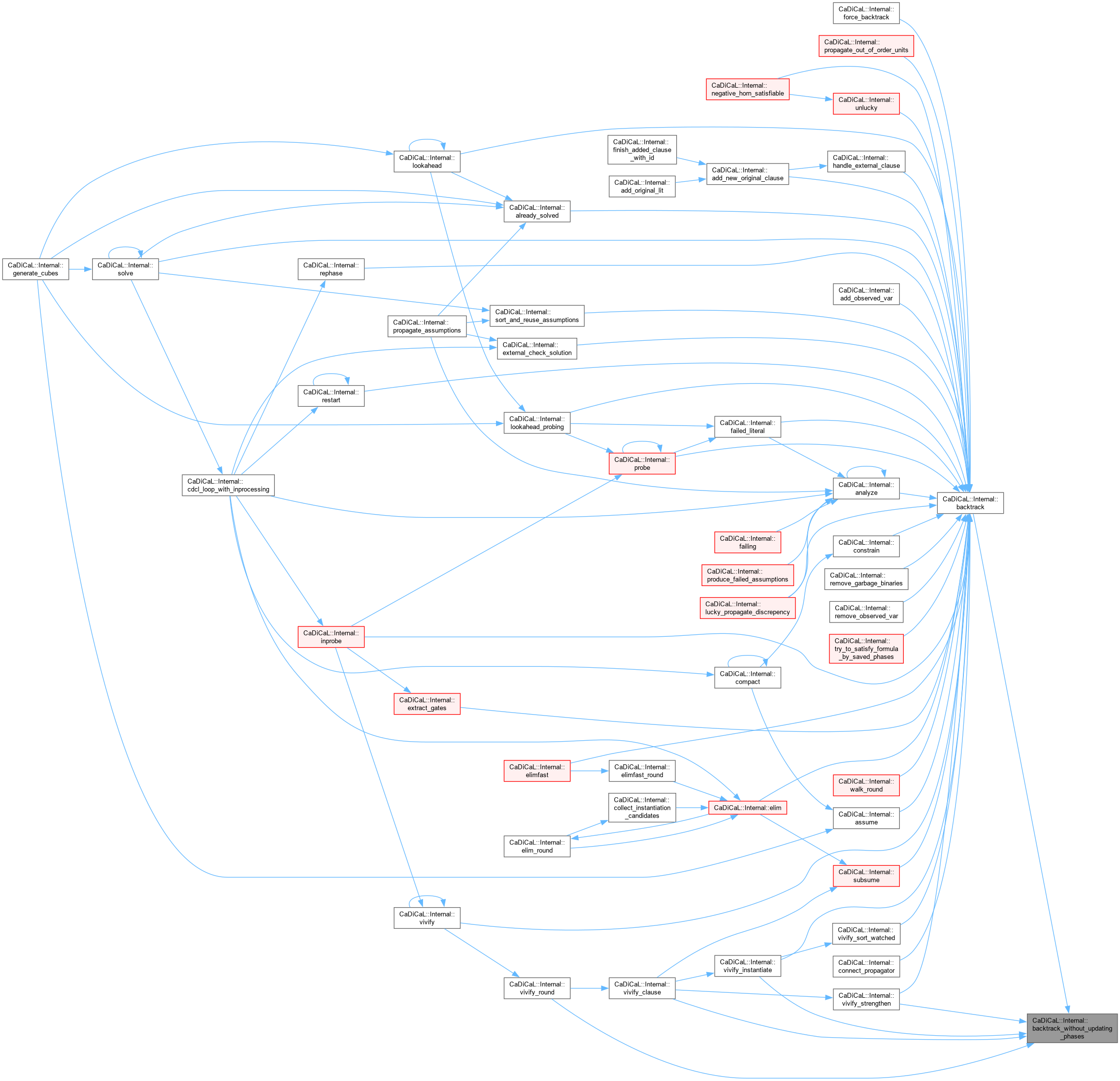
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::backtrack_without_updating_phases | ( | int | target_level = 0 | ) |
Definition at line 89 of file cadical_backtrack.cpp.
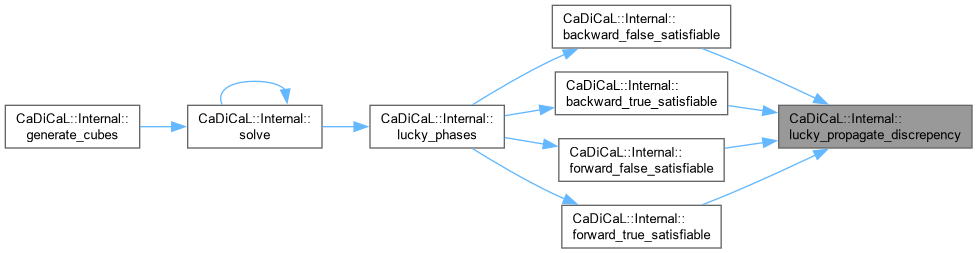
| int CaDiCaL::Internal::backward_false_satisfiable | ( | ) |
Definition at line 206 of file cadical_lucky.cpp.
| int CaDiCaL::Internal::backward_true_satisfiable | ( | ) |
Definition at line 231 of file cadical_lucky.cpp.
Definition at line 217 of file cadical_factor.cpp.
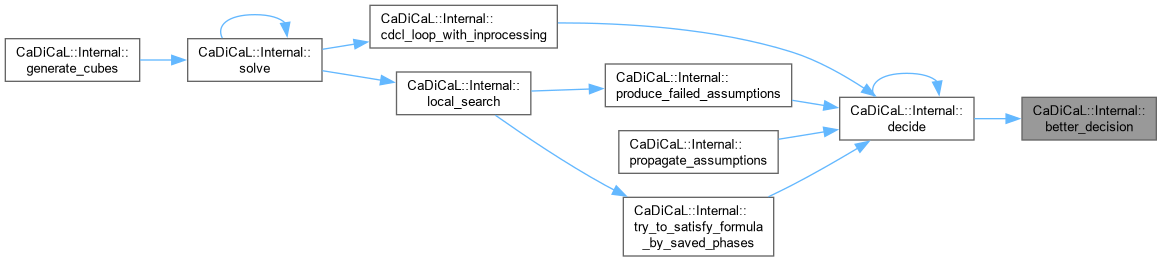
| bool CaDiCaL::Internal::better_decision | ( | int | lit, |
| int | other ) |
Definition at line 114 of file cadical_decide.cpp.
|
inline |
Definition at line 464 of file internal.hpp.

| bool CaDiCaL::Internal::block | ( | ) |
Definition at line 741 of file cadical_block.cpp.
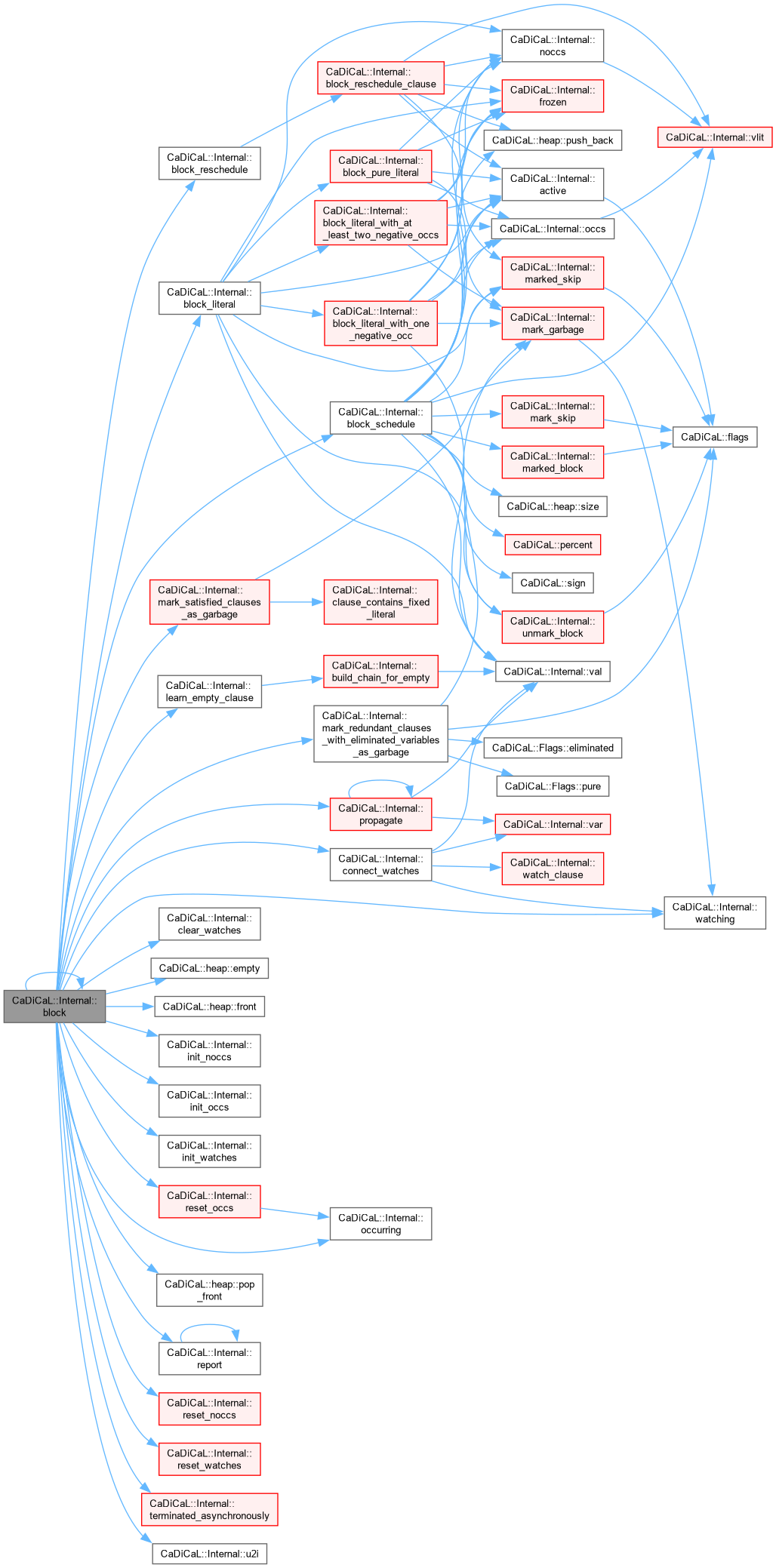
| size_t CaDiCaL::Internal::block_candidates | ( | Blocker & | blocker, |
| int | lit ) |
Definition at line 439 of file cadical_block.cpp.
Definition at line 504 of file cadical_block.cpp.
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::block_literal | ( | Blocker & | blocker, |
| int | lit ) |
Definition at line 694 of file cadical_block.cpp.
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::block_literal_with_at_least_two_negative_occs | ( | Blocker & | blocker, |
| int | lit ) |
Definition at line 549 of file cadical_block.cpp.
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::block_literal_with_one_negative_occ | ( | Blocker & | blocker, |
| int | lit ) |
Definition at line 302 of file cadical_block.cpp.
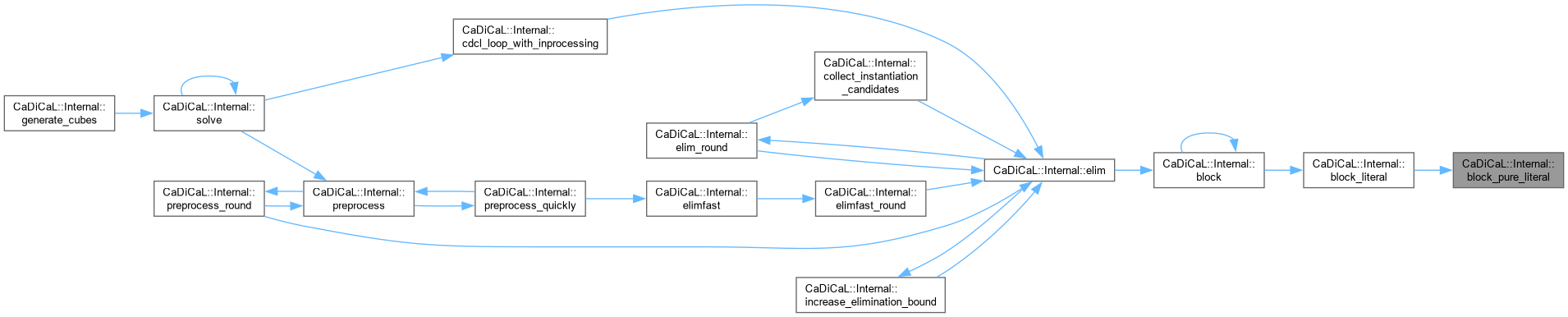
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::block_pure_literal | ( | Blocker & | blocker, |
| int | lit ) |
Definition at line 253 of file cadical_block.cpp.
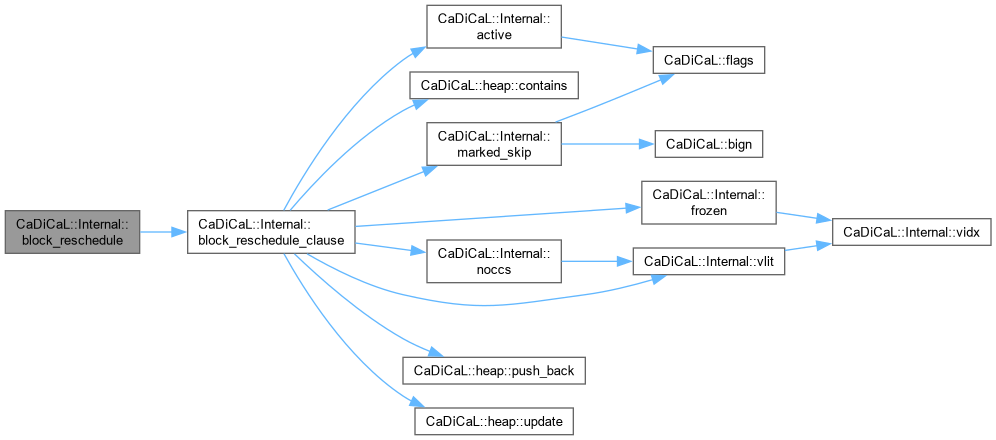
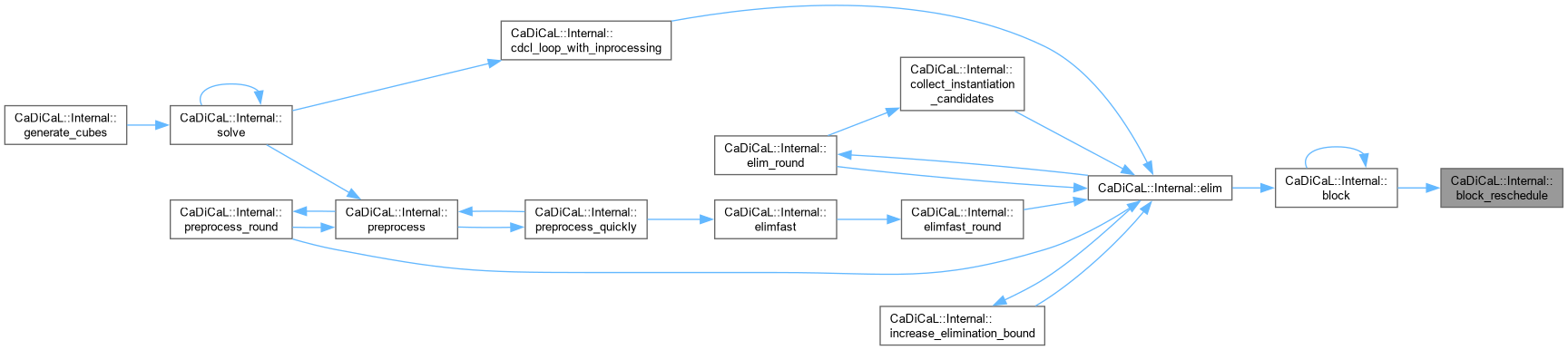
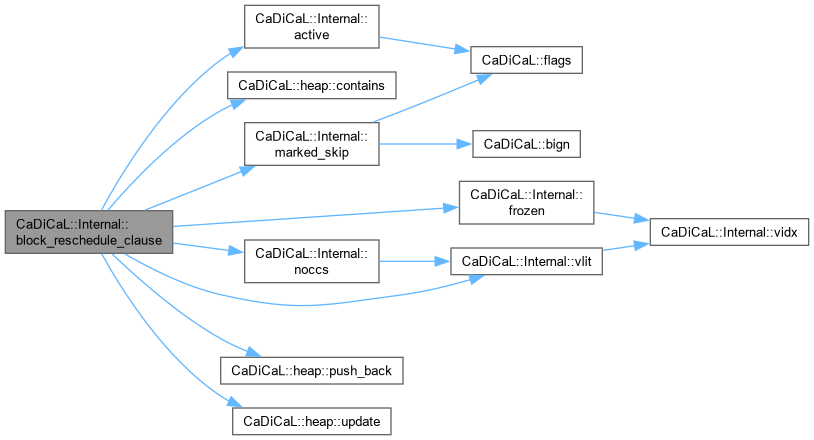
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::block_reschedule | ( | Blocker & | blocker, |
| int | lit ) |
Definition at line 684 of file cadical_block.cpp.
Definition at line 651 of file cadical_block.cpp.
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::block_schedule | ( | Blocker & | blocker | ) |
Definition at line 153 of file cadical_block.cpp.
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::blocked_clause | ( | Quotient * | q, |
| int | not_fresh ) |
Definition at line 613 of file cadical_factor.cpp.
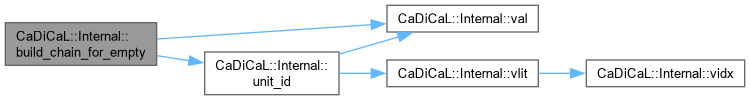
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::build_chain_for_empty | ( | ) |
Definition at line 89 of file cadical_propagate.cpp.
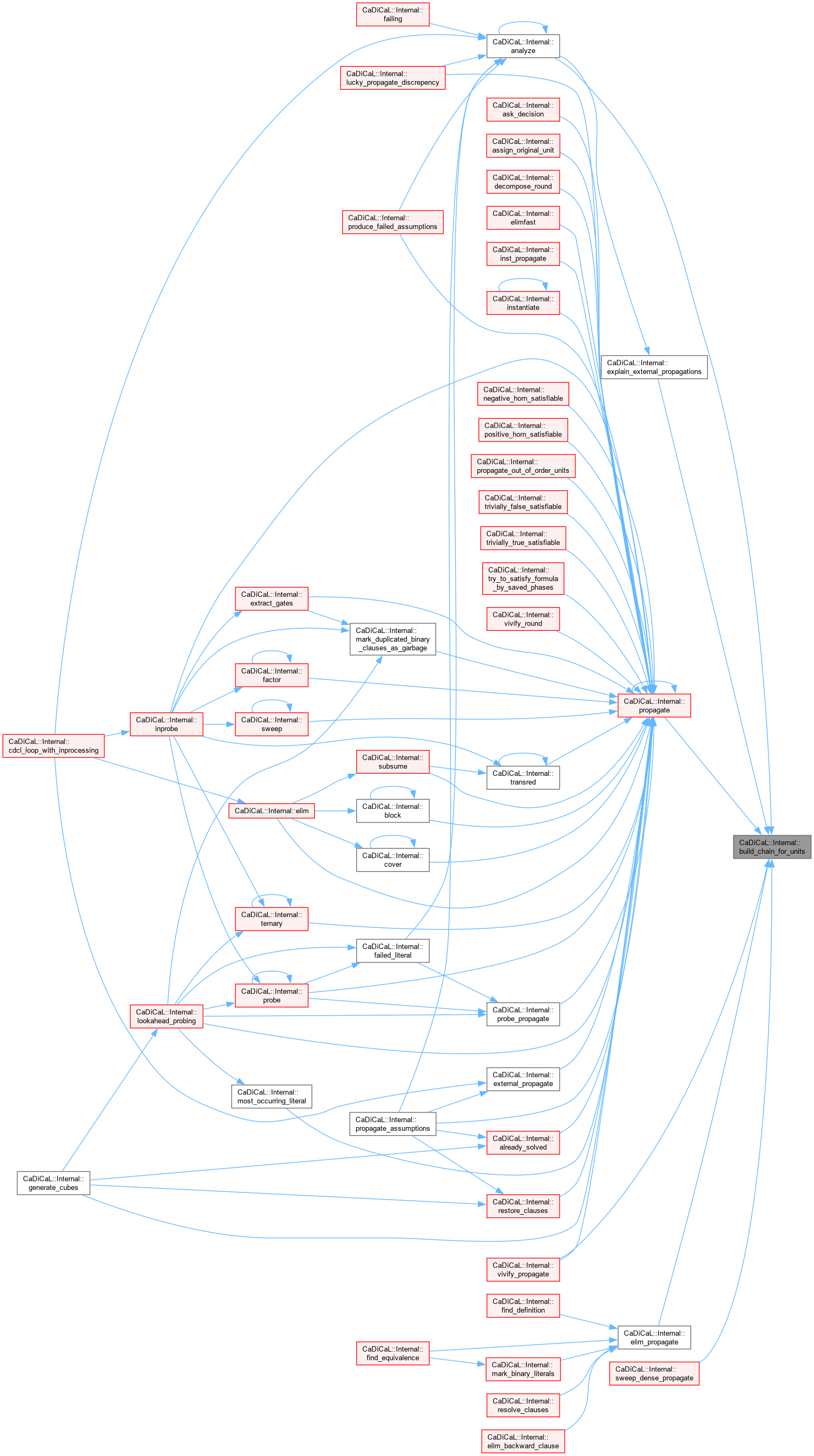
Definition at line 64 of file cadical_propagate.cpp.
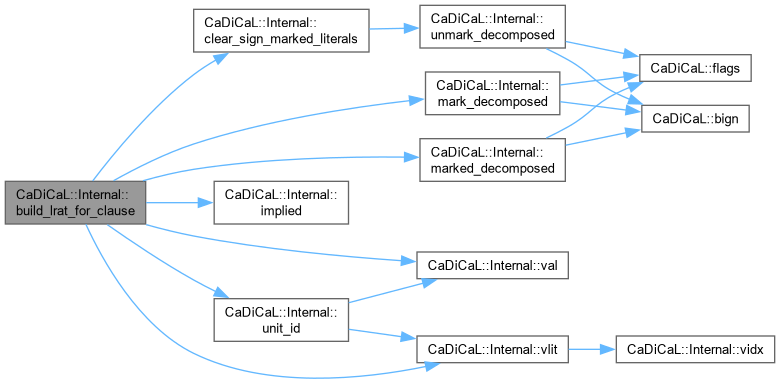
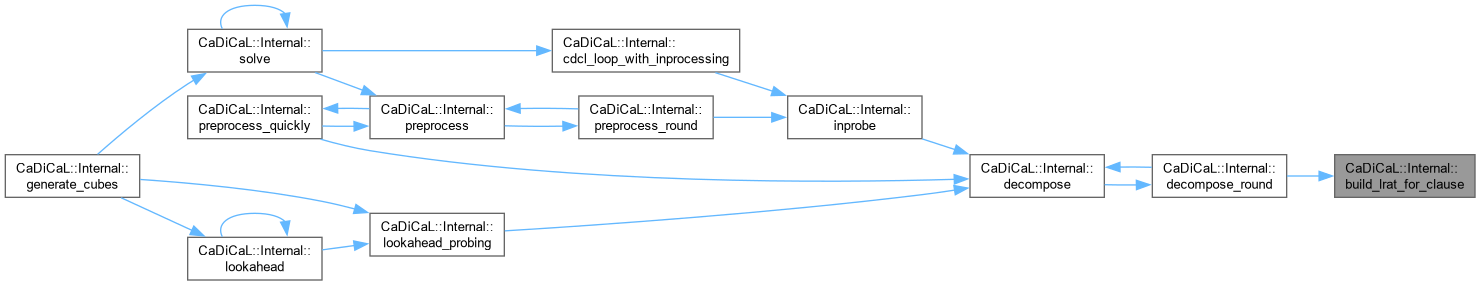
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::build_lrat_for_clause | ( | const vector< vector< Clause * > > & | dfs_chains, |
| bool | invert = false ) |
Definition at line 72 of file cadical_decompose.cpp.
|
inline |
Definition at line 387 of file cadical_analyze.cpp.

|
inline |
Definition at line 345 of file cadical_analyze.cpp.

|
inline |
Definition at line 362 of file cadical_analyze.cpp.
|
inline |
Definition at line 228 of file cadical_analyze.cpp.
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::bump_clause2 | ( | Clause * | c | ) |
Definition at line 245 of file cadical_analyze.cpp.

| void CaDiCaL::Internal::bump_queue | ( | int | idx | ) |
Definition at line 56 of file cadical_analyze.cpp.
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::bump_variable | ( | int | lit | ) |
Definition at line 131 of file cadical_analyze.cpp.
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::bump_variable_score | ( | int | lit | ) |
Definition at line 109 of file cadical_analyze.cpp.
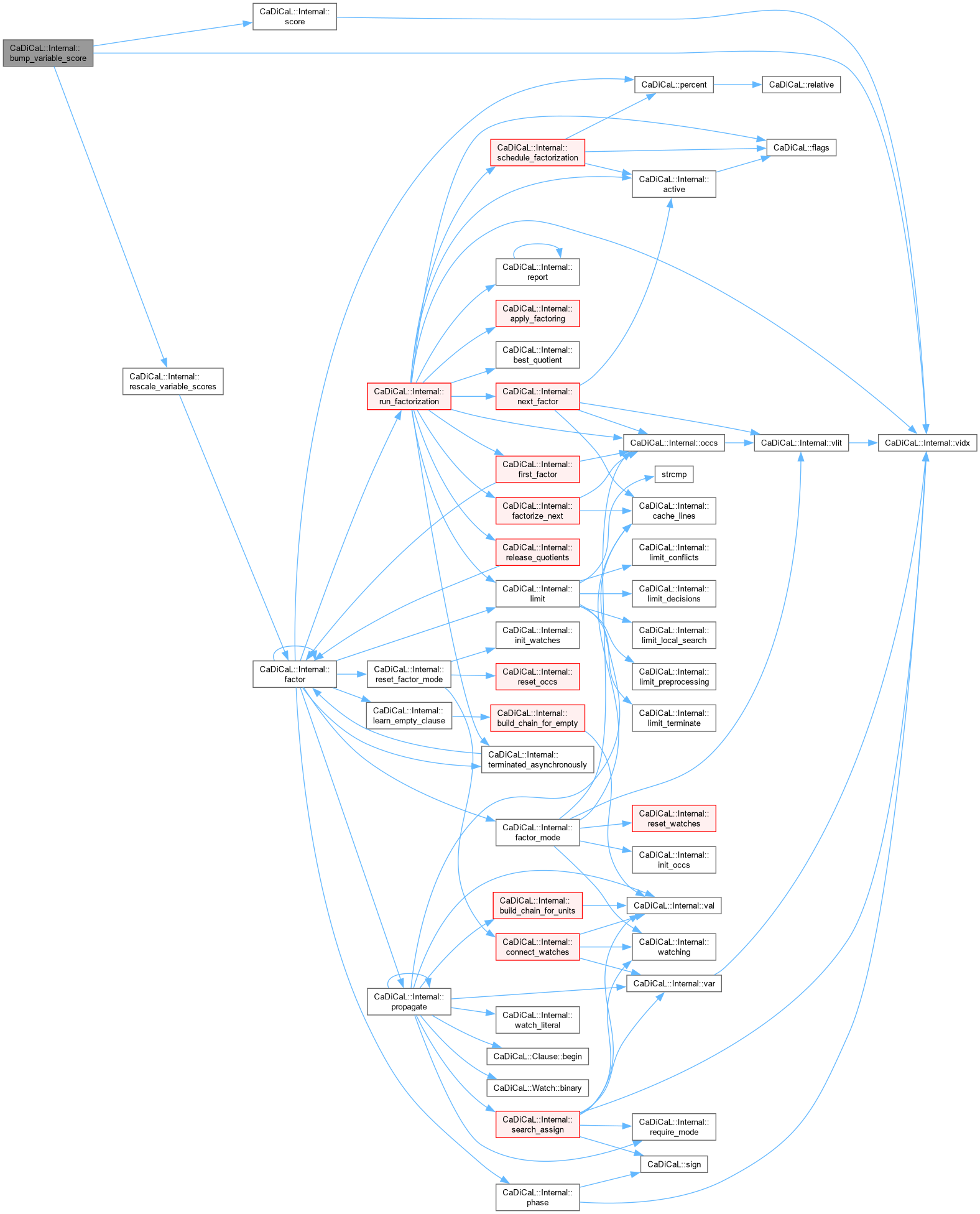
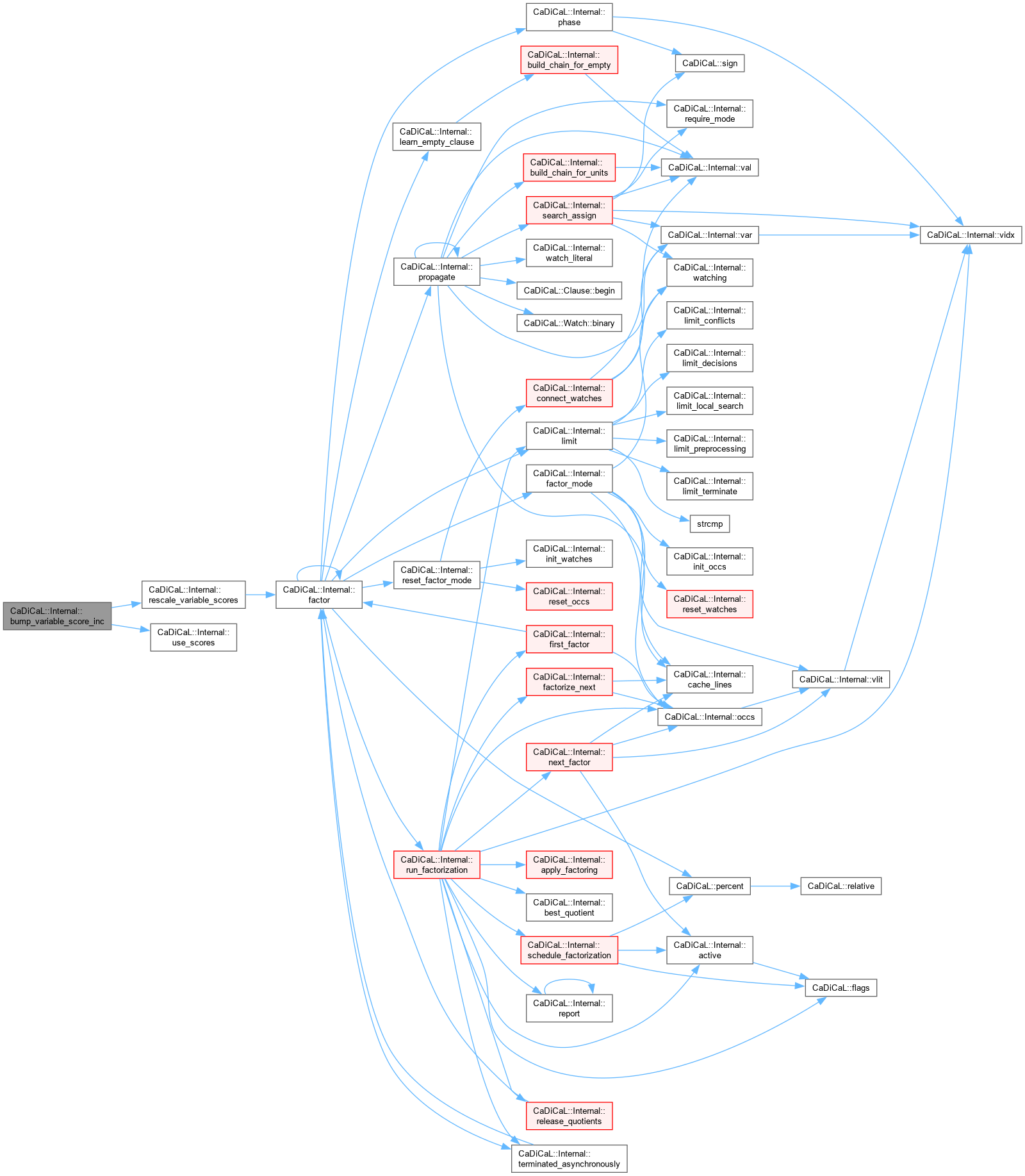
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::bump_variable_score_inc | ( | ) |
Definition at line 141 of file cadical_analyze.cpp.
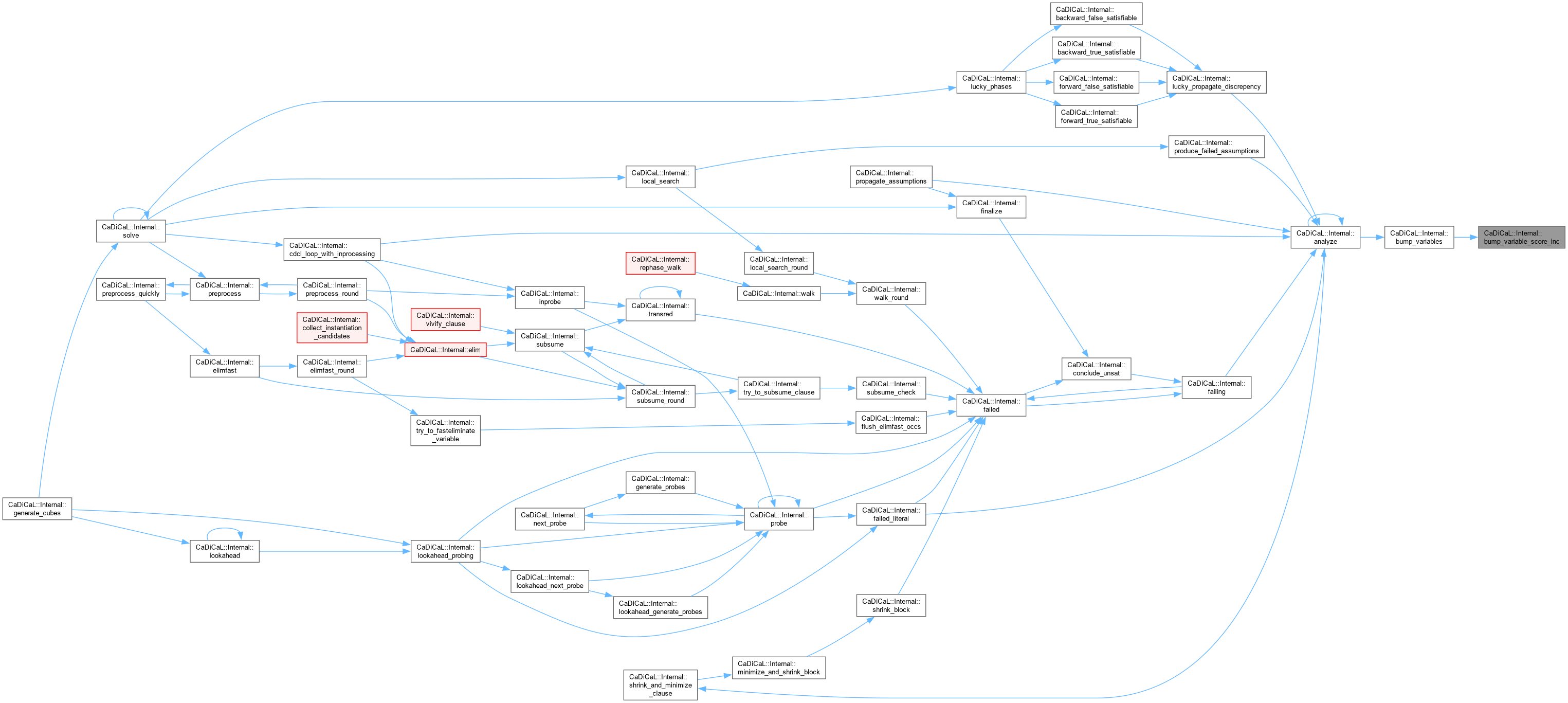
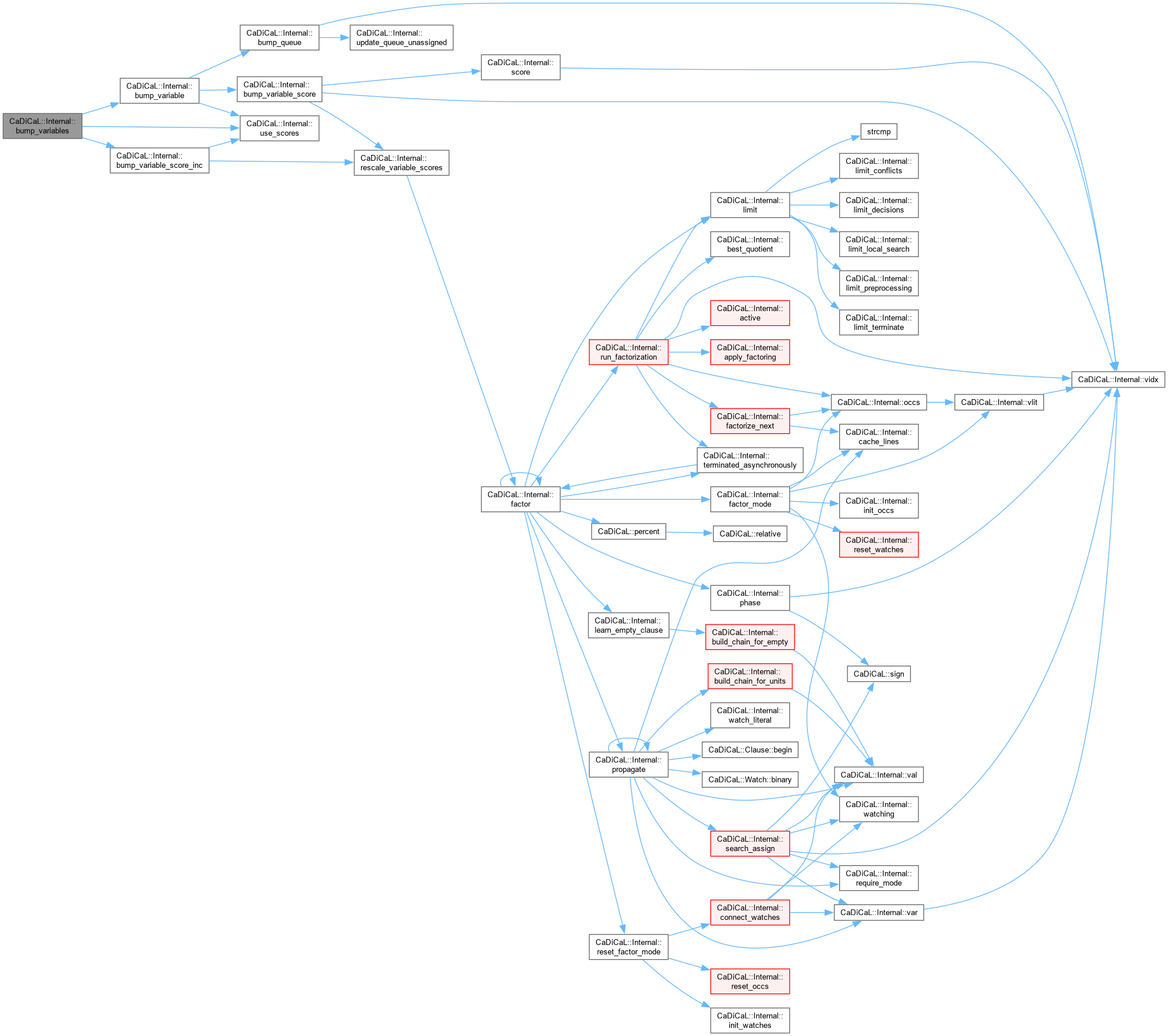
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::bump_variables | ( | ) |
Definition at line 179 of file cadical_analyze.cpp.
|
inline |
Definition at line 455 of file internal.hpp.
|
inline |
Definition at line 722 of file internal.hpp.
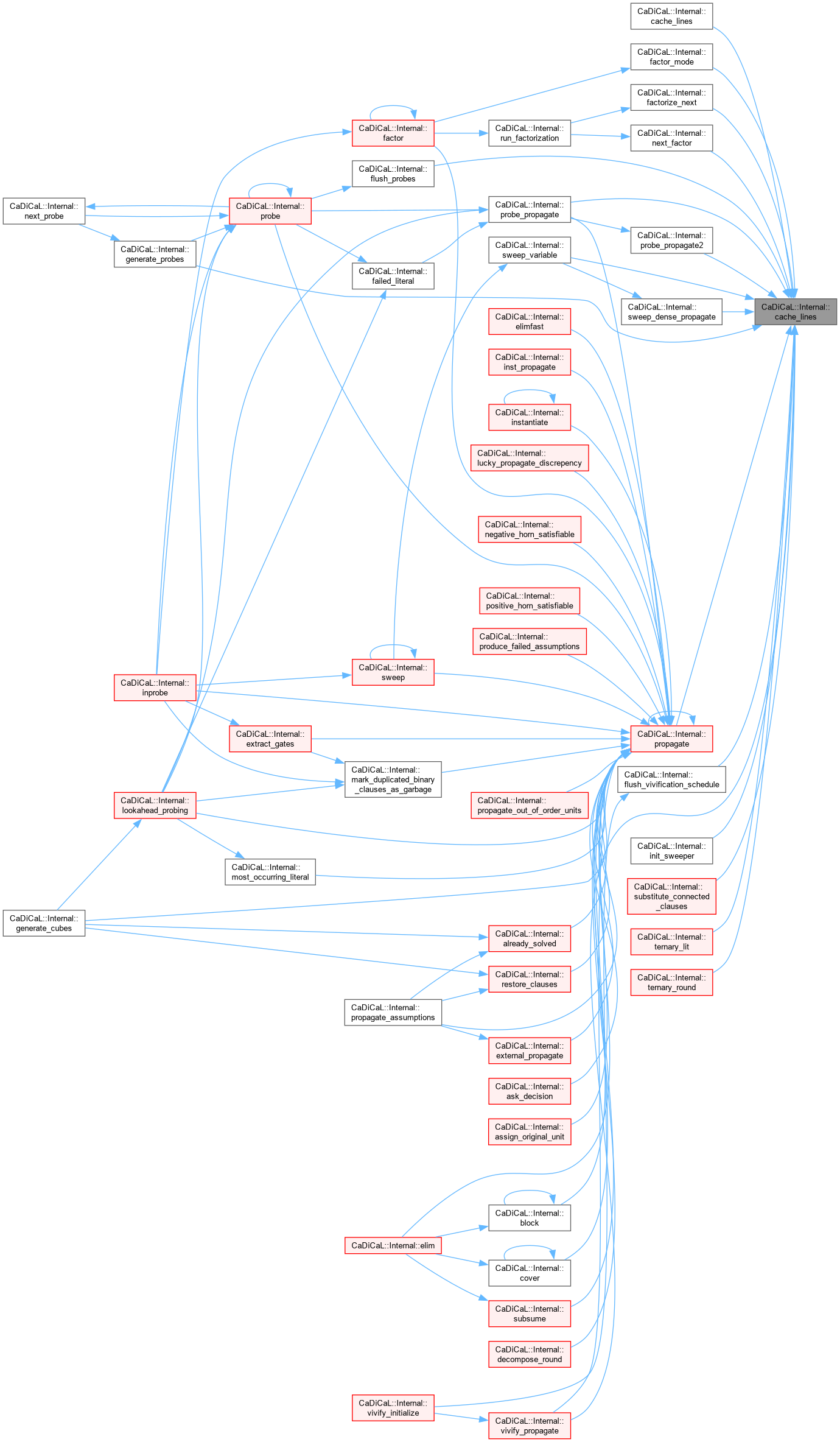
|
inline |
Definition at line 201 of file cadical_sweep.cpp.
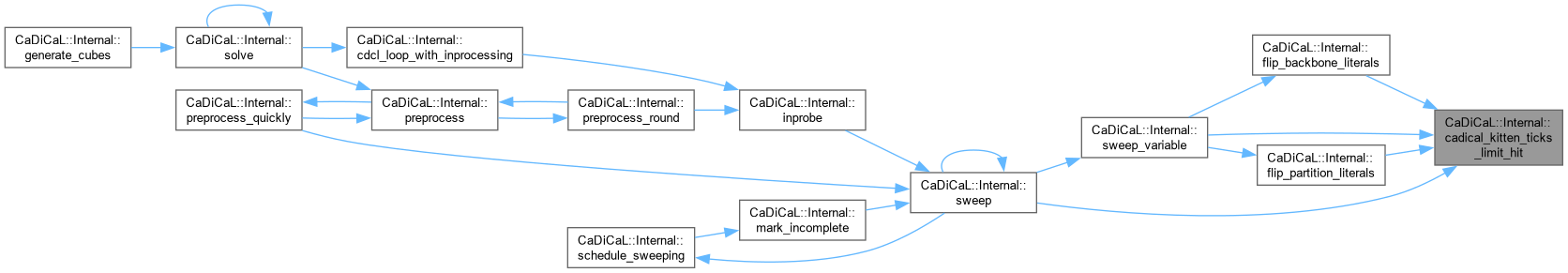
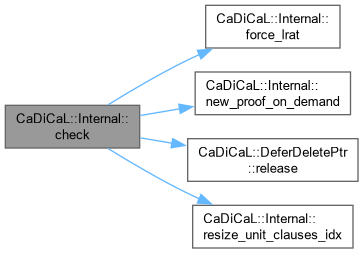
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::calculate_minimize_chain | ( | int | lit, |
| std::vector< int > & | stack ) |
Definition at line 159 of file cadical_minimize.cpp.
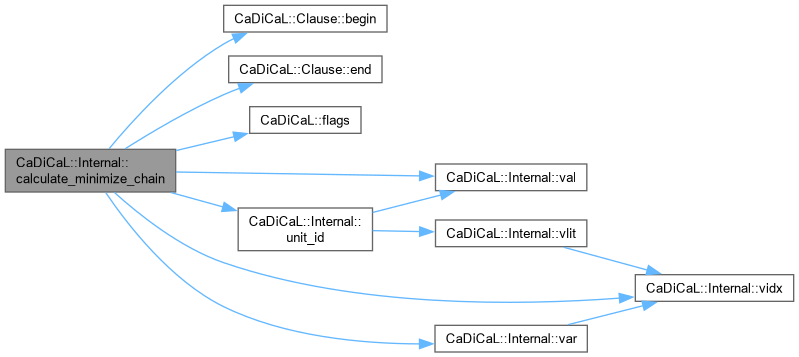
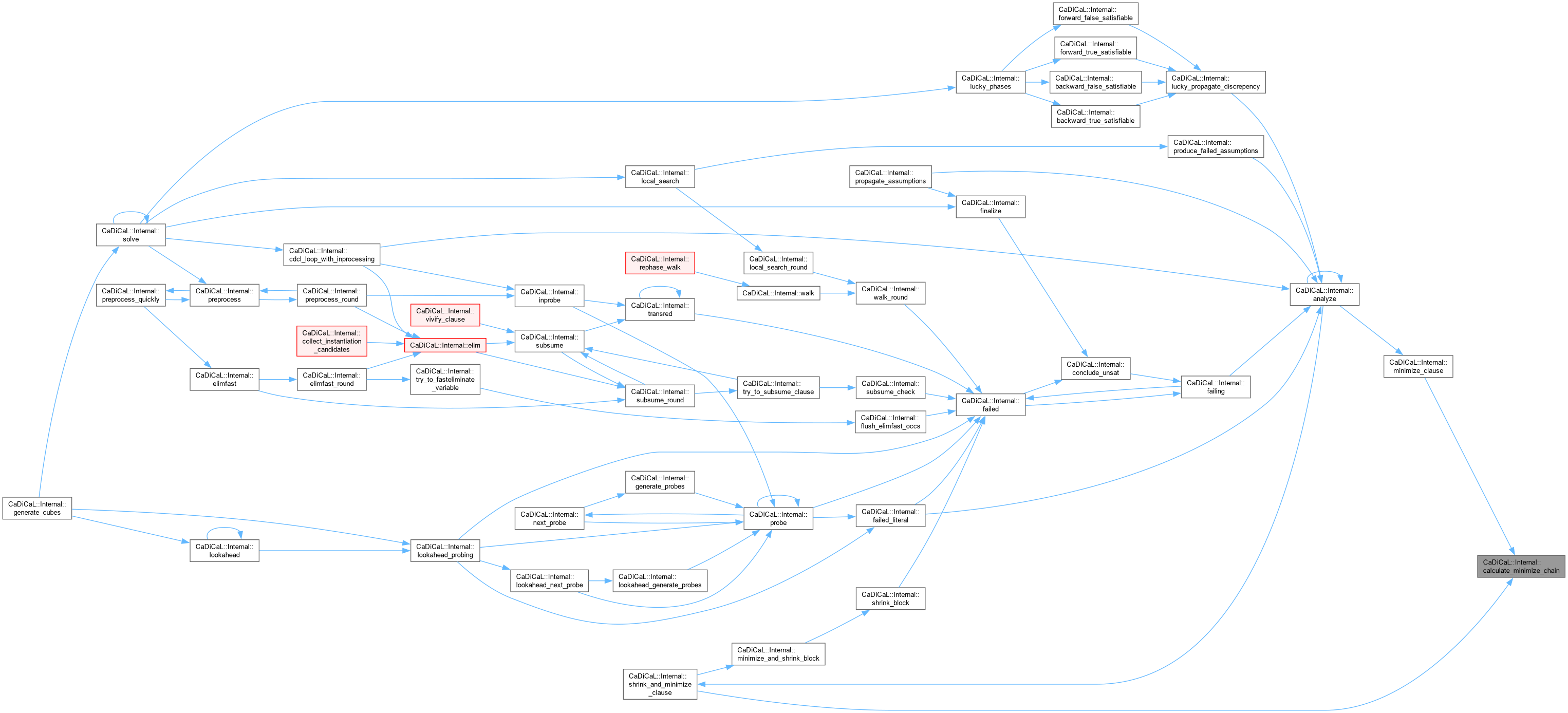
Definition at line 68 of file cadical_sweep.cpp.
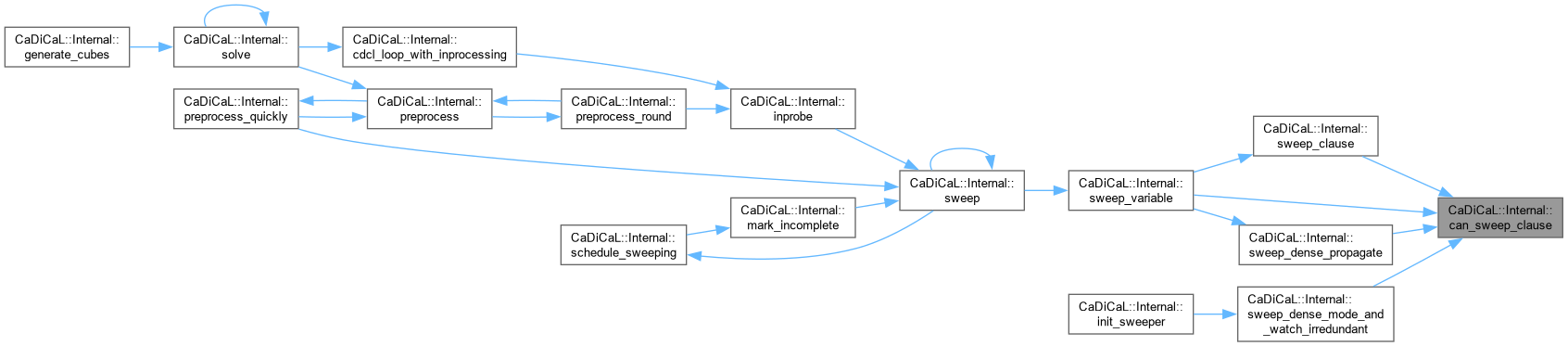
| int CaDiCaL::Internal::cdcl_loop_with_inprocessing | ( | ) |
Definition at line 276 of file cadical_internal.cpp.
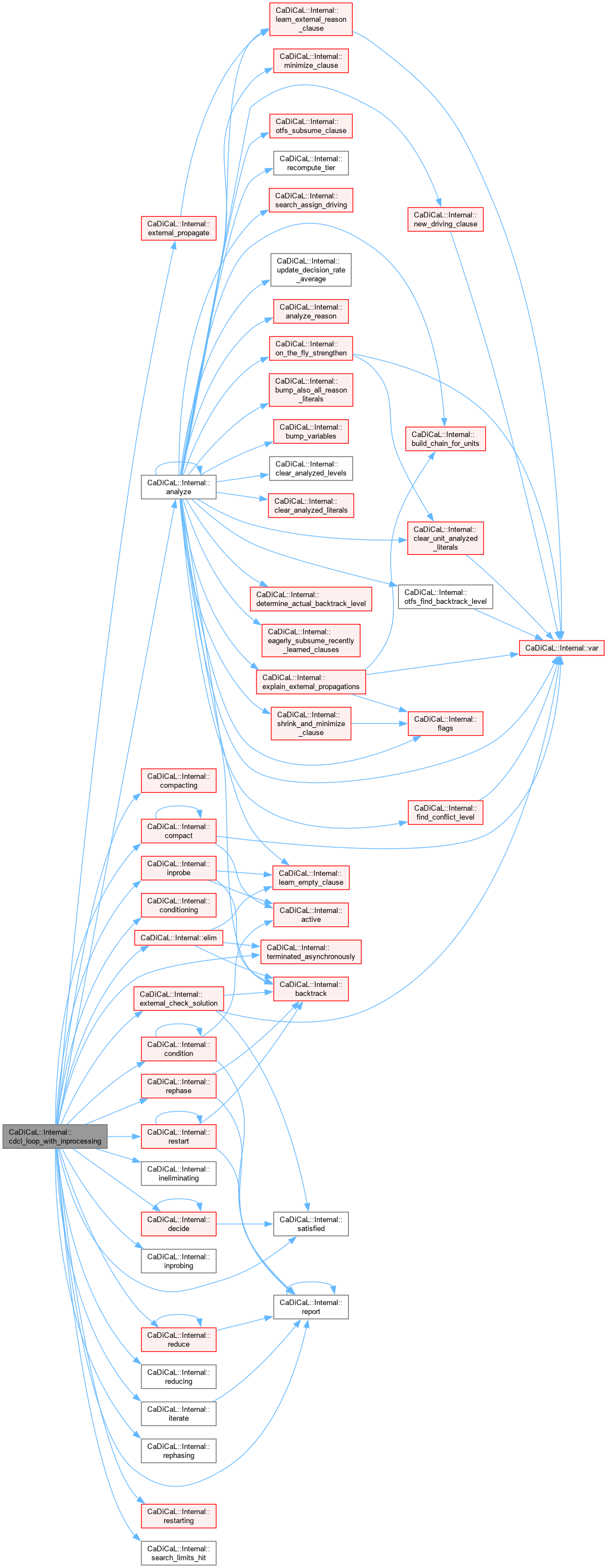

| void CaDiCaL::Internal::check | ( | ) |
Definition at line 162 of file cadical_proof.cpp.
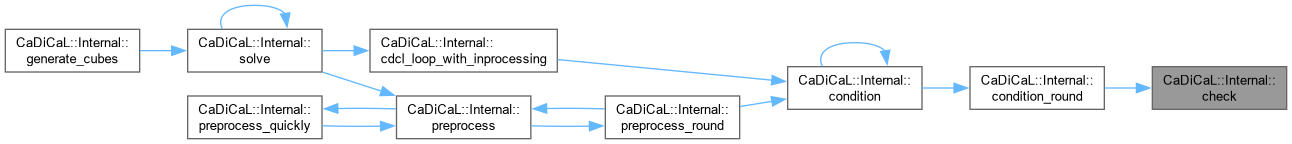
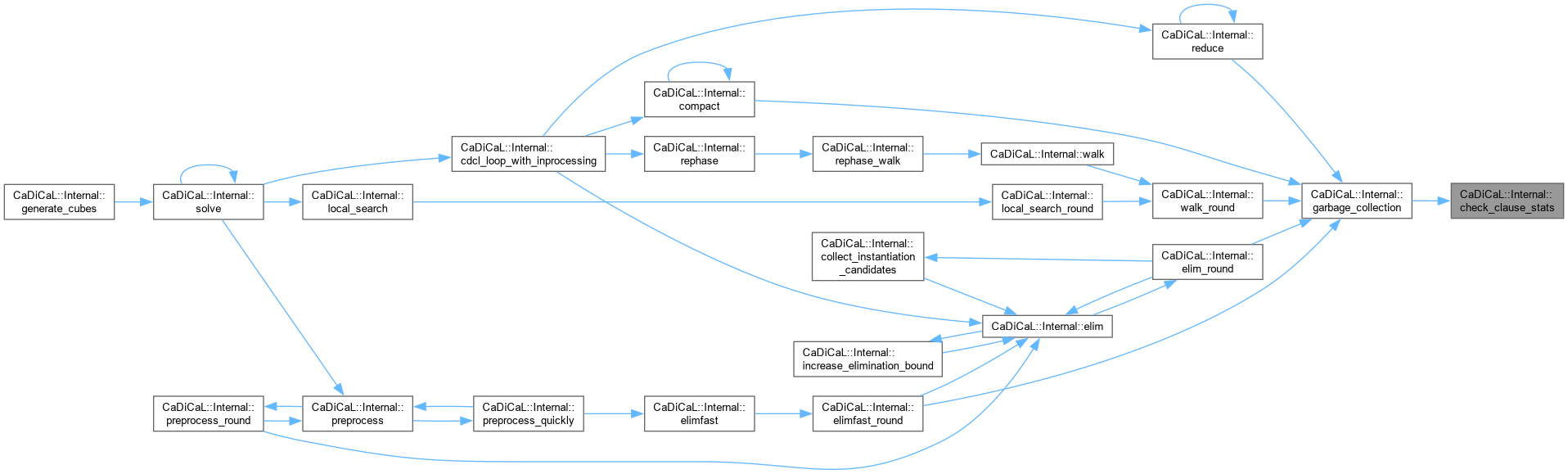
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::check_clause_stats | ( | ) |
Definition at line 452 of file cadical_collect.cpp.
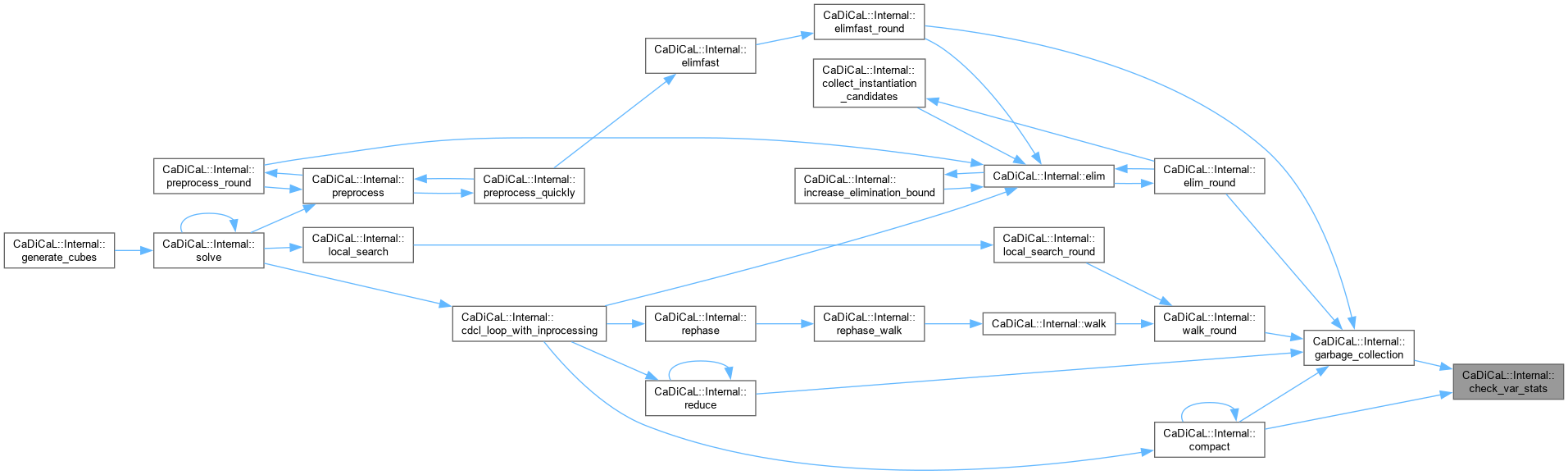
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::check_var_stats | ( | ) |
Definition at line 15 of file cadical_var.cpp.
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::check_watched_literal_invariants | ( | ) |
Definition at line 1085 of file cadical_external_propagate.cpp.


|
inline |
Definition at line 421 of file internal.hpp.
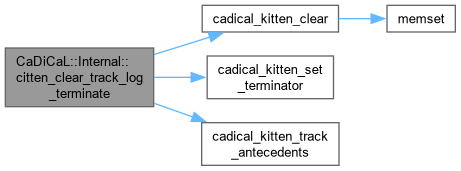
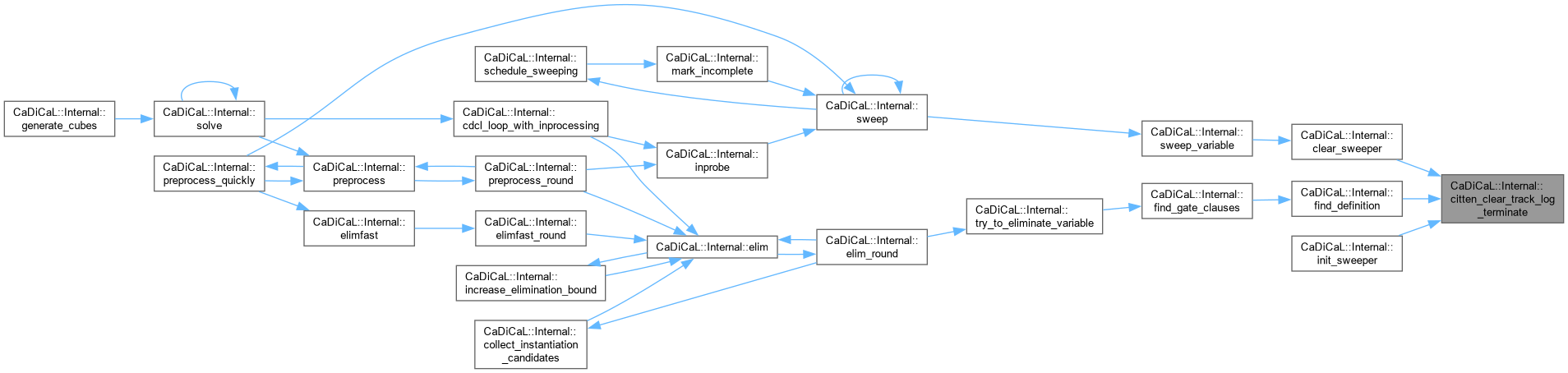
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::citten_clear_track_log_terminate | ( | ) |
Definition at line 482 of file cadical_sweep.cpp.
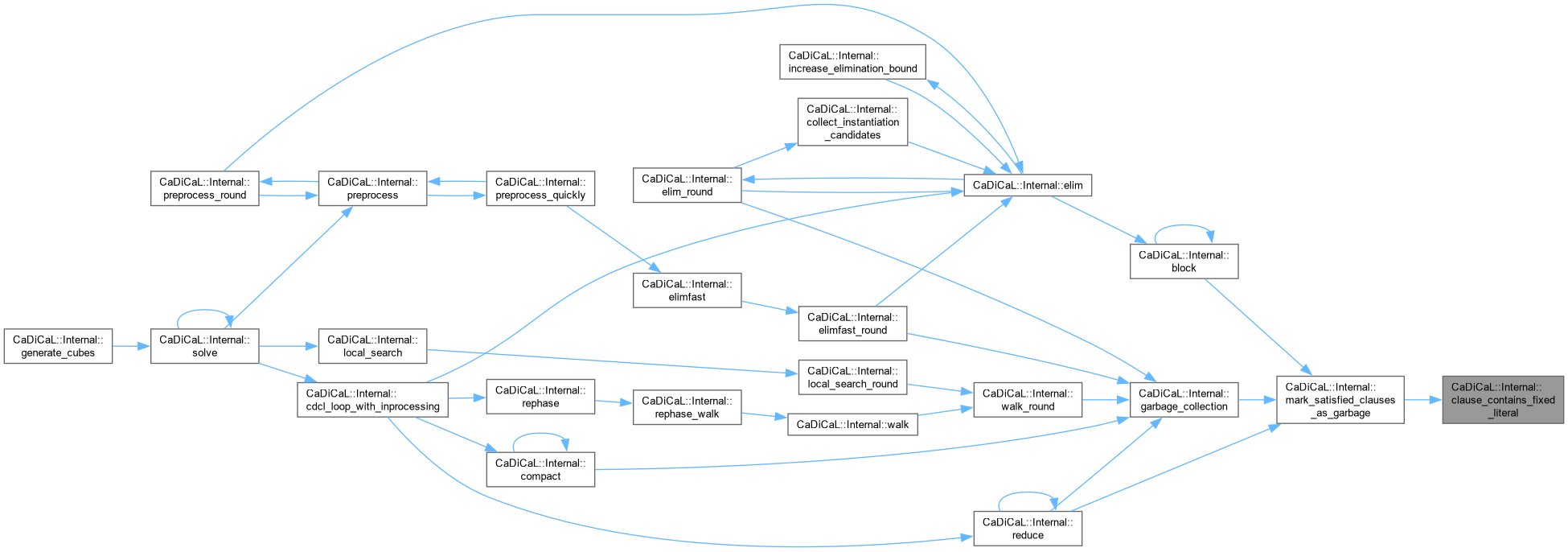
| int CaDiCaL::Internal::clause_contains_fixed_literal | ( | Clause * | c | ) |
Definition at line 16 of file cadical_collect.cpp.

|
inline |
Definition at line 385 of file internal.hpp.
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::clean_probehbr_lrat | ( | ) |
Definition at line 58 of file cadical_probe.cpp.
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::clear_analyzed_levels | ( | ) |
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::clear_analyzed_literals | ( | ) |
Definition at line 445 of file cadical_analyze.cpp.

| void CaDiCaL::Internal::clear_core | ( | Sweeper & | sweeper, |
| unsigned | core_idx ) |
Definition at line 612 of file cadical_sweep.cpp.
Definition at line 209 of file cadical_factor.cpp.
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::clear_minimized_literals | ( | ) |
Definition at line 215 of file cadical_minimize.cpp.

| void CaDiCaL::Internal::clear_noccs | ( | ) |
Definition at line 43 of file cadical_occs.cpp.
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::clear_nounted | ( | vector< int > & | nounted | ) |
Definition at line 201 of file cadical_factor.cpp.
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::clear_occs | ( | ) |
Definition at line 25 of file cadical_occs.cpp.
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::clear_phases | ( | vector< signed char > & | dst | ) |
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::clear_sign_marked_literals | ( | ) |
Definition at line 120 of file cadical_decompose.cpp.

| void CaDiCaL::Internal::clear_sweeper | ( | Sweeper & | sweeper | ) |
Definition at line 298 of file cadical_sweep.cpp.
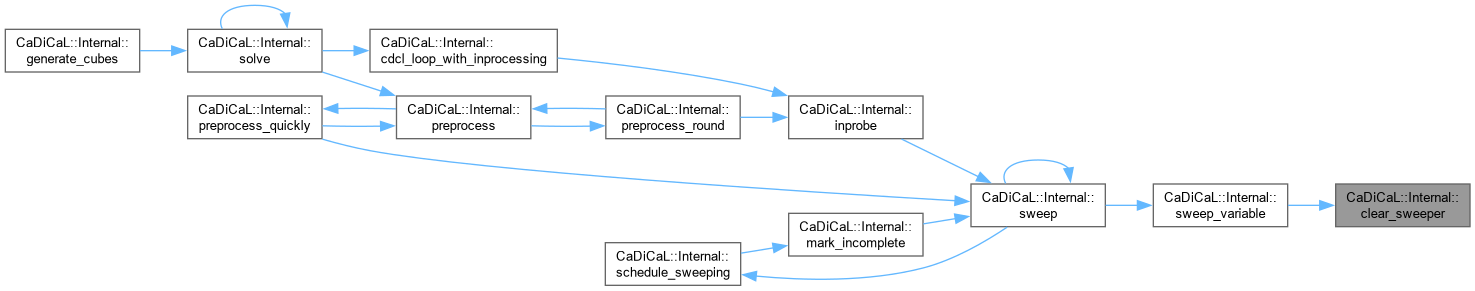
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::clear_unit_analyzed_literals | ( | ) |
Definition at line 431 of file cadical_analyze.cpp.

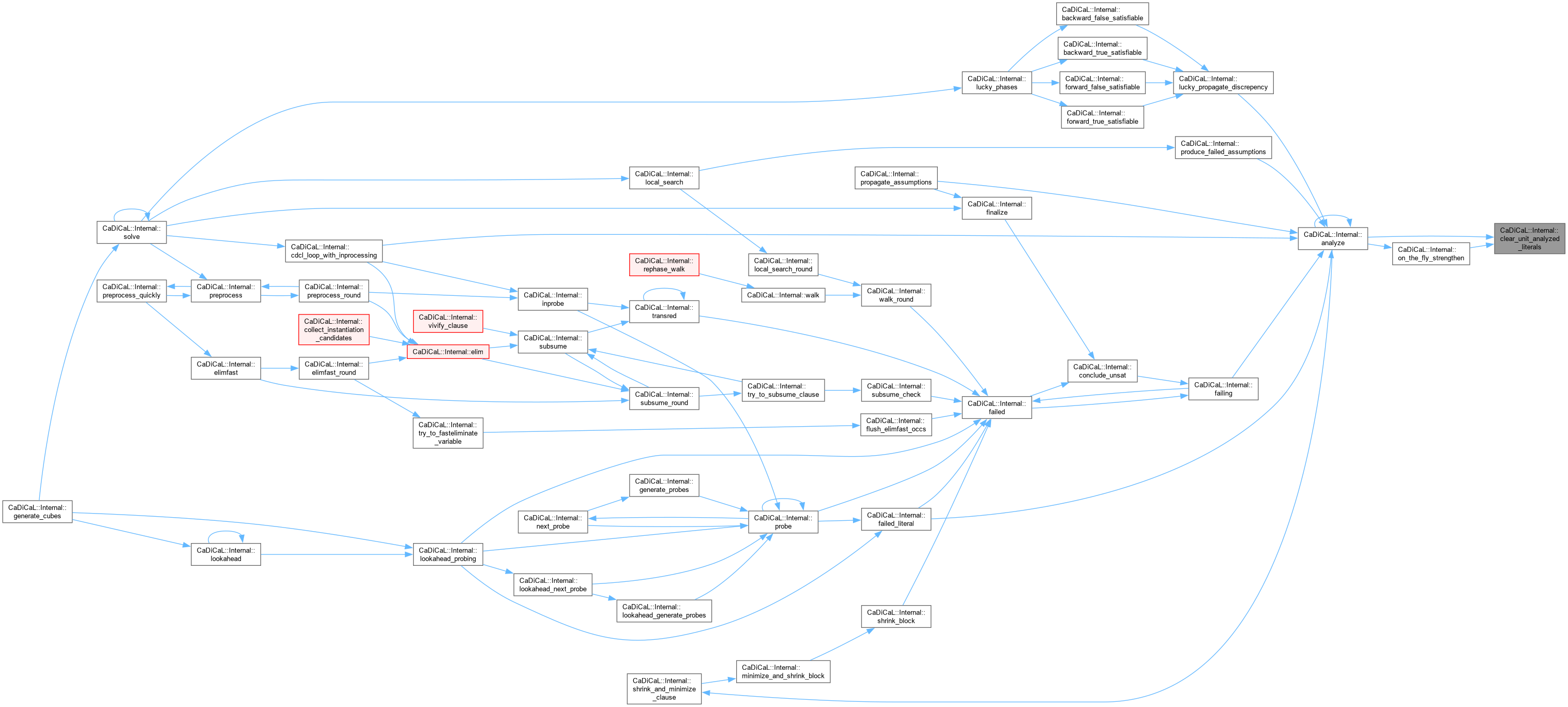
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::clear_watches | ( | ) |
Definition at line 16 of file cadical_watch.cpp.
Definition at line 188 of file cadical_proof.cpp.
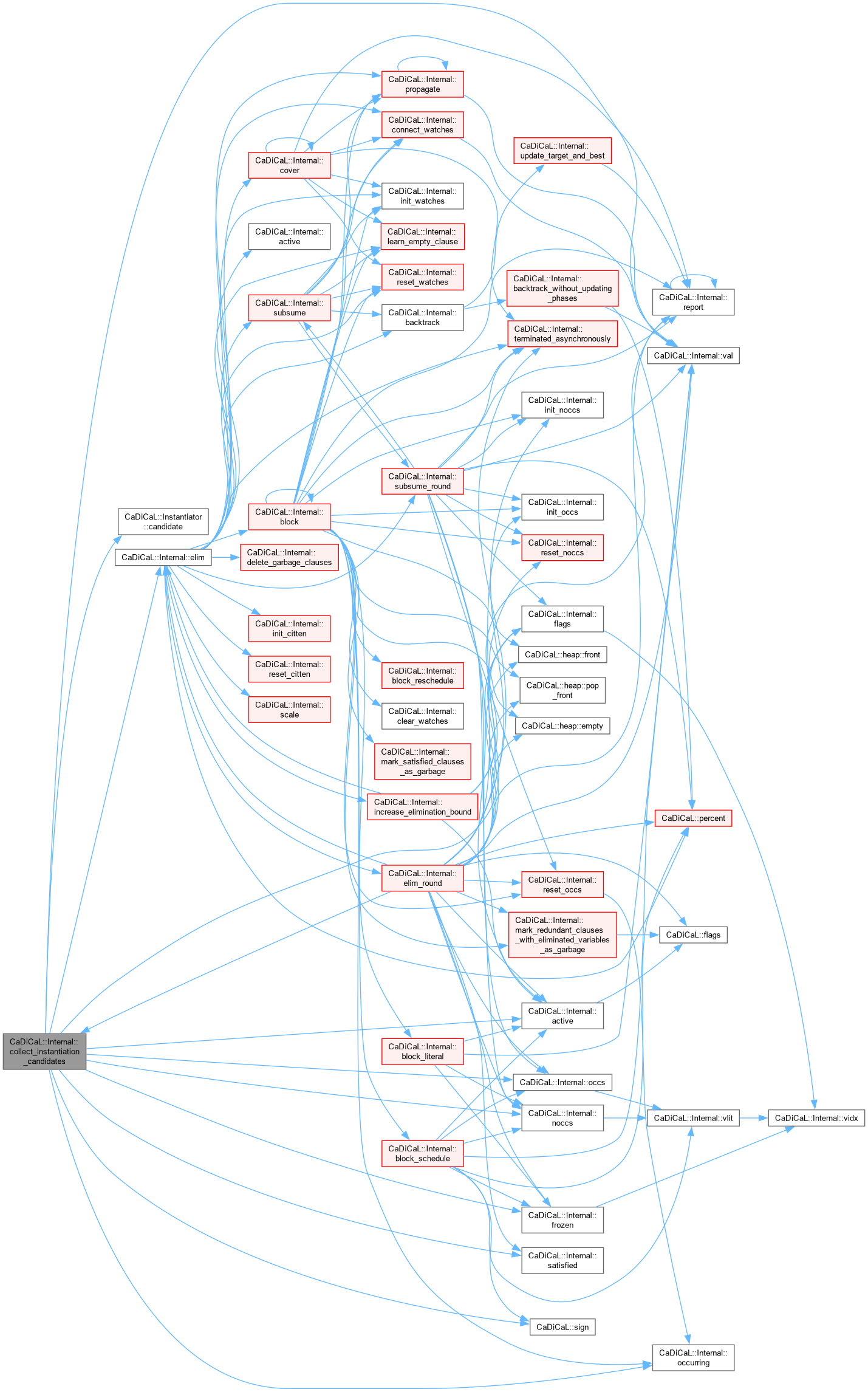
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::collect_instantiation_candidates | ( | Instantiator & | instantiator | ) |
Definition at line 18 of file cadical_instantiate.cpp.
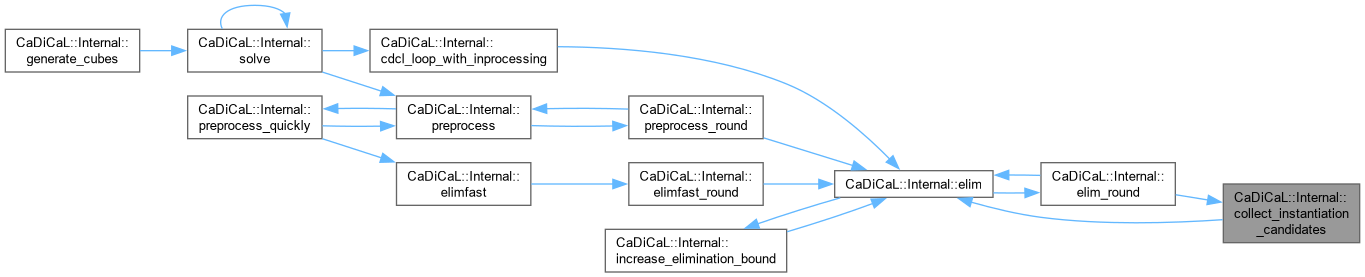
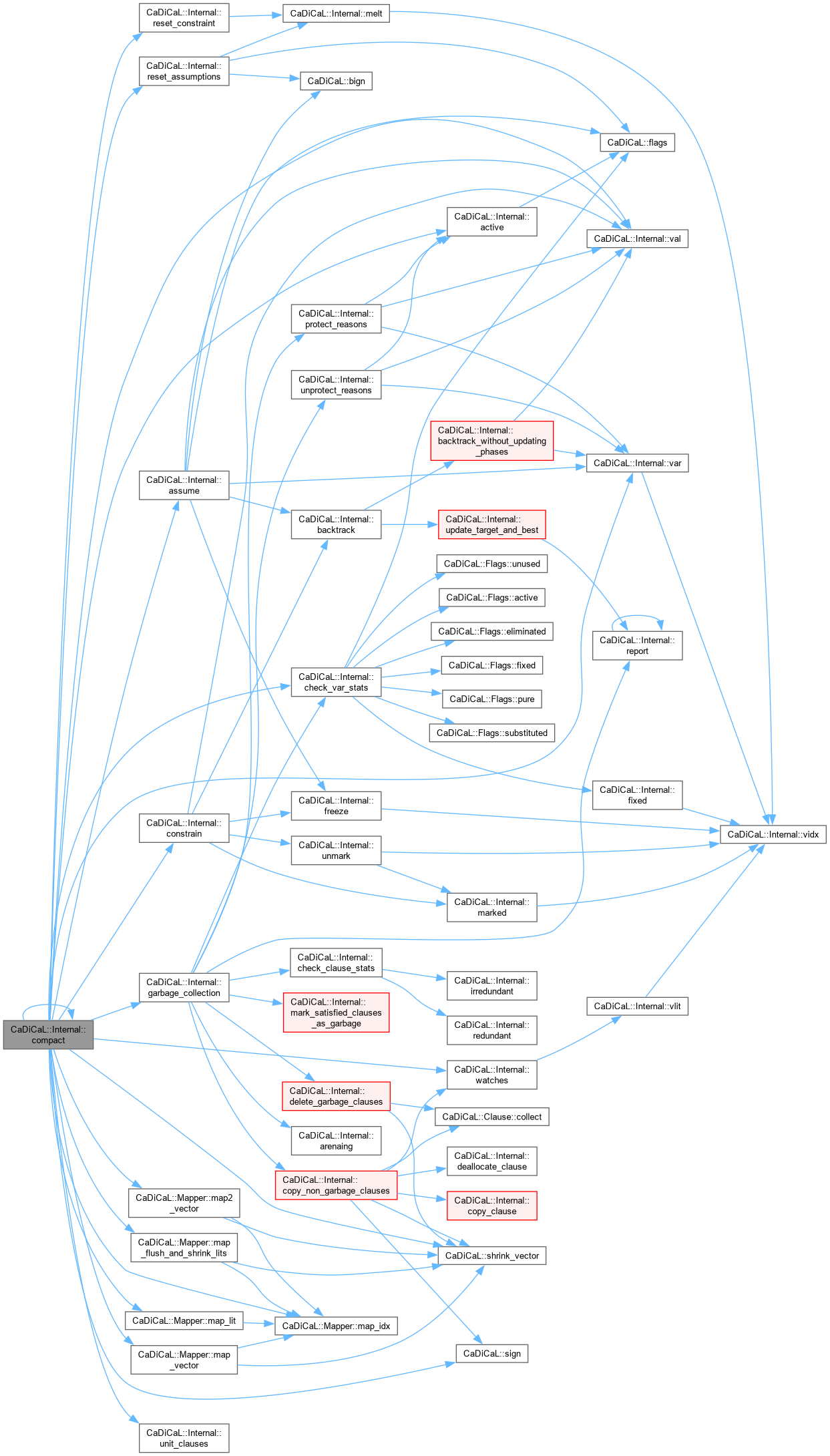
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::compact | ( | ) |
Definition at line 166 of file cadical_compact.cpp.
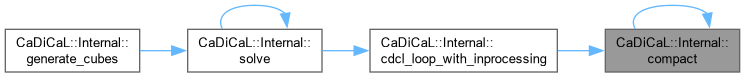
| bool CaDiCaL::Internal::compacting | ( | ) |
Definition at line 17 of file cadical_compact.cpp.
|
inline |
Definition at line 25 of file cadical_elim.cpp.
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::compute_tier_limits | ( | Vivifier & | vivifier | ) |
Definition at line 1792 of file cadical_vivify.cpp.
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::conclude_unsat | ( | ) |
Definition at line 465 of file cadical_assume.cpp.
Definition at line 899 of file cadical_condition.cpp.
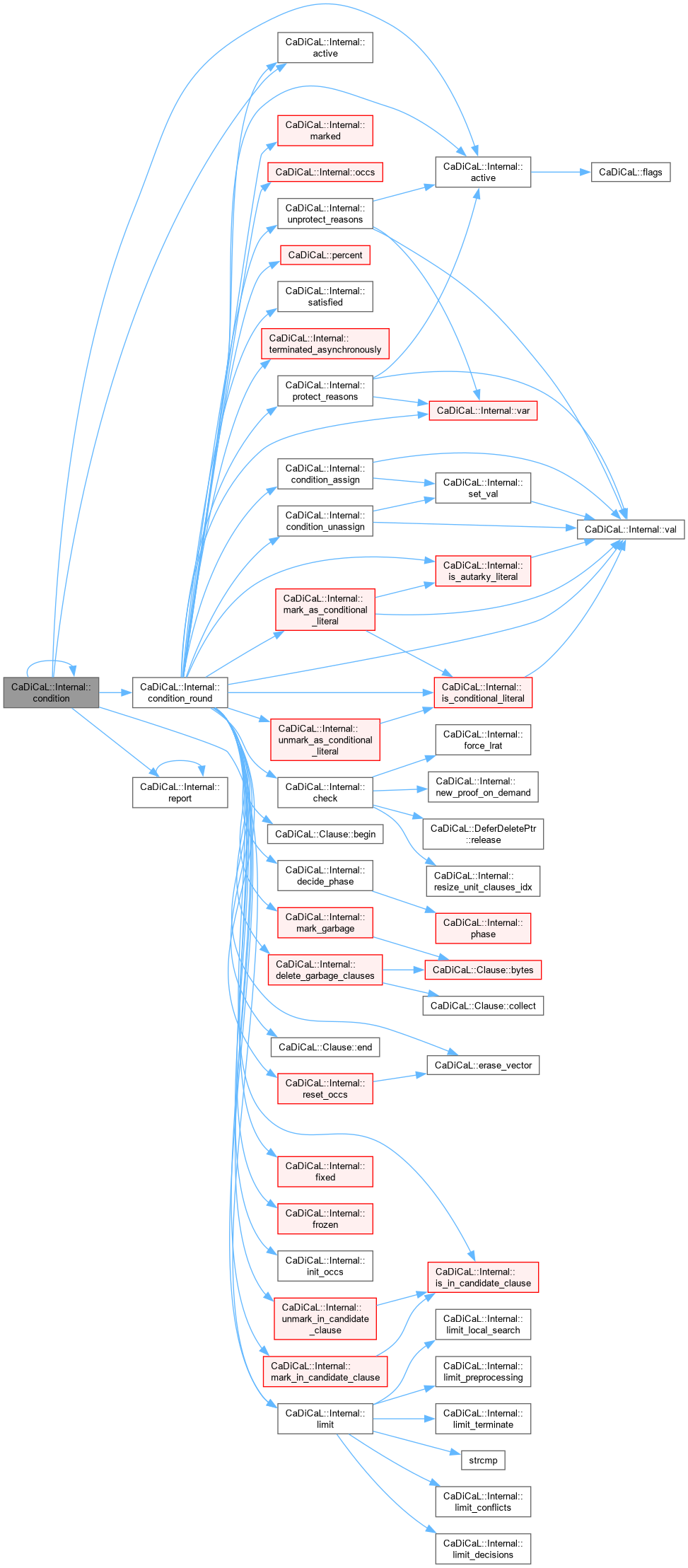

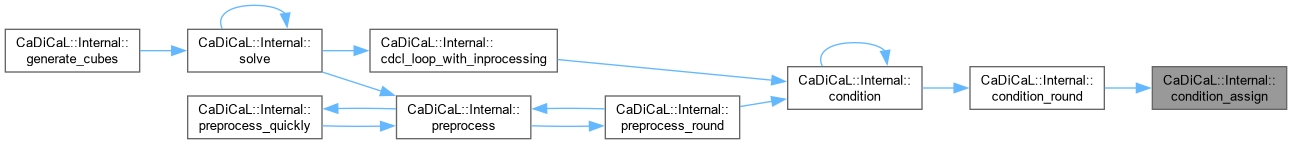
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::condition_assign | ( | int | lit | ) |
Definition at line 90 of file cadical_condition.cpp.

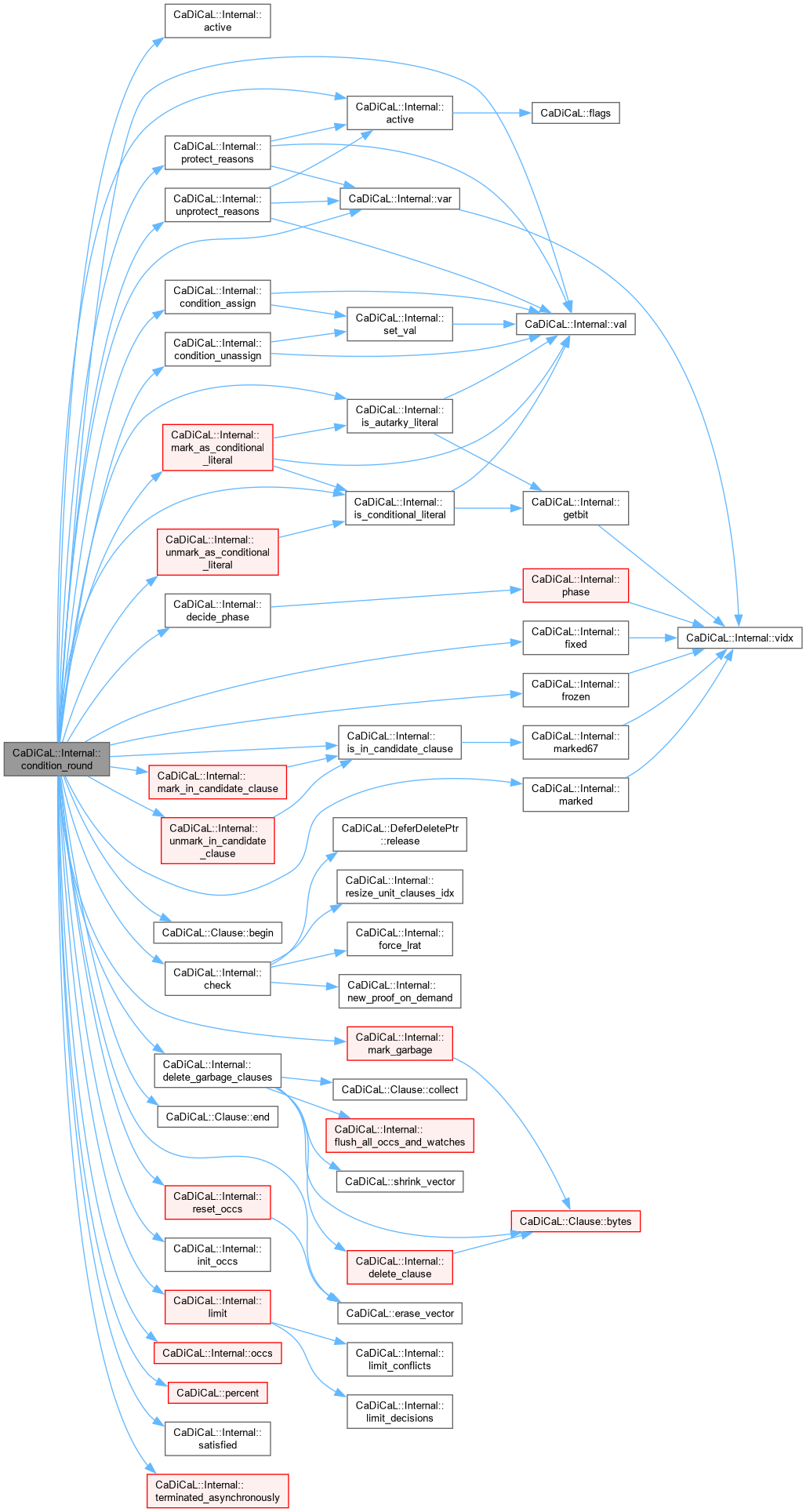
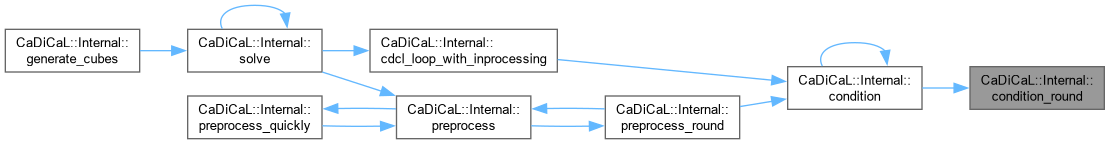
| long CaDiCaL::Internal::condition_round | ( | long | unassigned_literal_propagation_limit | ) |
Definition at line 159 of file cadical_condition.cpp.
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::condition_unassign | ( | int | lit | ) |
Definition at line 84 of file cadical_condition.cpp.

| bool CaDiCaL::Internal::conditioning | ( | ) |
Definition at line 39 of file cadical_condition.cpp.
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::connect_binary_watches | ( | ) |
Definition at line 86 of file cadical_watch.cpp.
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::connect_proof_tracer | ( | FileTracer * | tracer, |
| bool | antecedents, | ||
| bool | finalize_clauses = false ) |
Definition at line 73 of file cadical_proof.cpp.
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::connect_proof_tracer | ( | InternalTracer * | tracer, |
| bool | antecedents, | ||
| bool | finalize_clauses = false ) |
Definition at line 46 of file cadical_proof.cpp.
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::connect_proof_tracer | ( | StatTracer * | tracer, |
| bool | antecedents, | ||
| bool | finalize_clauses = false ) |
Definition at line 60 of file cadical_proof.cpp.
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::connect_proof_tracer | ( | Tracer * | tracer, |
| bool | antecedents, | ||
| bool | finalize_clauses = false ) |
Definition at line 34 of file cadical_proof.cpp.
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::connect_propagator | ( | ) |
Definition at line 968 of file cadical_external_propagate.cpp.
Definition at line 30 of file cadical_watch.cpp.
Definition at line 511 of file cadical_vivify.cpp.

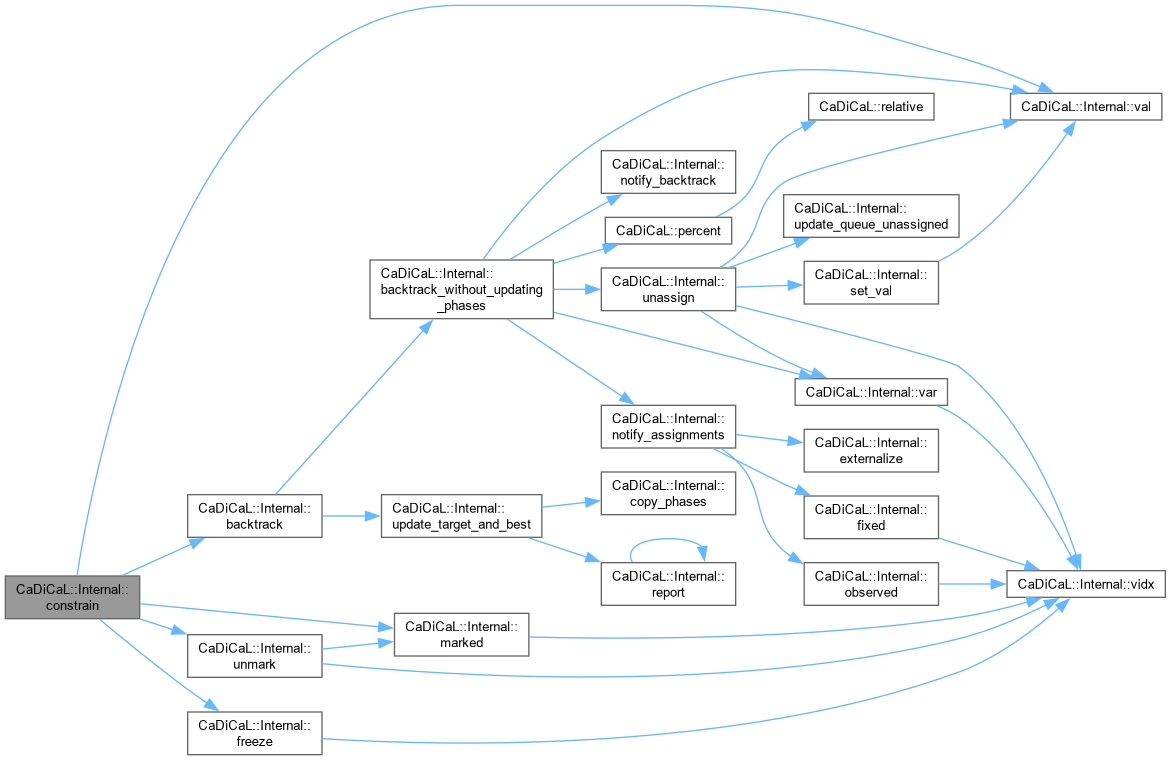
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::constrain | ( | int | lit | ) |
Definition at line 9 of file cadical_constrain.cpp.

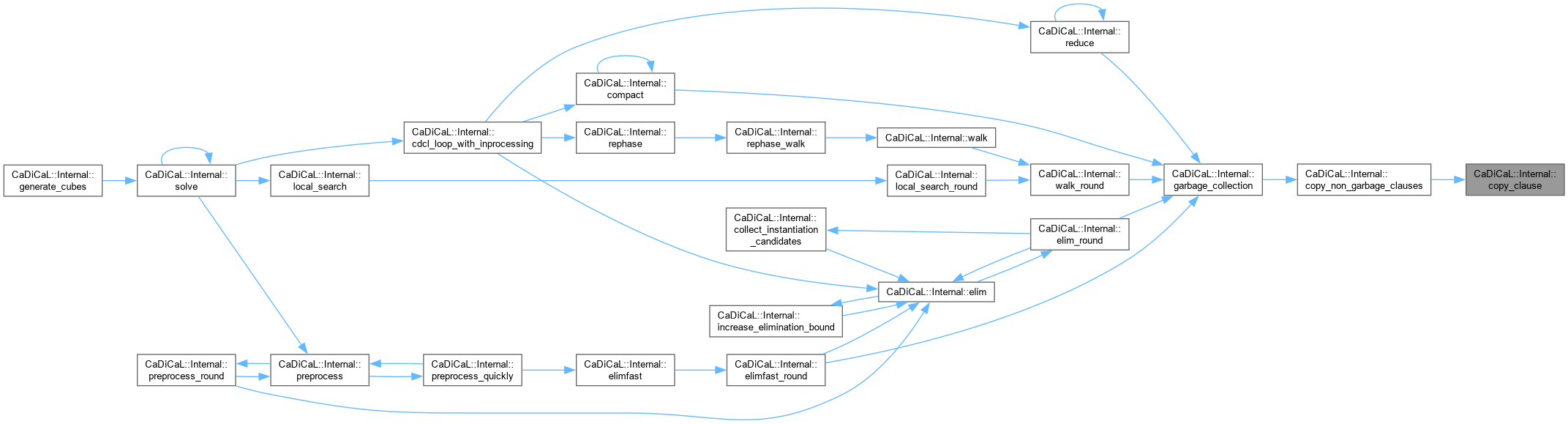
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::copy_clause | ( | Clause * | c | ) |
Definition at line 315 of file cadical_collect.cpp.

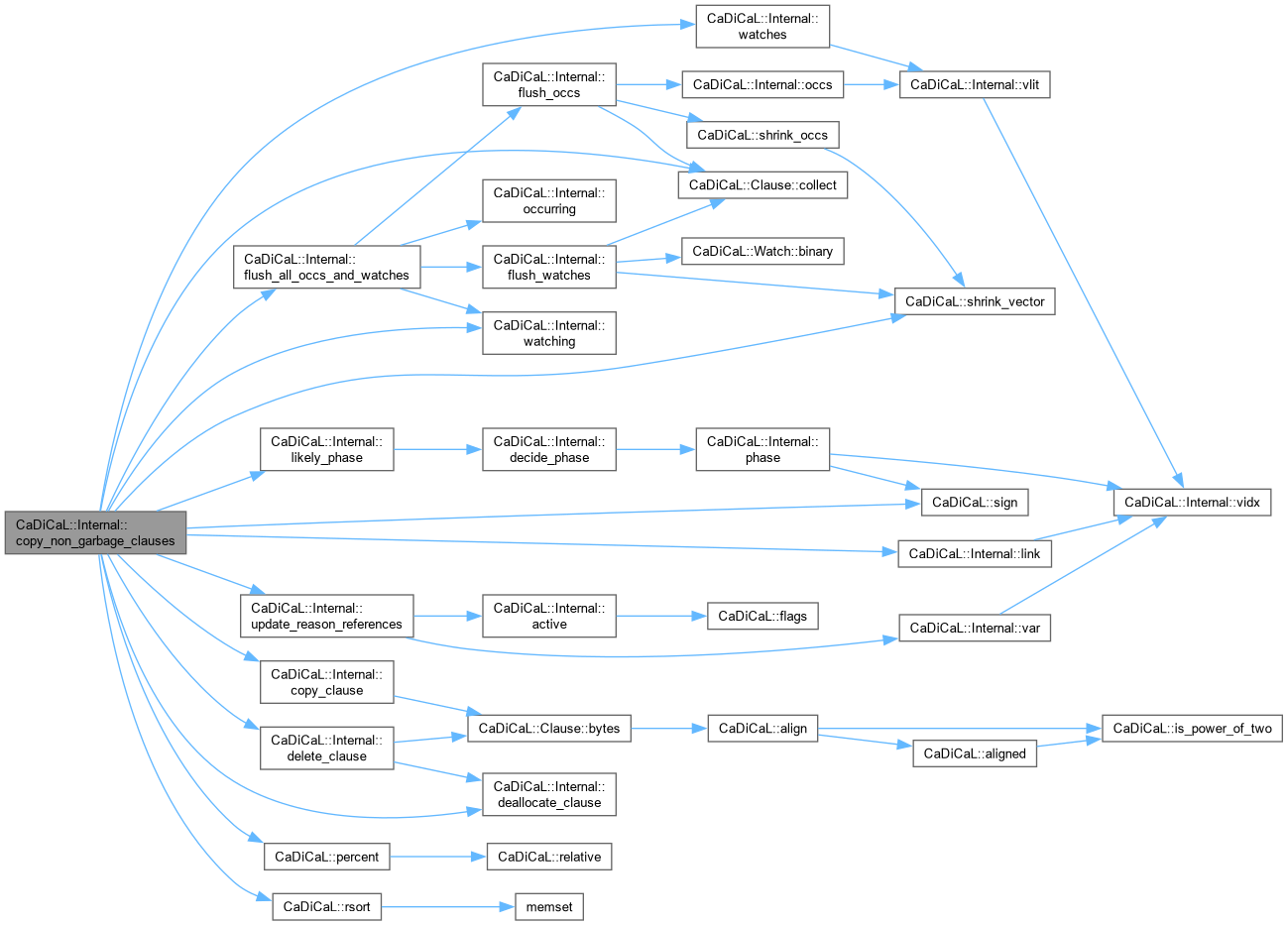
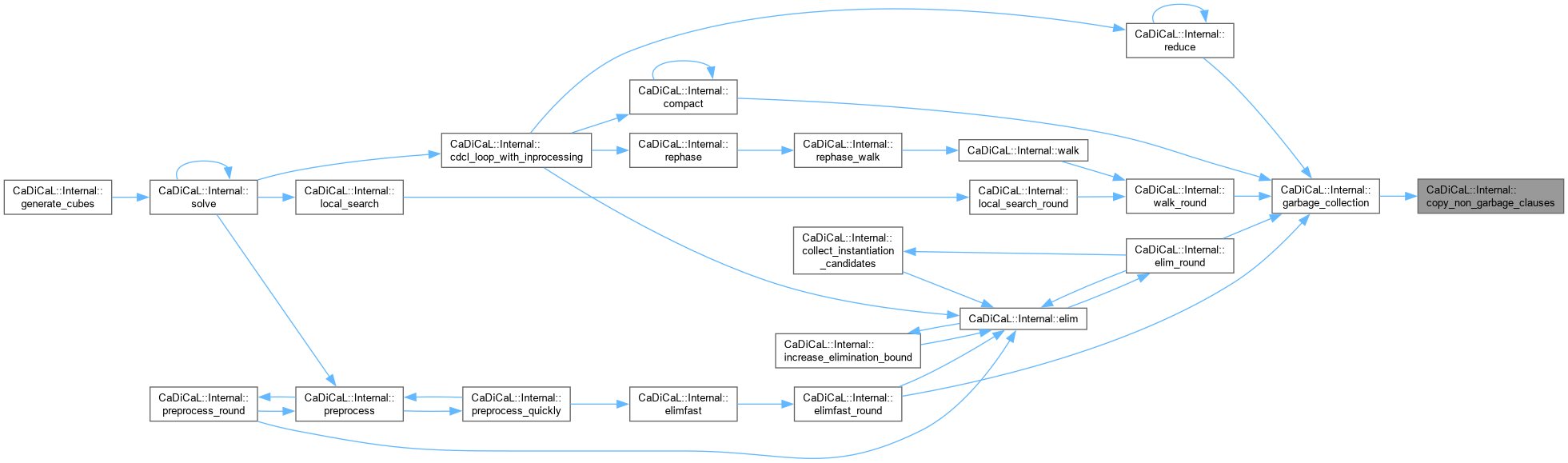
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::copy_non_garbage_clauses | ( | ) |
Definition at line 328 of file cadical_collect.cpp.
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::copy_phases | ( | vector< signed char > & | dst | ) |
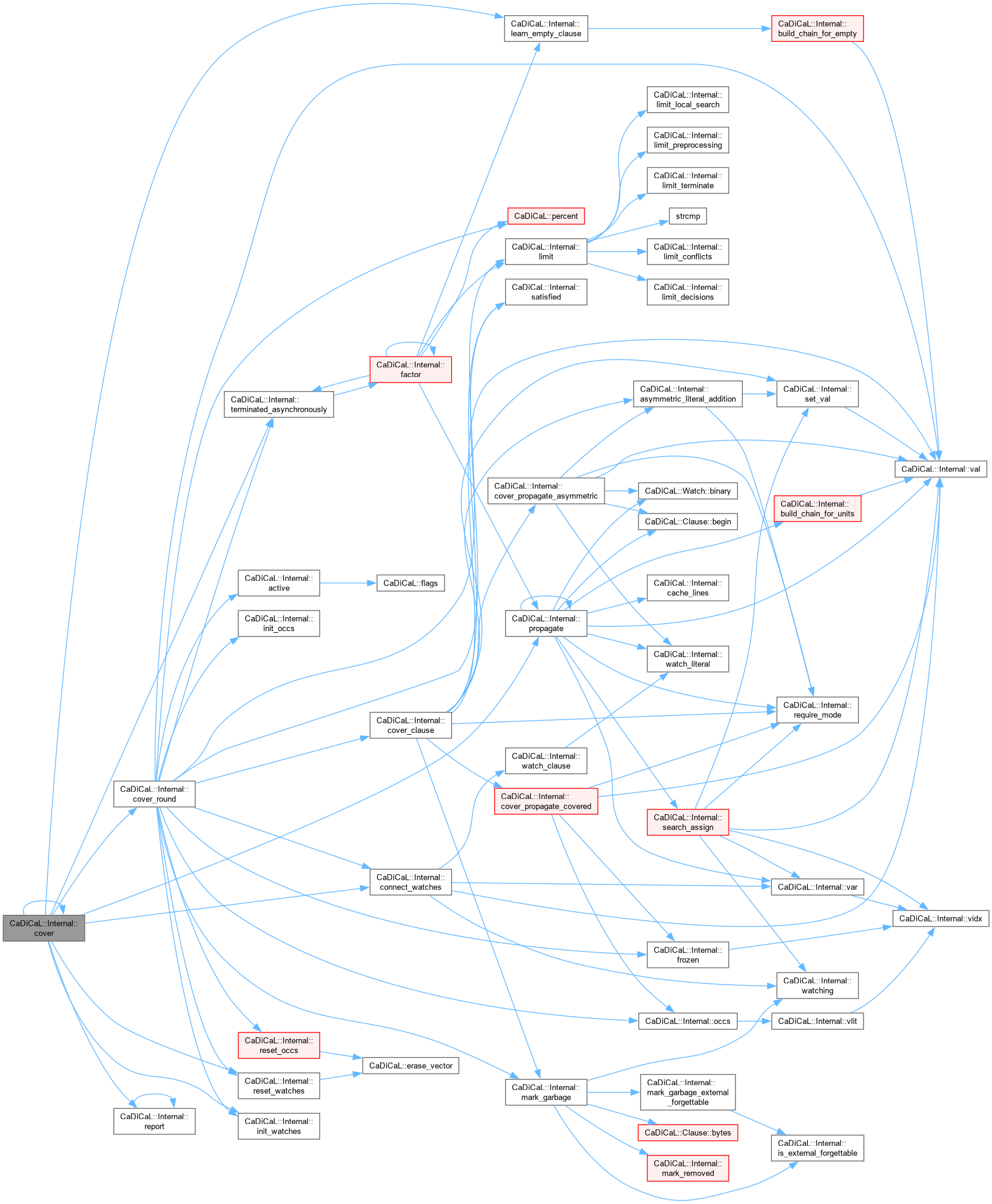
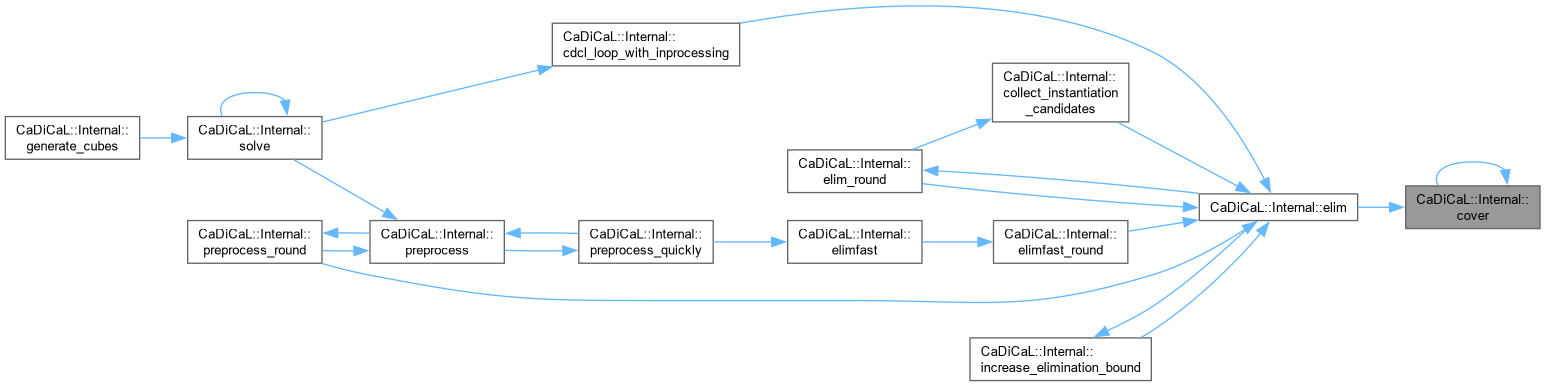
| bool CaDiCaL::Internal::cover | ( | ) |
Definition at line 649 of file cadical_cover.cpp.
Definition at line 327 of file cadical_cover.cpp.
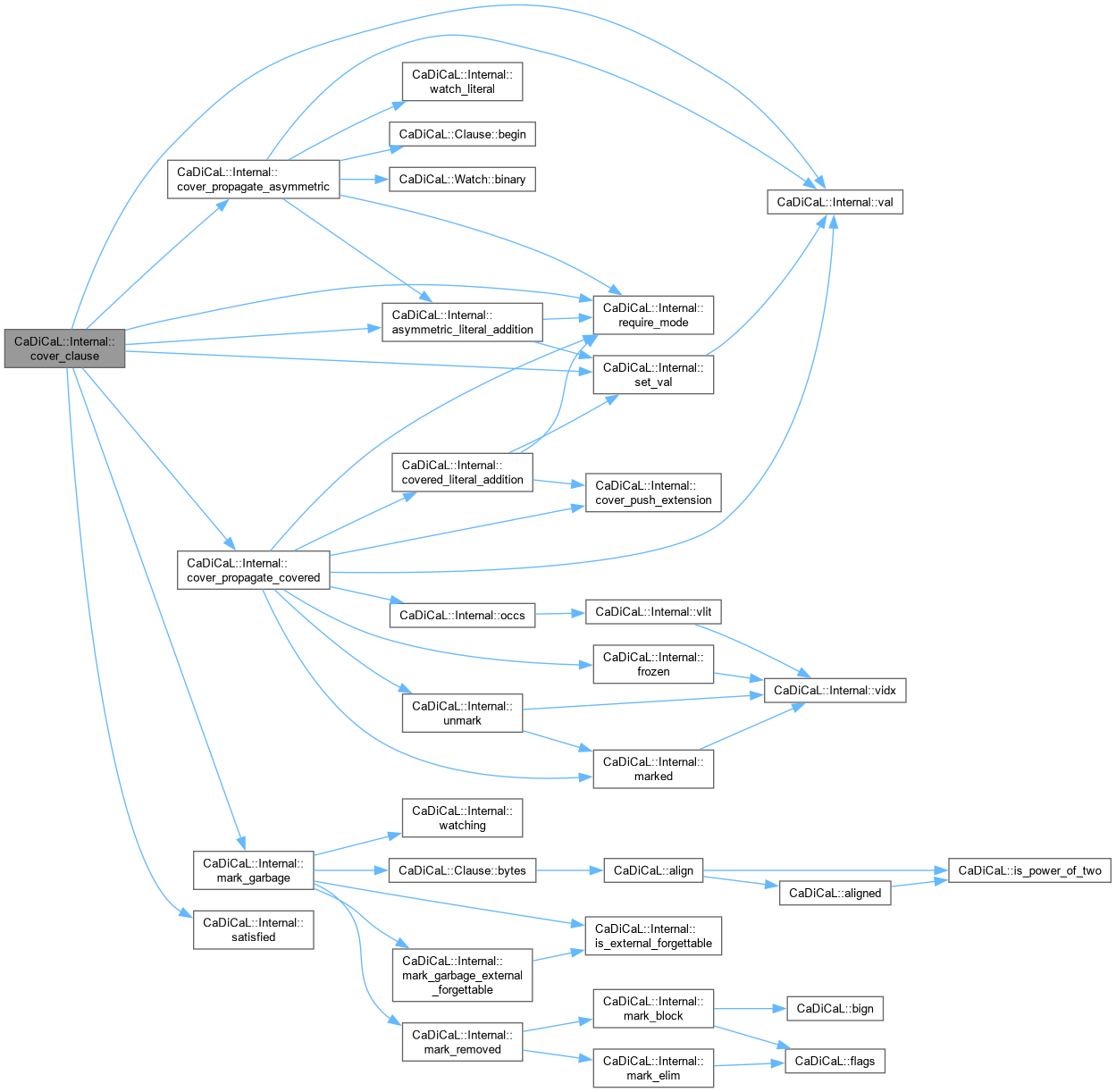
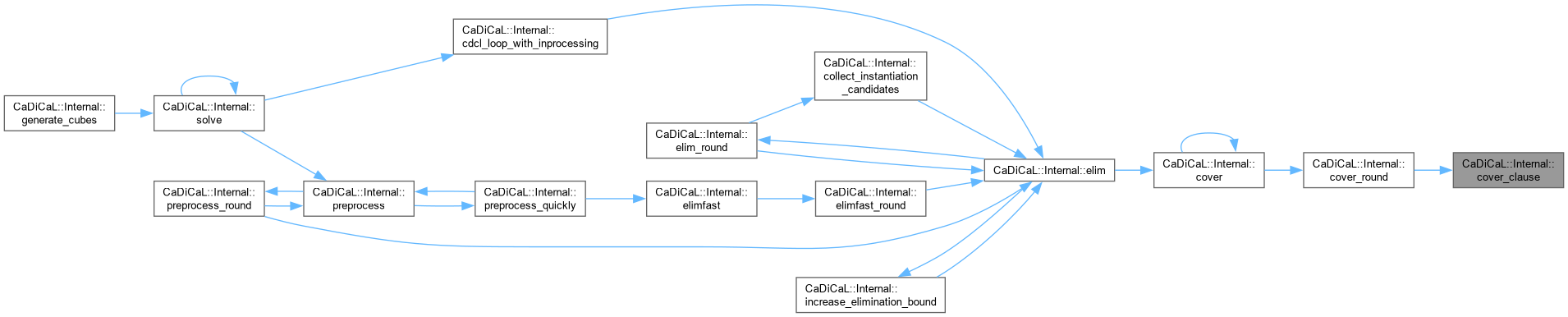
Definition at line 104 of file cadical_cover.cpp.
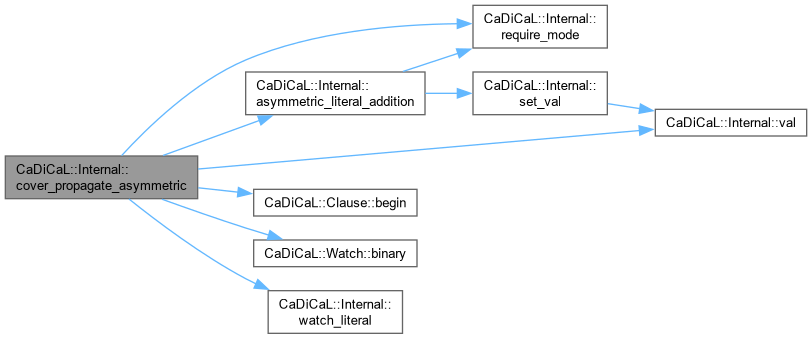
Definition at line 185 of file cadical_cover.cpp.
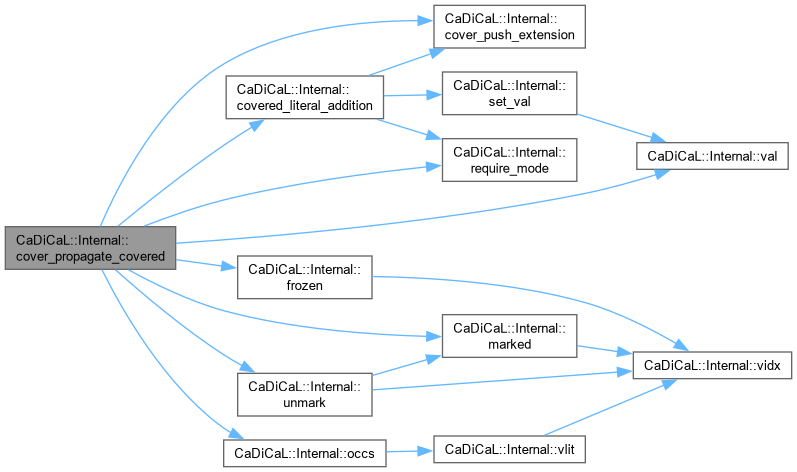
|
inline |
Definition at line 53 of file cadical_cover.cpp.
| int64_t CaDiCaL::Internal::cover_round | ( | ) |
Definition at line 483 of file cadical_cover.cpp.
|
inline |
Definition at line 68 of file cadical_cover.cpp.
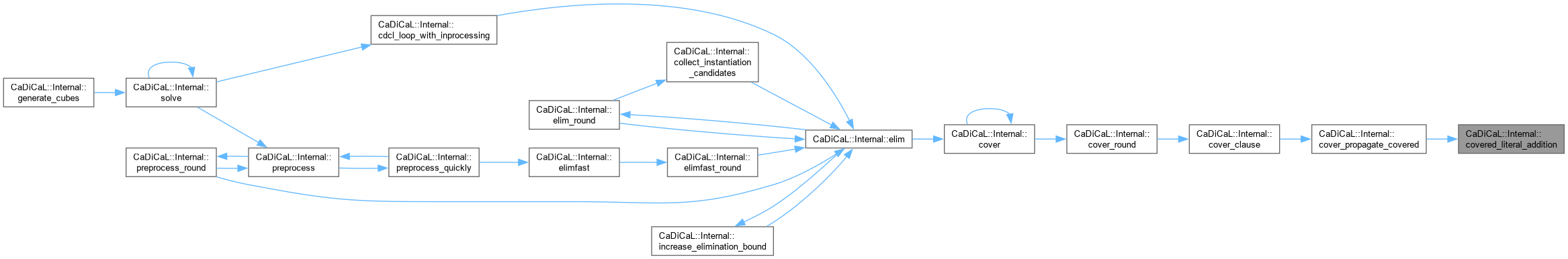
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::deallocate_clause | ( | Clause * | c | ) |
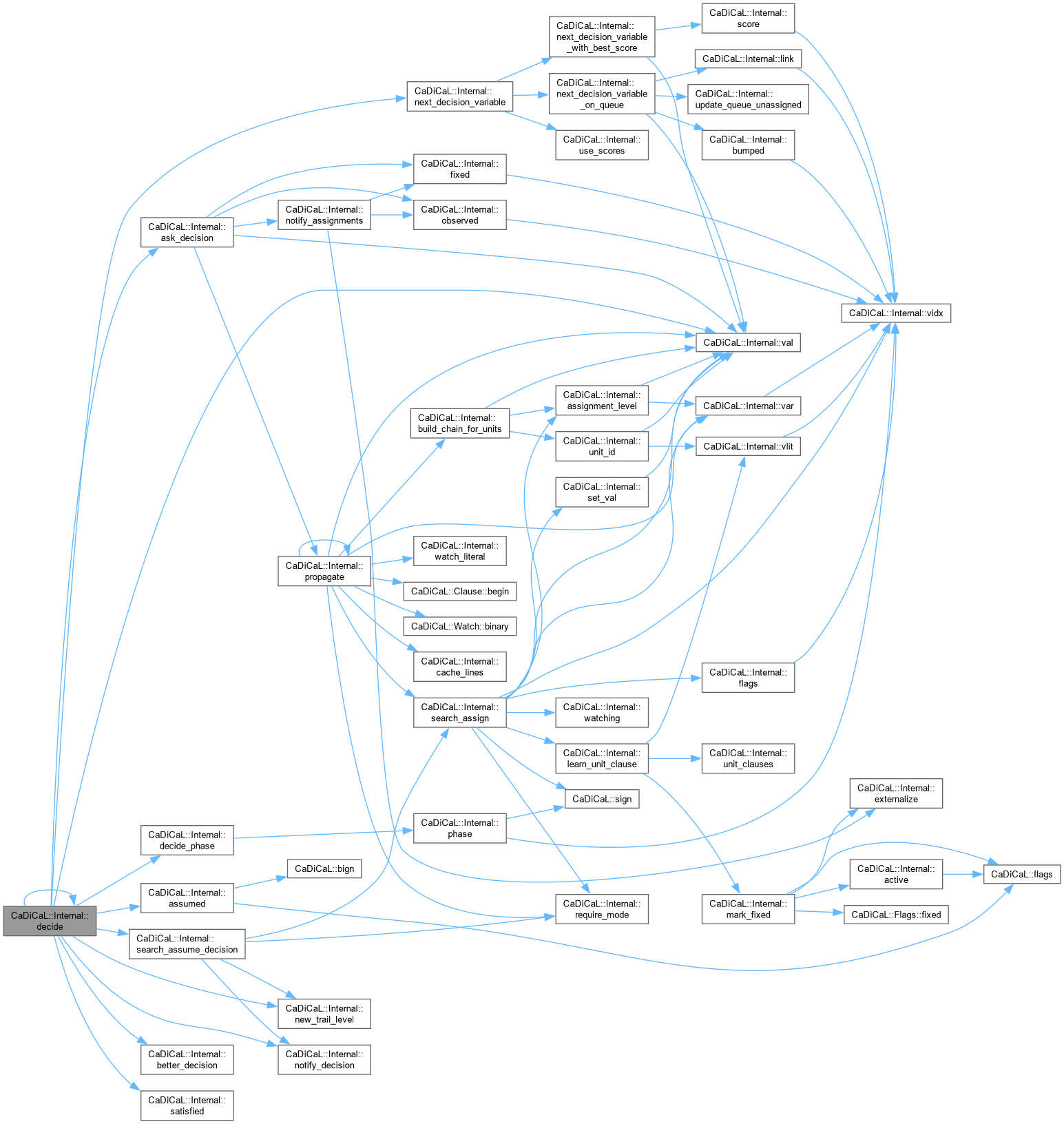
| int CaDiCaL::Internal::decide | ( | ) |
Definition at line 126 of file cadical_decide.cpp.
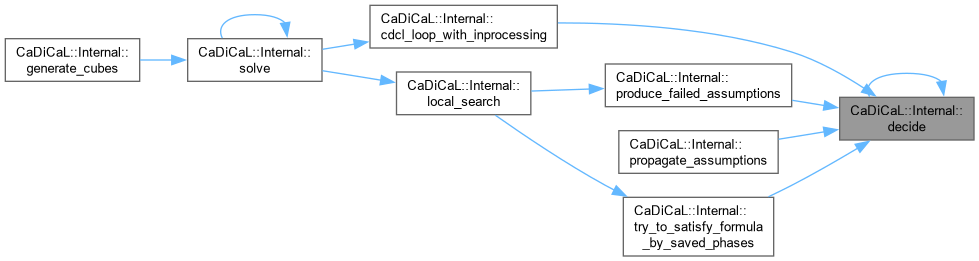
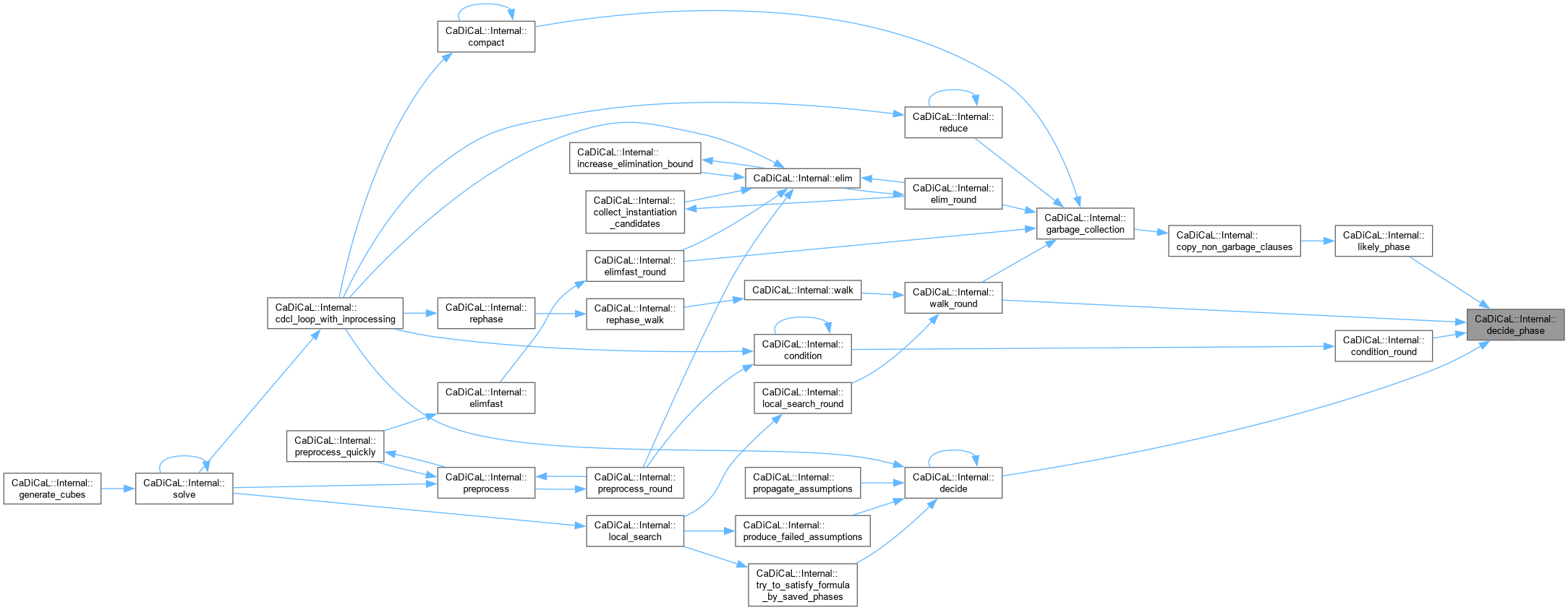
| int CaDiCaL::Internal::decide_phase | ( | int | idx, |
| bool | target ) |
Definition at line 57 of file cadical_decide.cpp.

| void CaDiCaL::Internal::decompose | ( | ) |
Definition at line 731 of file cadical_decompose.cpp.
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::decompose_analyze_binary_chain | ( | DFS * | dfs, |
| int | from ) |
Definition at line 9 of file cadical_decompose.cpp.
Definition at line 29 of file cadical_decompose.cpp.

Definition at line 52 of file cadical_decompose.cpp.
| bool CaDiCaL::Internal::decompose_round | ( | ) |
Definition at line 134 of file cadical_decompose.cpp.
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::delete_clause | ( | Clause * | c | ) |
Definition at line 258 of file cadical_clause.cpp.
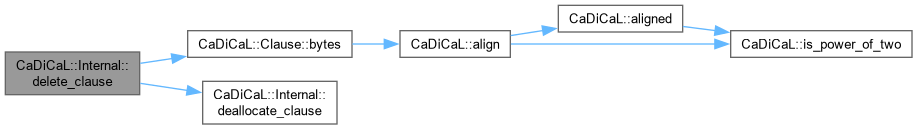
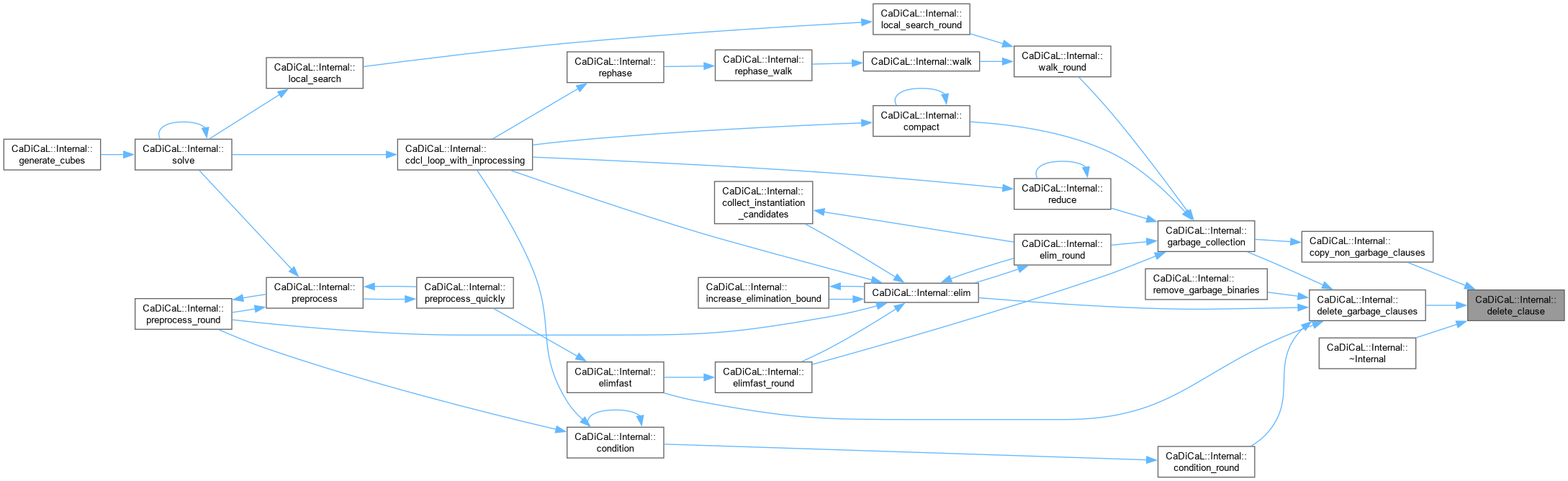
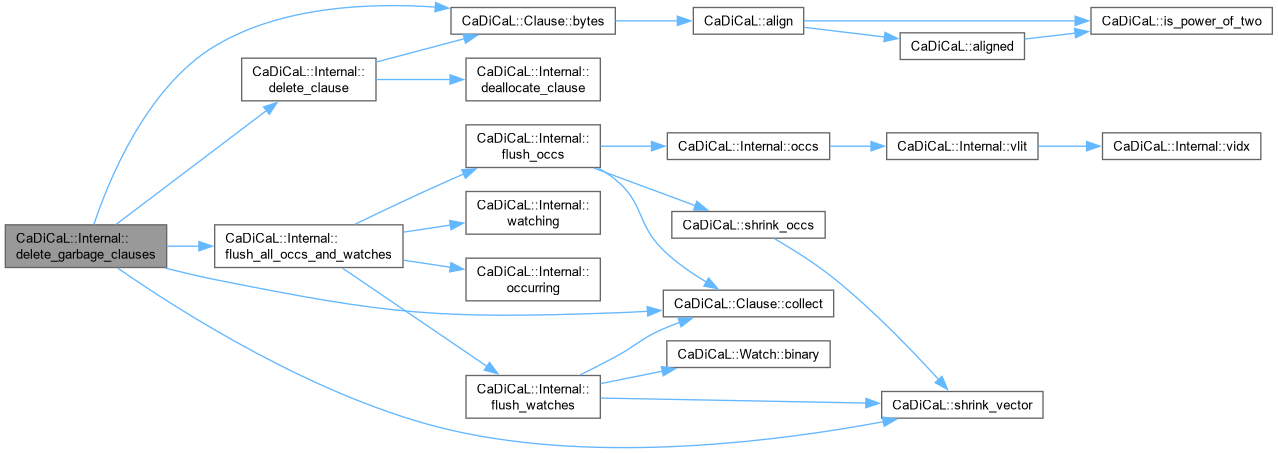
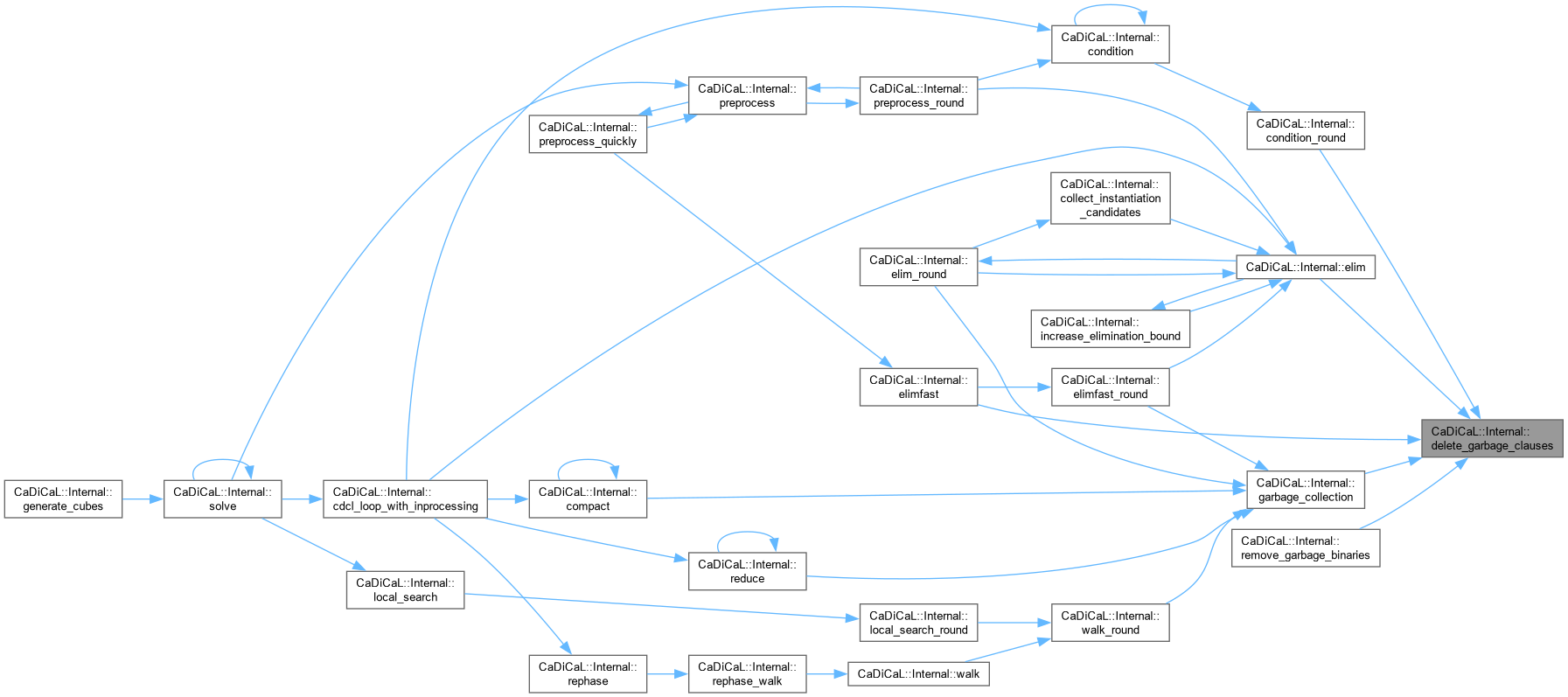
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::delete_garbage_clauses | ( | ) |
Definition at line 279 of file cadical_collect.cpp.
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::delete_sweep_binary | ( | const sweep_binary & | sb | ) |
Definition at line 931 of file cadical_sweep.cpp.
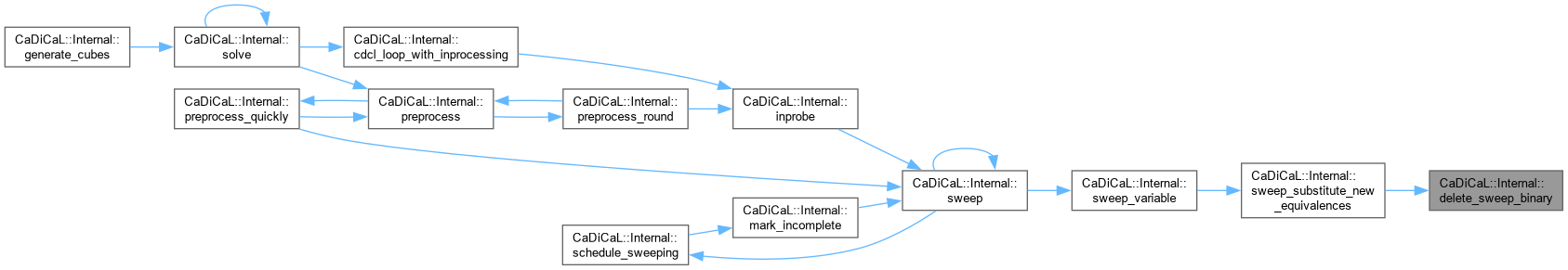
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::delete_unfactored | ( | Quotient * | q | ) |
Definition at line 690 of file cadical_factor.cpp.
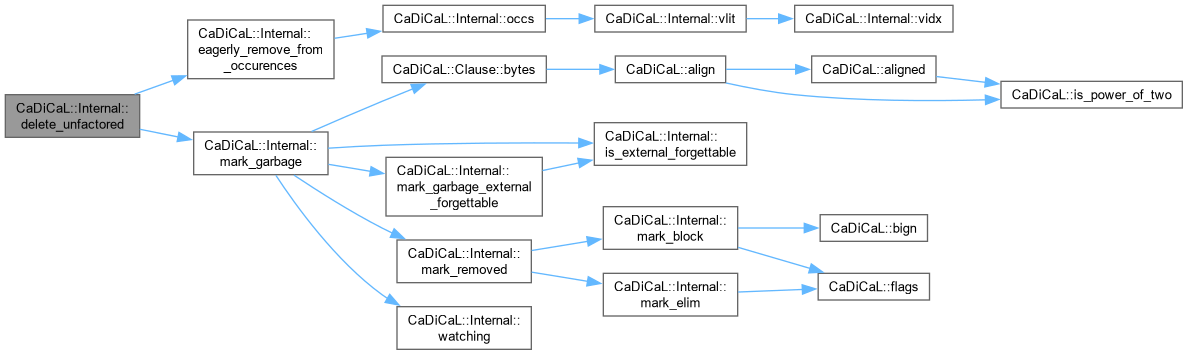
|
inline |
Definition at line 120 of file cadical_vivify.cpp.

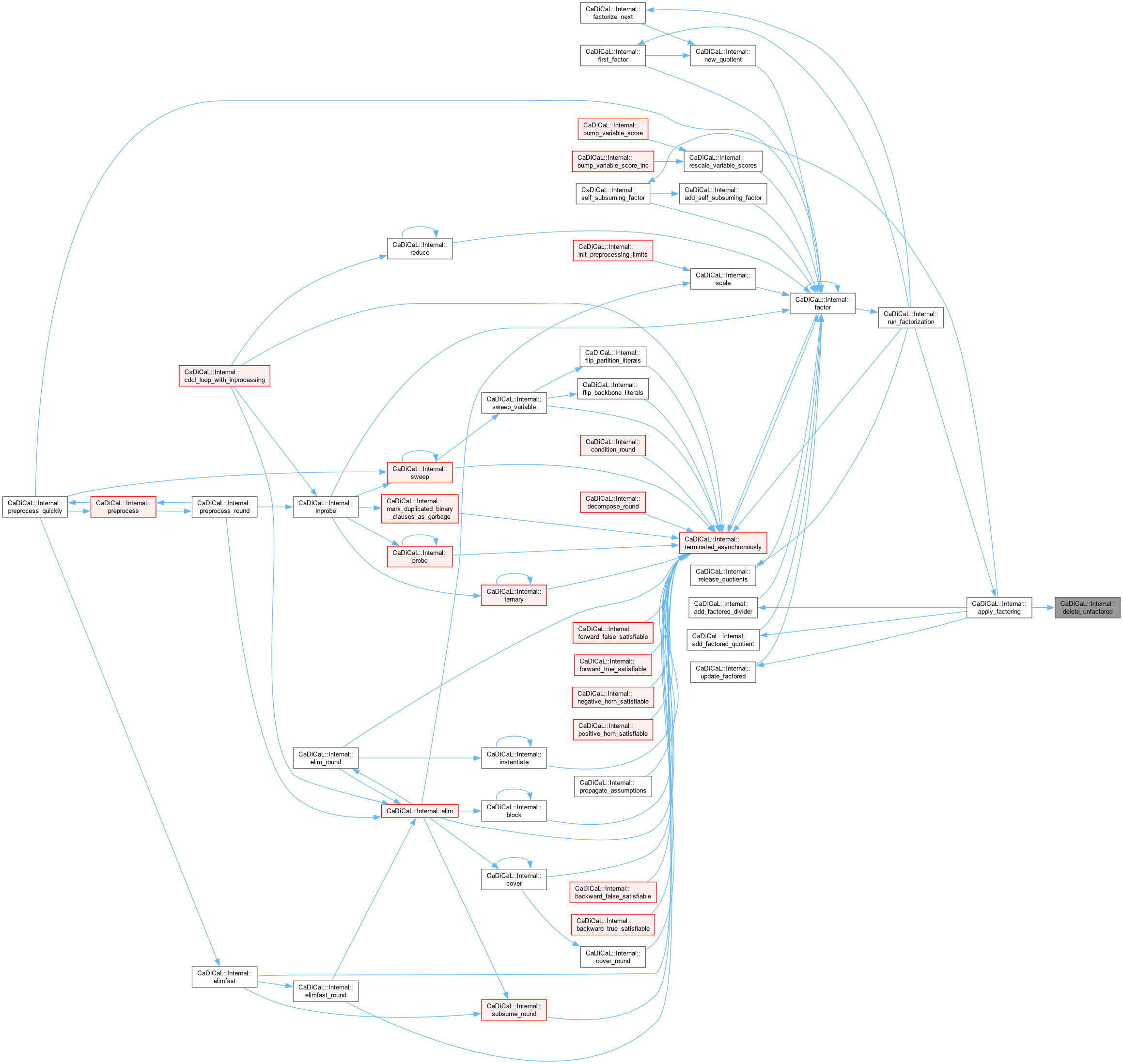
|
inline |
Definition at line 652 of file cadical_analyze.cpp.
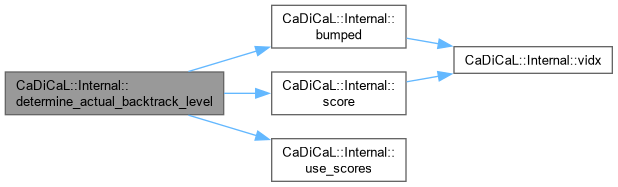
| bool CaDiCaL::Internal::disconnect_proof_tracer | ( | FileTracer * | tracer | ) |
Definition at line 108 of file cadical_proof.cpp.
| bool CaDiCaL::Internal::disconnect_proof_tracer | ( | StatTracer * | tracer | ) |
Definition at line 97 of file cadical_proof.cpp.
Definition at line 86 of file cadical_proof.cpp.
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::dump | ( | ) |
Definition at line 1114 of file cadical_internal.cpp.


| void CaDiCaL::Internal::dump | ( | Clause * | c | ) |
Definition at line 1108 of file cadical_internal.cpp.
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::eagerly_remove_from_occurences | ( | Clause * | c | ) |
Definition at line 672 of file cadical_factor.cpp.

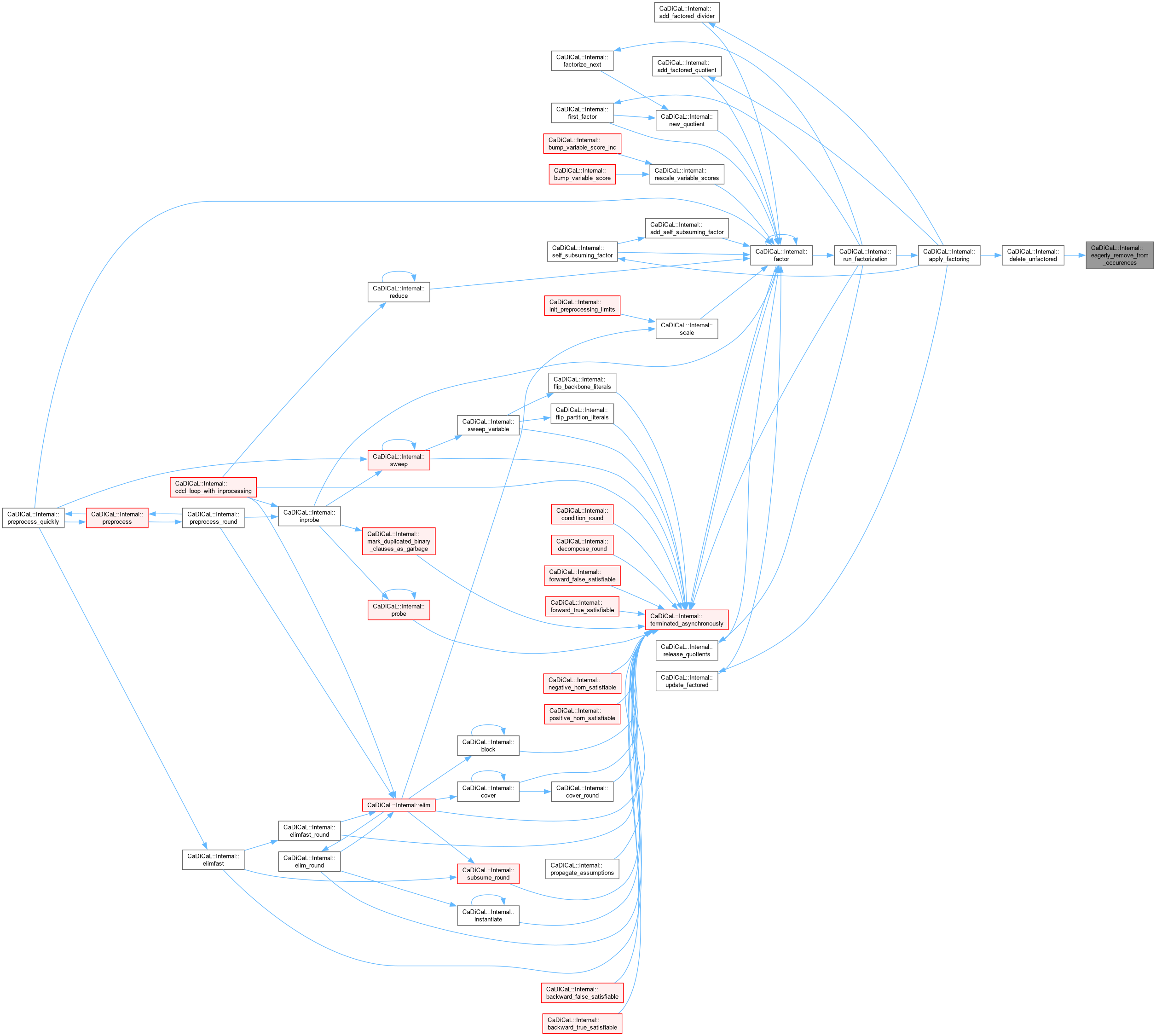
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::eagerly_subsume_recently_learned_clauses | ( | Clause * | c | ) |
Definition at line 731 of file cadical_analyze.cpp.
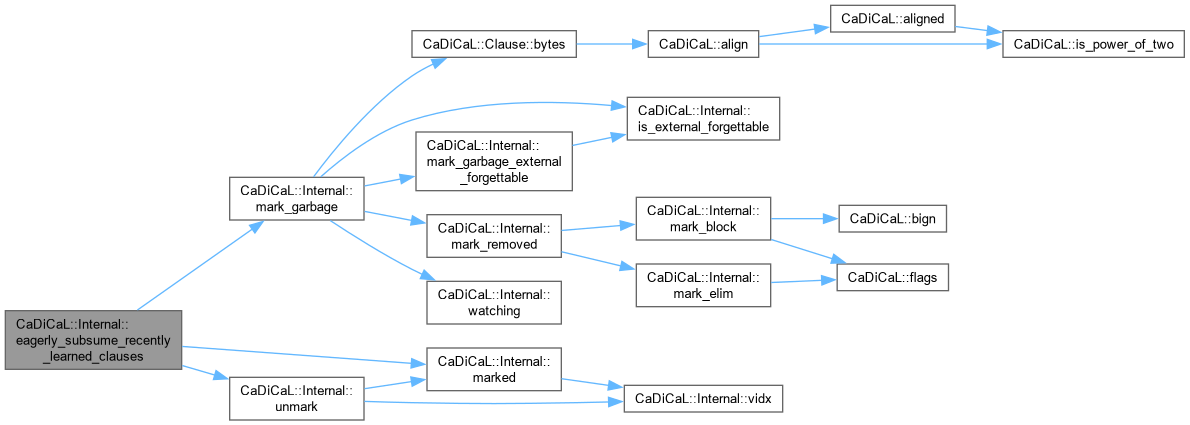
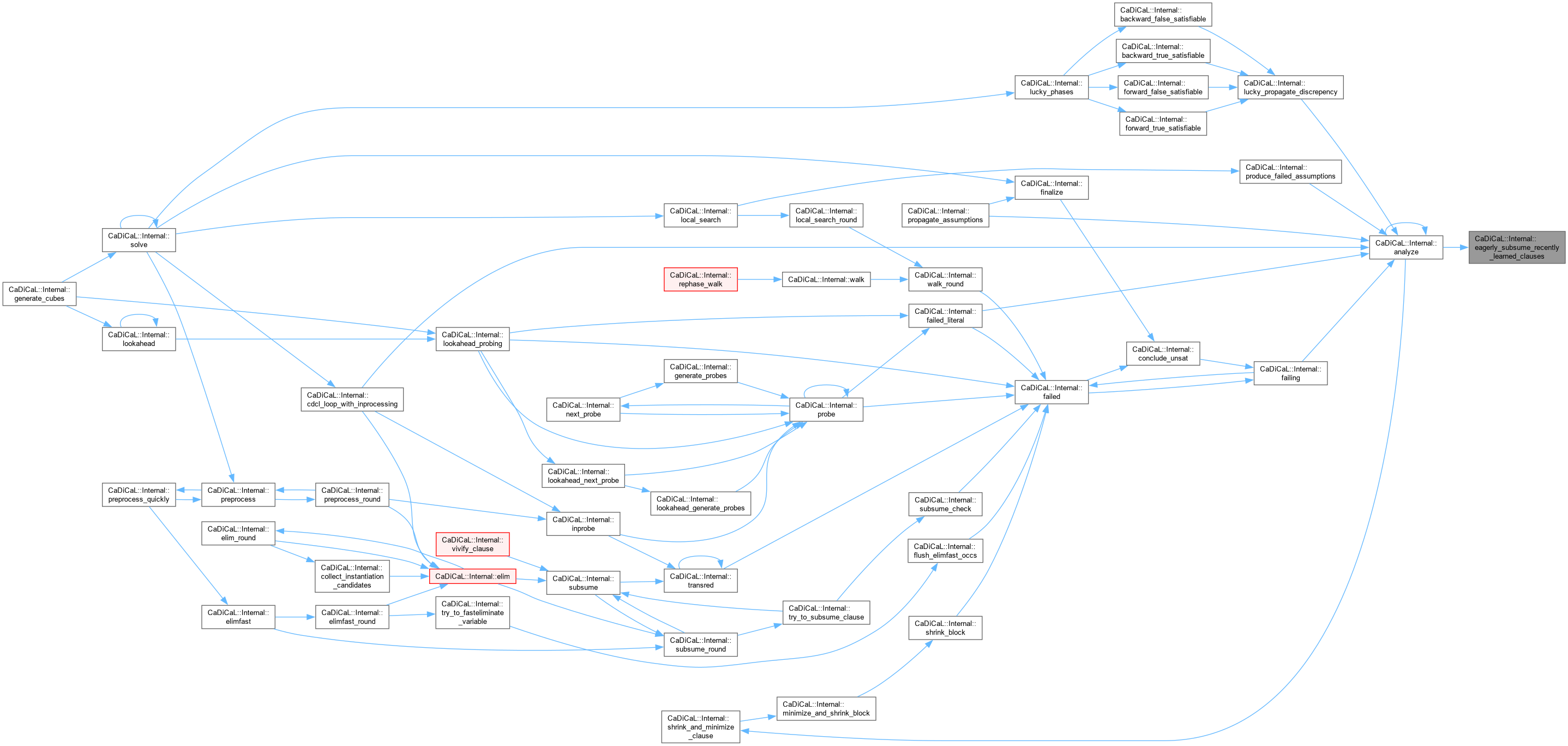
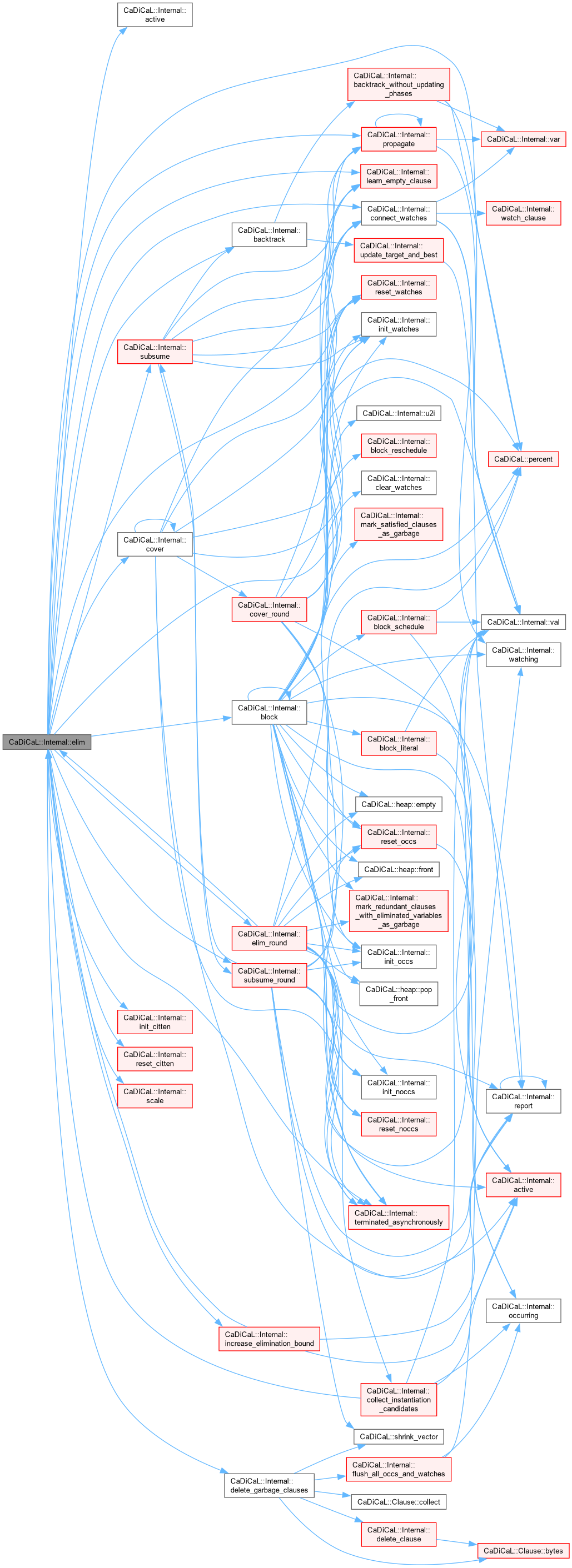
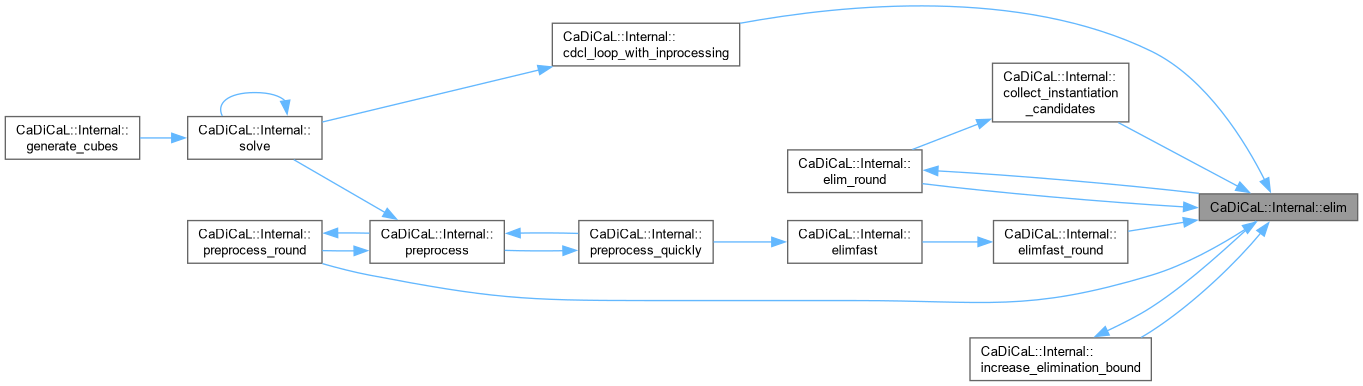
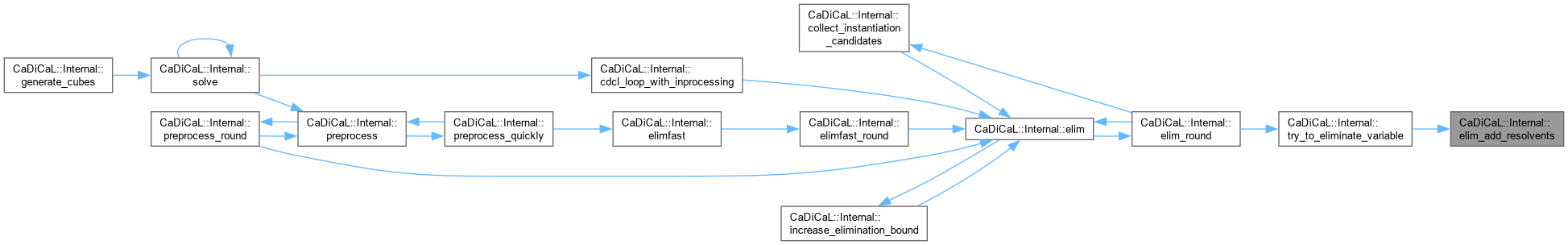
Definition at line 1020 of file cadical_elim.cpp.
|
inline |
Definition at line 542 of file cadical_elim.cpp.
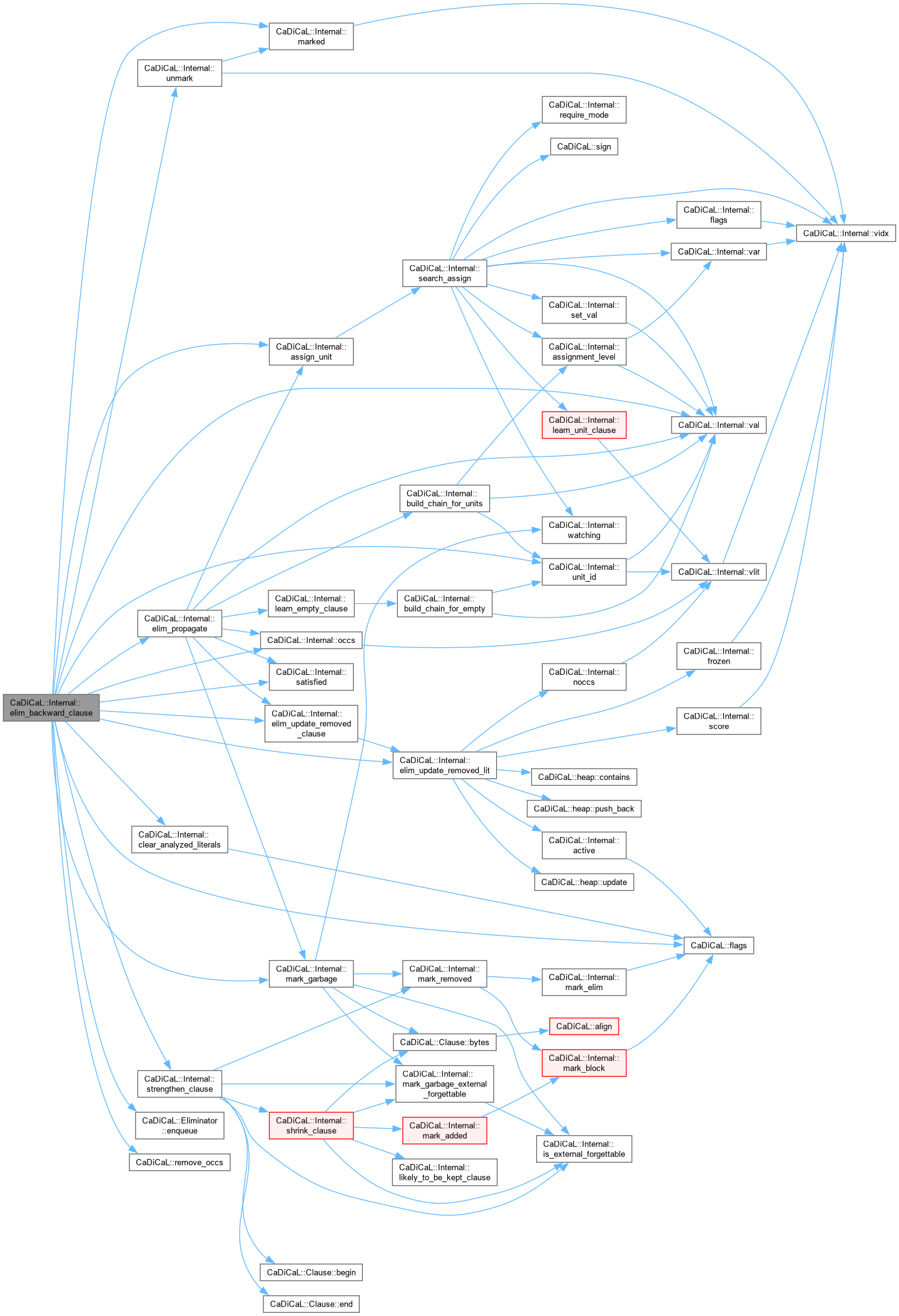
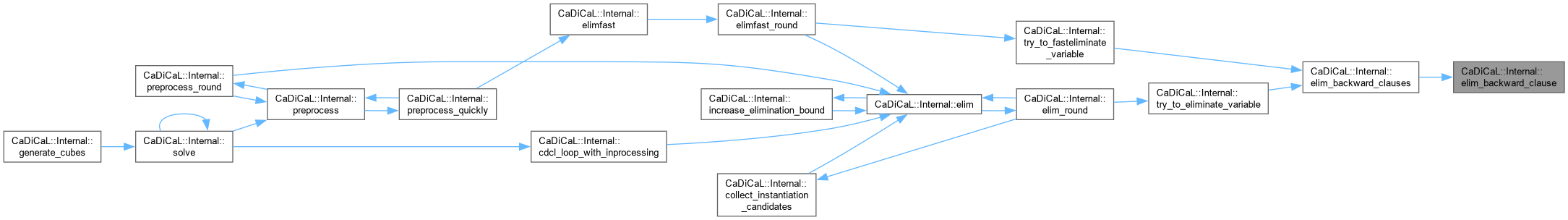
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::elim_backward_clause | ( | Eliminator & | eliminator, |
| Clause * | c ) |
Definition at line 44 of file cadical_backward.cpp.
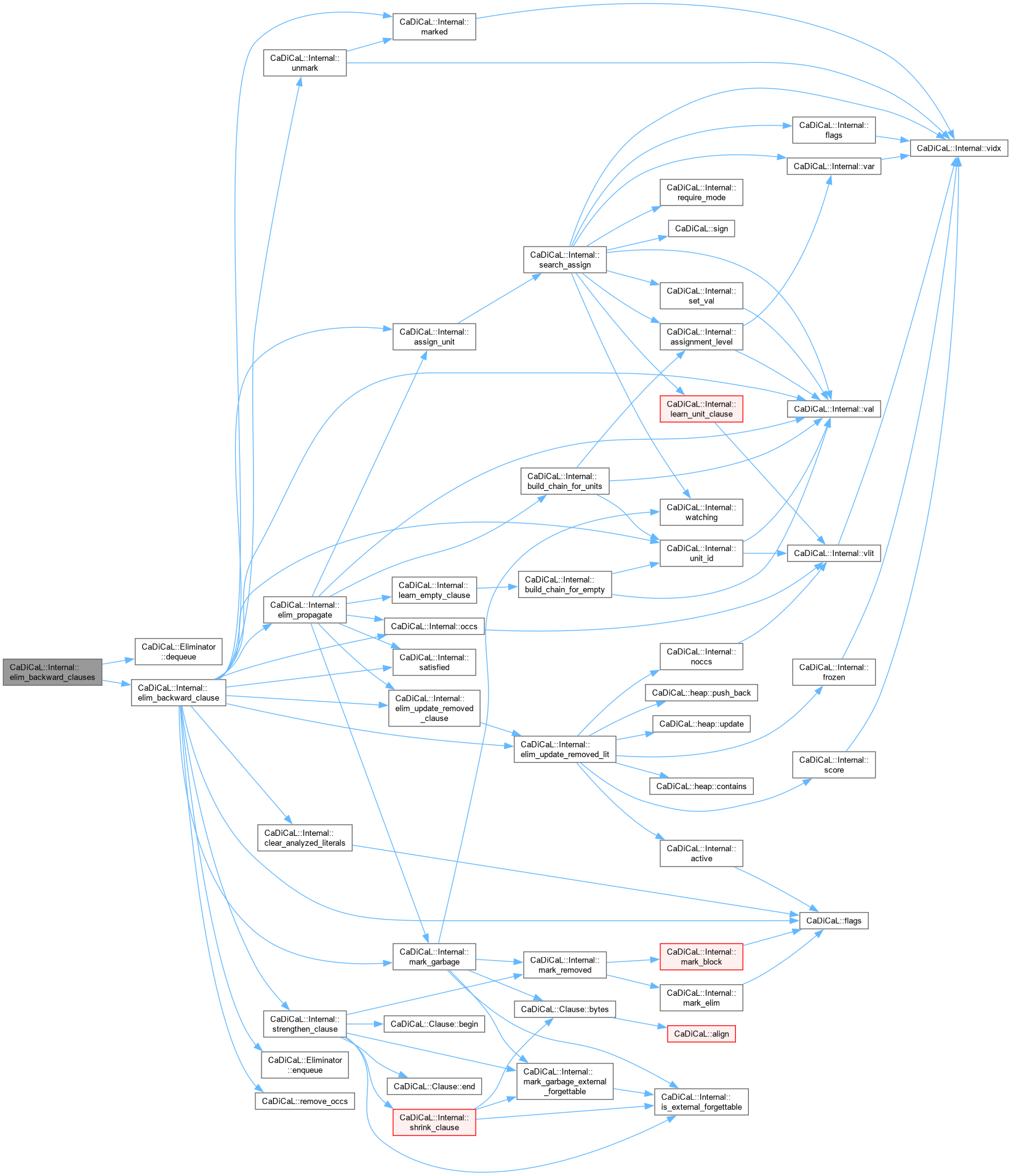
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::elim_backward_clauses | ( | Eliminator & | eliminator | ) |
Definition at line 219 of file cadical_backward.cpp.
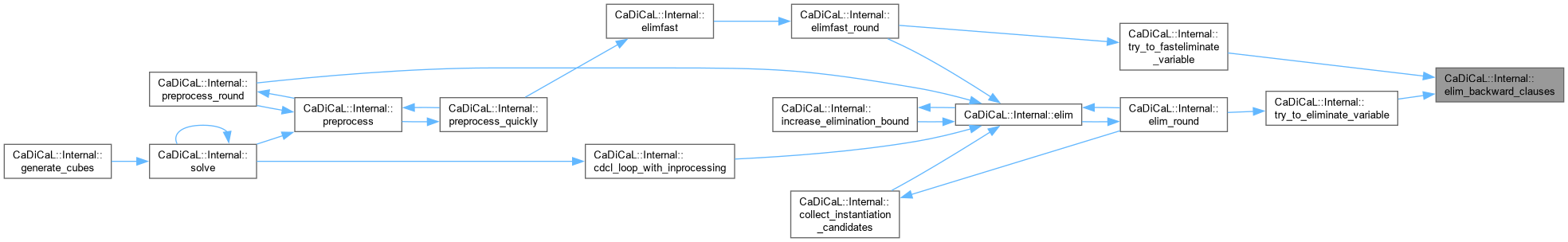
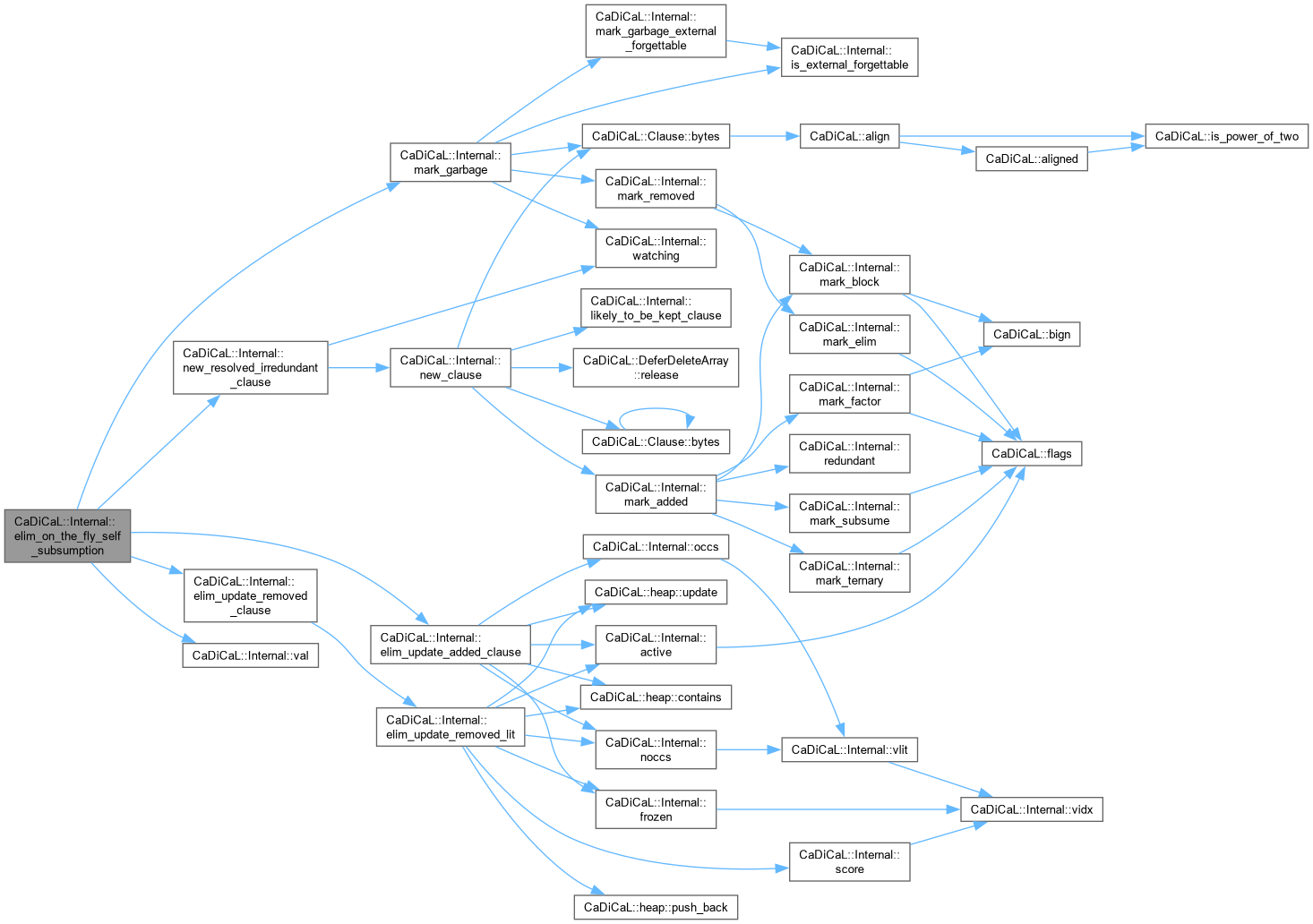
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::elim_on_the_fly_self_subsumption | ( | Eliminator & | eliminator, |
| Clause * | c, | ||
| int | pivot ) |
Definition at line 214 of file cadical_elim.cpp.
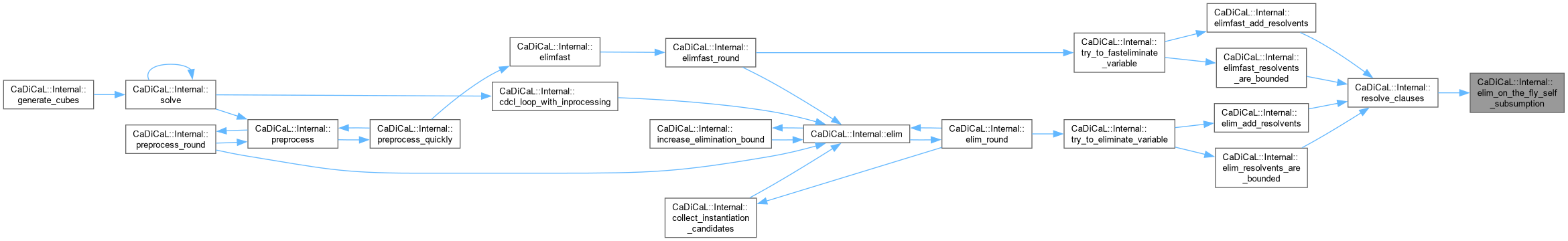
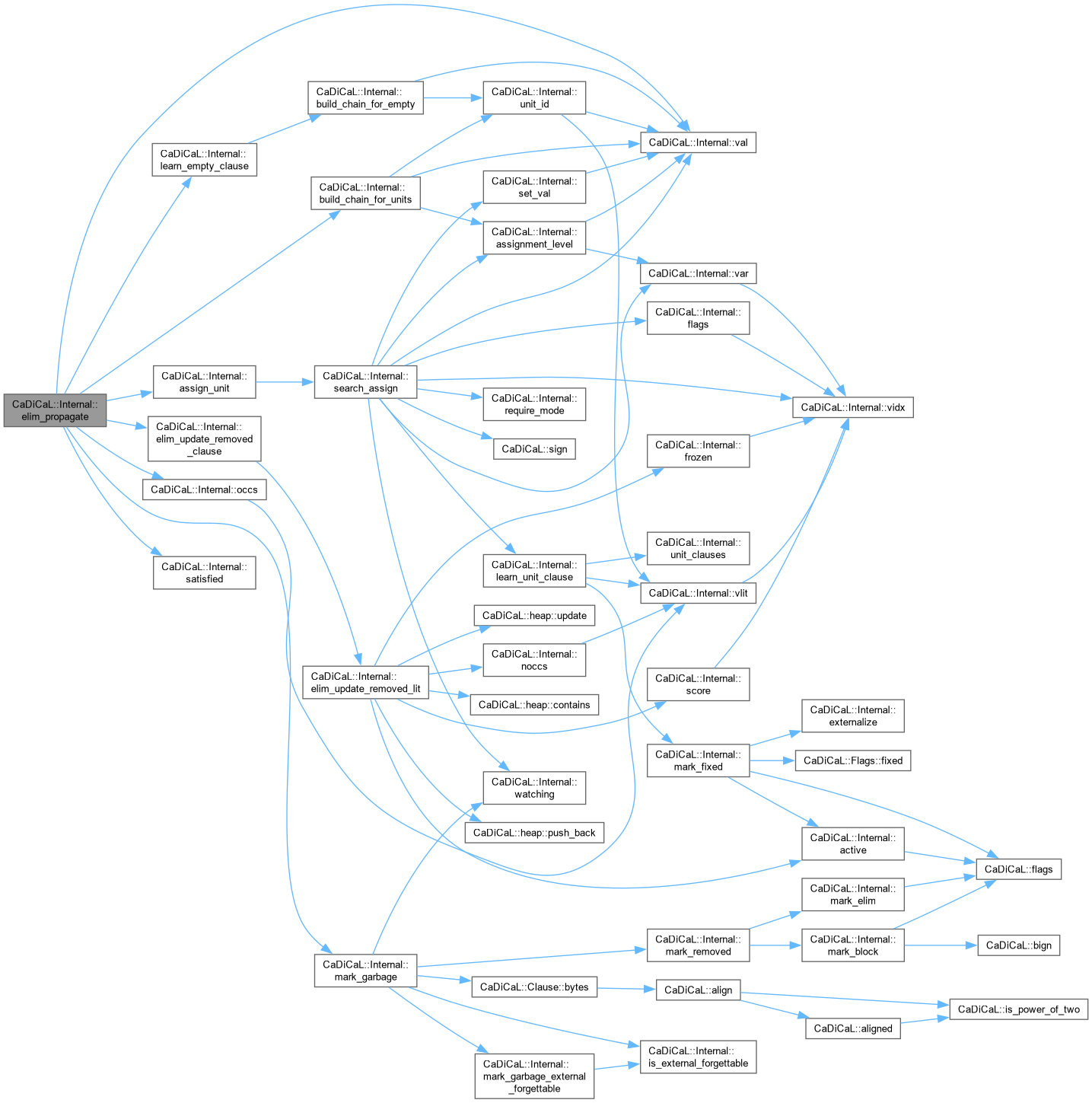
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::elim_propagate | ( | Eliminator & | eliminator, |
| int | unit ) |
Definition at line 147 of file cadical_elim.cpp.

| bool CaDiCaL::Internal::elim_resolvents_are_bounded | ( | Eliminator & | eliminator, |
| int | pivot ) |
Definition at line 467 of file cadical_elim.cpp.
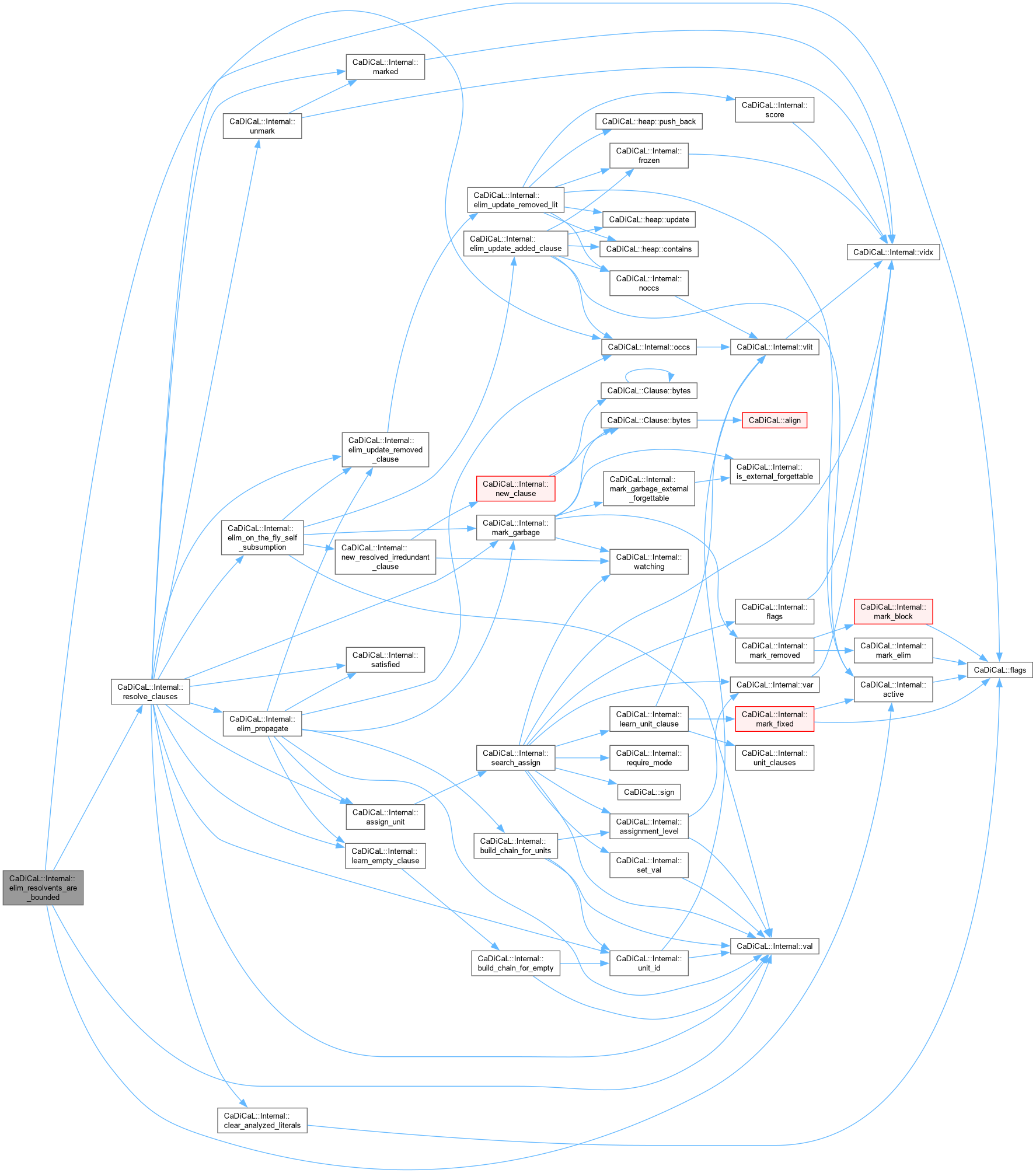
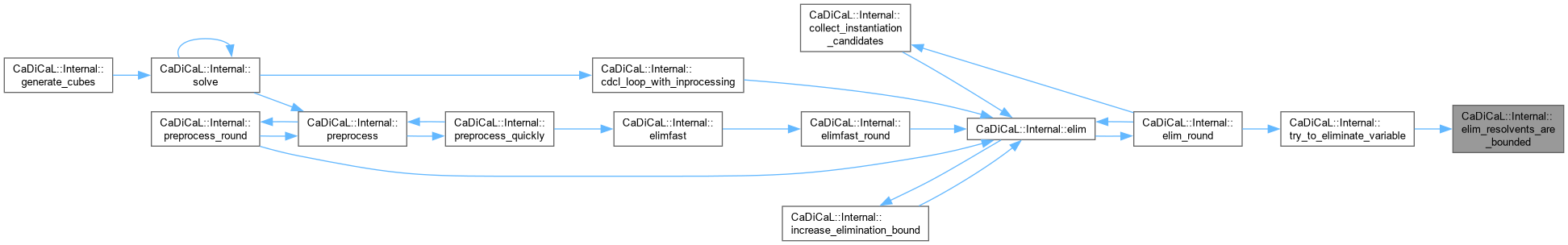
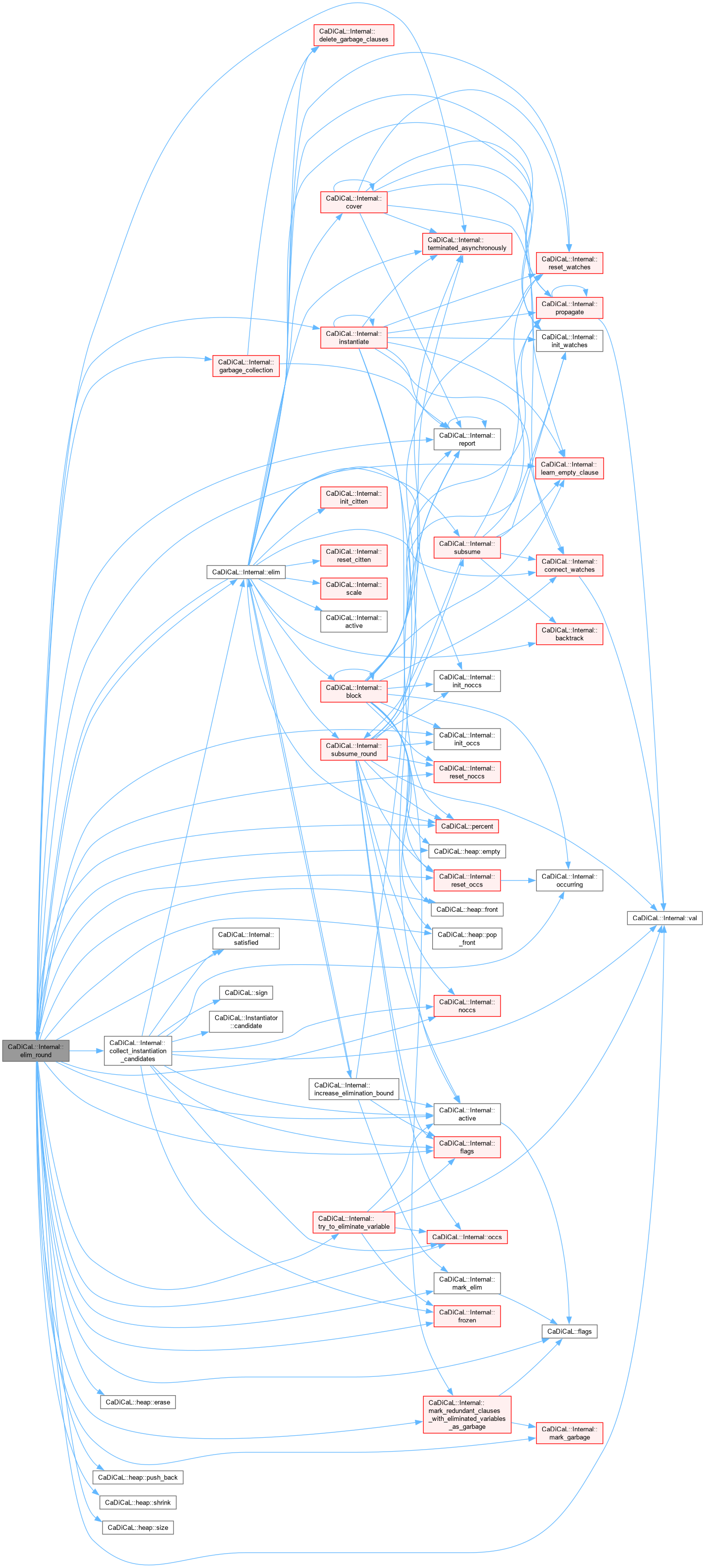
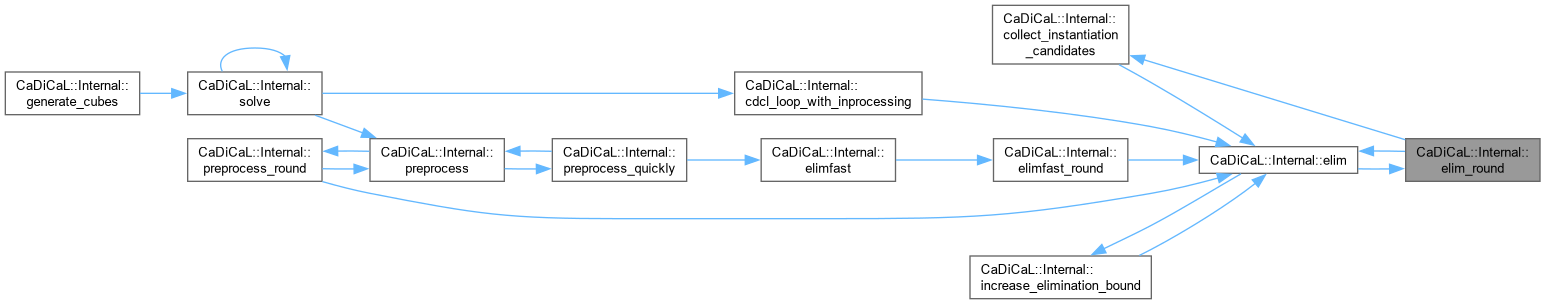
Definition at line 771 of file cadical_elim.cpp.
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::elim_update_added_clause | ( | Eliminator & | eliminator, |
| Clause * | c ) |
Definition at line 95 of file cadical_elim.cpp.
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::elim_update_removed_clause | ( | Eliminator & | eliminator, |
| Clause * | c, | ||
| int | except = 0 ) |
Definition at line 130 of file cadical_elim.cpp.
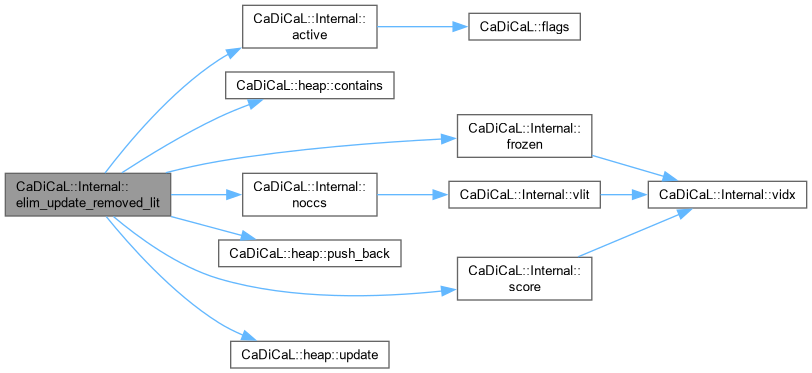
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::elim_update_removed_lit | ( | Eliminator & | eliminator, |
| int | lit ) |
Definition at line 112 of file cadical_elim.cpp.
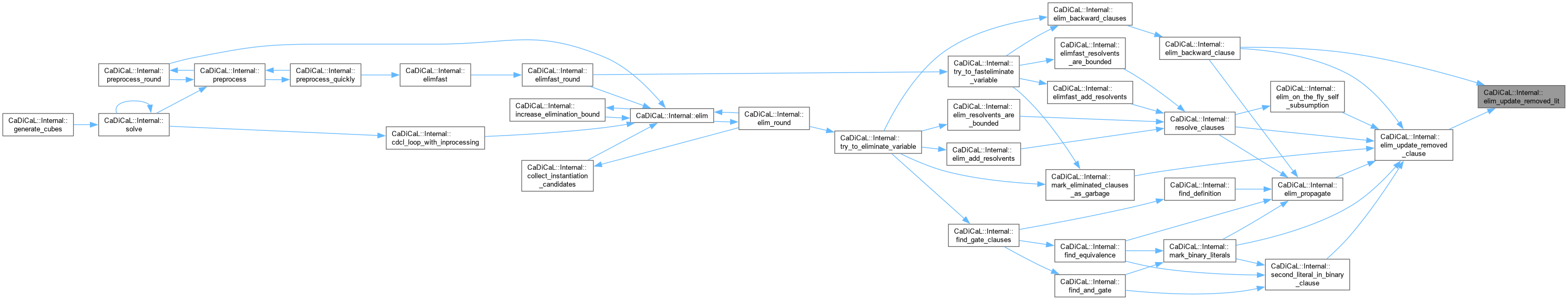
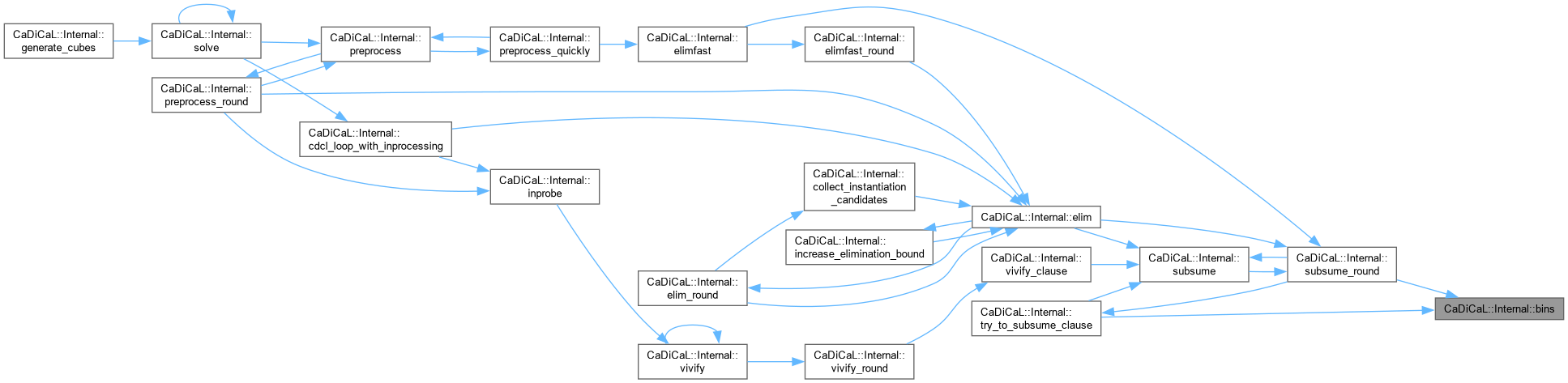
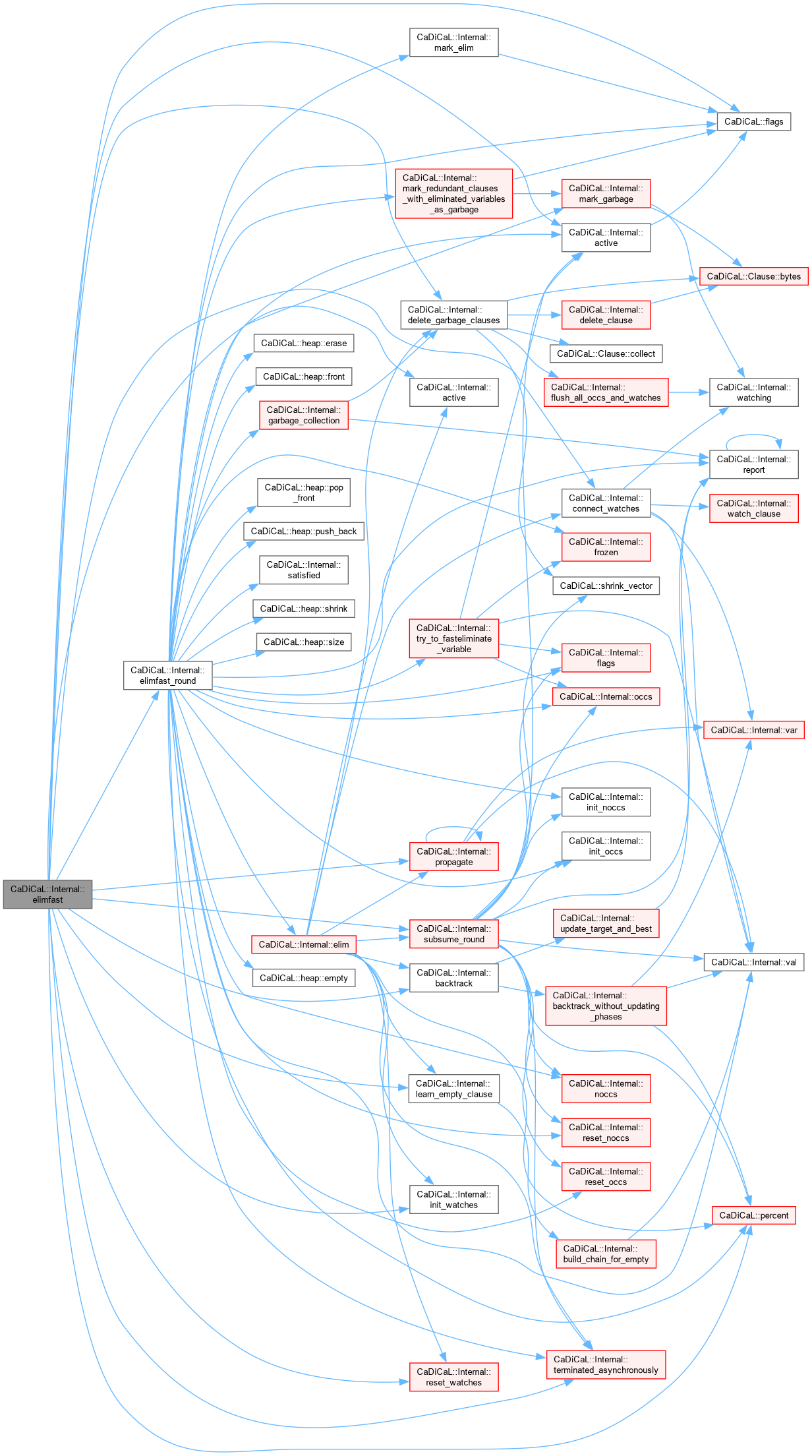
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::elimfast | ( | ) |
Definition at line 442 of file cadical_elimfast.cpp.
|
inline |
Definition at line 143 of file cadical_elimfast.cpp.
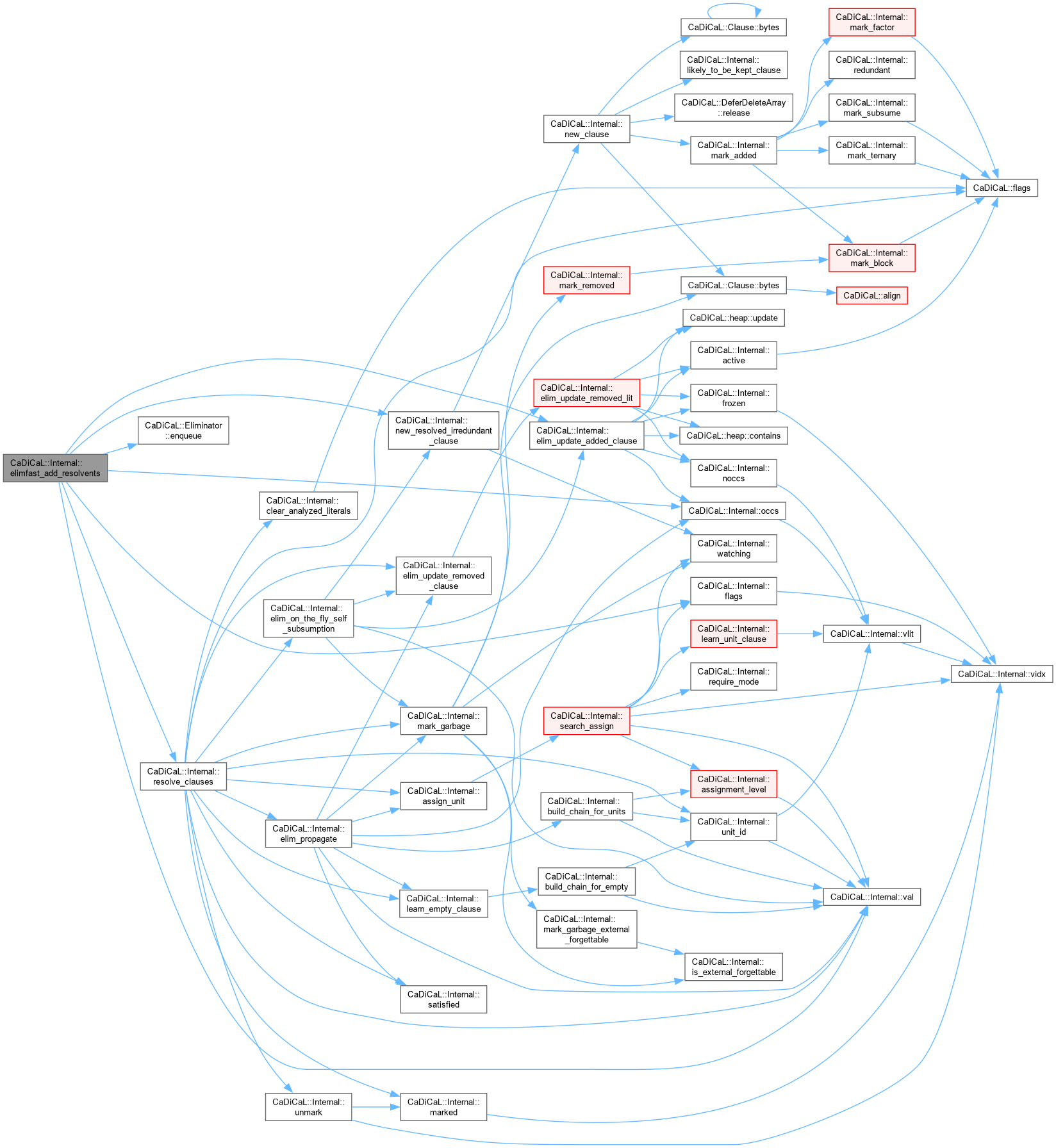
| bool CaDiCaL::Internal::elimfast_resolvents_are_bounded | ( | Eliminator & | eliminator, |
| int | pivot ) |
Definition at line 59 of file cadical_elimfast.cpp.
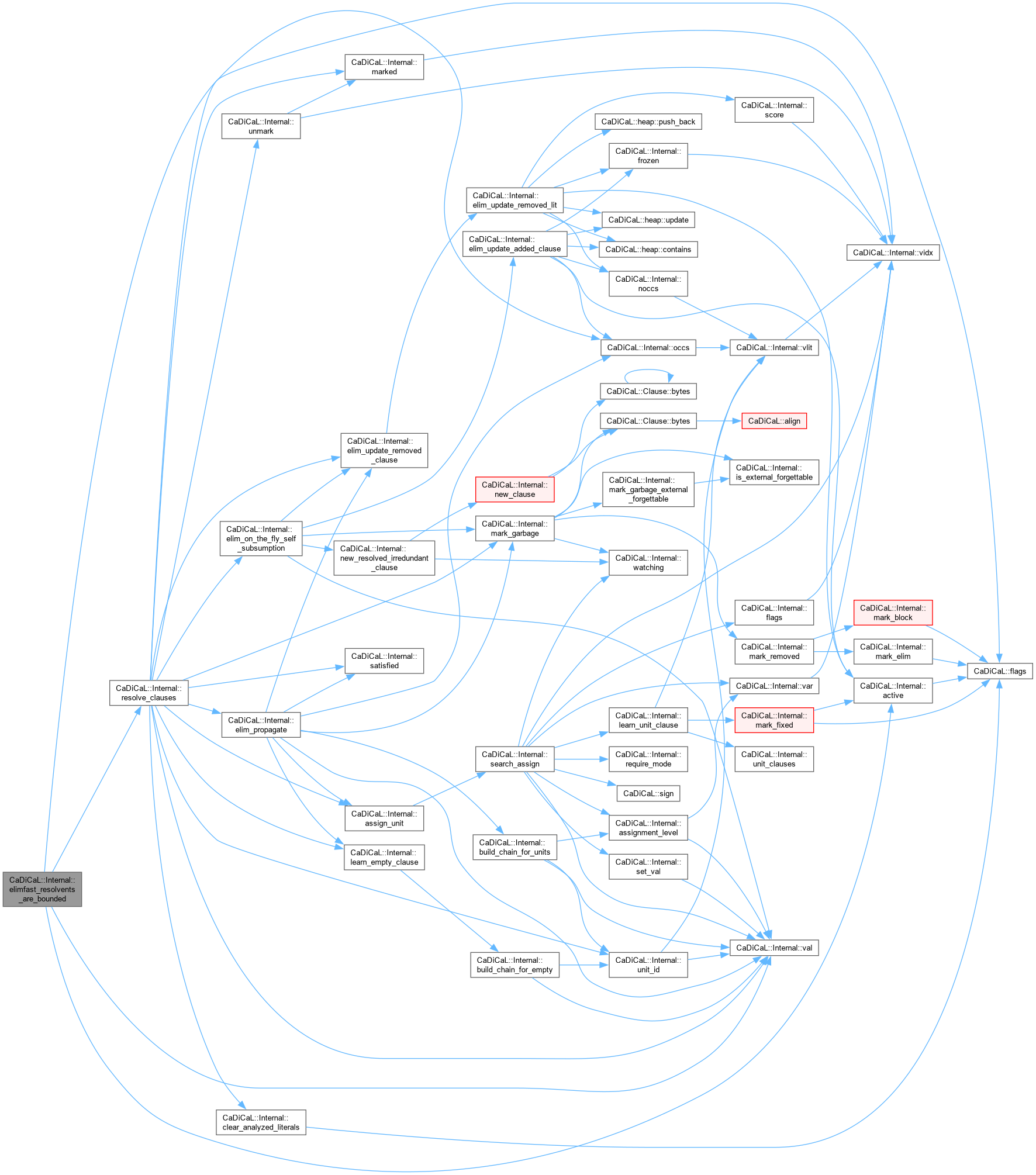
Definition at line 268 of file cadical_elimfast.cpp.
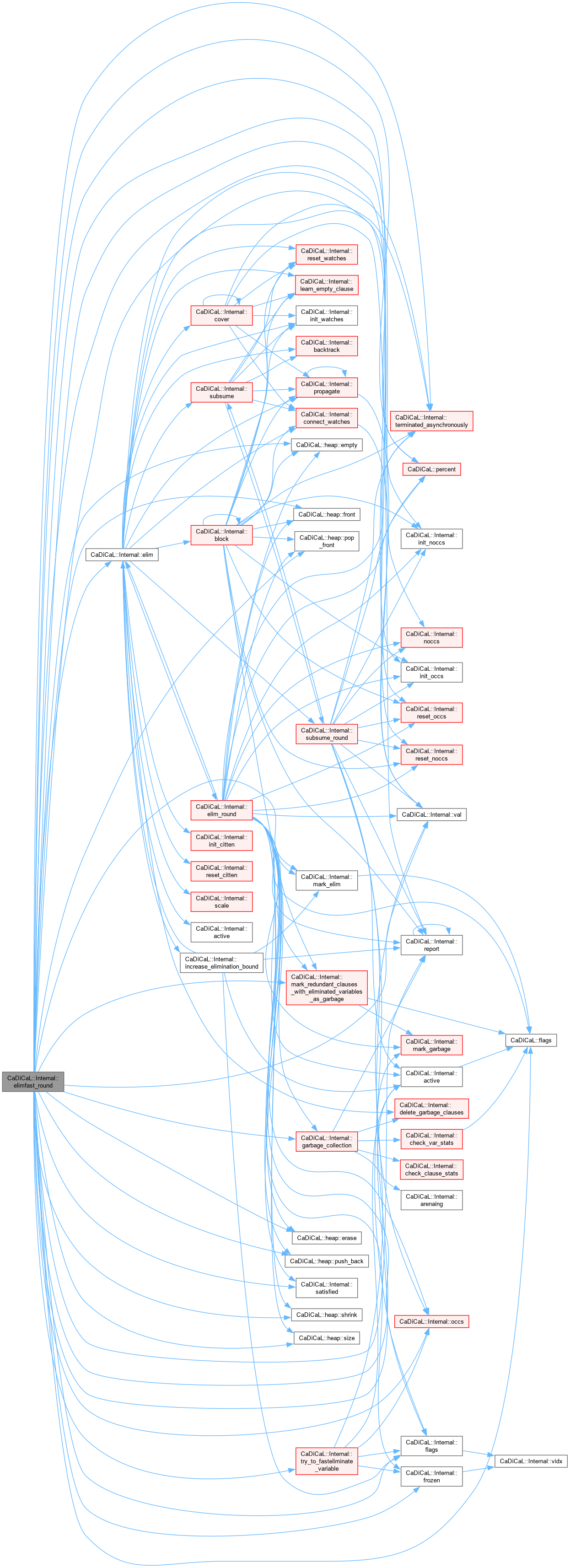
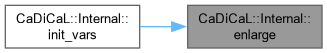
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::enlarge | ( | int | new_max_var | ) |
Definition at line 121 of file cadical_internal.cpp.
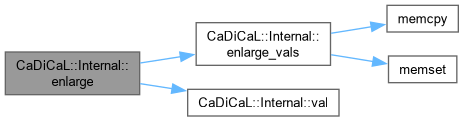
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::enlarge_vals | ( | size_t | new_vsize | ) |
Definition at line 102 of file cadical_internal.cpp.

| void CaDiCaL::Internal::error | ( | const char * | fmt, |
| ... ) |
Definition at line 181 of file cadical_message.cpp.
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::error_message_end | ( | ) |
Definition at line 168 of file cadical_message.cpp.


| void CaDiCaL::Internal::error_message_start | ( | ) |
Definition at line 158 of file cadical_message.cpp.

| void CaDiCaL::Internal::explain_external_propagations | ( | ) |
Definition at line 583 of file cadical_external_propagate.cpp.
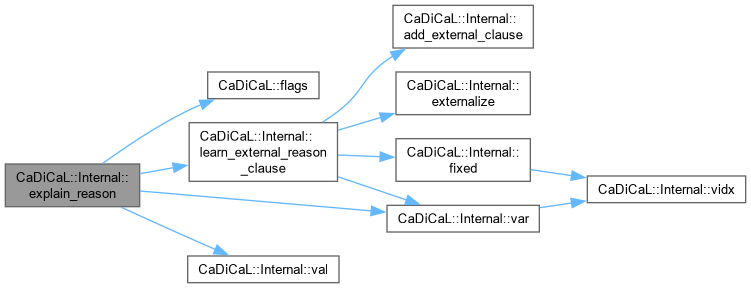
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::explain_reason | ( | int | lit, |
| Clause * | reason, | ||
| int & | open ) |
Definition at line 534 of file cadical_external_propagate.cpp.
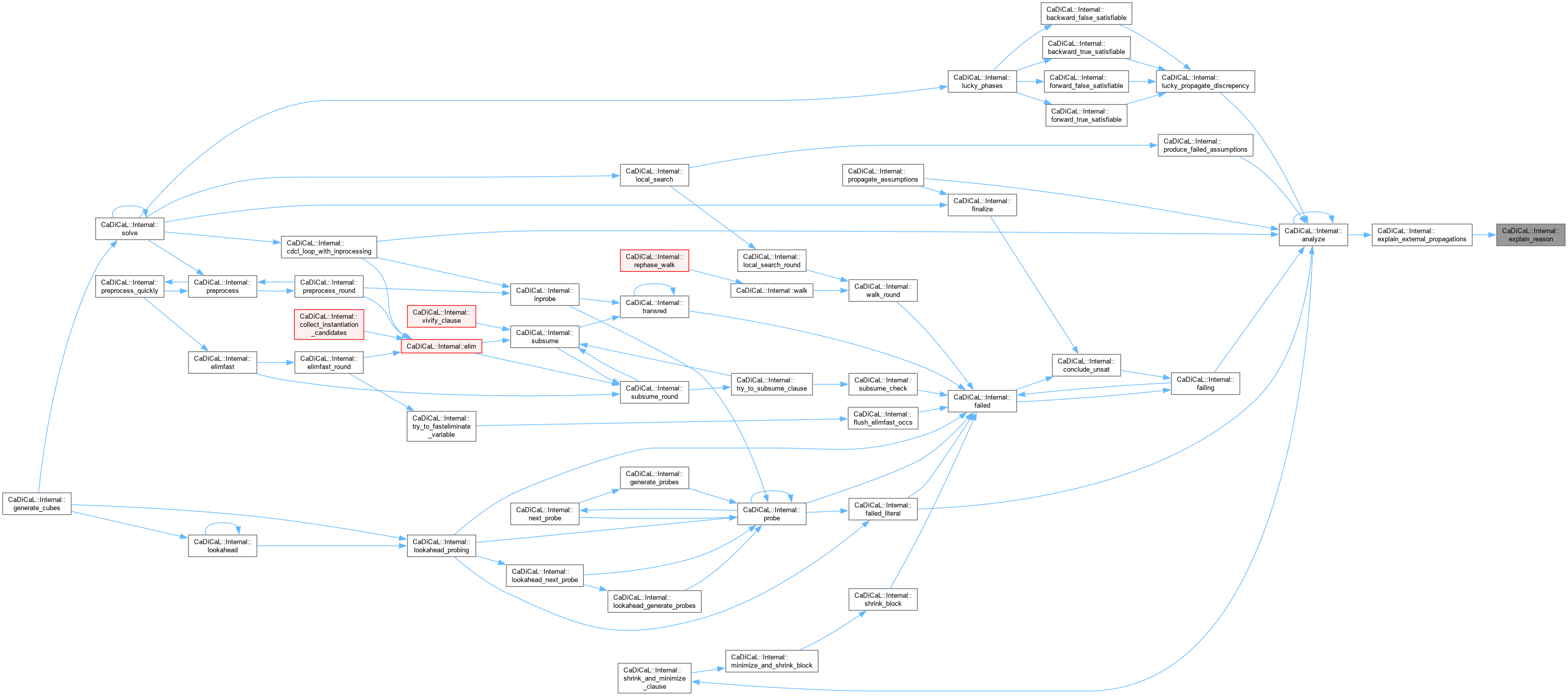
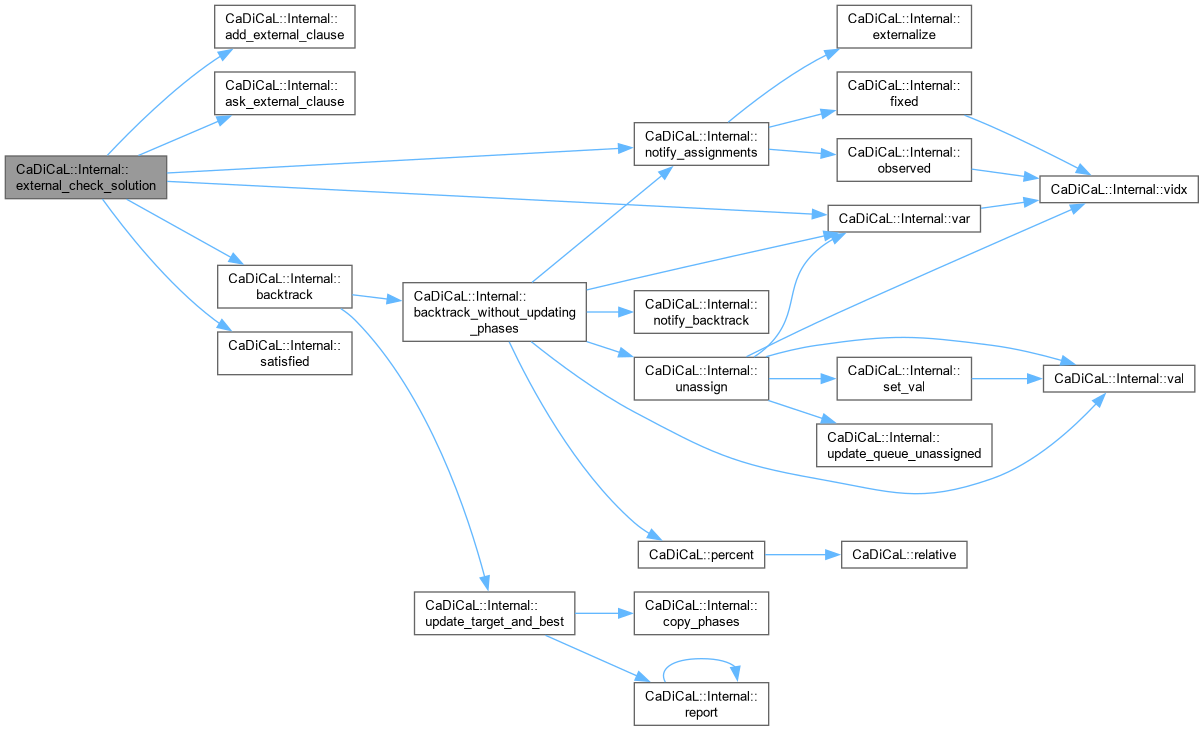
| bool CaDiCaL::Internal::external_check_solution | ( | ) |
Definition at line 830 of file cadical_external_propagate.cpp.
| bool CaDiCaL::Internal::external_propagate | ( | ) |
Definition at line 235 of file cadical_external_propagate.cpp.
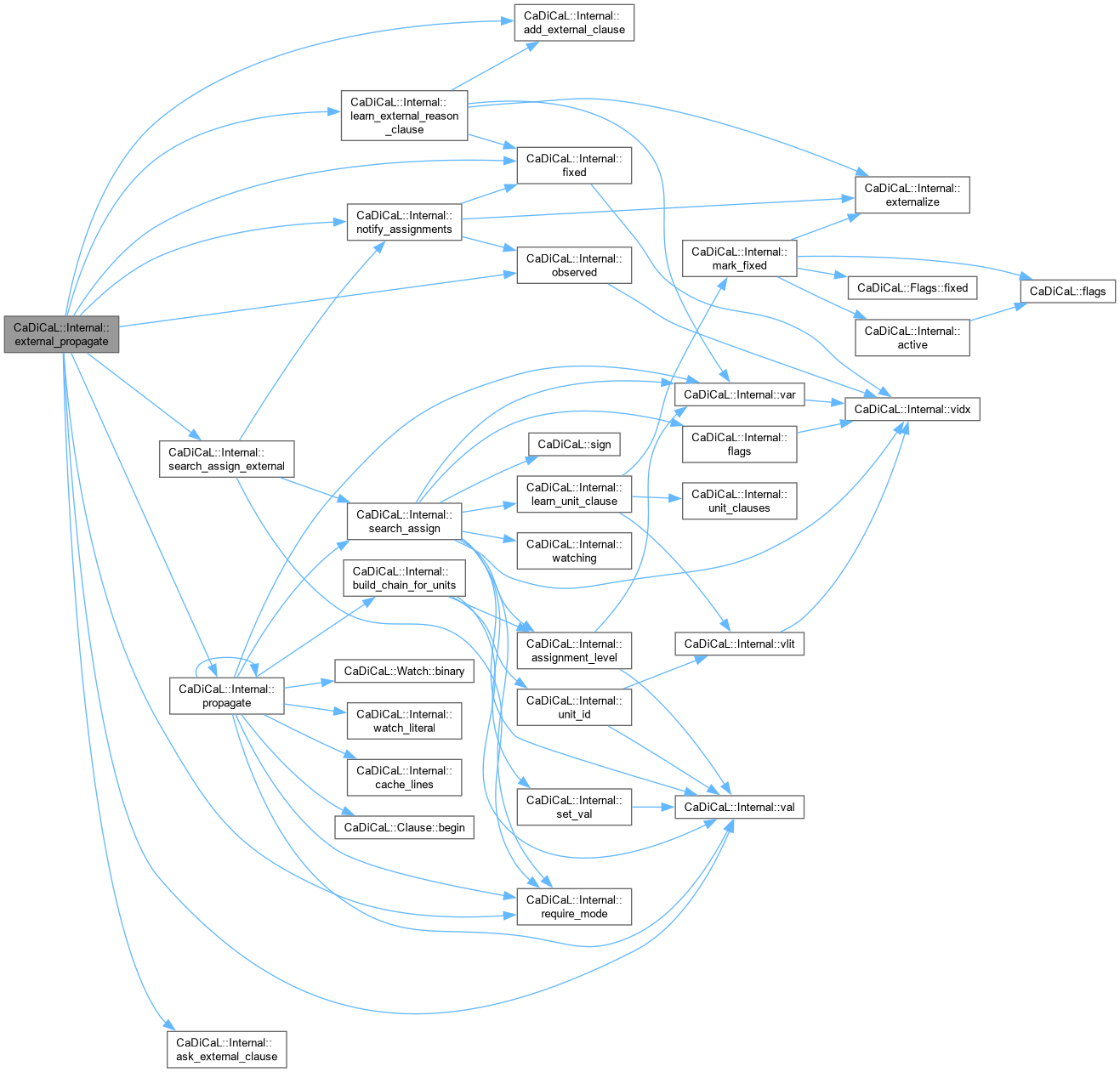
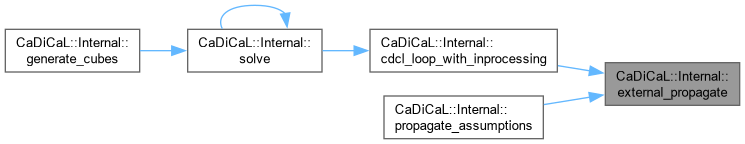
|
inline |
Definition at line 1557 of file internal.hpp.
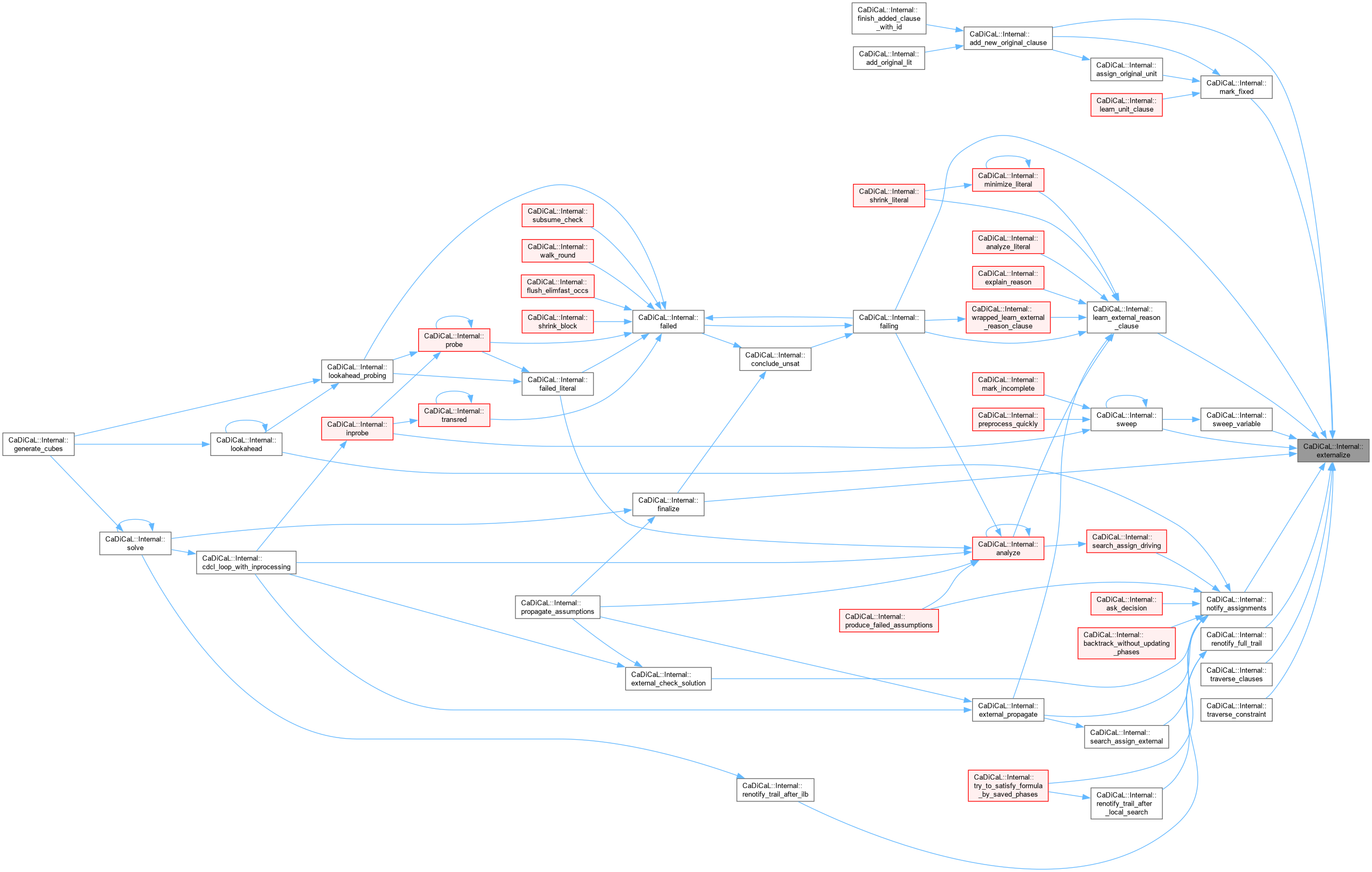
| bool CaDiCaL::Internal::extract_gates | ( | ) |
Definition at line 7429 of file cadical_congruence.cpp.
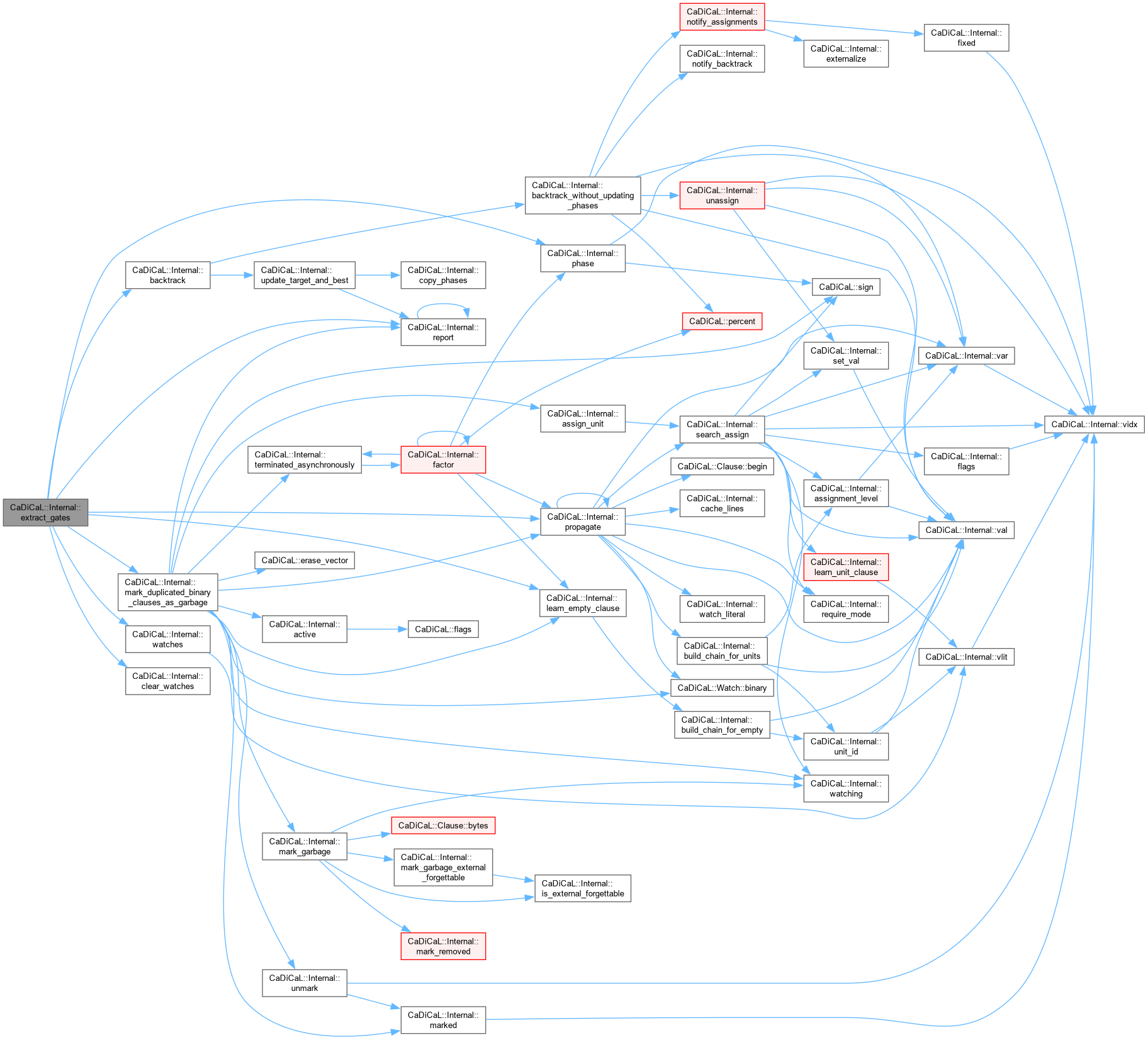
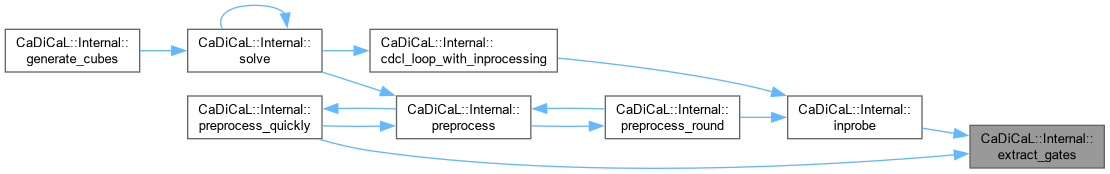
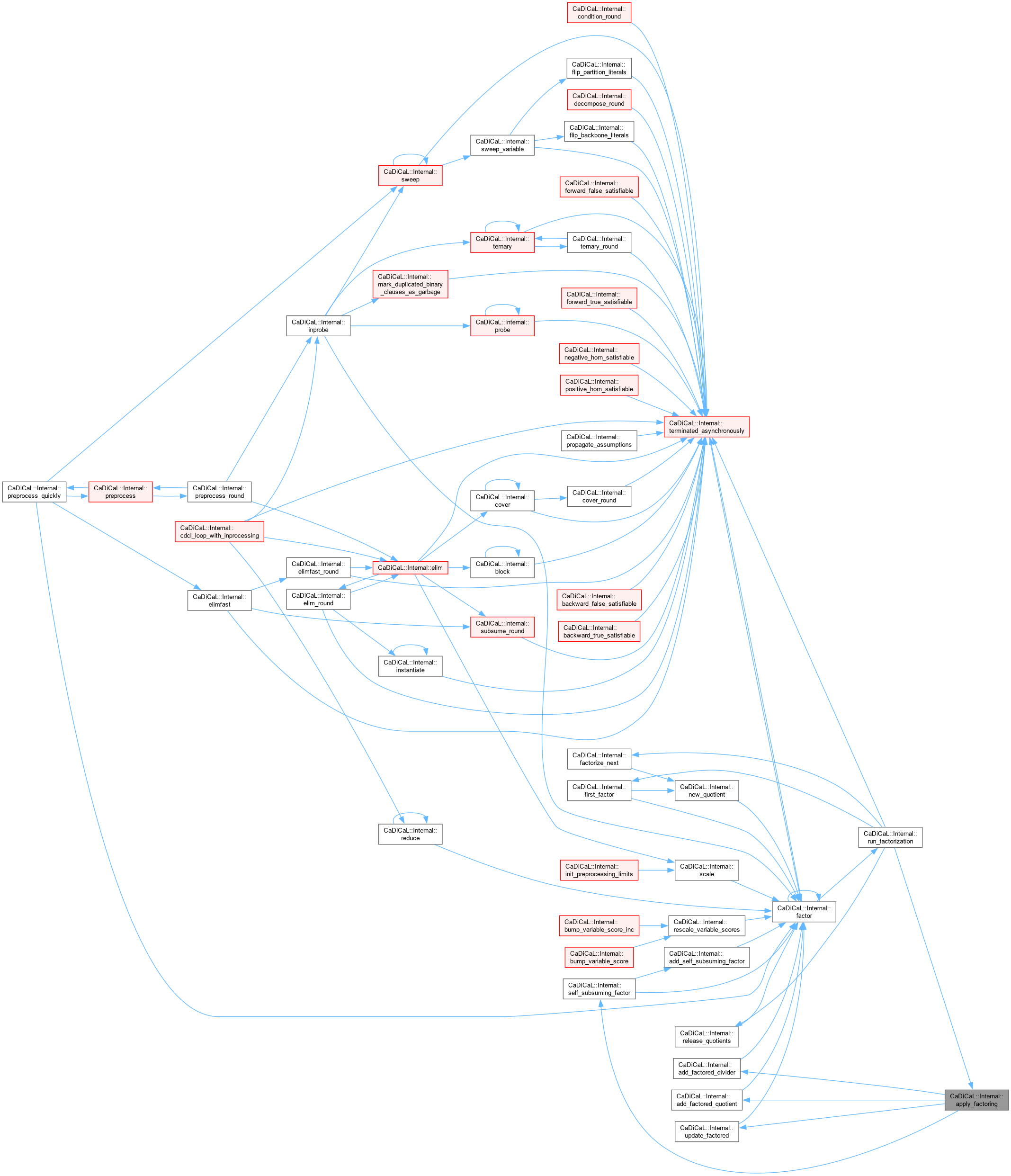
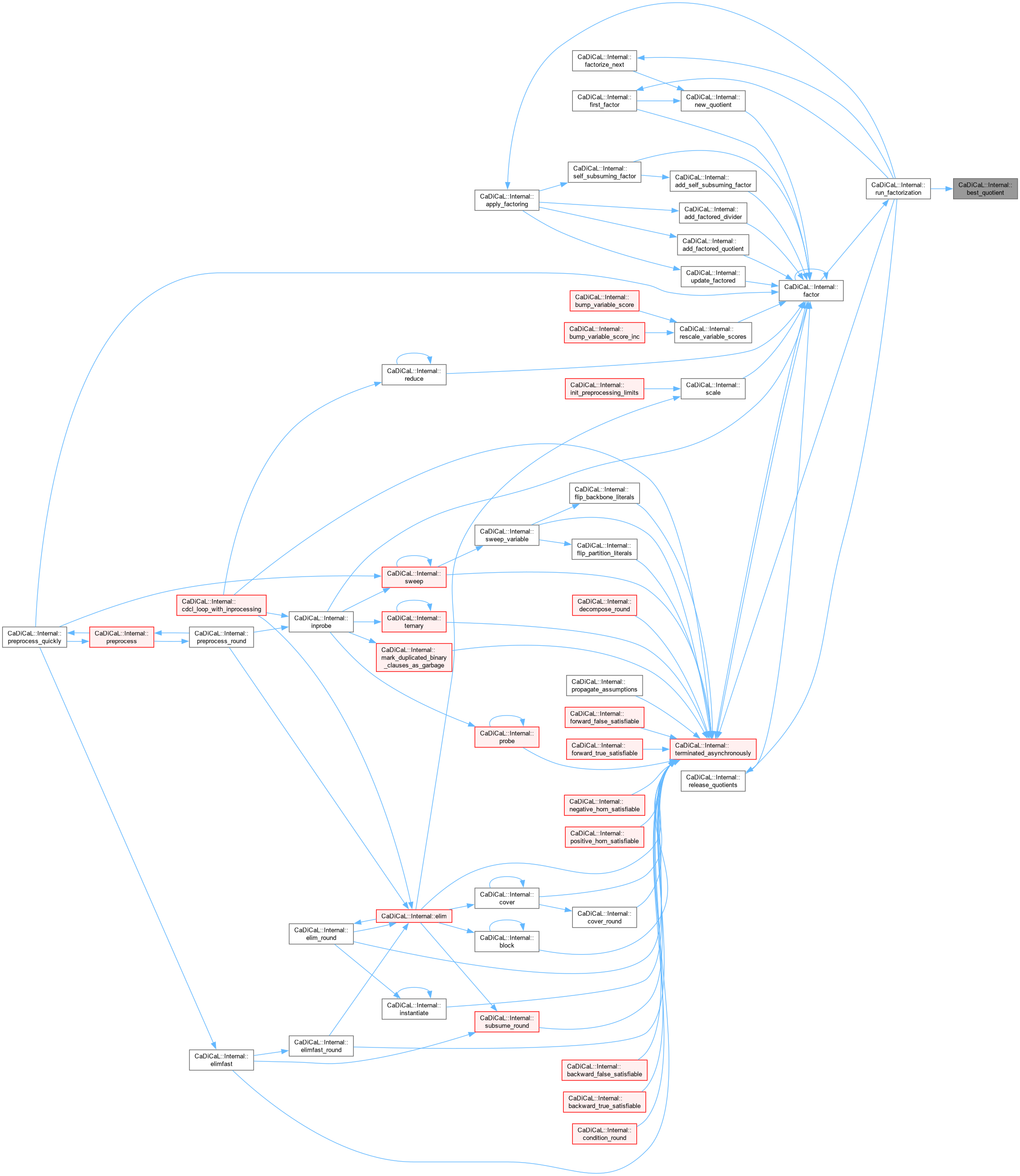
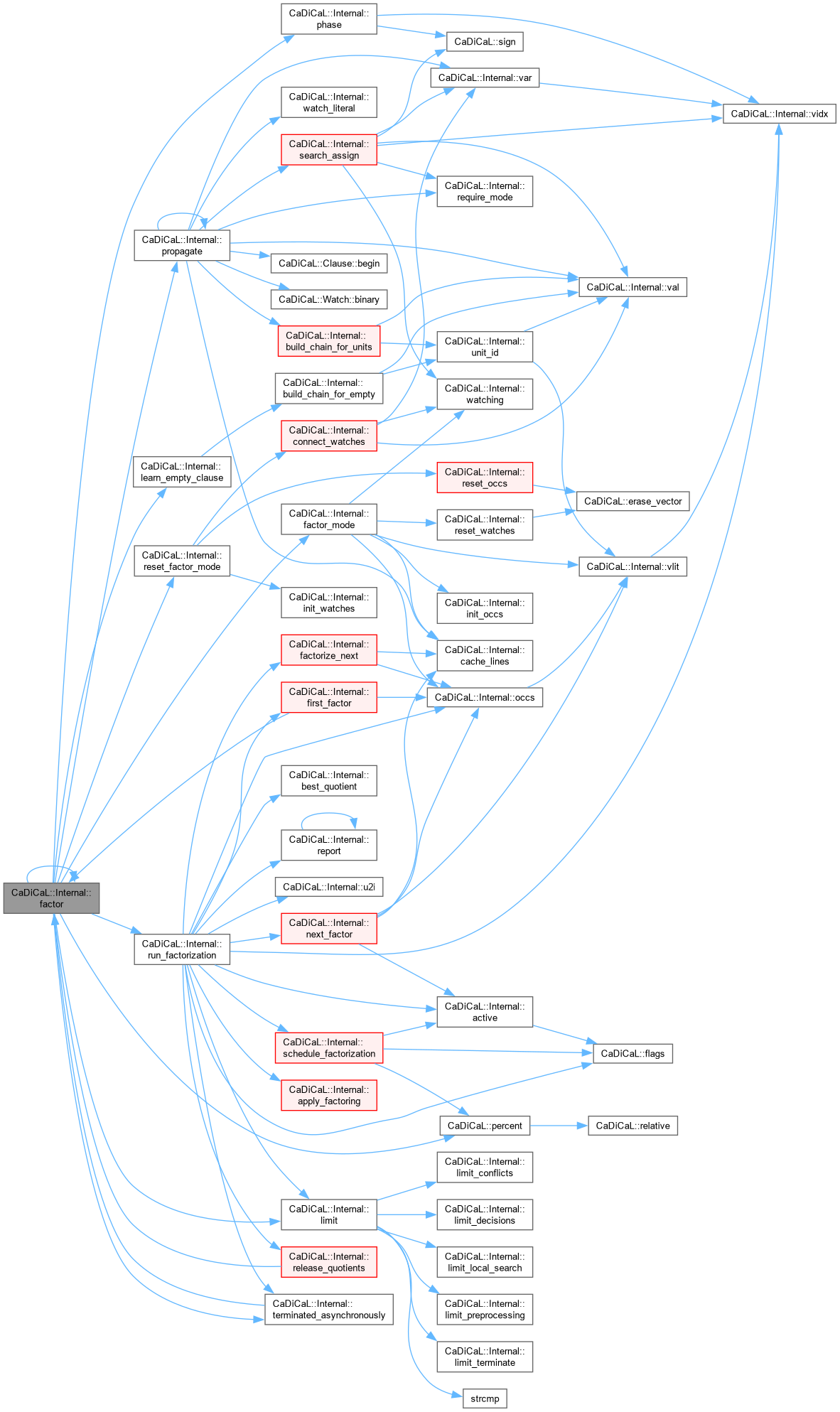
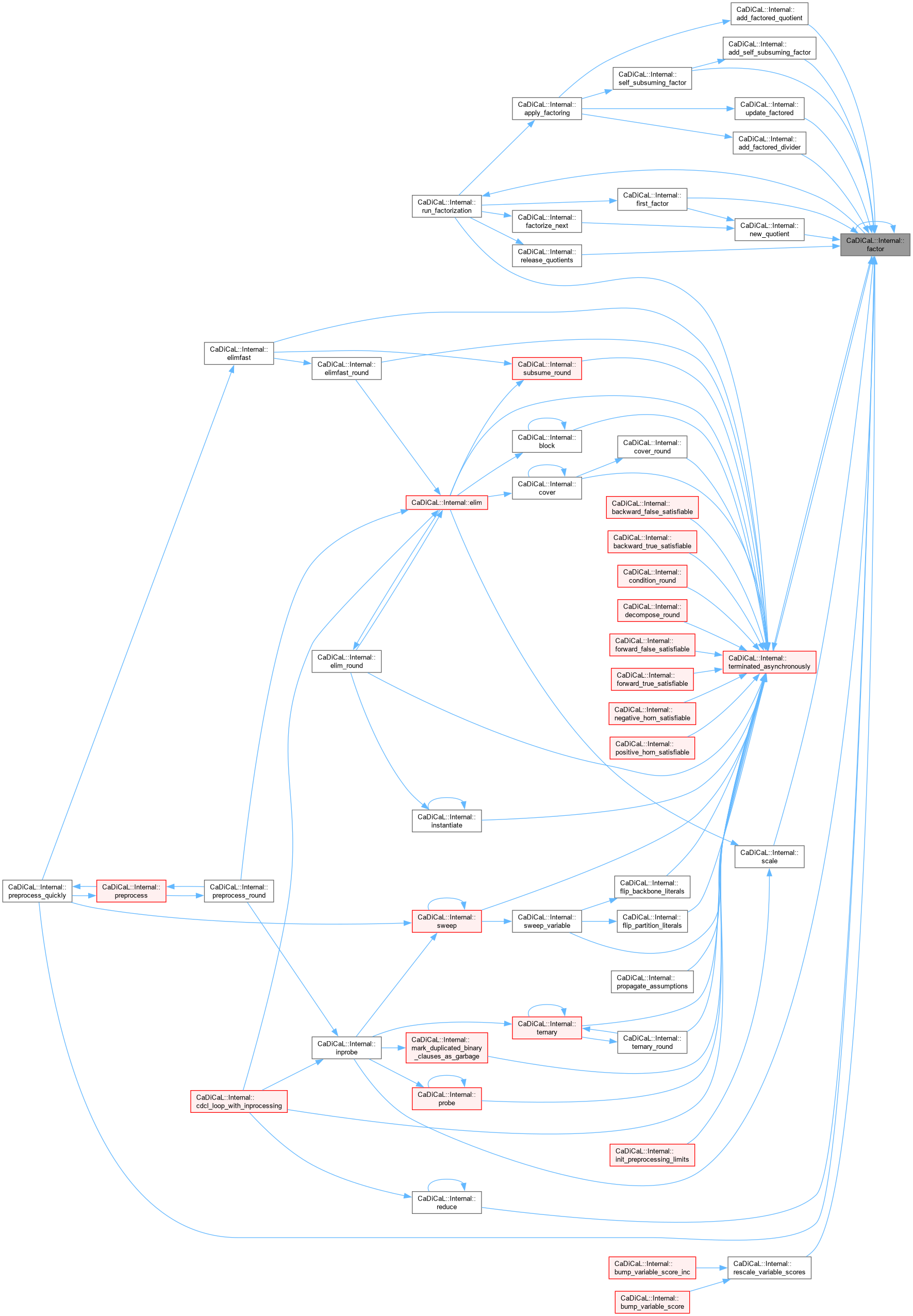
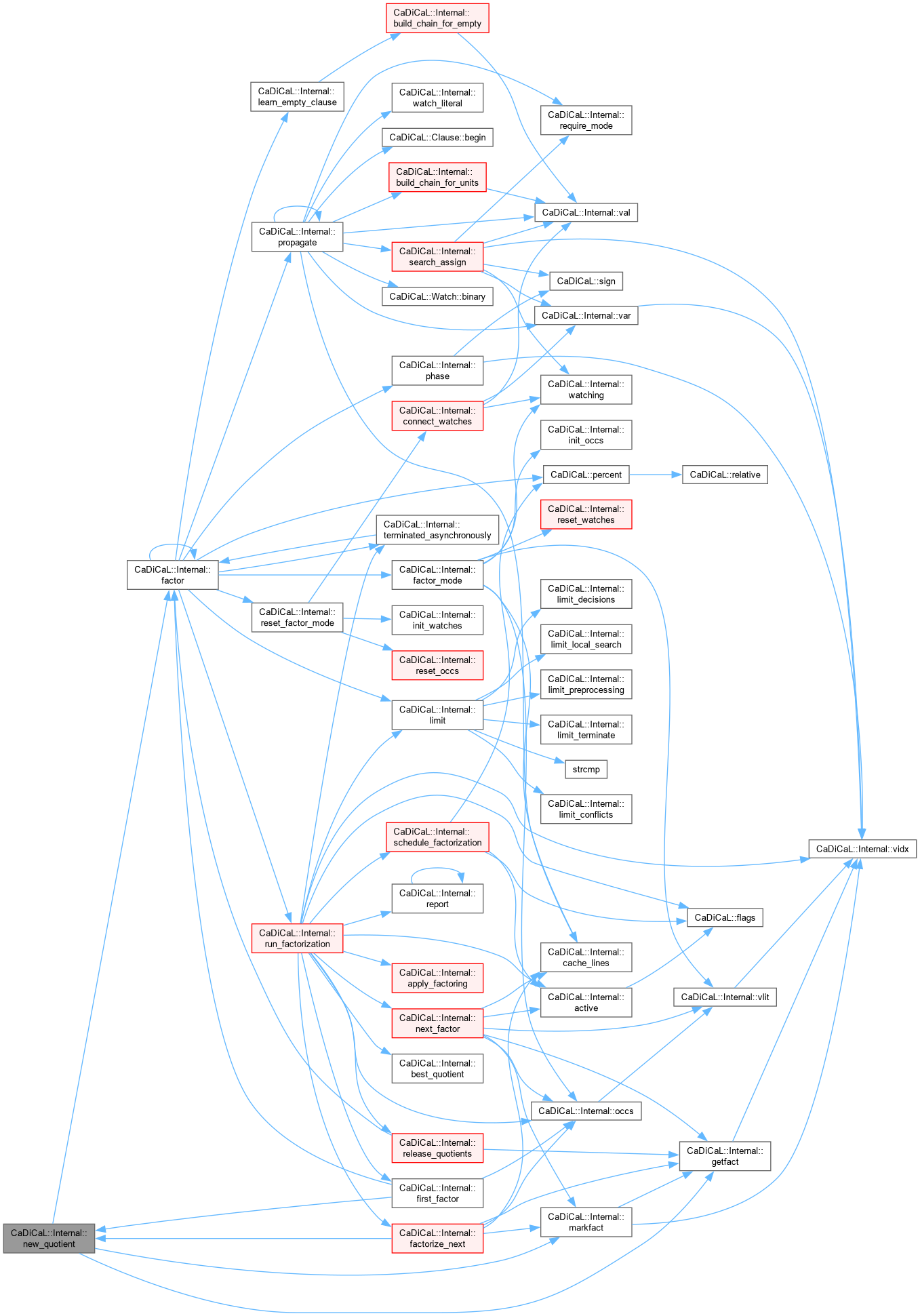
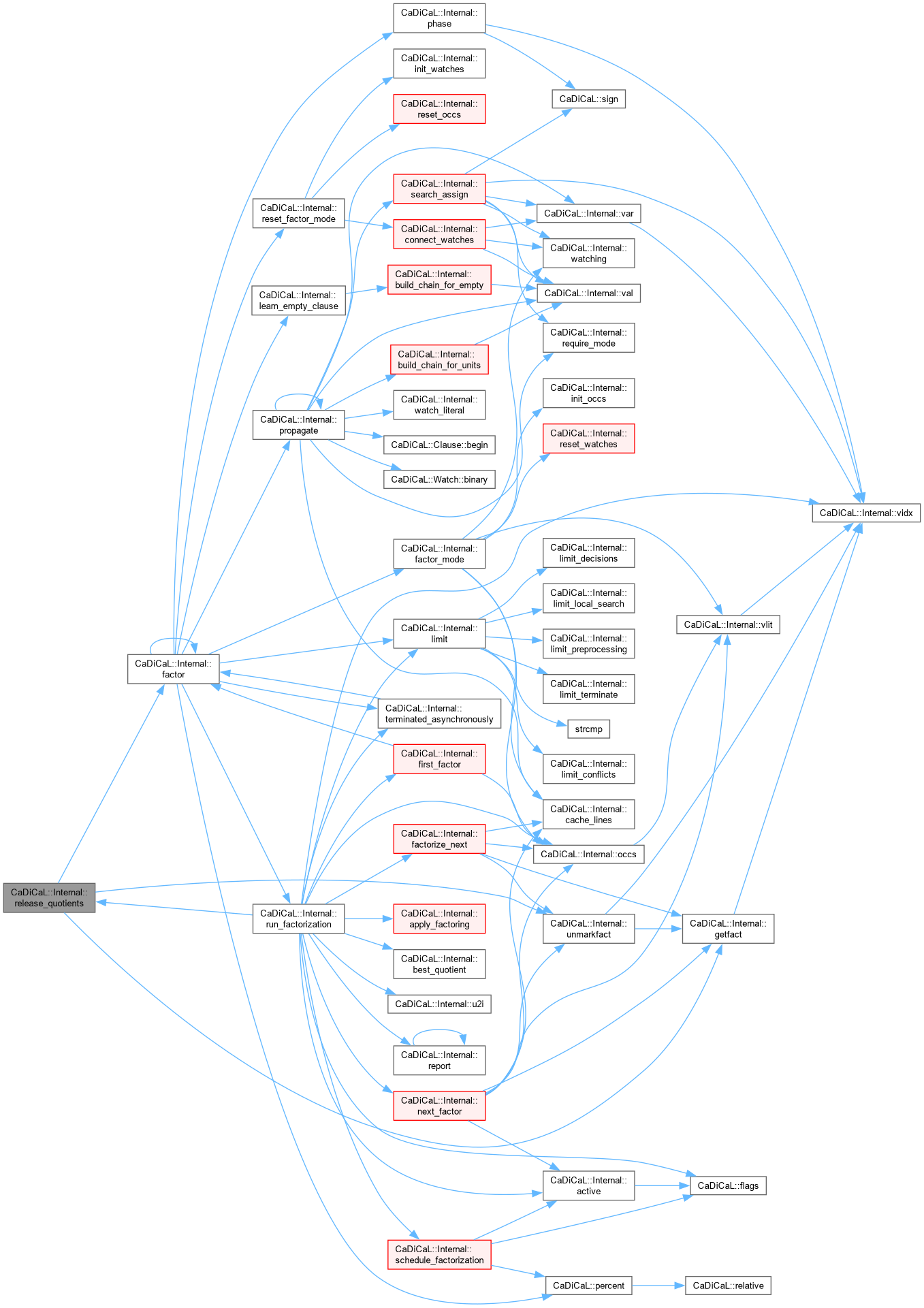
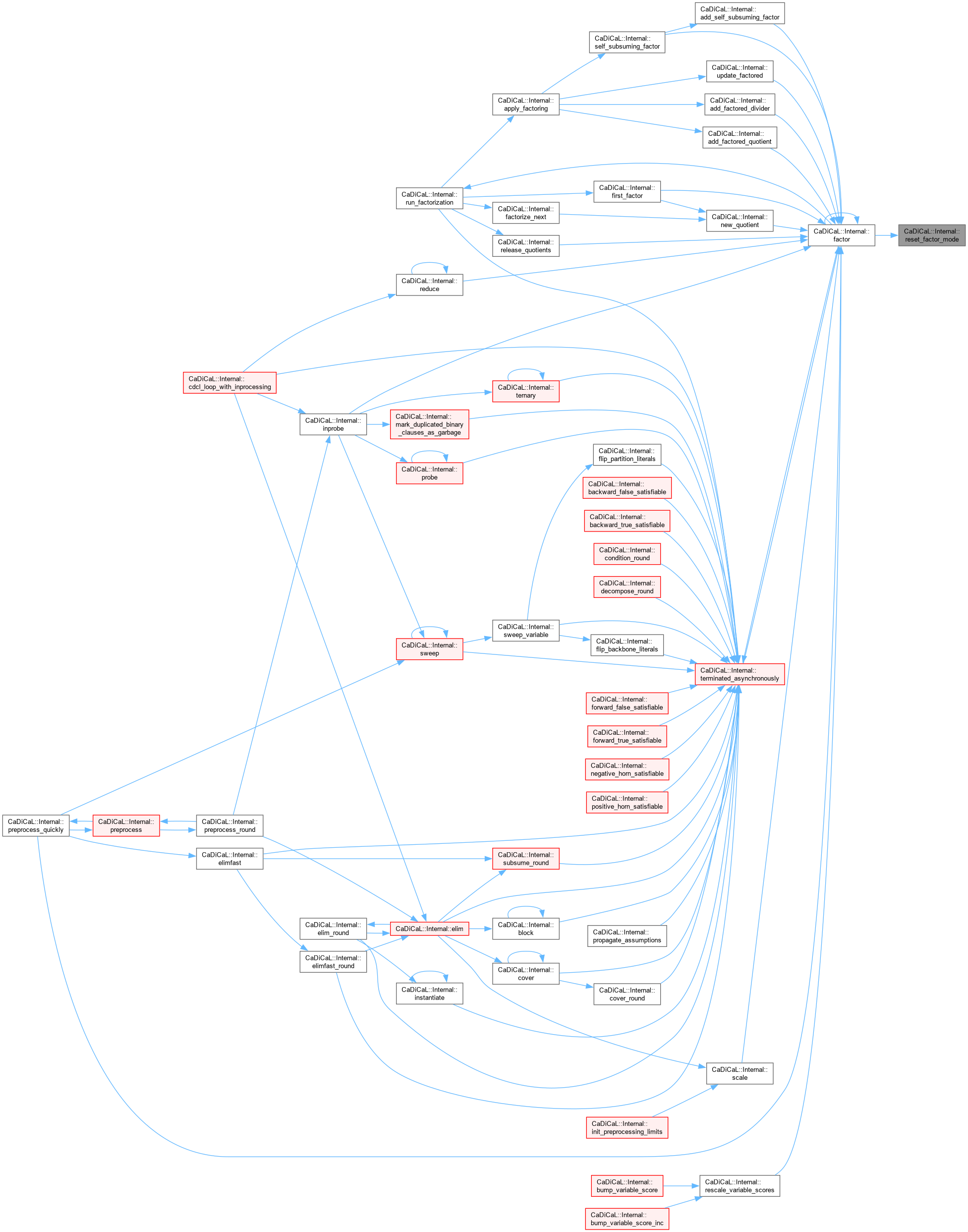
| bool CaDiCaL::Internal::factor | ( | ) |
Definition at line 859 of file cadical_factor.cpp.
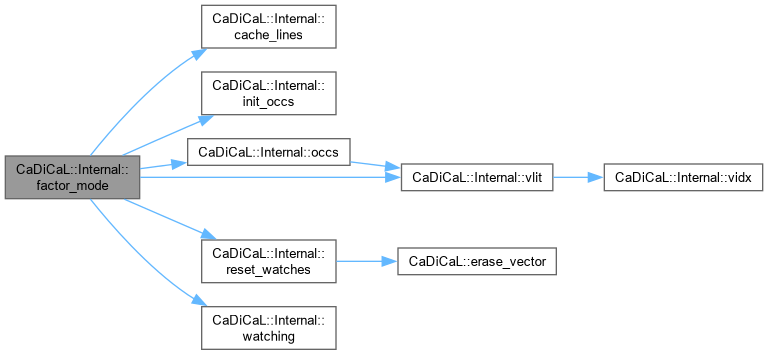
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::factor_mode | ( | ) |
Definition at line 24 of file cadical_factor.cpp.
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::factorize_next | ( | Factoring & | factoring, |
| int | next, | ||
| unsigned | expected_next_count ) |
Definition at line 391 of file cadical_factor.cpp.
| bool CaDiCaL::Internal::failed | ( | int | lit | ) |
Definition at line 453 of file cadical_assume.cpp.
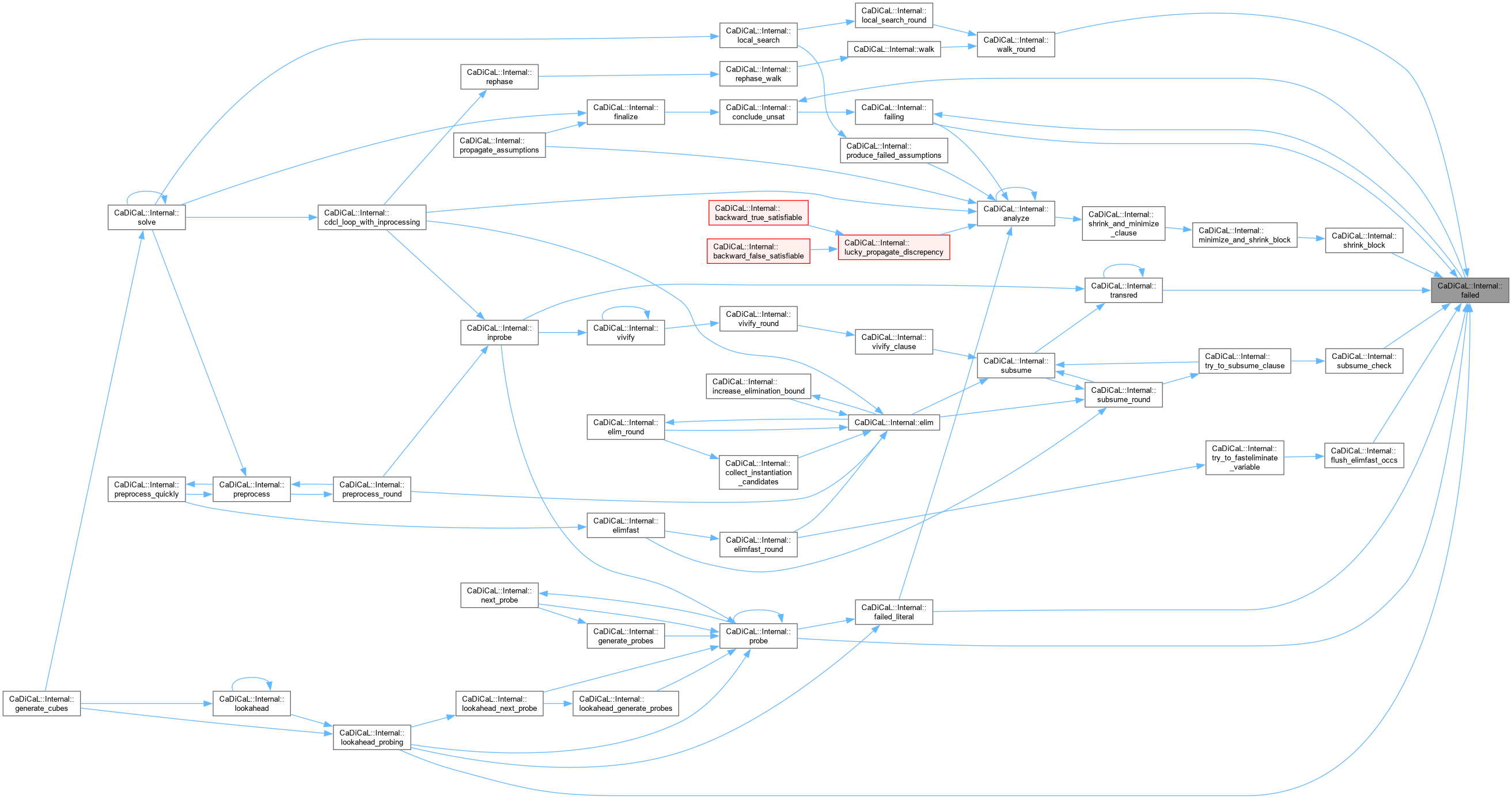
| bool CaDiCaL::Internal::failed_constraint | ( | ) |
Definition at line 57 of file cadical_constrain.cpp.
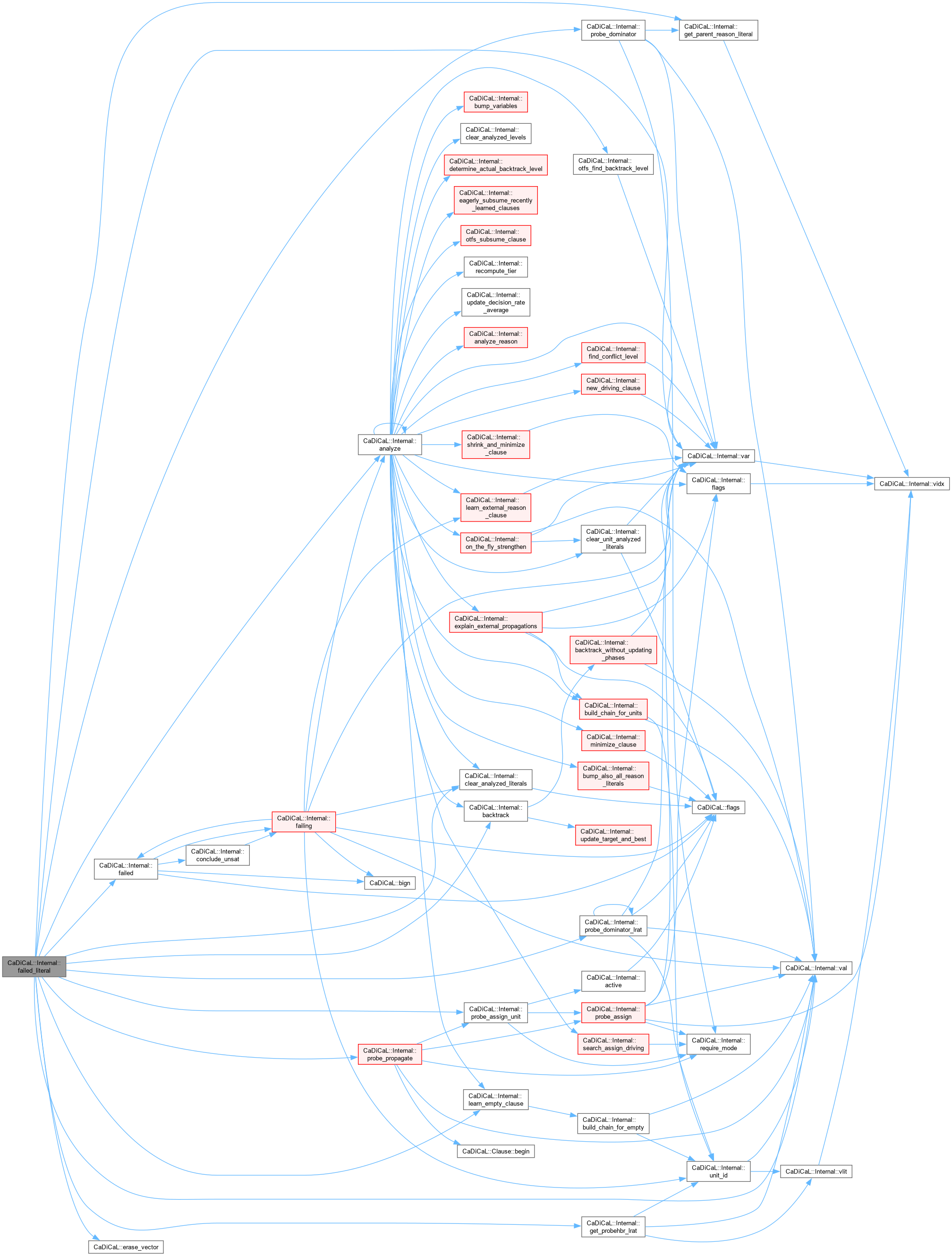
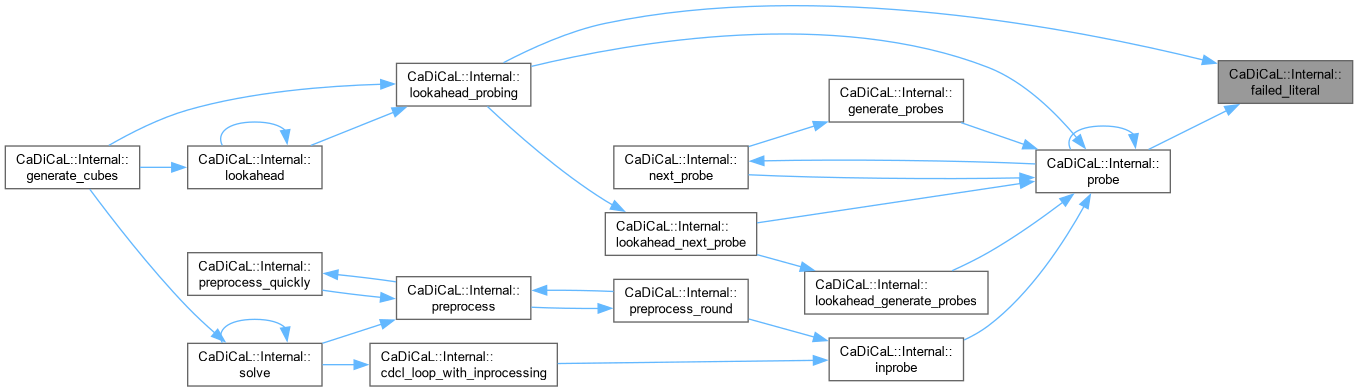
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::failed_literal | ( | int | lit | ) |
Definition at line 517 of file cadical_probe.cpp.
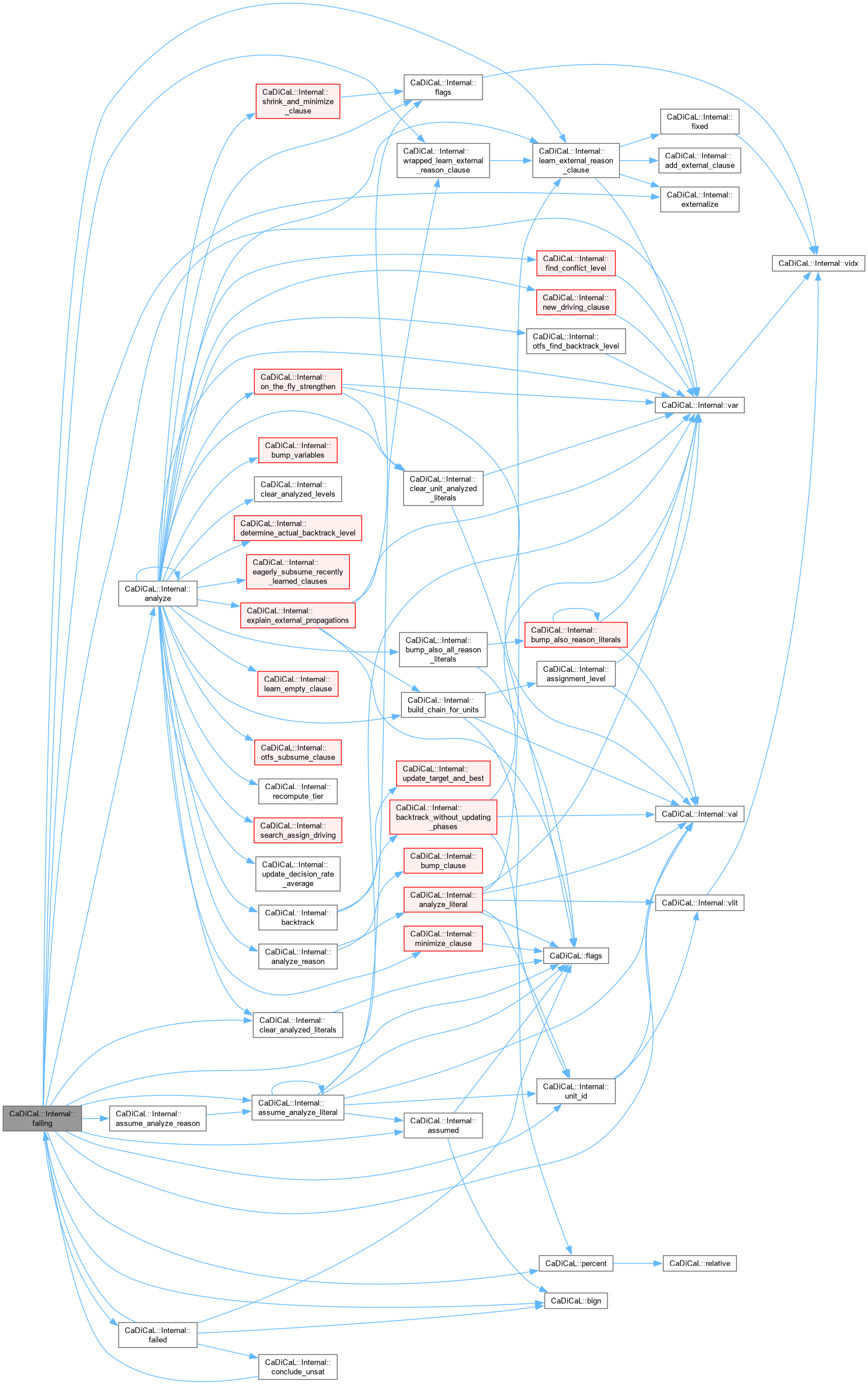
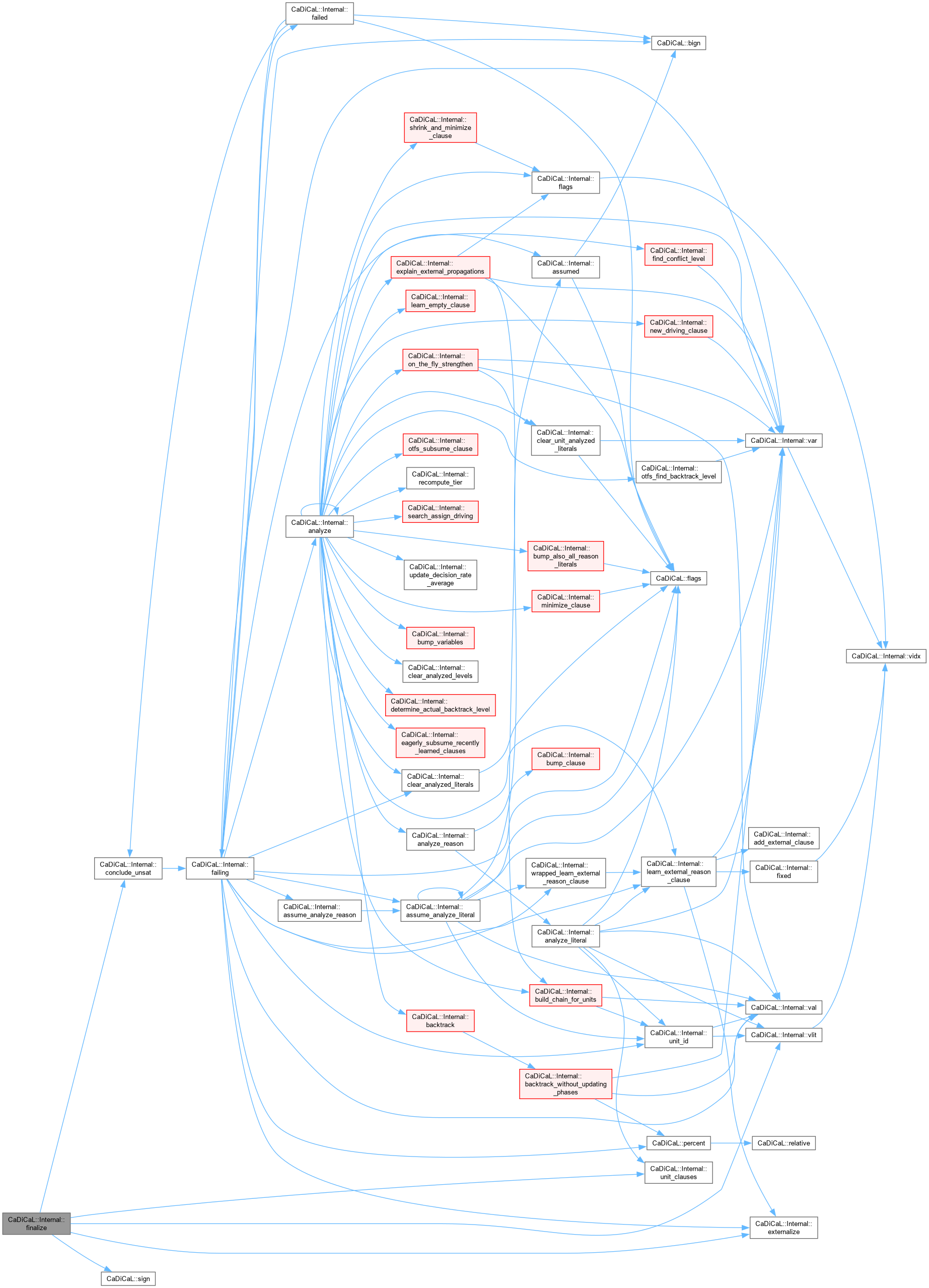
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::failing | ( | ) |
Definition at line 81 of file cadical_assume.cpp.
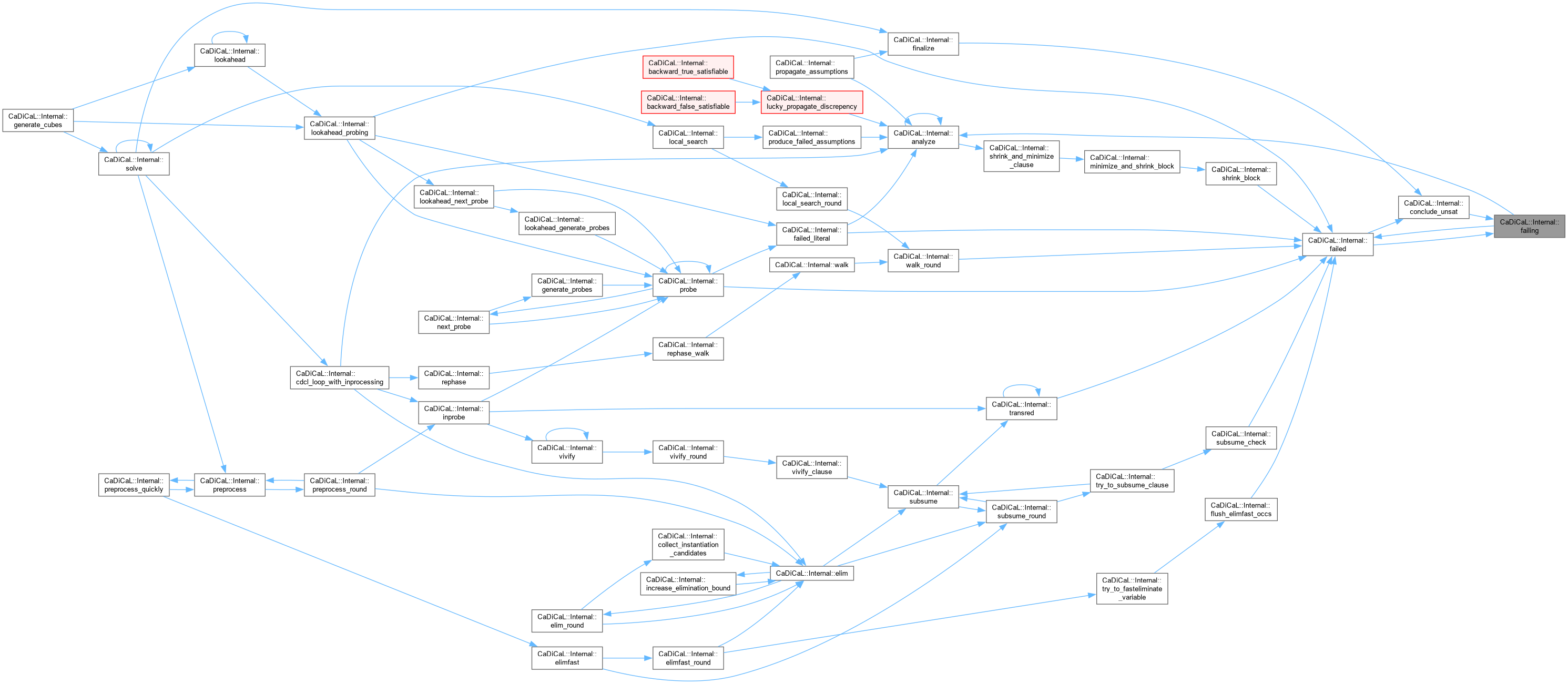
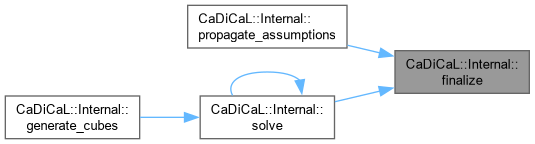
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::finalize | ( | int | res | ) |
Definition at line 1041 of file cadical_internal.cpp.
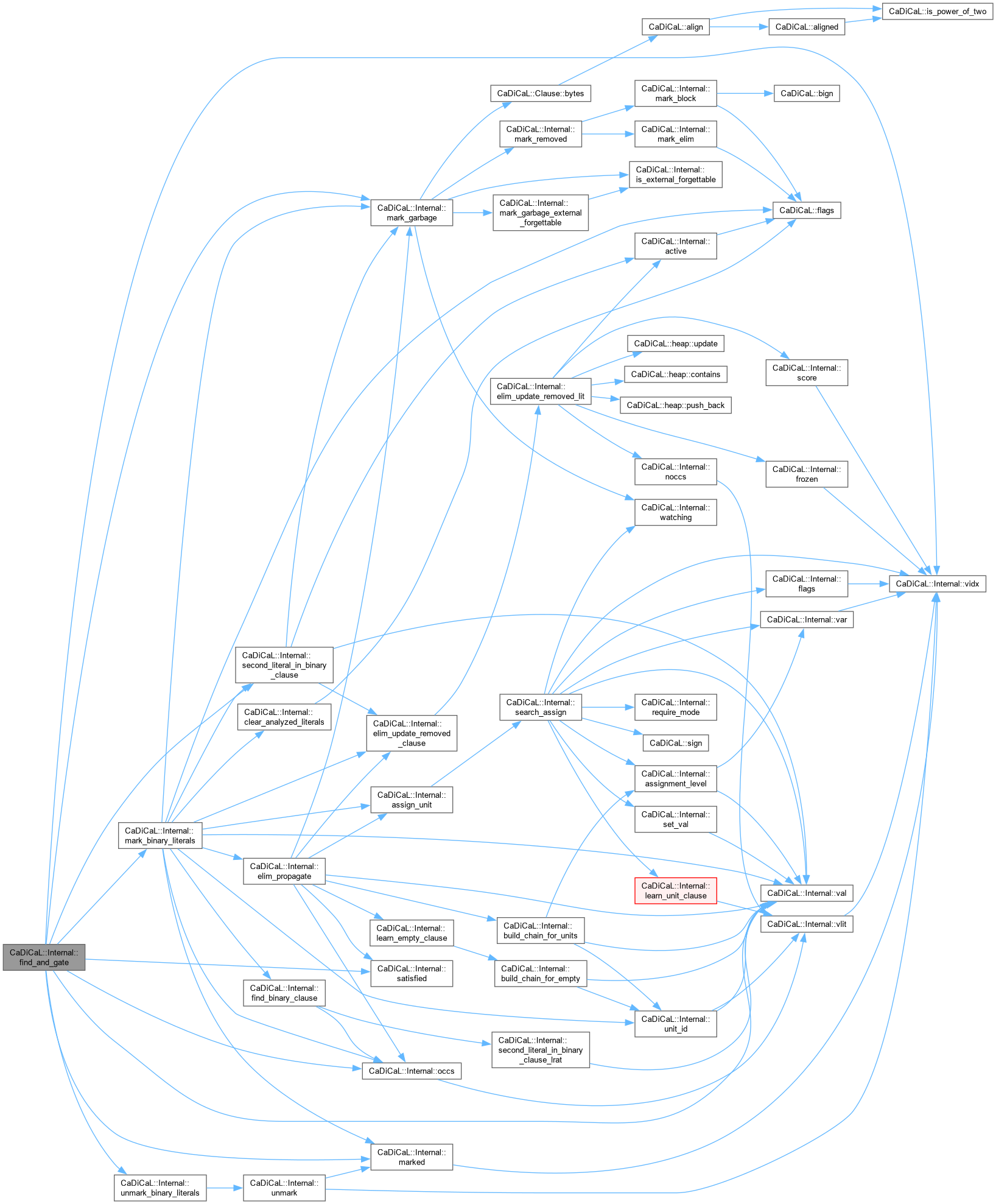
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::find_and_gate | ( | Eliminator & | eliminator, |
| int | pivot ) |
Definition at line 323 of file cadical_gates.cpp.
| Clause * CaDiCaL::Internal::find_binary_clause | ( | int | first, |
| int | second ) |
Definition at line 94 of file cadical_gates.cpp.
Definition at line 621 of file cadical_gates.cpp.
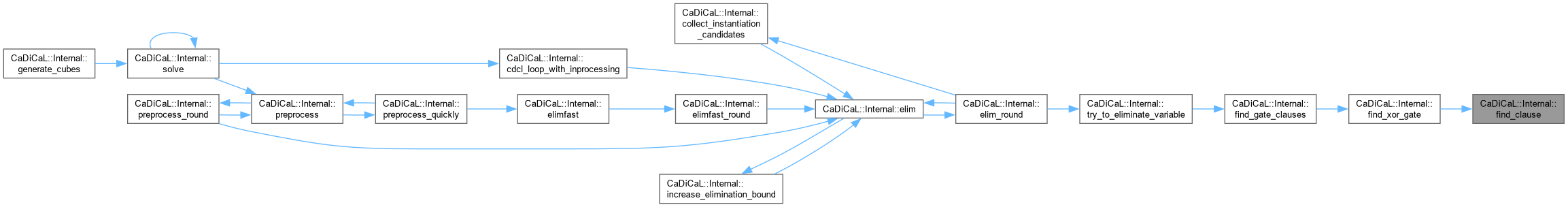
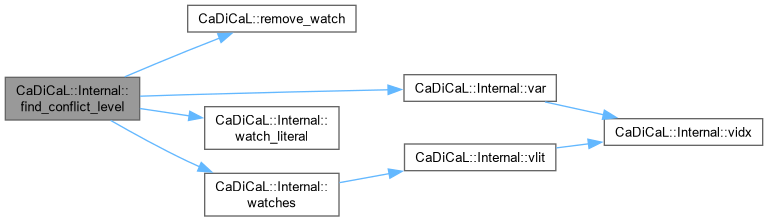
|
inline |
Definition at line 575 of file cadical_analyze.cpp.
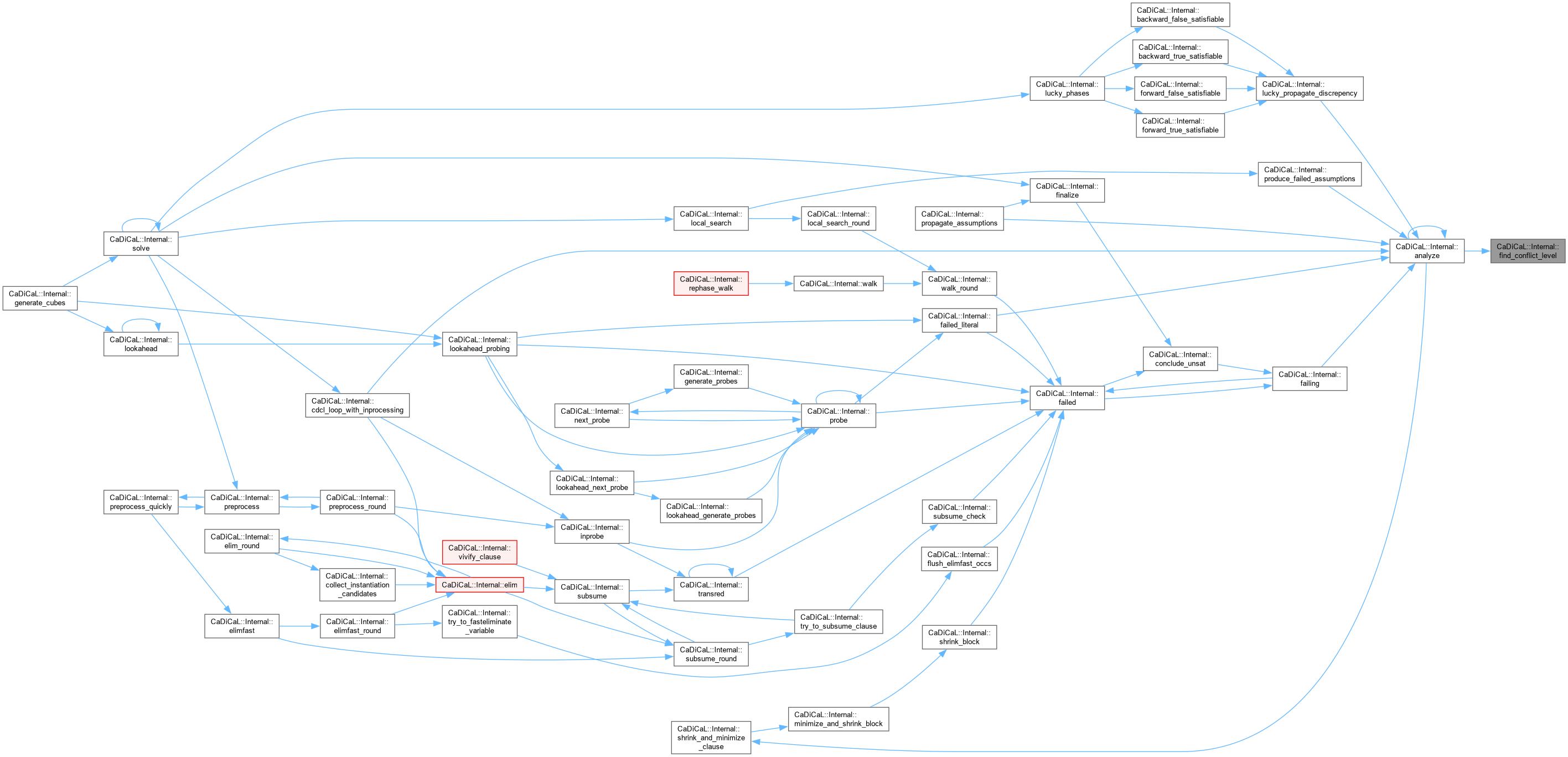
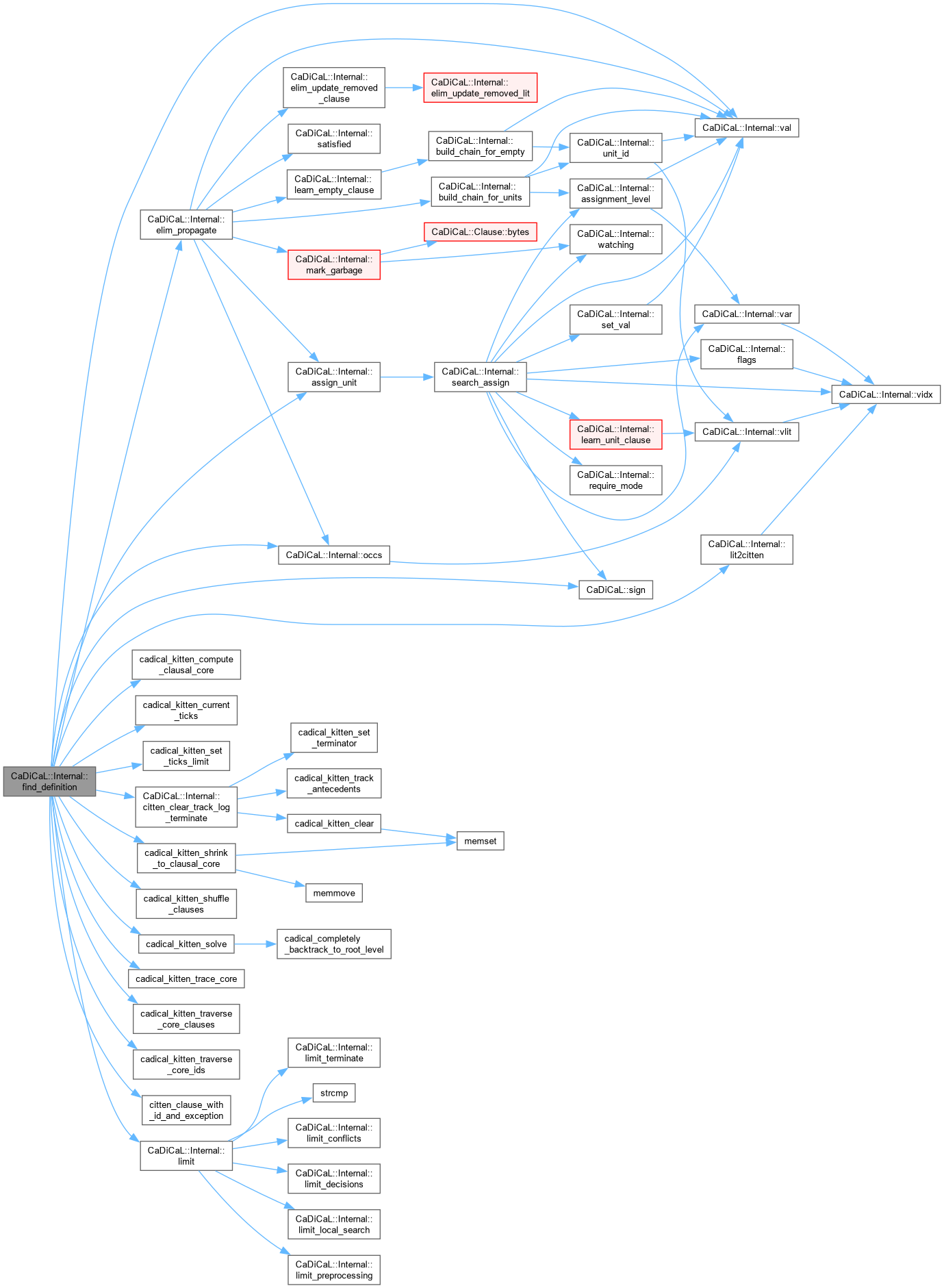
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::find_definition | ( | Eliminator & | eliminator, |
| int | lit ) |
Definition at line 182 of file cadical_definition.cpp.
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::find_equivalence | ( | Eliminator & | eliminator, |
| int | pivot ) |
Definition at line 204 of file cadical_gates.cpp.
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::find_gate_clauses | ( | Eliminator & | eliminator, |
| int | pivot ) |
Definition at line 739 of file cadical_gates.cpp.
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::find_if_then_else | ( | Eliminator & | eliminator, |
| int | pivot ) |
Definition at line 505 of file cadical_gates.cpp.
| Clause * CaDiCaL::Internal::find_ternary_clause | ( | int | a, |
| int | b, | ||
| int | c ) |
Definition at line 490 of file cadical_gates.cpp.
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::find_xor_gate | ( | Eliminator & | eliminator, |
| int | pivot ) |
Definition at line 636 of file cadical_gates.cpp.
Definition at line 219 of file cadical_internal.cpp.
| size_t CaDiCaL::Internal::first_factor | ( | Factoring & | factoring, |
| int | factor ) |
Definition at line 184 of file cadical_factor.cpp.
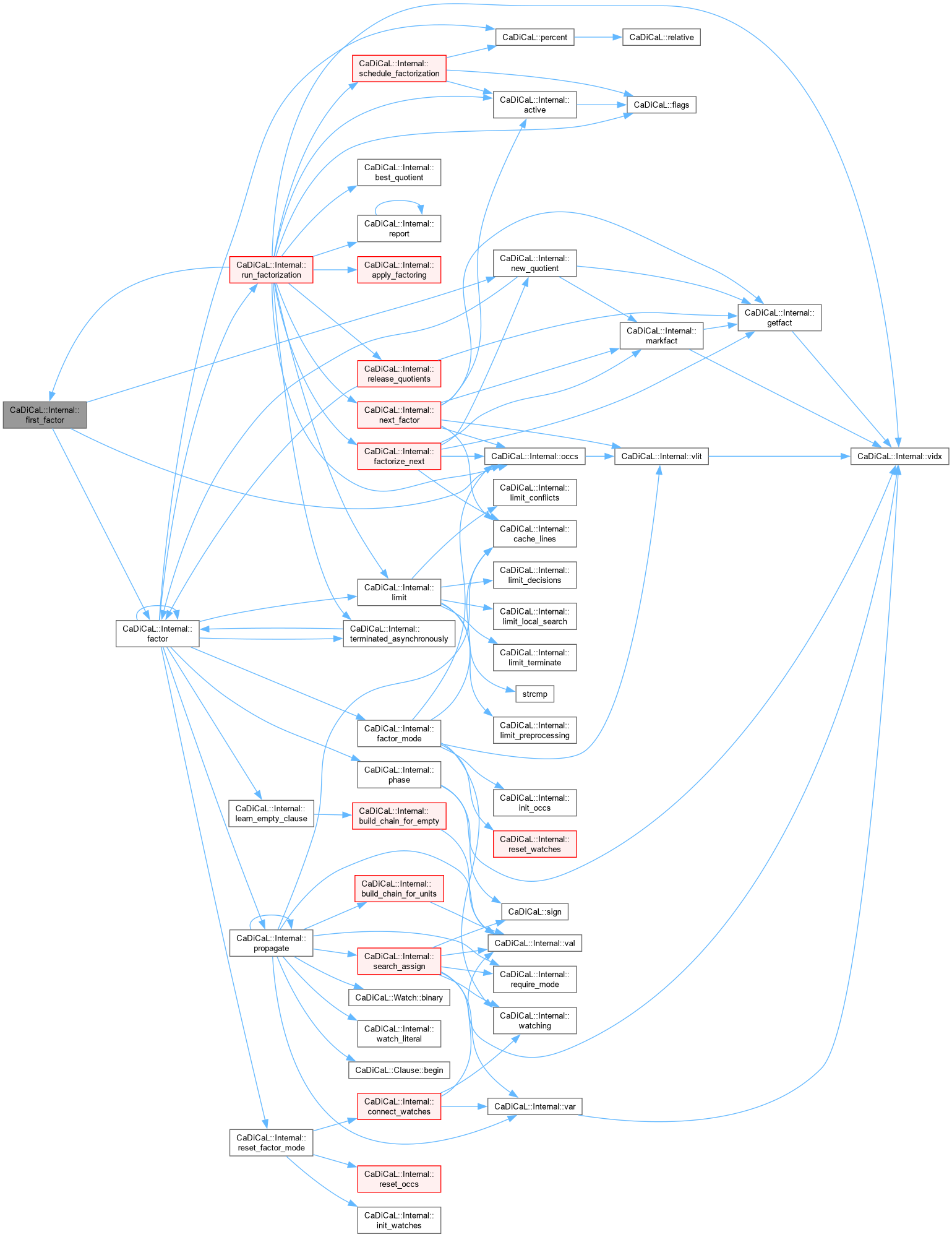
|
inline |
Definition at line 1542 of file internal.hpp.
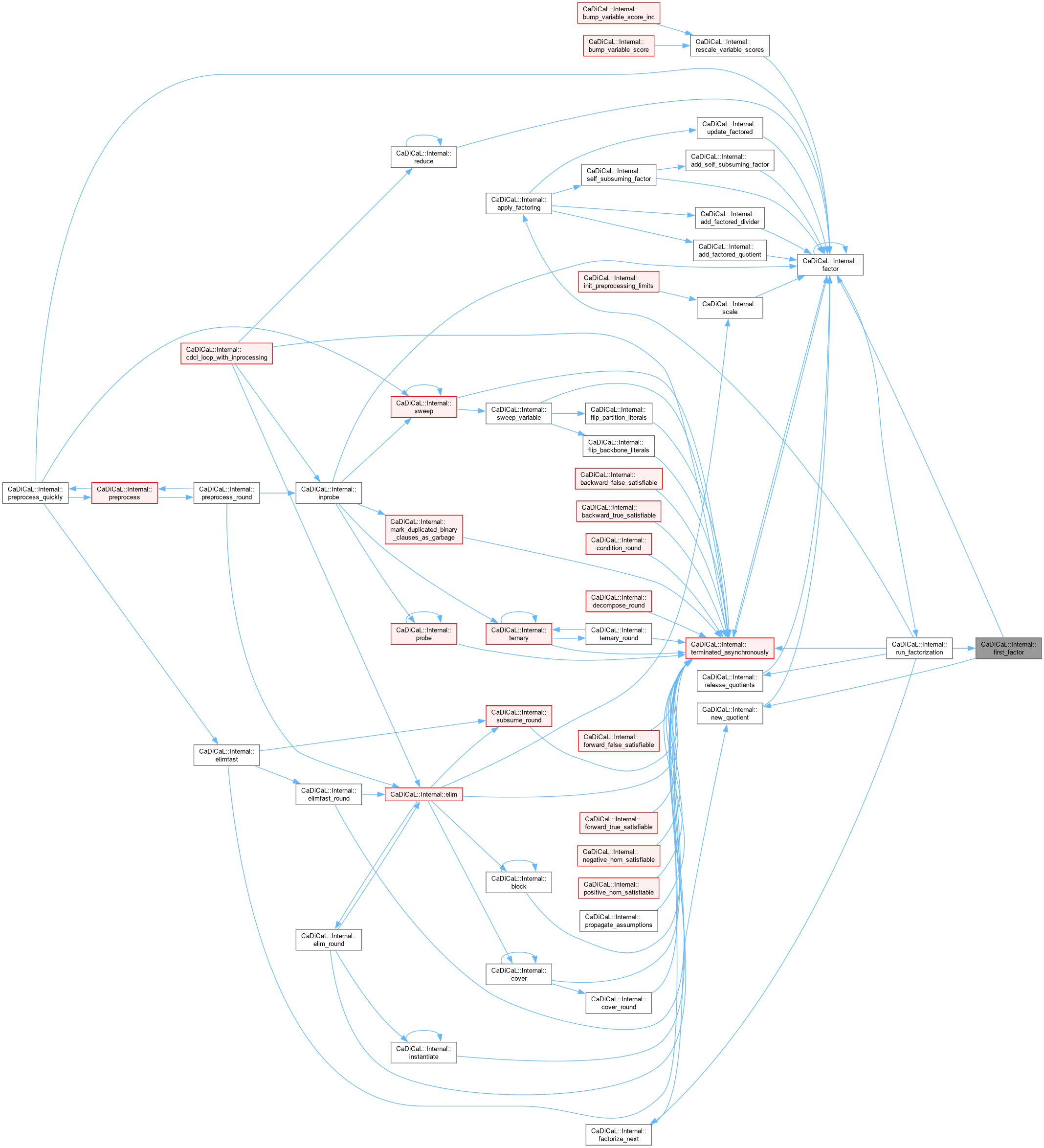
|
inline |
Definition at line 454 of file internal.hpp.
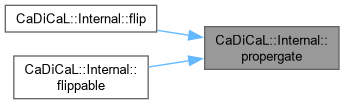
| bool CaDiCaL::Internal::flip | ( | int | lit | ) |
Definition at line 9 of file cadical_flip.cpp.
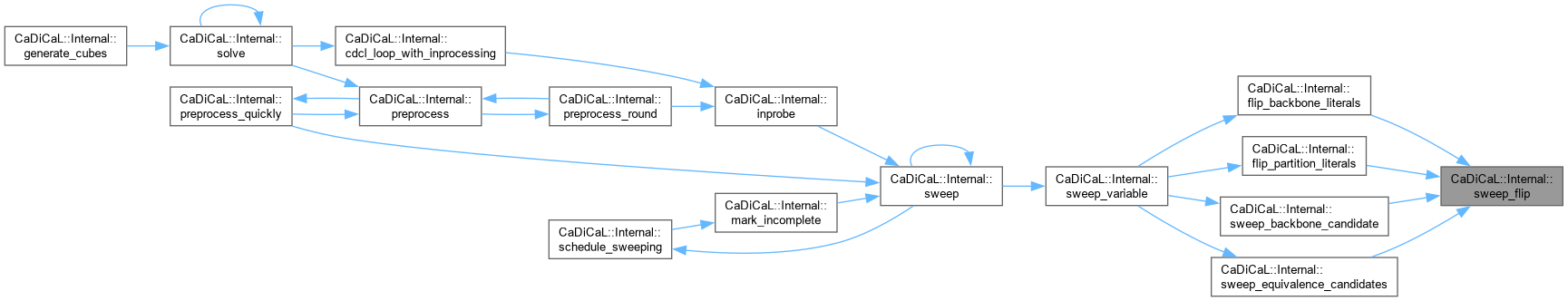
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::flip_backbone_literals | ( | struct Sweeper & | sweeper | ) |
Definition at line 774 of file cadical_sweep.cpp.
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::flip_partition_literals | ( | struct Sweeper & | sweeper | ) |
Definition at line 1273 of file cadical_sweep.cpp.
| bool CaDiCaL::Internal::flippable | ( | int | lit | ) |
Definition at line 169 of file cadical_flip.cpp.
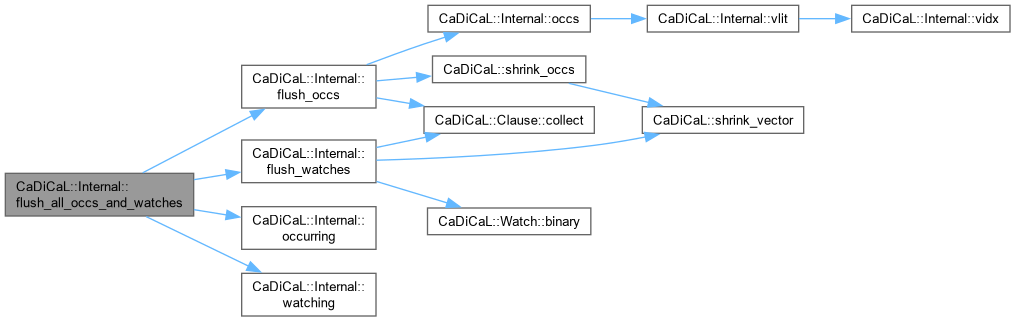
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::flush_all_occs_and_watches | ( | ) |
Definition at line 232 of file cadical_collect.cpp.
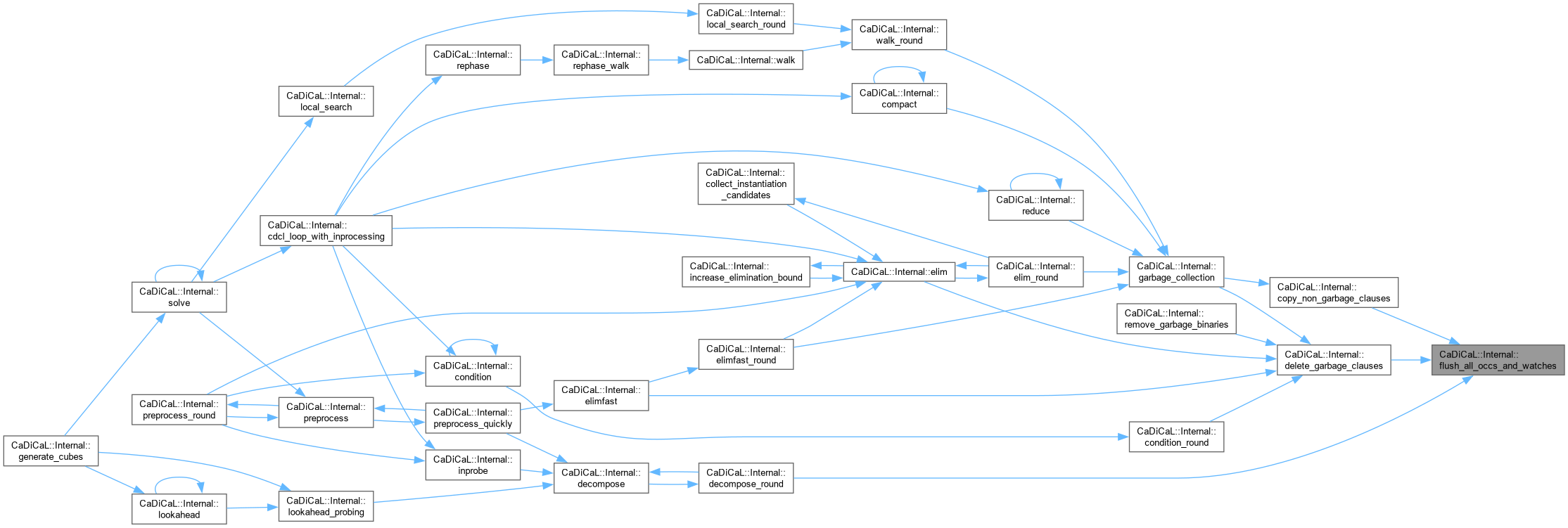
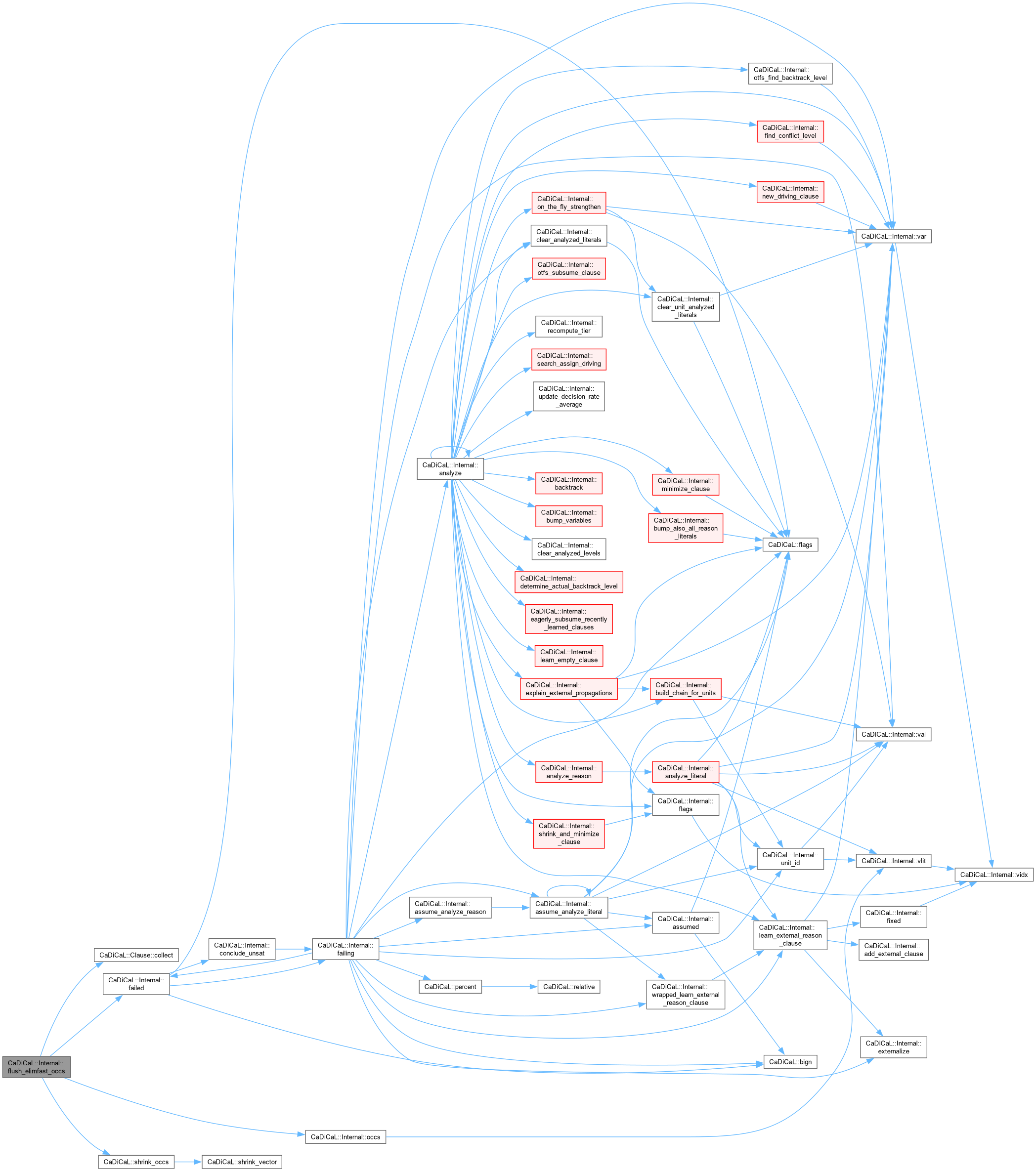
| int64_t CaDiCaL::Internal::flush_elimfast_occs | ( | int | lit | ) |
Definition at line 19 of file cadical_elimfast.cpp.
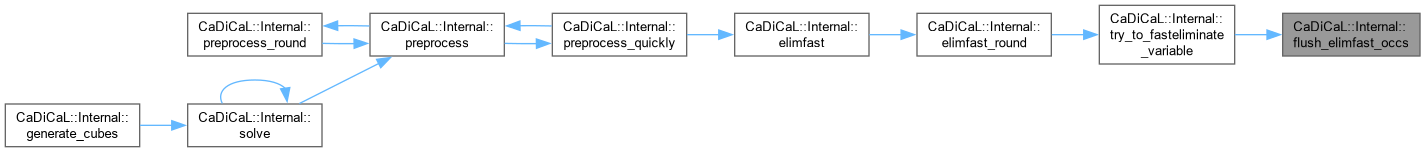
| size_t CaDiCaL::Internal::flush_occs | ( | int | lit | ) |
Definition at line 176 of file cadical_collect.cpp.
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::flush_probes | ( | ) |
Definition at line 702 of file cadical_probe.cpp.
Definition at line 195 of file cadical_proof.cpp.
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::flush_unmatched_clauses | ( | Quotient * | q | ) |
Definition at line 479 of file cadical_factor.cpp.
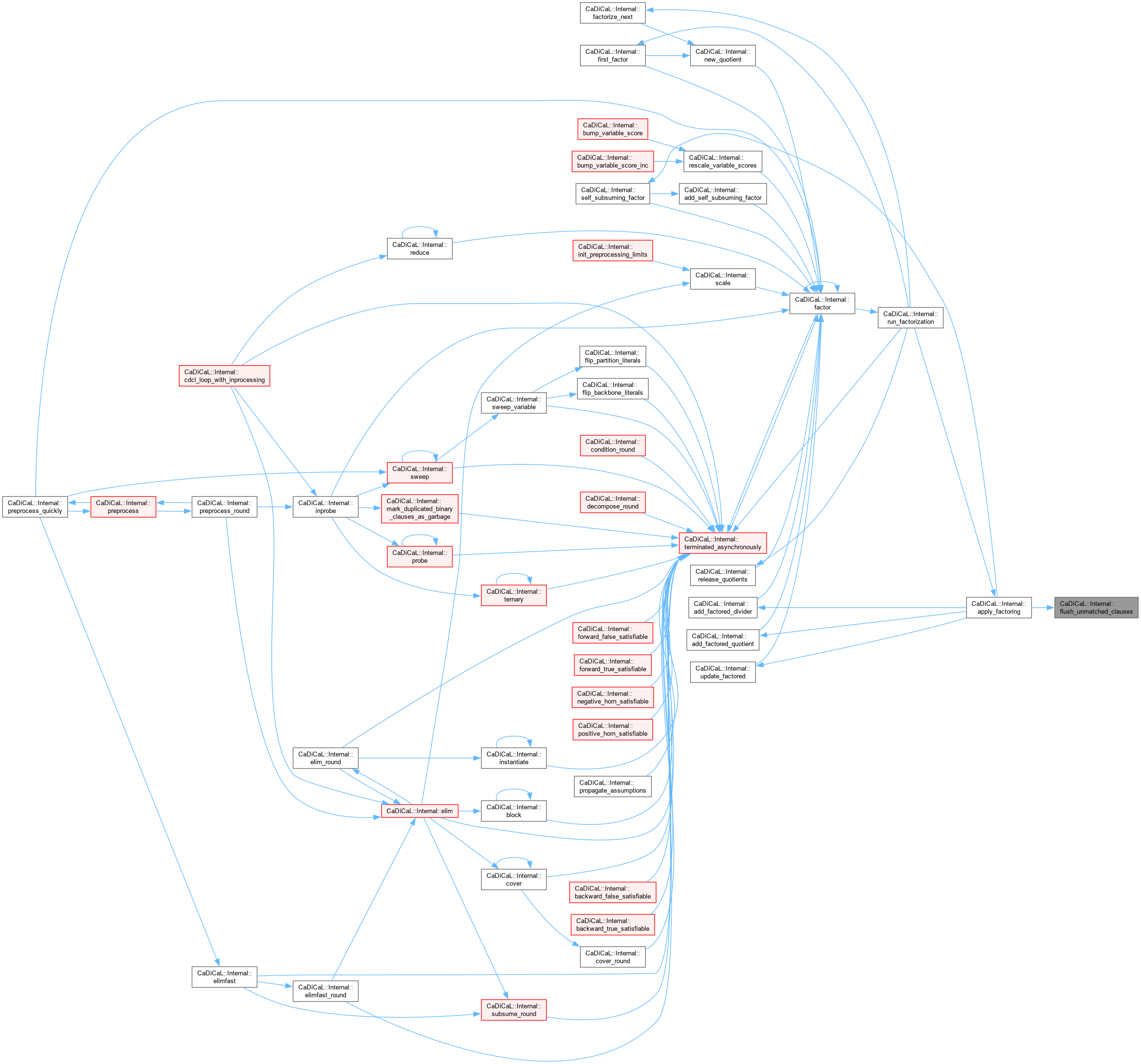
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::flush_vivification_schedule | ( | std::vector< Clause * > & | schedule, |
| int64_t & | ticks ) |
Definition at line 456 of file cadical_vivify.cpp.
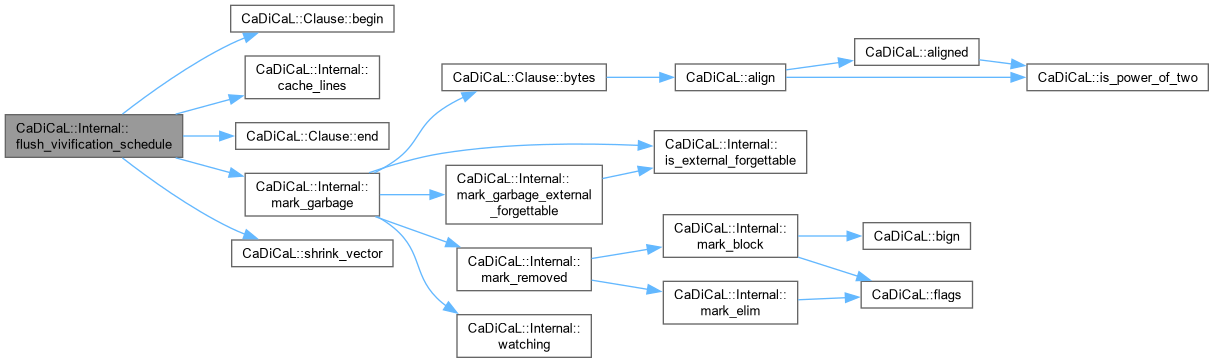

|
inline |
Definition at line 202 of file cadical_collect.cpp.
| bool CaDiCaL::Internal::flushing | ( | ) |
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::force_backtrack | ( | size_t | new_level | ) |
Definition at line 214 of file cadical_external_propagate.cpp.
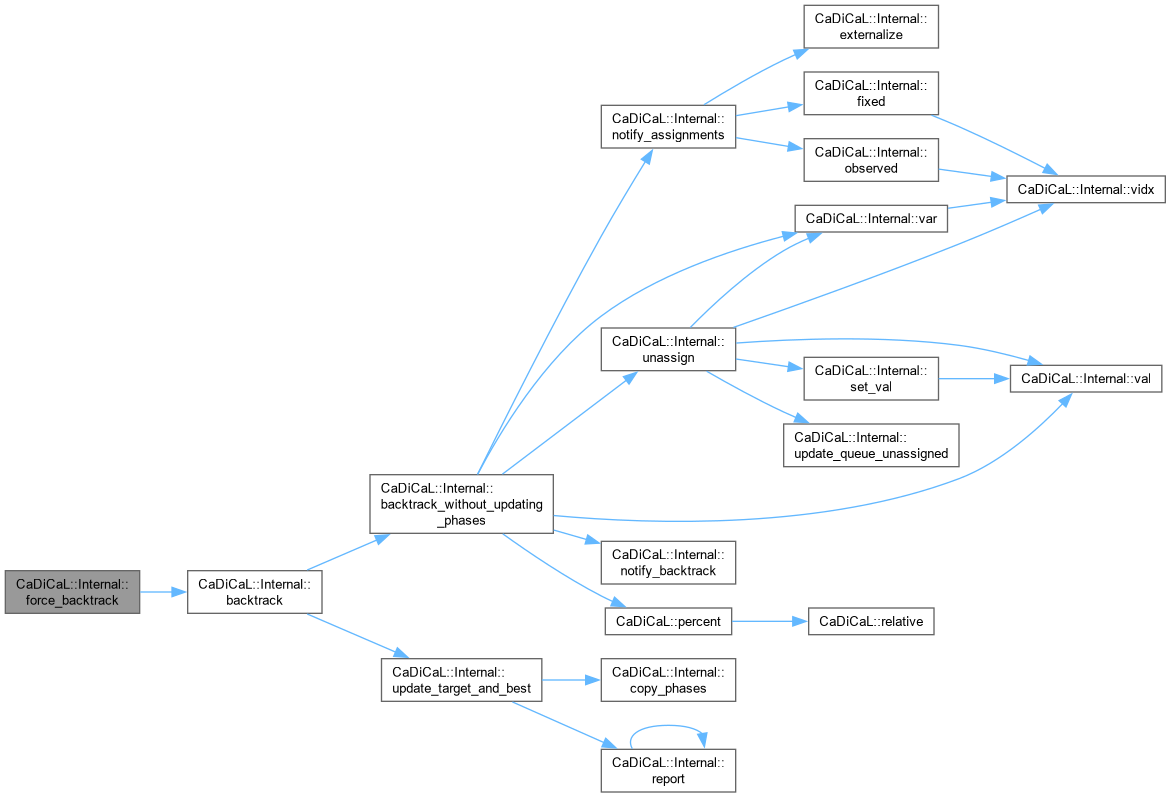
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::force_lrat | ( | ) |
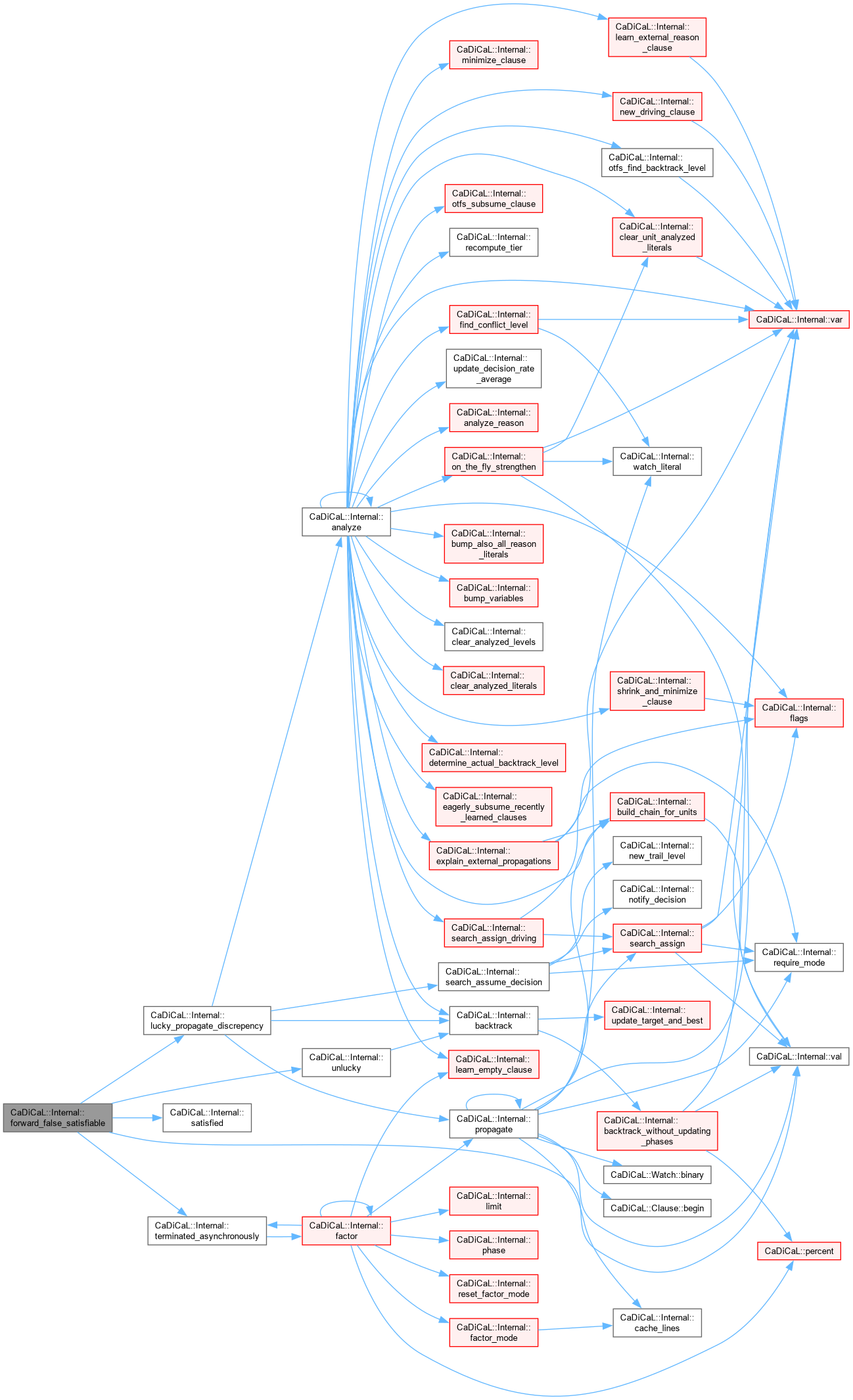
| int CaDiCaL::Internal::forward_false_satisfiable | ( | ) |
Definition at line 154 of file cadical_lucky.cpp.
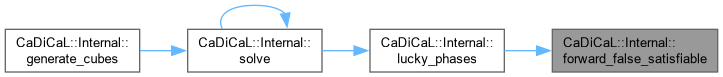
| int CaDiCaL::Internal::forward_true_satisfiable | ( | ) |
Definition at line 179 of file cadical_lucky.cpp.
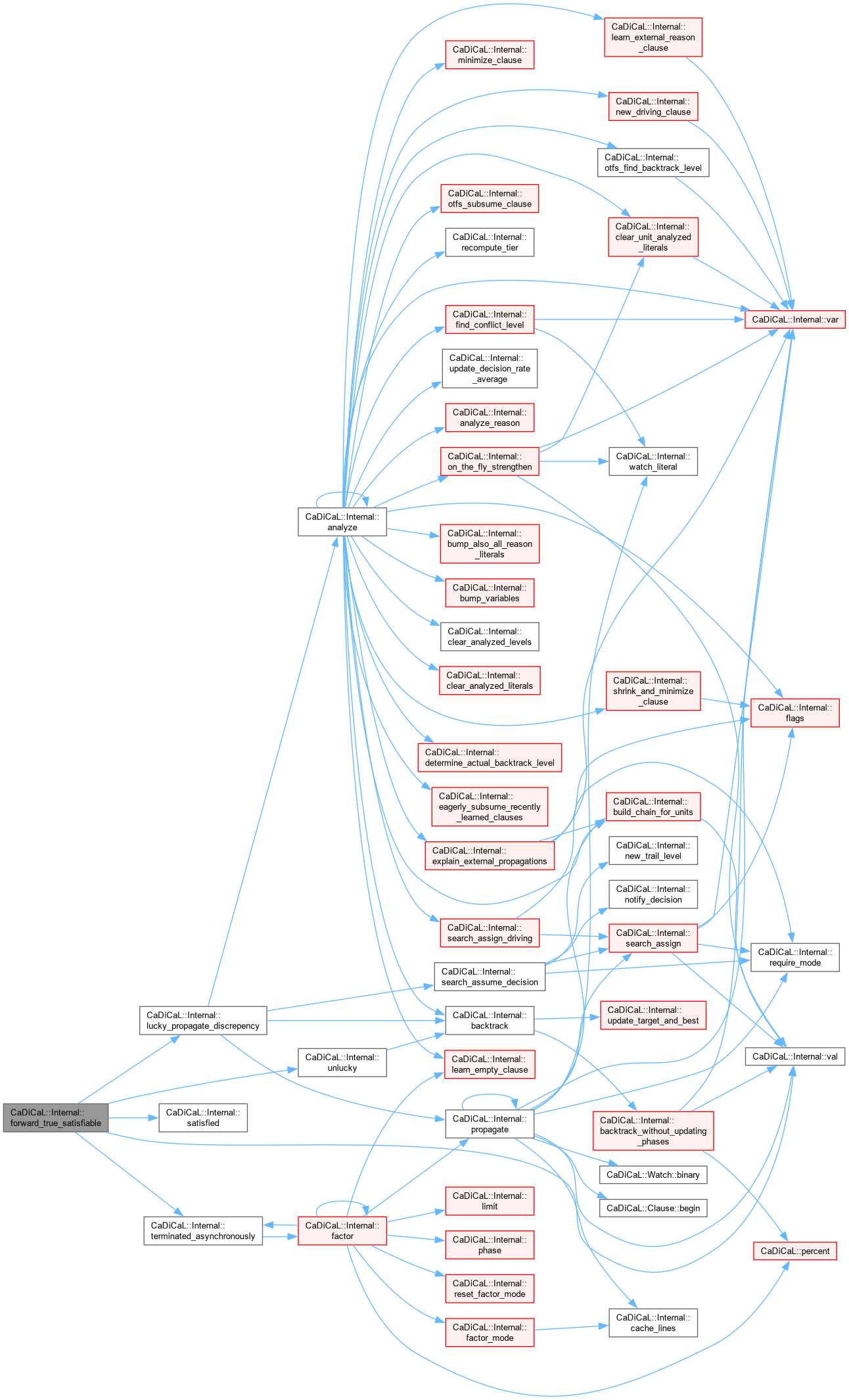
|
inline |
Definition at line 1570 of file internal.hpp.
|
inline |
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::garbage_collection | ( | ) |
Definition at line 529 of file cadical_collect.cpp.
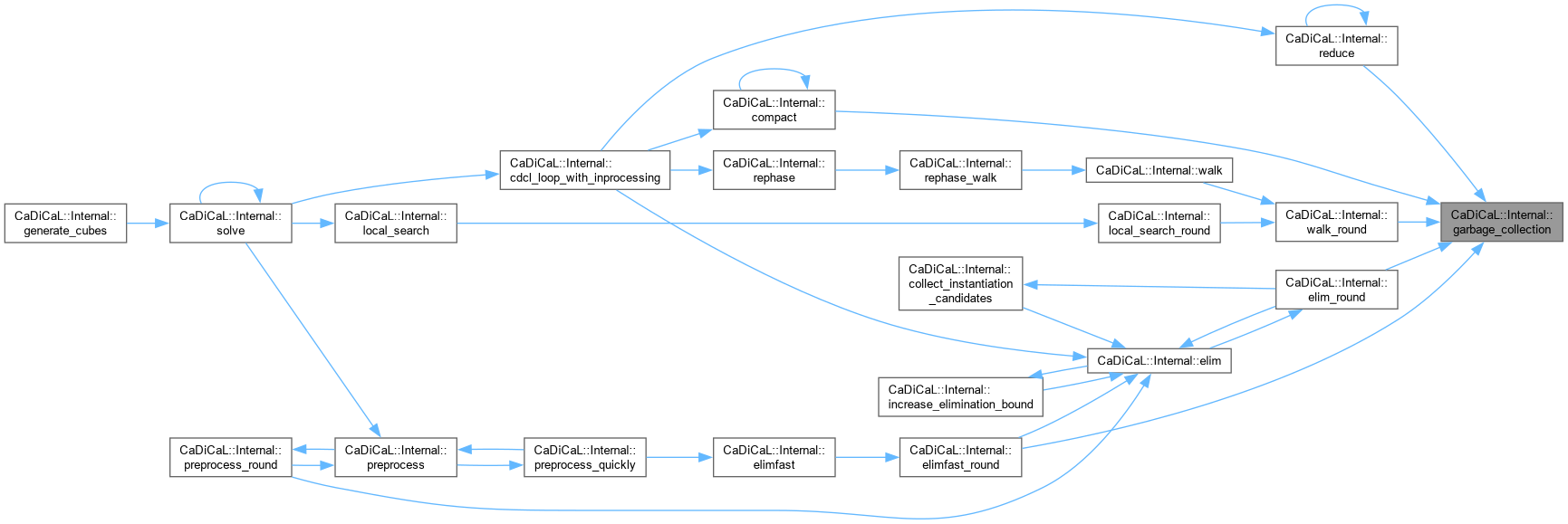
| CubesWithStatus CaDiCaL::Internal::generate_cubes | ( | int | depth, |
| int | min_depth ) |
Definition at line 408 of file cadical_lookahead.cpp.
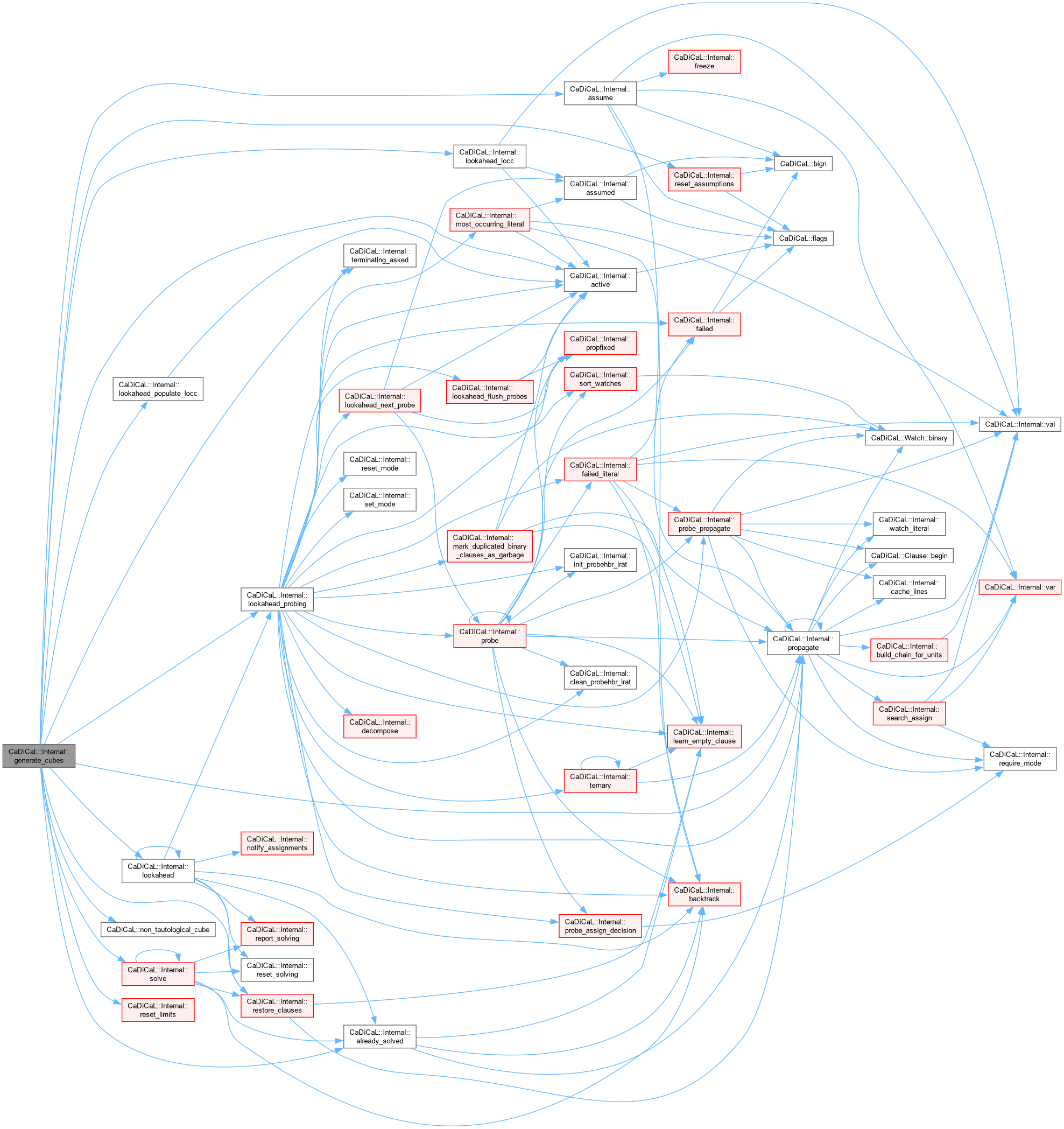
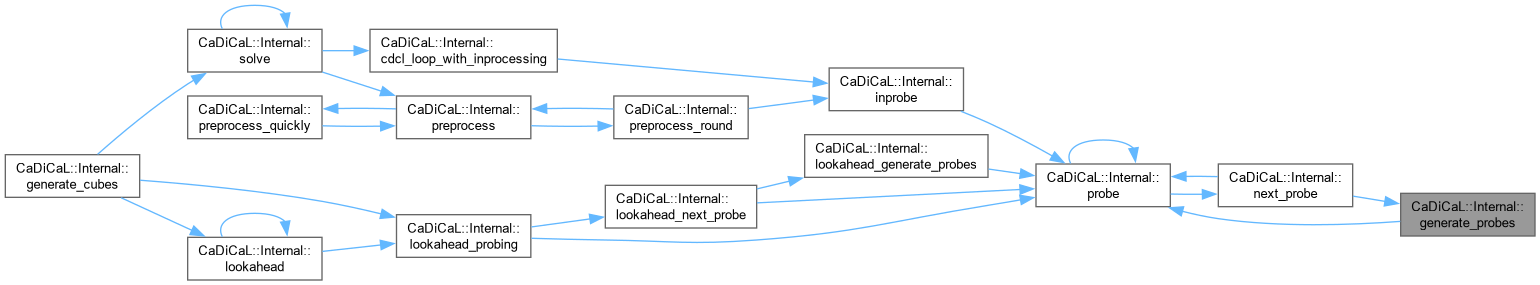
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::generate_probes | ( | ) |
Definition at line 637 of file cadical_probe.cpp.
Definition at line 582 of file cadical_gates.cpp.
| int CaDiCaL::Internal::get_new_extension_variable | ( | ) |
Definition at line 845 of file cadical_factor.cpp.
|
inline |
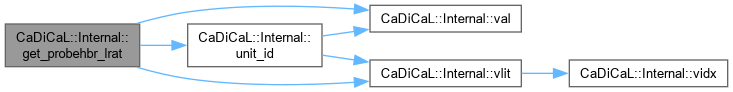
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::get_probehbr_lrat | ( | int | lit, |
| int | uip ) |
Definition at line 90 of file cadical_probe.cpp.
Definition at line 452 of file cadical_gates.cpp.
|
inline |
Definition at line 536 of file internal.hpp.
|
inline |
Definition at line 568 of file internal.hpp.
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::handle_external_clause | ( | Clause * | res | ) |
Definition at line 744 of file cadical_external_propagate.cpp.
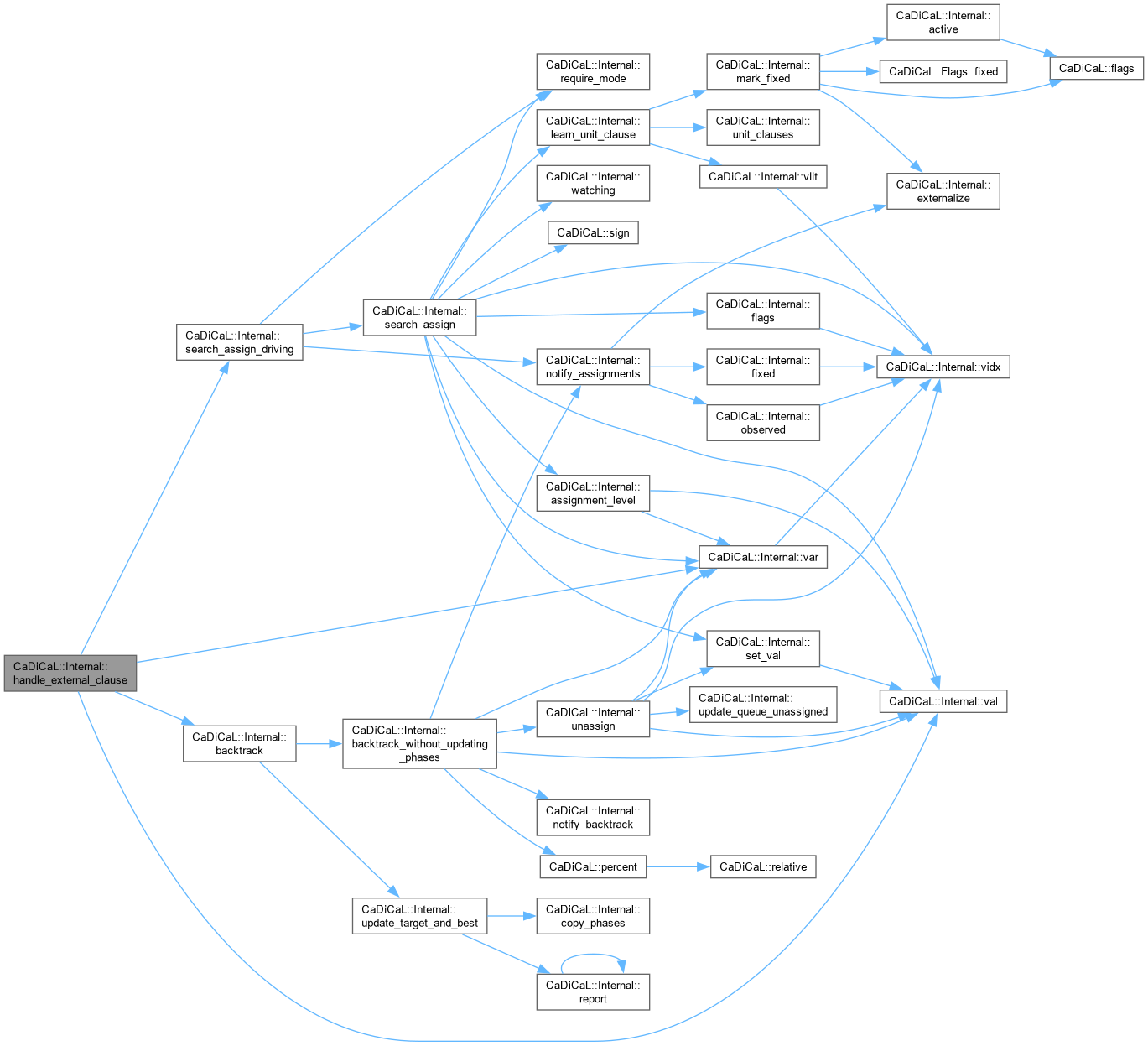

|
inline |
Definition at line 222 of file cadical_probe.cpp.
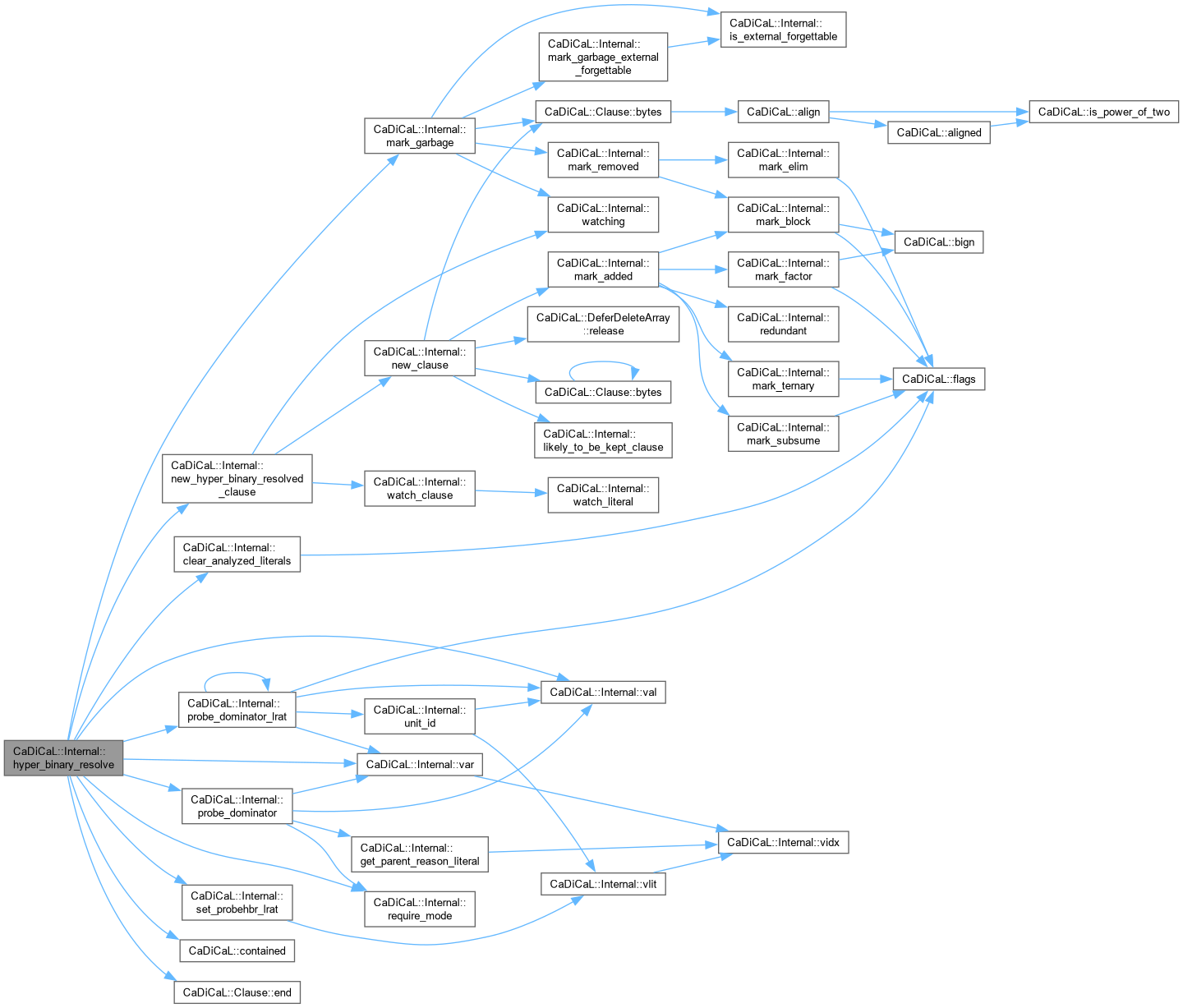
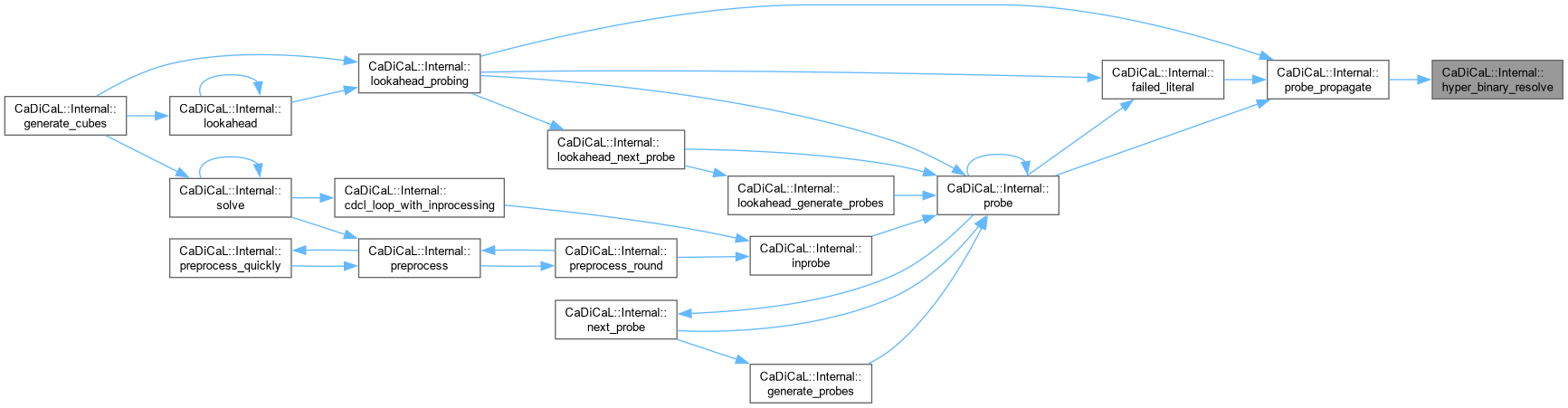
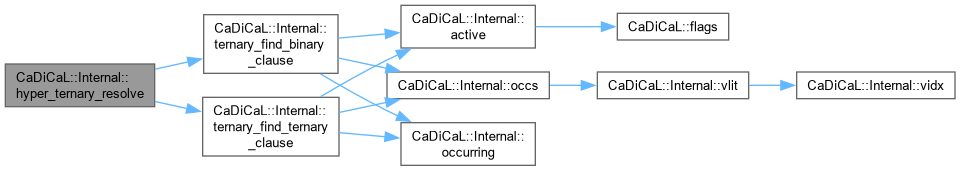
Definition at line 113 of file cadical_ternary.cpp.
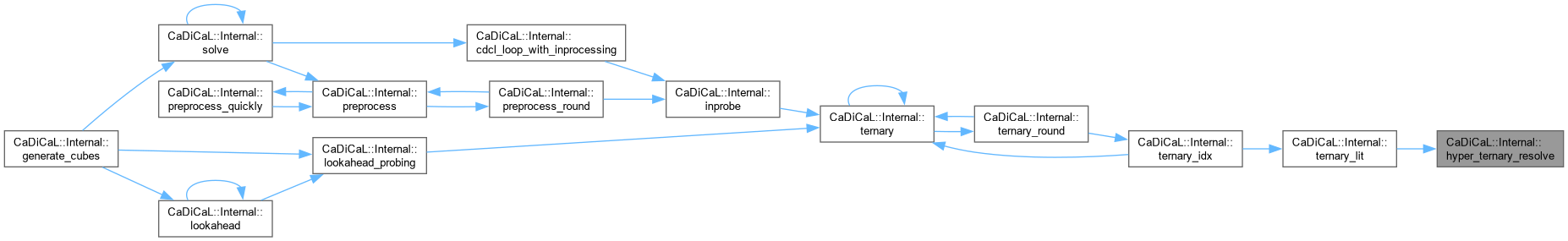
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::implied | ( | std::vector< int > & | entrailed | ) |
Definition at line 418 of file cadical_internal.cpp.
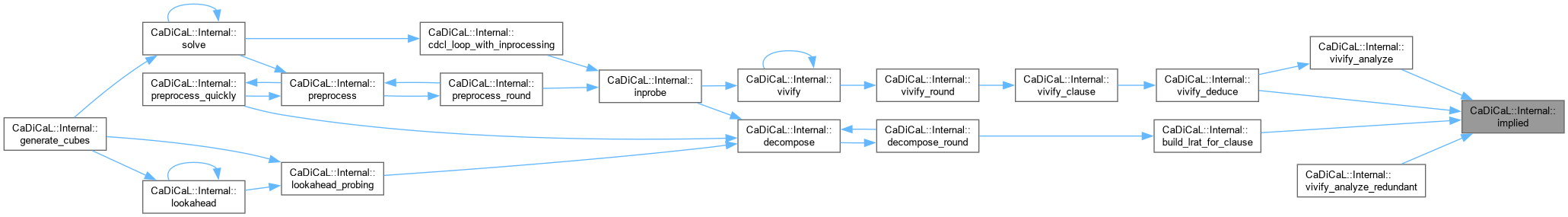
Definition at line 164 of file internal.hpp.
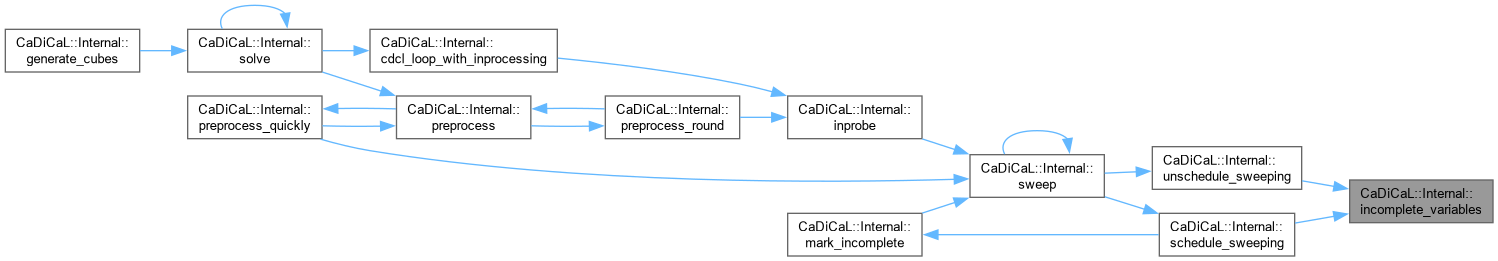
| unsigned CaDiCaL::Internal::incomplete_variables | ( | ) |
Definition at line 1793 of file cadical_sweep.cpp.
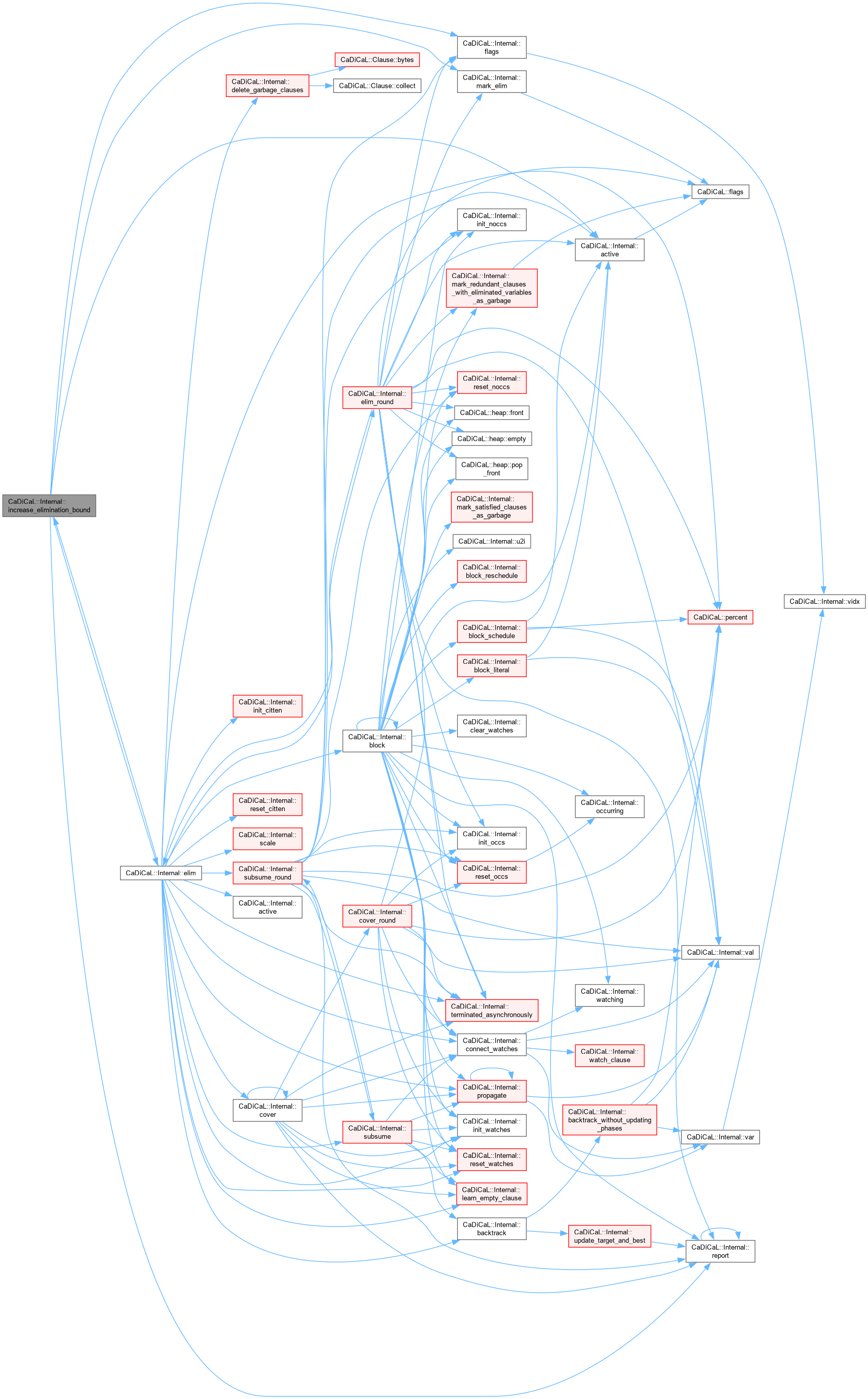
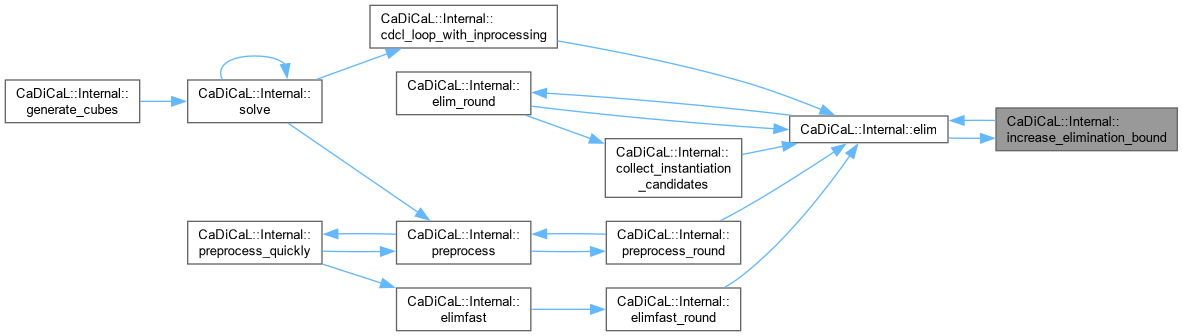
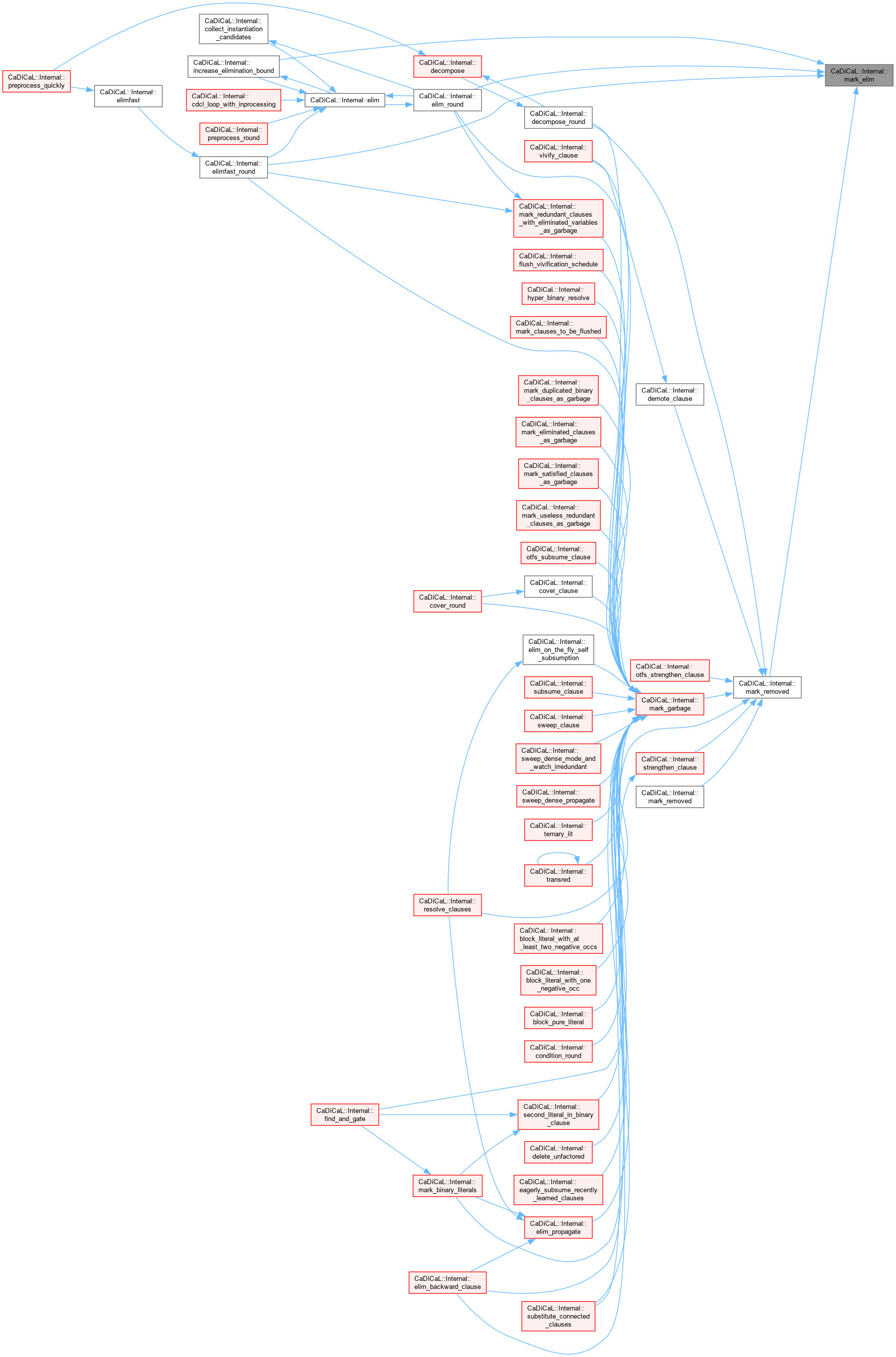
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::increase_elimination_bound | ( | ) |
Definition at line 966 of file cadical_elim.cpp.
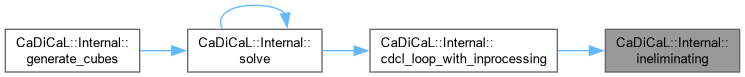
| bool CaDiCaL::Internal::ineliminating | ( | ) |
Definition at line 65 of file cadical_elim.cpp.
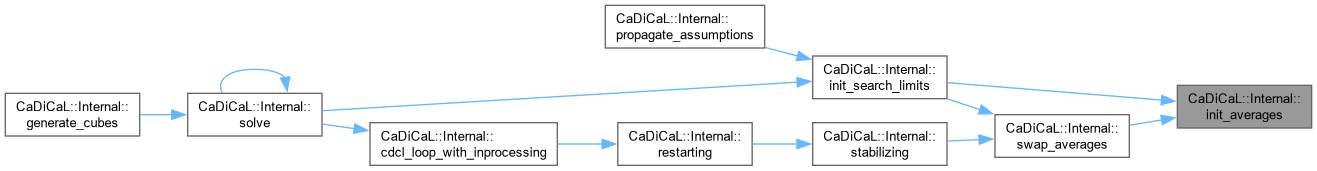
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::init_averages | ( | ) |
Definition at line 9 of file cadical_averages.cpp.
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::init_backbone_and_partition | ( | Sweeper & | sweeper | ) |
Definition at line 632 of file cadical_sweep.cpp.
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::init_bins | ( | ) |
Definition at line 13 of file cadical_bins.cpp.
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::init_citten | ( | ) |
Definition at line 1004 of file cadical_elim.cpp.
|
inline |
Definition at line 12 of file cadical_queue.cpp.

| void CaDiCaL::Internal::init_noccs | ( | ) |
Definition at line 36 of file cadical_occs.cpp.
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::init_occs | ( | ) |
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::init_preprocessing_limits | ( | ) |
Definition at line 443 of file cadical_internal.cpp.

| void CaDiCaL::Internal::init_probehbr_lrat | ( | ) |
Definition at line 70 of file cadical_probe.cpp.
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::init_queue | ( | int | old_max_var, |
| int | new_max_var ) |
Definition at line 51 of file cadical_queue.cpp.

| void CaDiCaL::Internal::init_report_limits | ( | ) |
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::init_scores | ( | int | old_max_var, |
| int | new_max_var ) |
Definition at line 13 of file cadical_score.cpp.
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::init_search_limits | ( | ) |
Definition at line 520 of file cadical_internal.cpp.

| void CaDiCaL::Internal::init_sweeper | ( | Sweeper & | sweeper | ) |
Definition at line 216 of file cadical_sweep.cpp.
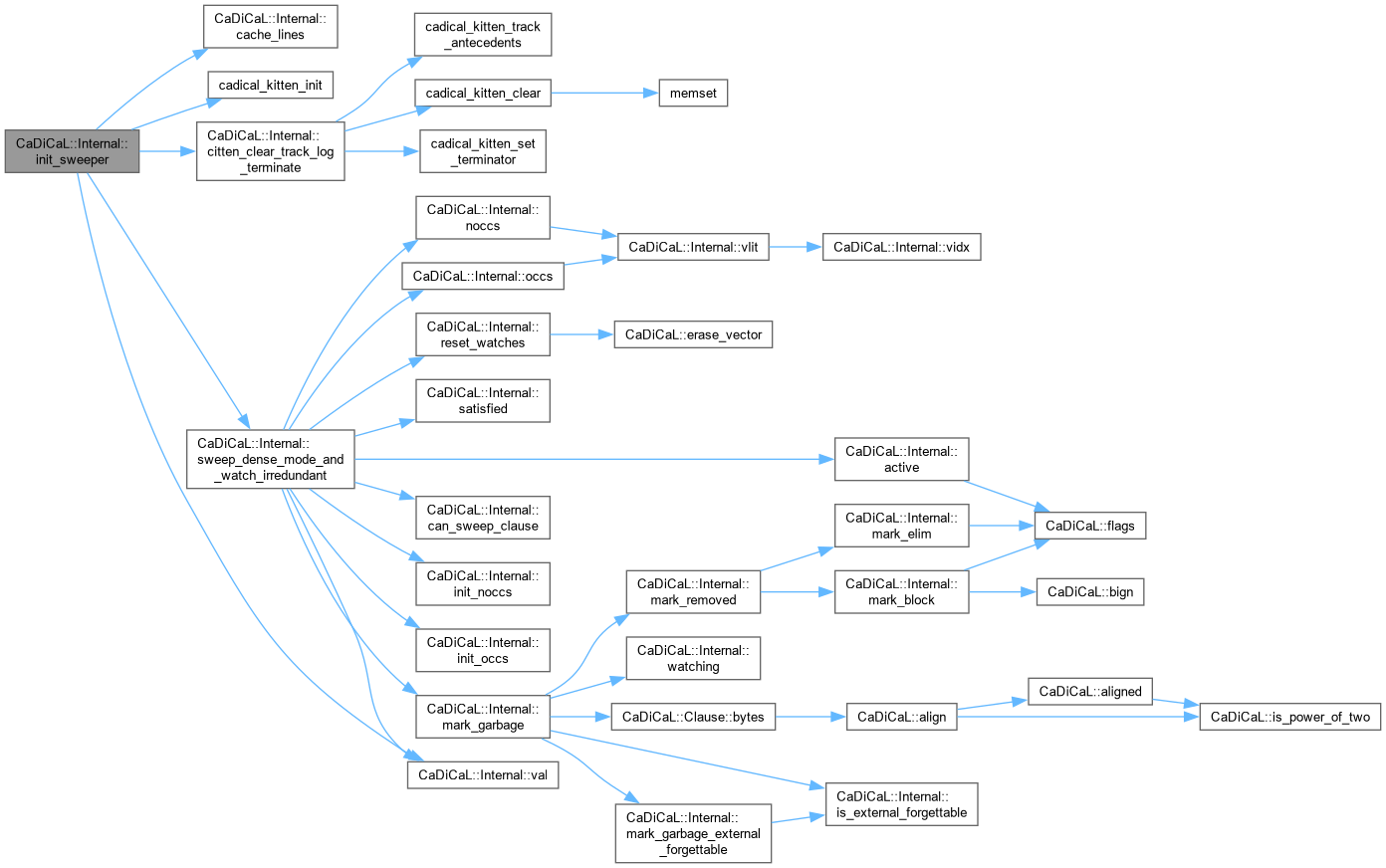
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::init_vars | ( | int | new_max_var | ) |
Definition at line 154 of file cadical_internal.cpp.
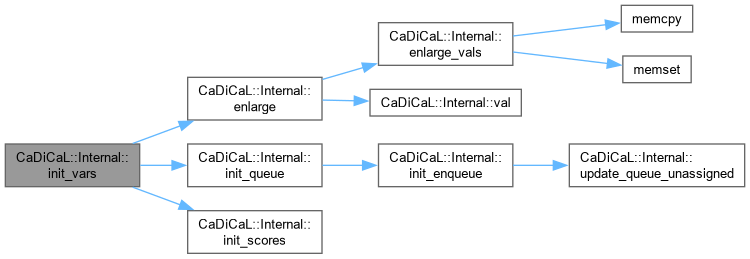
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::init_watches | ( | ) |
Definition at line 918 of file cadical_probe.cpp.
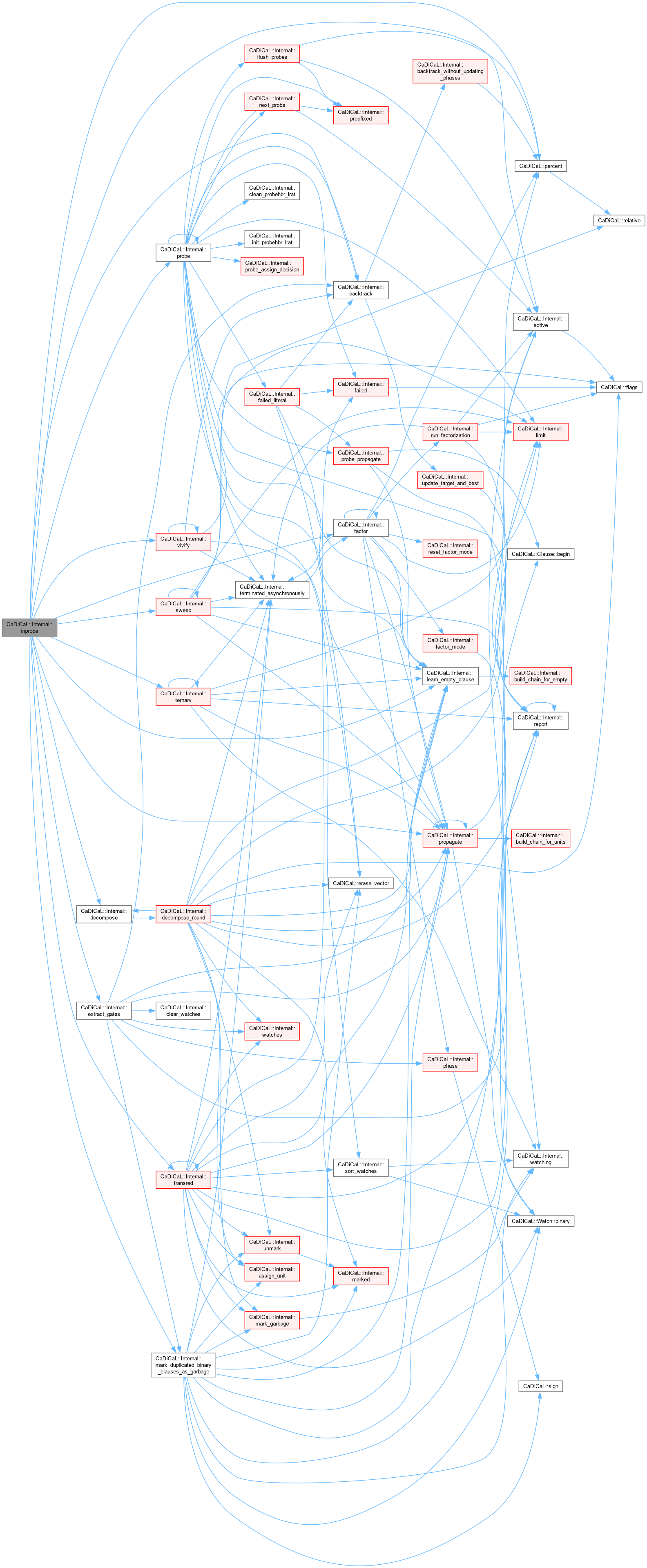

| bool CaDiCaL::Internal::inprobing | ( | ) |
Definition at line 20 of file cadical_probe.cpp.
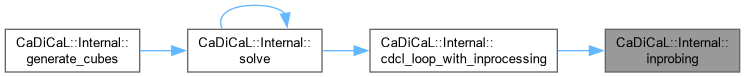
|
inline |
Definition at line 68 of file cadical_instantiate.cpp.

| bool CaDiCaL::Internal::inst_propagate | ( | ) |
Definition at line 82 of file cadical_instantiate.cpp.
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::instantiate | ( | Instantiator & | instantiator | ) |
Definition at line 316 of file cadical_instantiate.cpp.
Definition at line 179 of file cadical_instantiate.cpp.
|
inline |
|
inline |
Definition at line 105 of file cadical_condition.cpp.

Definition at line 600 of file cadical_probe.cpp.
Definition at line 47 of file cadical_block.cpp.
Definition at line 600 of file cadical_gates.cpp.
|
inline |
| bool CaDiCaL::Internal::is_decision | ( | int | ilit | ) |
Definition at line 196 of file cadical_external_propagate.cpp.
| bool CaDiCaL::Internal::is_external_forgettable | ( | int64_t | id | ) |
Definition at line 1058 of file cadical_external_propagate.cpp.
|
inline |
Definition at line 130 of file cadical_condition.cpp.

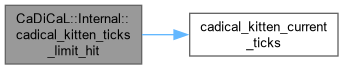
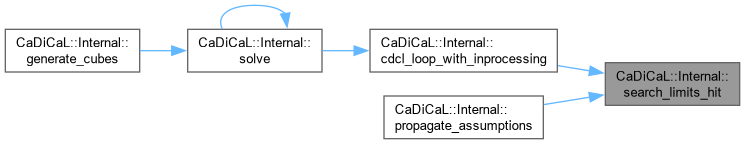
Definition at line 93 of file cadical_limit.cpp.

| void CaDiCaL::Internal::iterate | ( | ) |
Definition at line 1278 of file cadical_analyze.cpp.
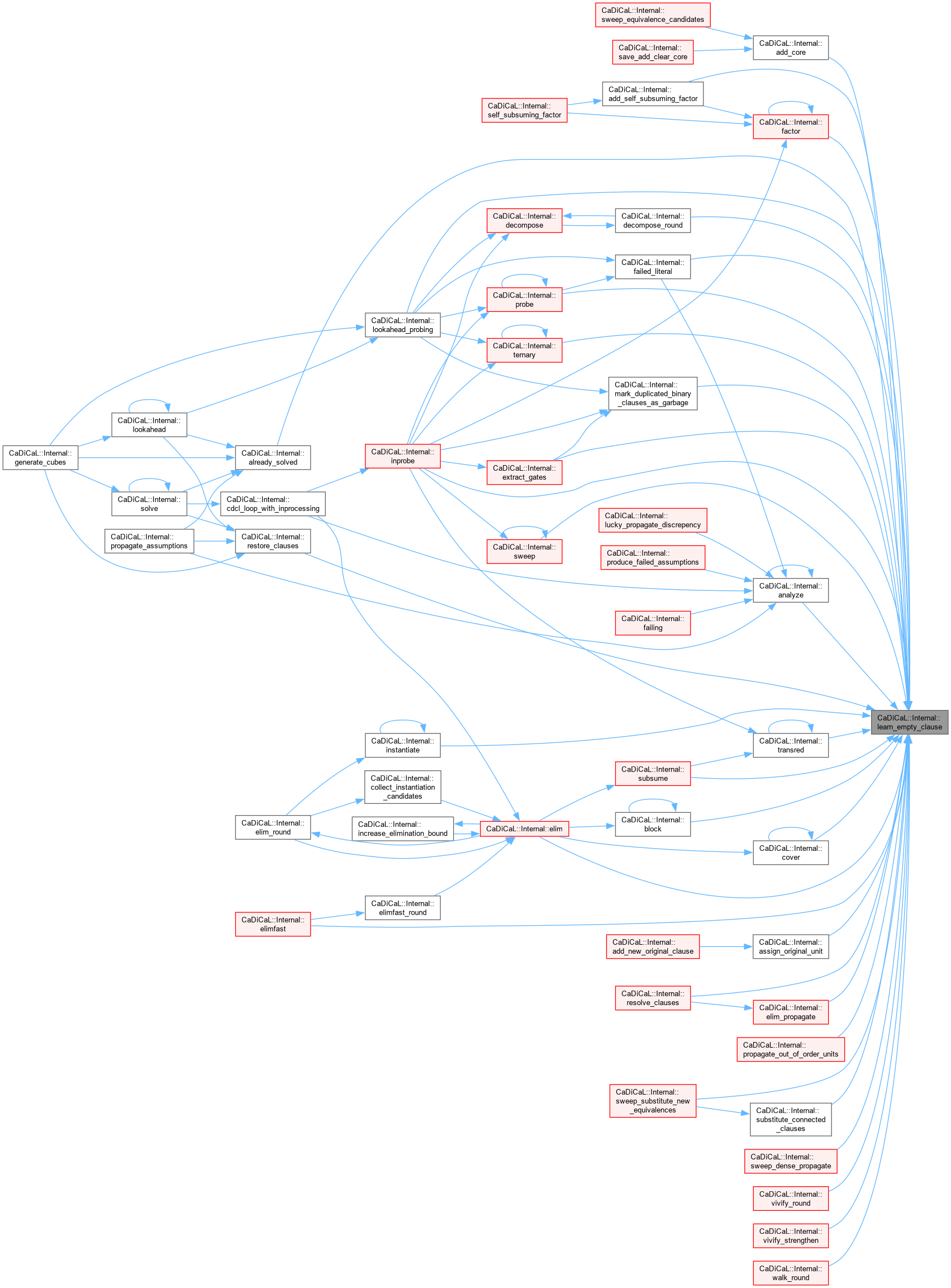
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::learn_empty_clause | ( | ) |
Definition at line 19 of file cadical_analyze.cpp.

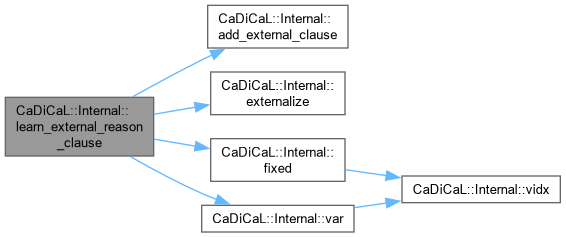
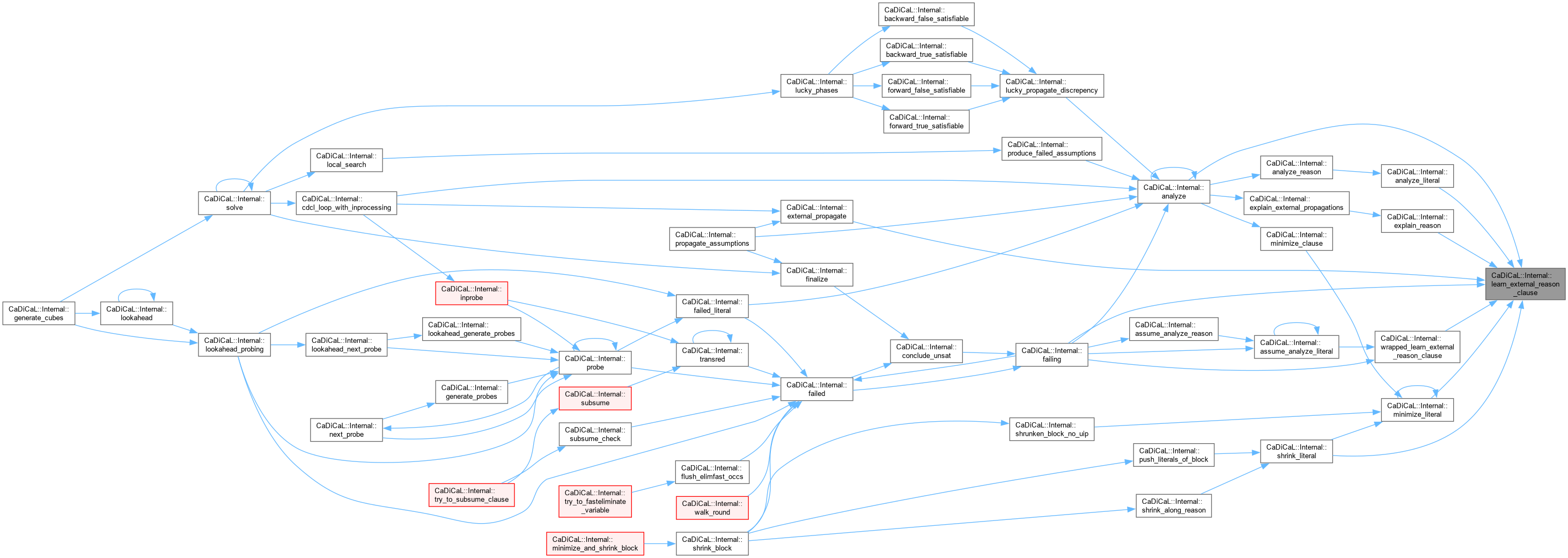
| Clause * CaDiCaL::Internal::learn_external_reason_clause | ( | int | lit, |
| int | falsified_elit = 0, | ||
| bool | no_backtrack = false ) |
Definition at line 668 of file cadical_external_propagate.cpp.
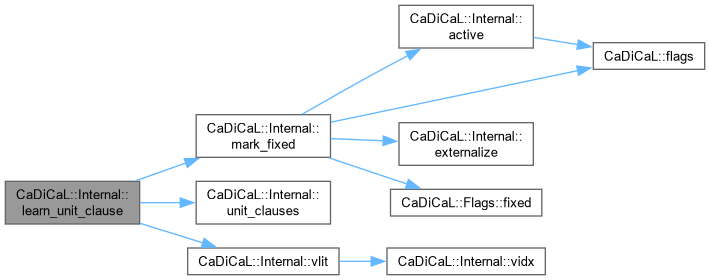
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::learn_unit_clause | ( | int | lit | ) |
Definition at line 35 of file cadical_analyze.cpp.
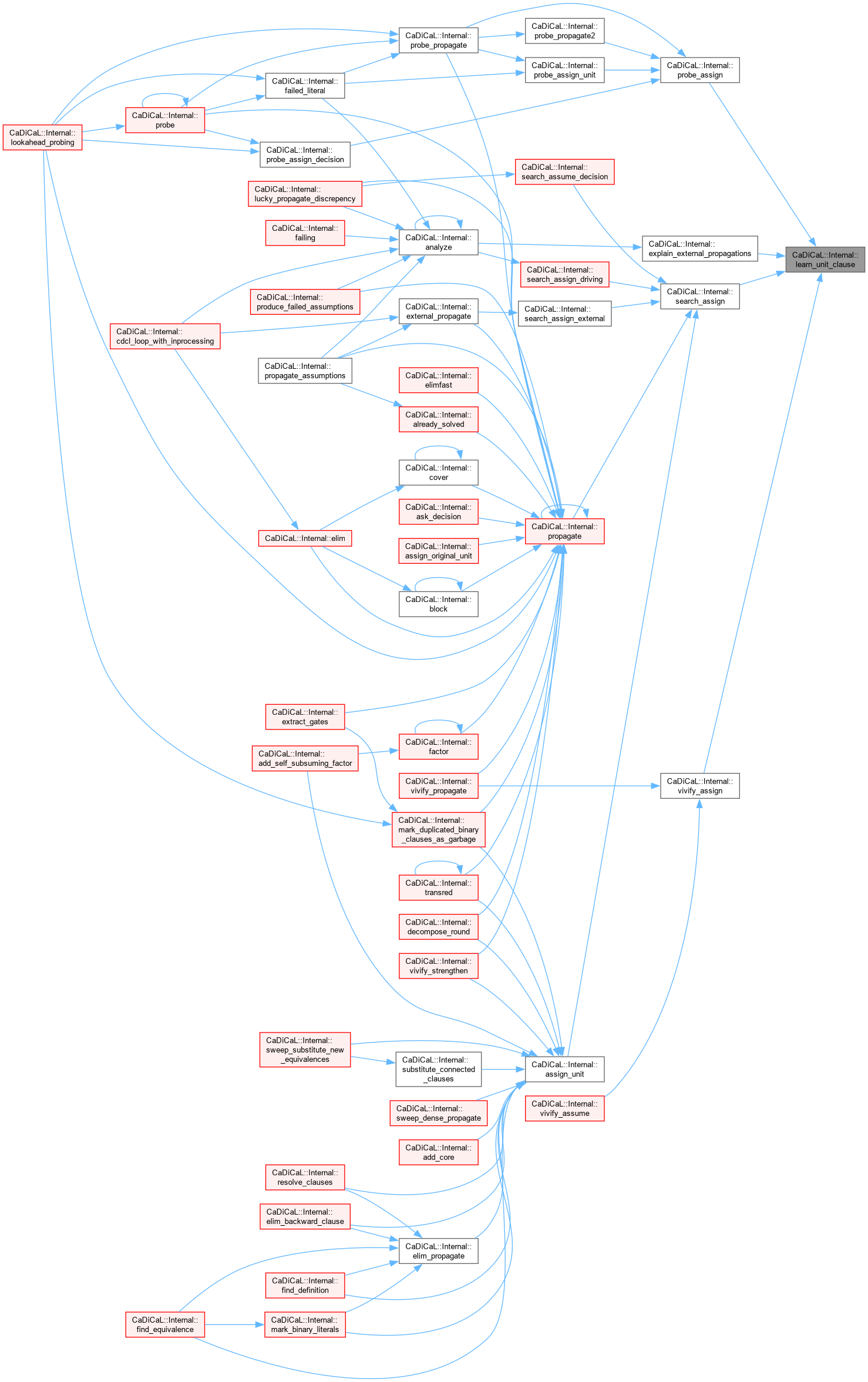
| int CaDiCaL::Internal::likely_phase | ( | int | idx | ) |
Definition at line 89 of file cadical_decide.cpp.
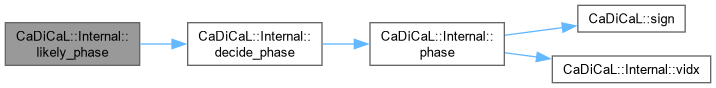
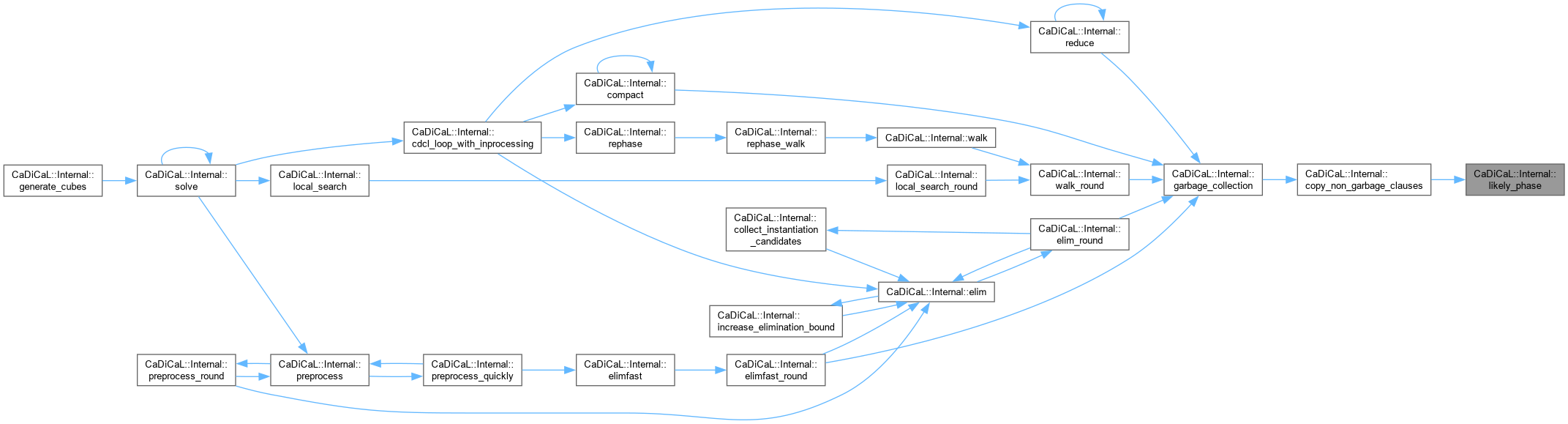
Definition at line 1006 of file internal.hpp.
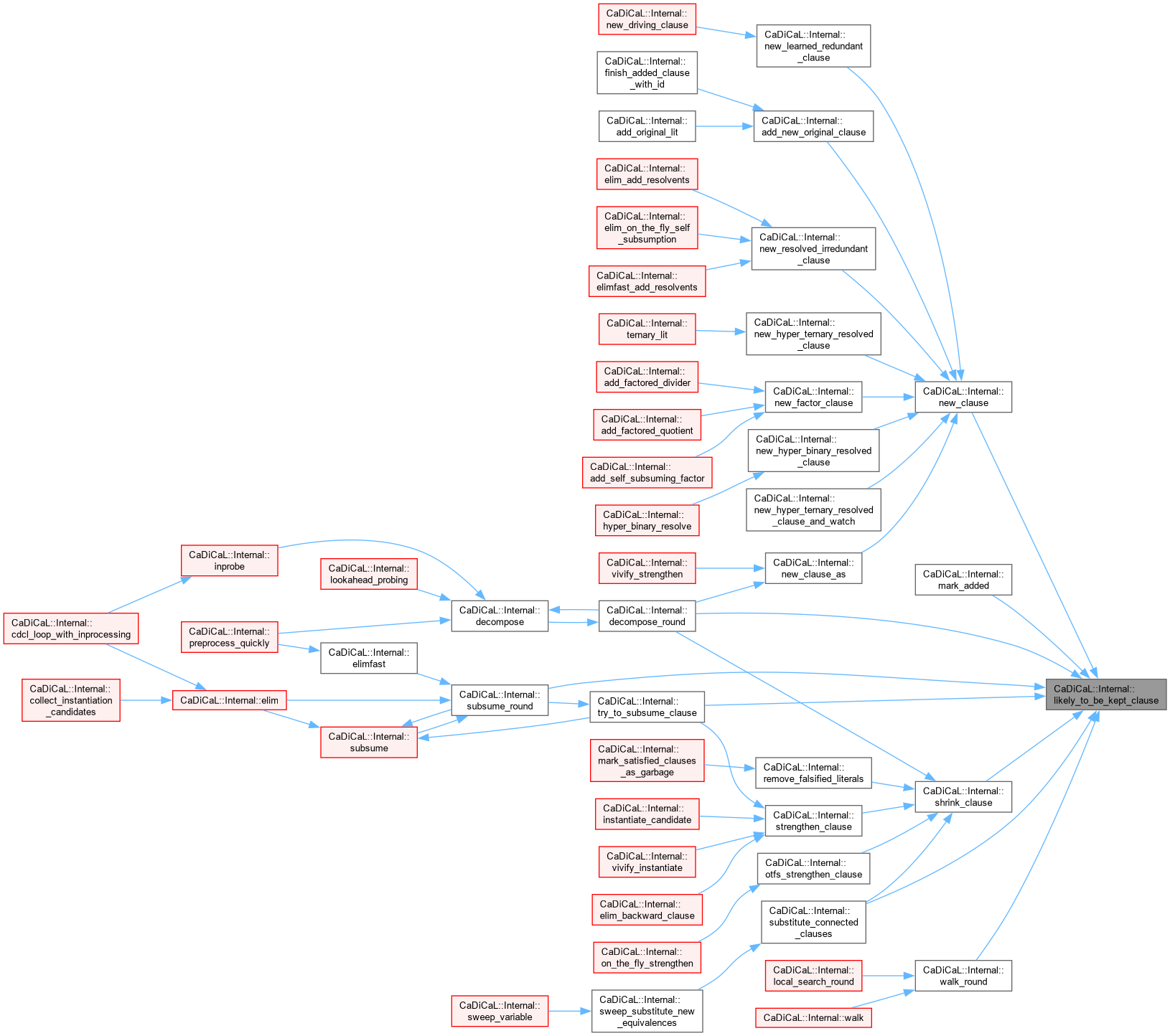
Definition at line 107 of file cadical_limit.cpp.
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::limit_conflicts | ( | int | l | ) |
Definition at line 45 of file cadical_limit.cpp.
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::limit_decisions | ( | int | l | ) |
Definition at line 57 of file cadical_limit.cpp.
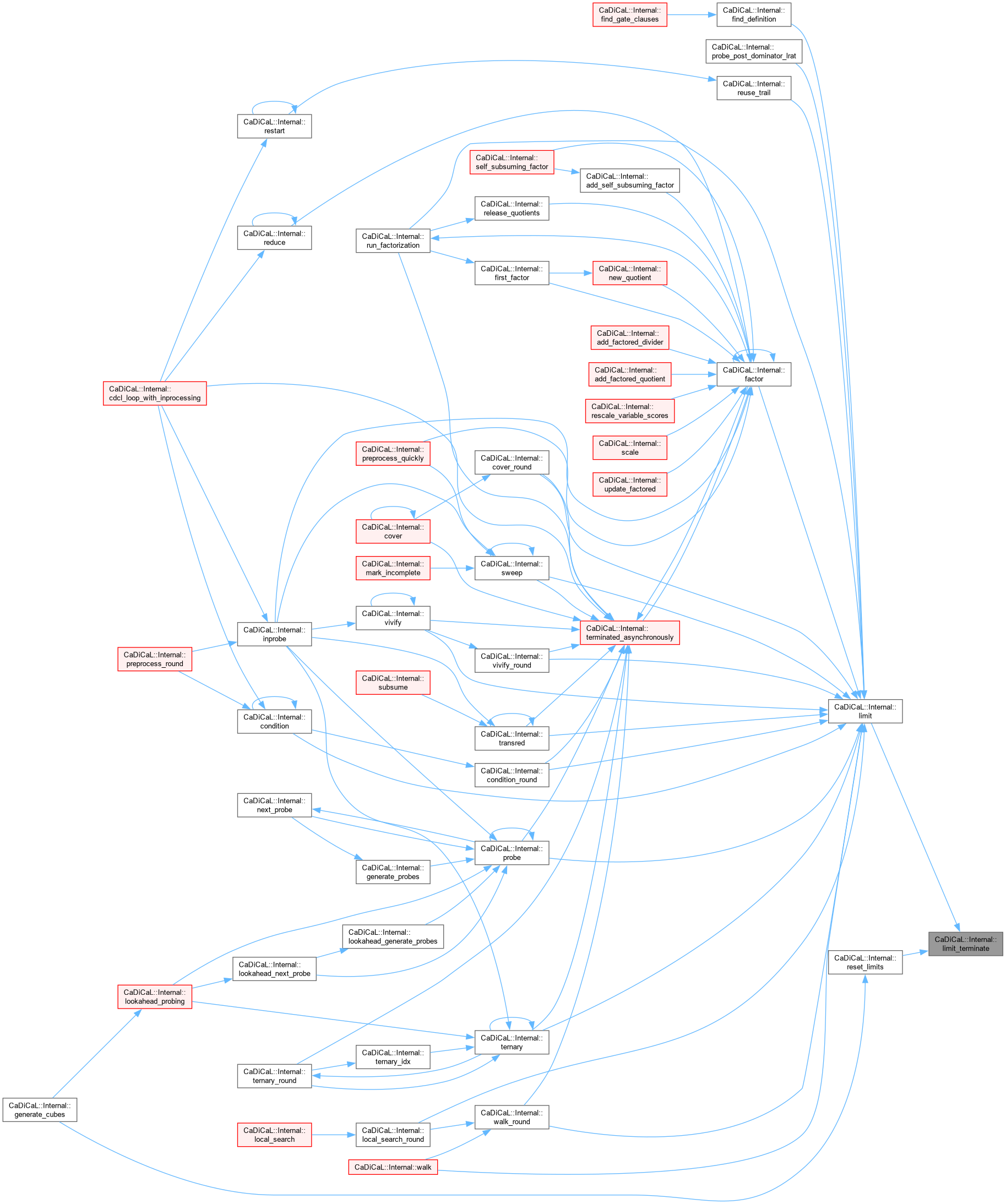
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::limit_local_search | ( | int | l | ) |
Definition at line 81 of file cadical_limit.cpp.
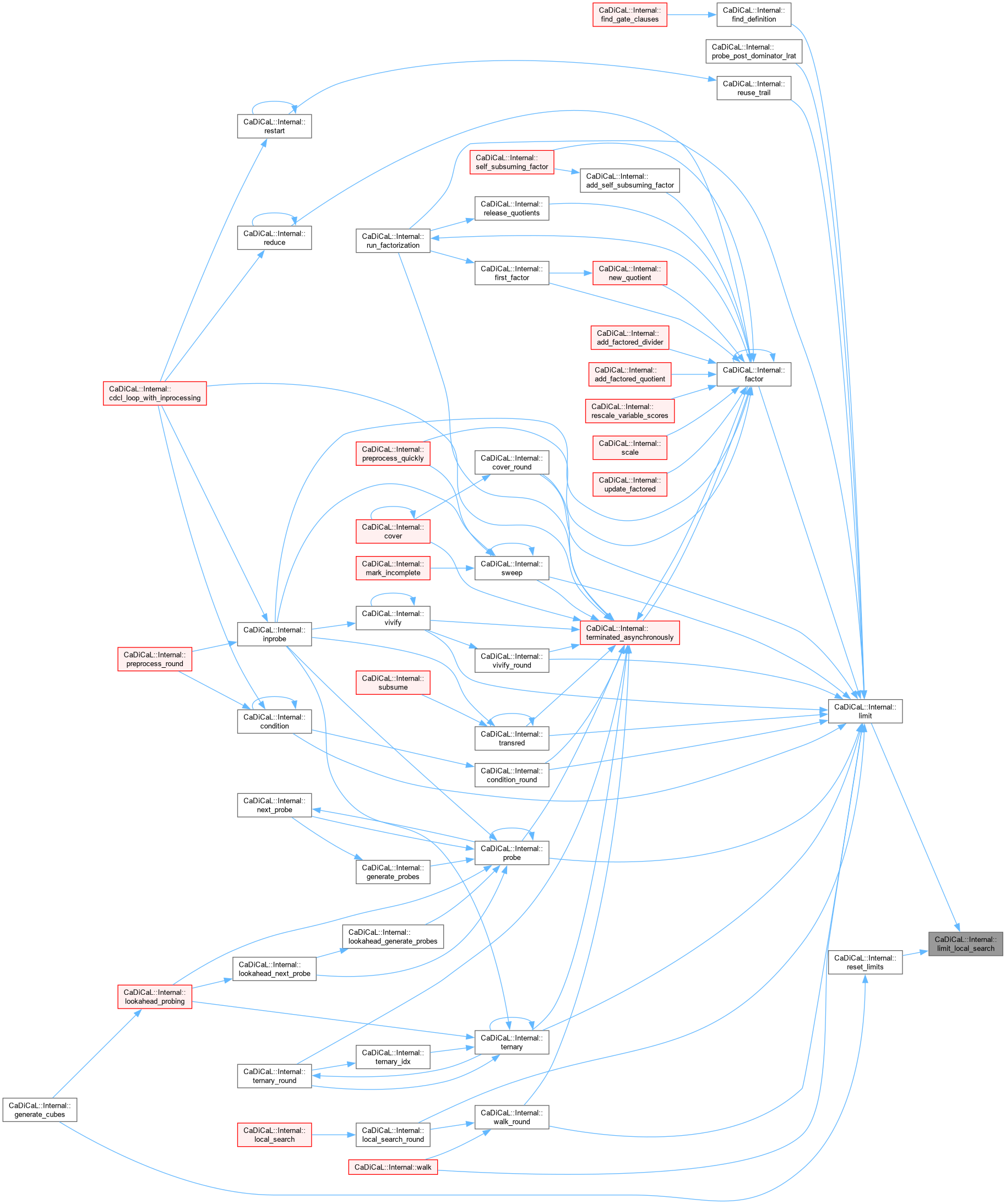
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::limit_preprocessing | ( | int | l | ) |
Definition at line 69 of file cadical_limit.cpp.
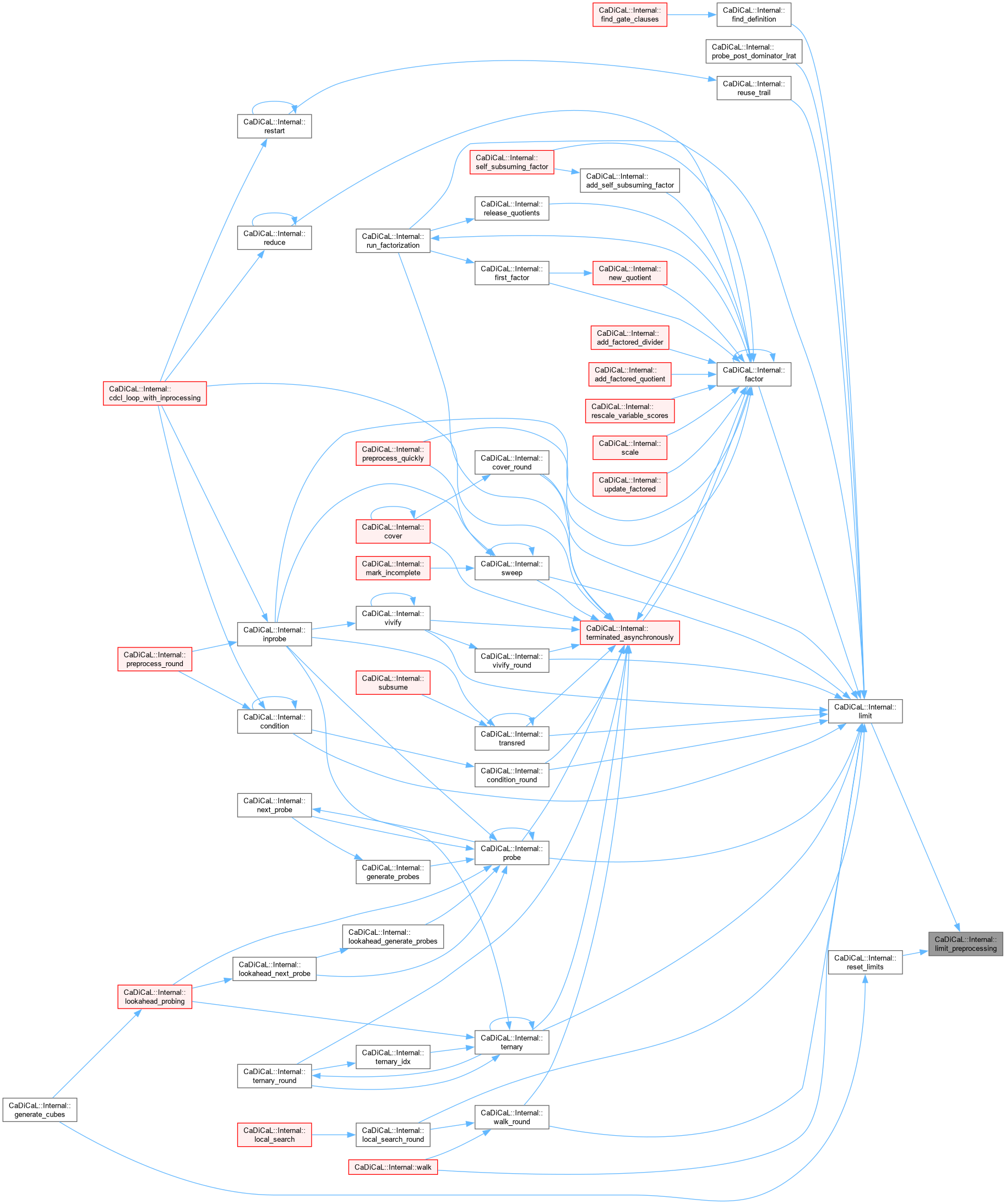
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::limit_terminate | ( | int | l | ) |
Definition at line 33 of file cadical_limit.cpp.
|
inline |
Definition at line 453 of file internal.hpp.

|
inline |
Definition at line 429 of file internal.hpp.
| int CaDiCaL::Internal::local_search | ( | ) |
Definition at line 850 of file cadical_internal.cpp.

| int CaDiCaL::Internal::local_search_round | ( | int | round | ) |
Definition at line 817 of file cadical_internal.cpp.
| int CaDiCaL::Internal::lookahead | ( | ) |
Definition at line 1004 of file cadical_internal.cpp.
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::lookahead_flush_probes | ( | ) |
Definition at line 98 of file cadical_lookahead.cpp.
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::lookahead_generate_probes | ( | ) |
Definition at line 145 of file cadical_lookahead.cpp.

| int CaDiCaL::Internal::lookahead_locc | ( | const std::vector< int > & | loccs | ) |
| int CaDiCaL::Internal::lookahead_next_probe | ( | ) |
Definition at line 215 of file cadical_lookahead.cpp.
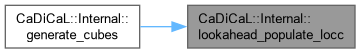
| std::vector< int > CaDiCaL::Internal::lookahead_populate_locc | ( | ) |
Definition at line 21 of file cadical_lookahead.cpp.

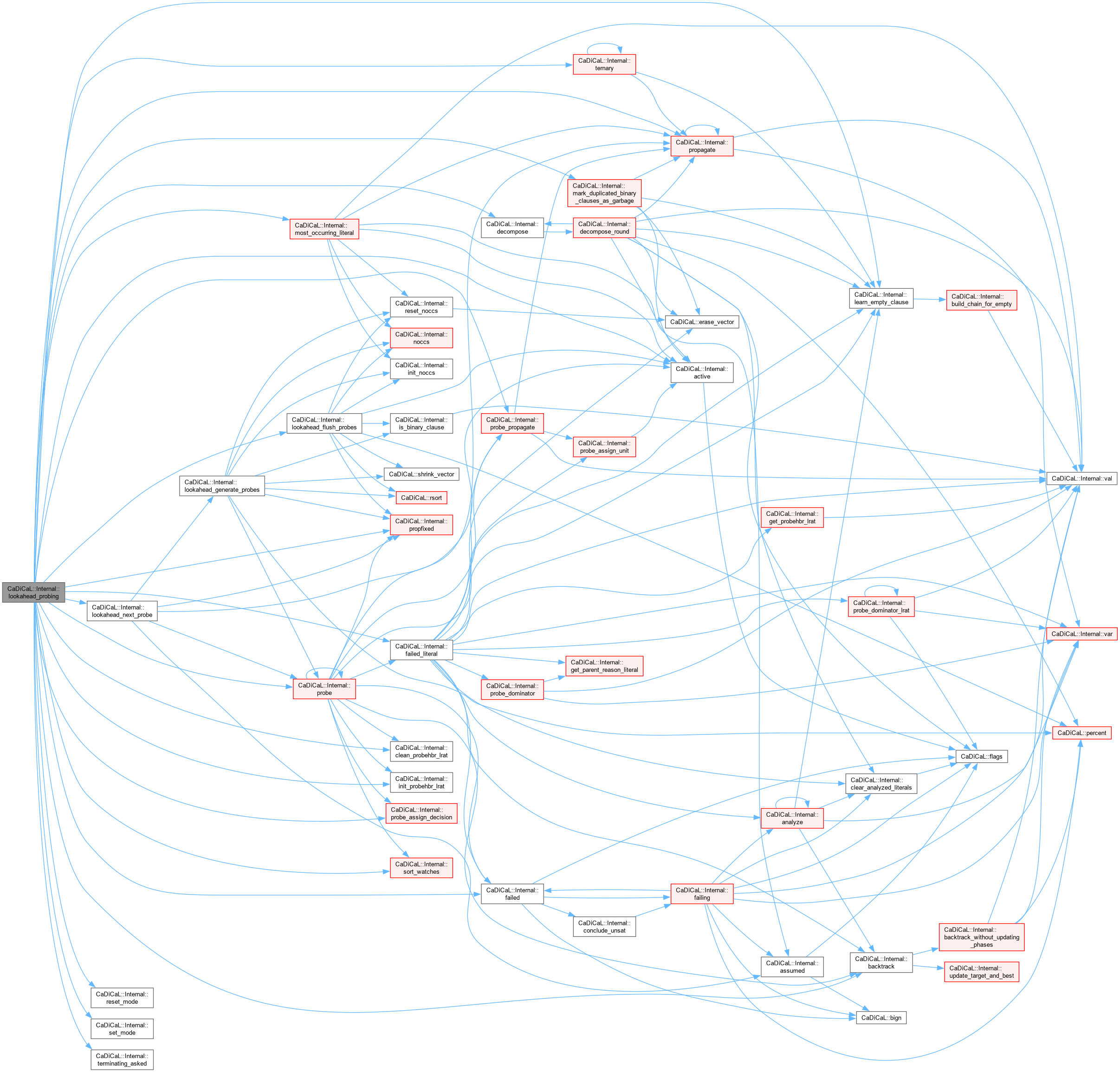
| int CaDiCaL::Internal::lookahead_probing | ( | ) |
Definition at line 290 of file cadical_lookahead.cpp.

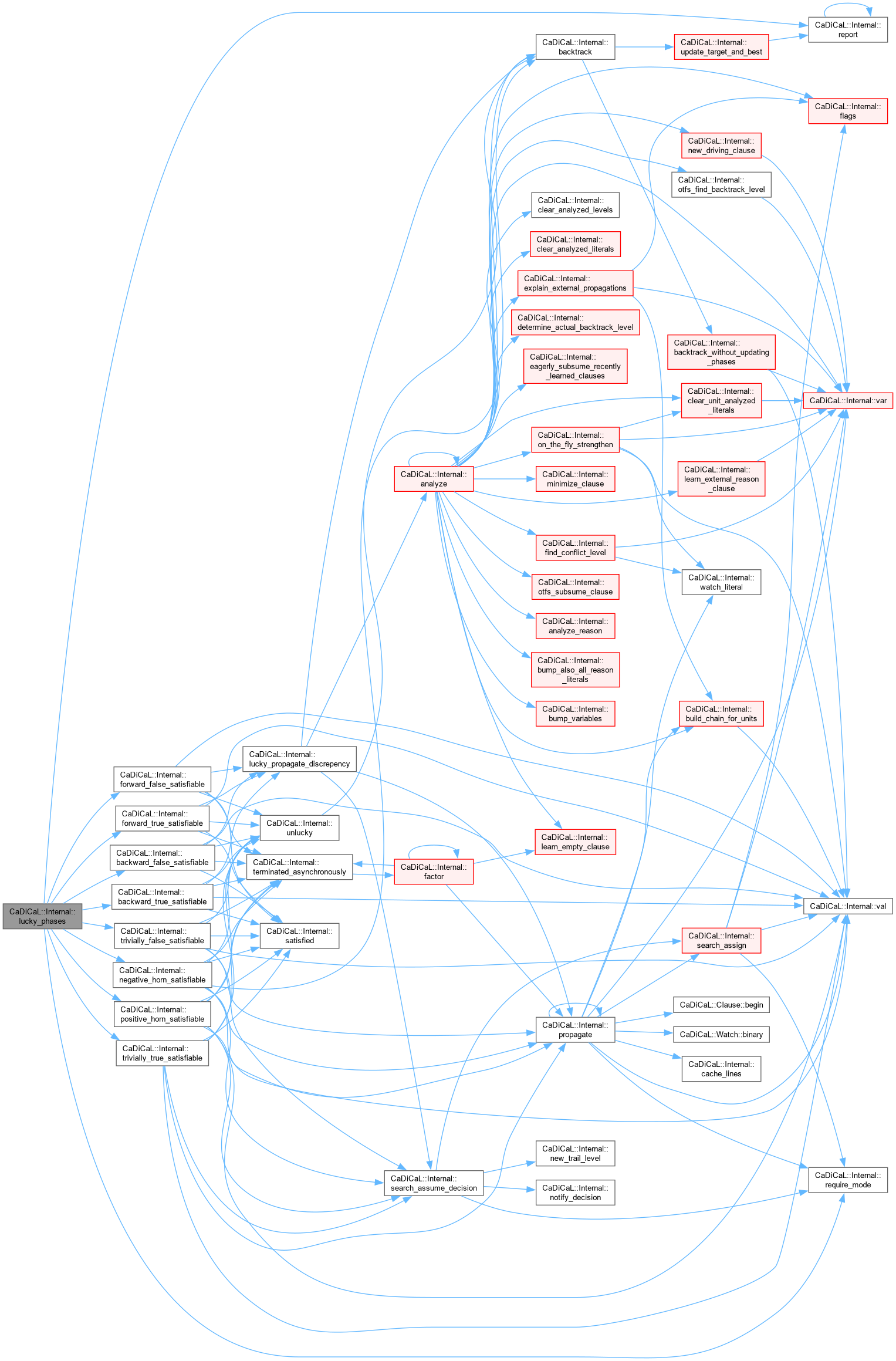
| int CaDiCaL::Internal::lucky_phases | ( | ) |
Definition at line 386 of file cadical_lucky.cpp.

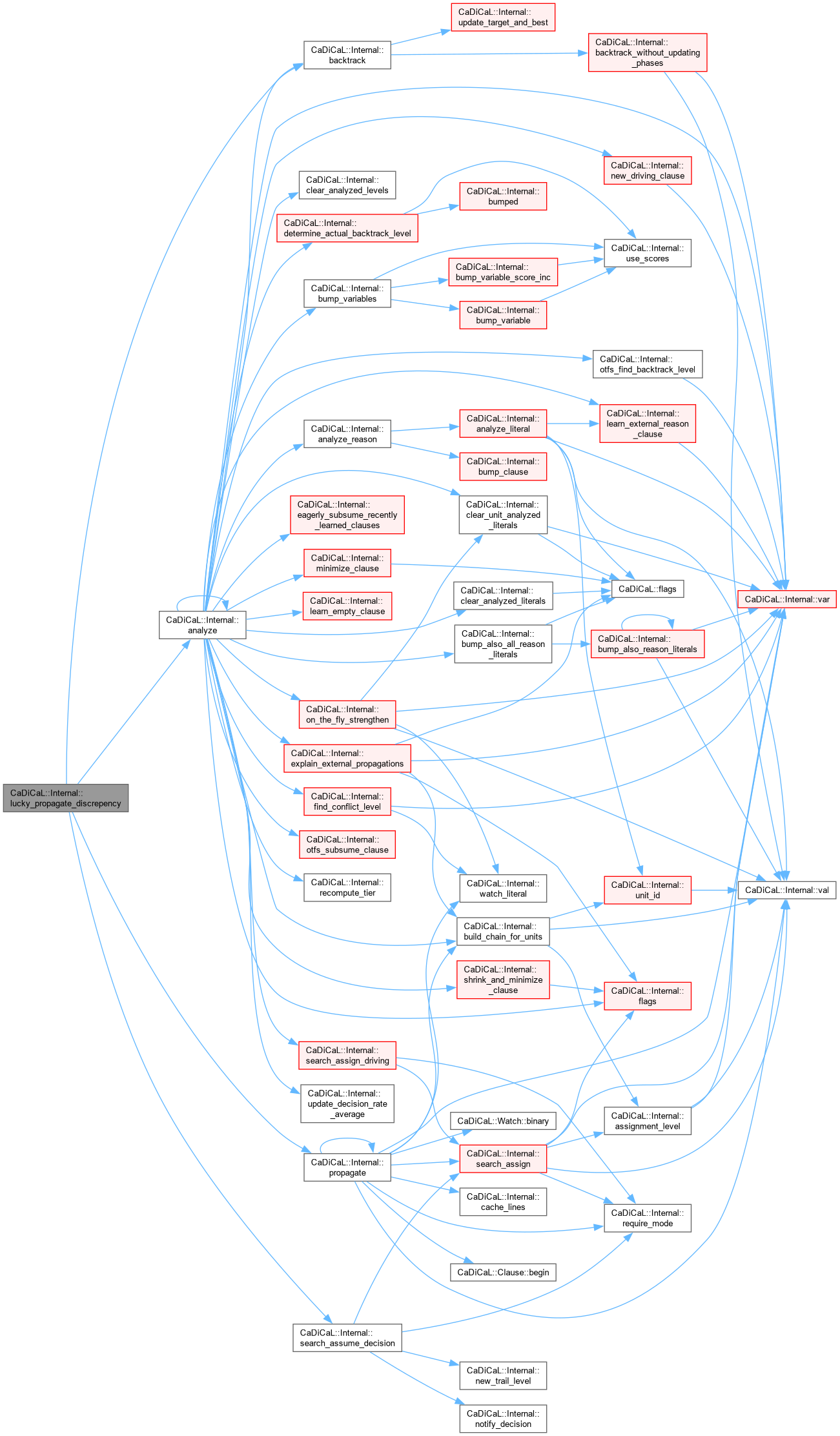
|
inline |
Definition at line 129 of file cadical_lucky.cpp.
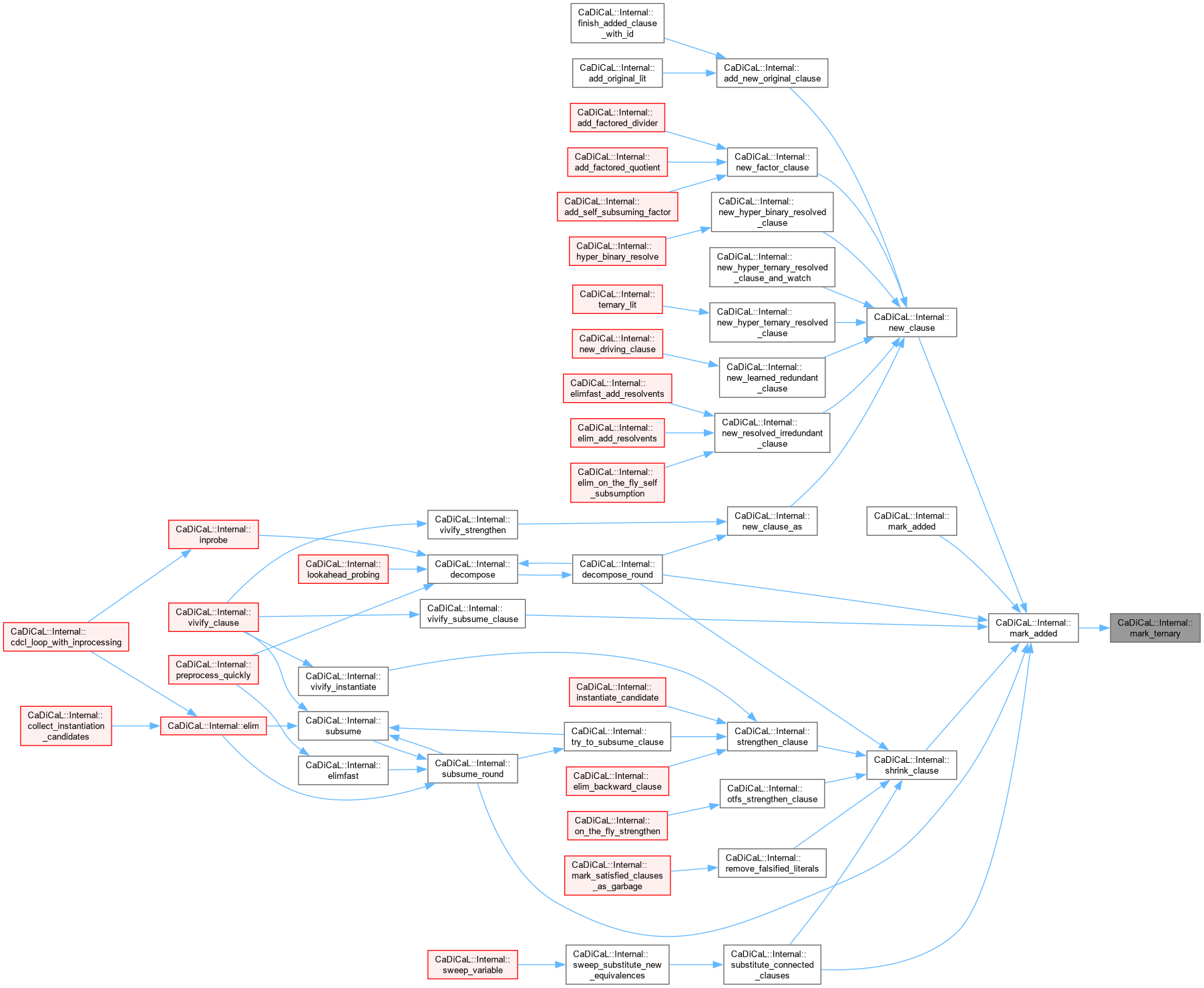
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::mark | ( | Clause * | c | ) |
Definition at line 13 of file cadical_clause.cpp.
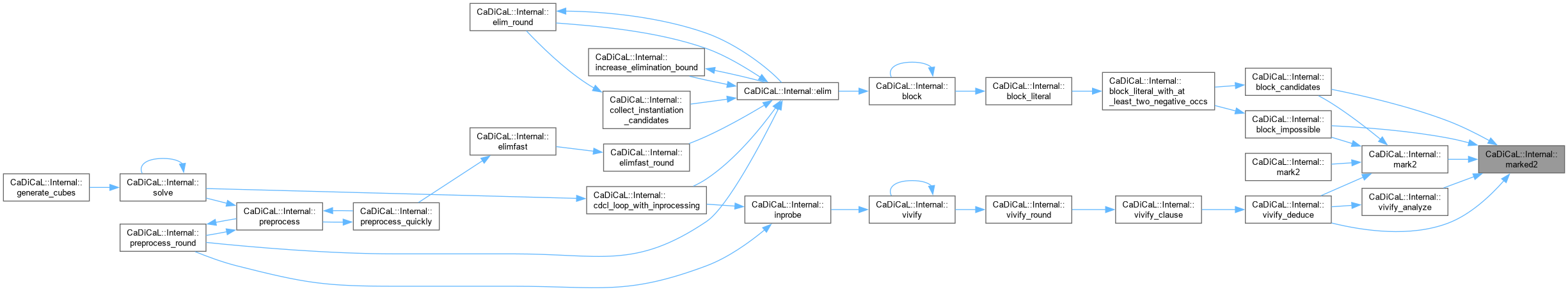
|
inline |
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::mark2 | ( | Clause * | c | ) |
|
inline |
Definition at line 561 of file internal.hpp.

|
inline |
Definition at line 504 of file internal.hpp.

| void CaDiCaL::Internal::mark_active | ( | int | lit | ) |
Definition at line 80 of file cadical_flags.cpp.

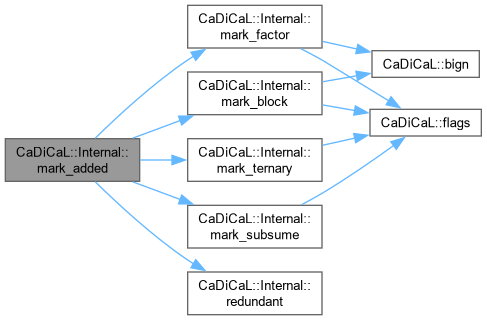
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::mark_added | ( | Clause * | c | ) |
Definition at line 73 of file cadical_clause.cpp.
|
inline |
Definition at line 63 of file cadical_clause.cpp.
|
inline |
Definition at line 109 of file cadical_condition.cpp.
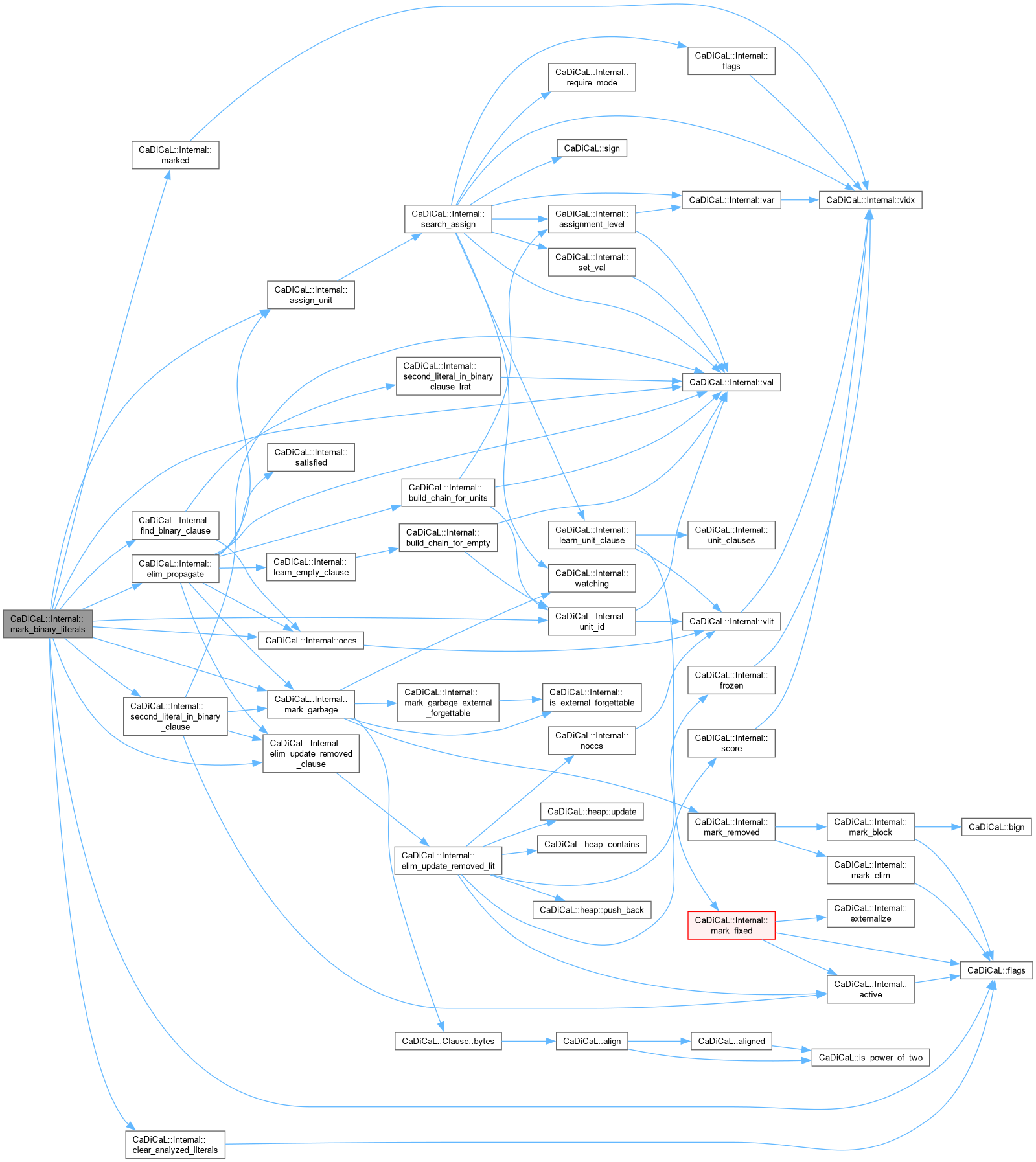
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::mark_binary_literals | ( | Eliminator & | eliminator, |
| int | pivot ) |
Definition at line 113 of file cadical_gates.cpp.
|
inline |
Definition at line 1072 of file internal.hpp.
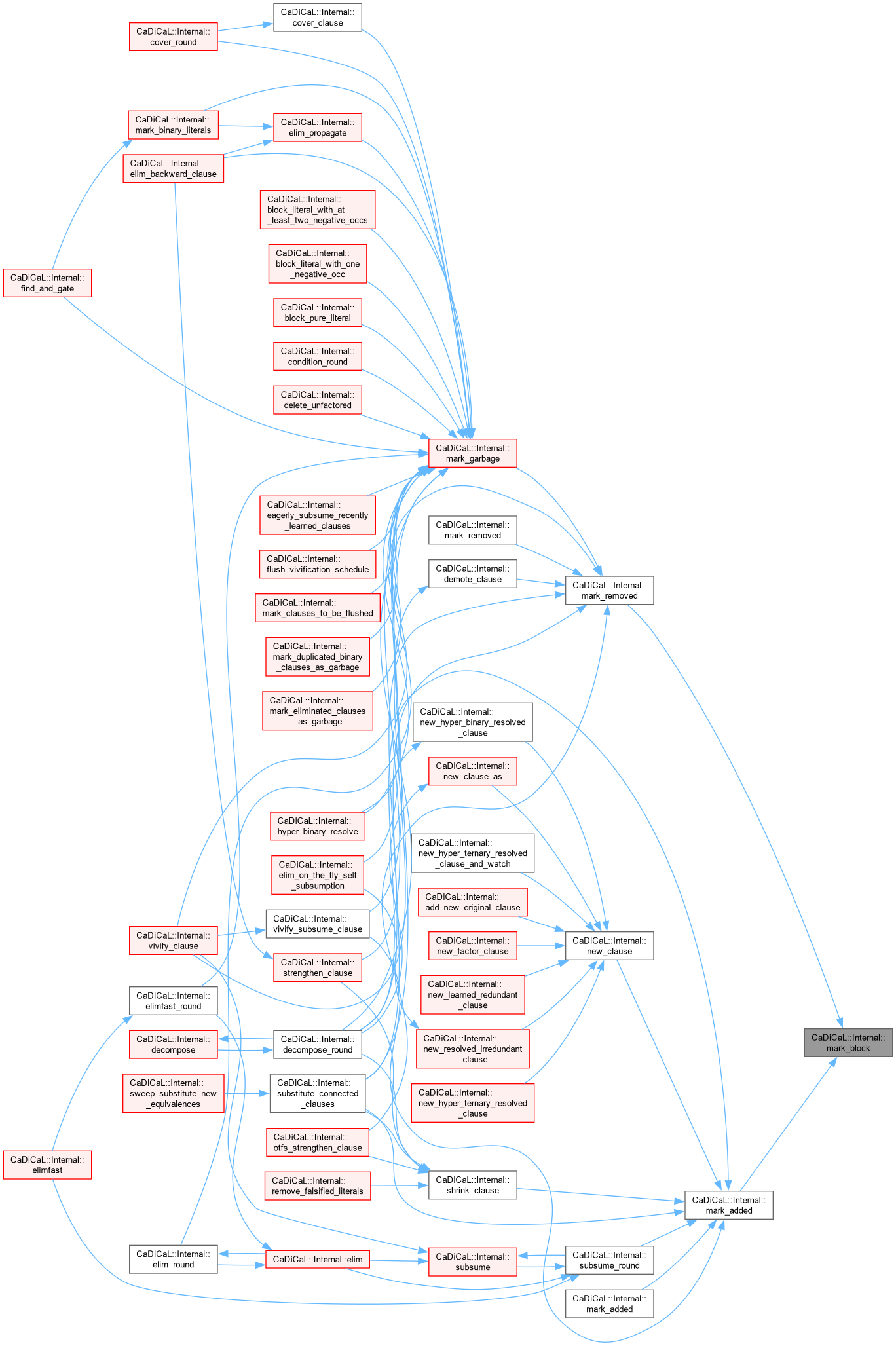
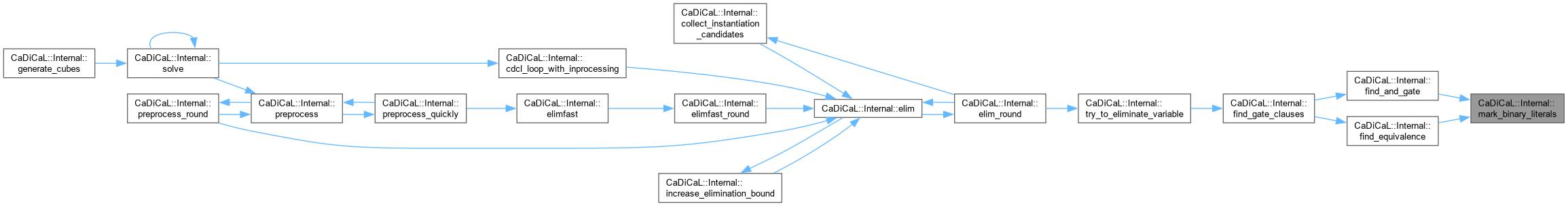
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::mark_clause | ( | ) |
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::mark_clauses_to_be_flushed | ( | ) |
Definition at line 38 of file cadical_reduce.cpp.

|
inline |
Definition at line 1119 of file internal.hpp.
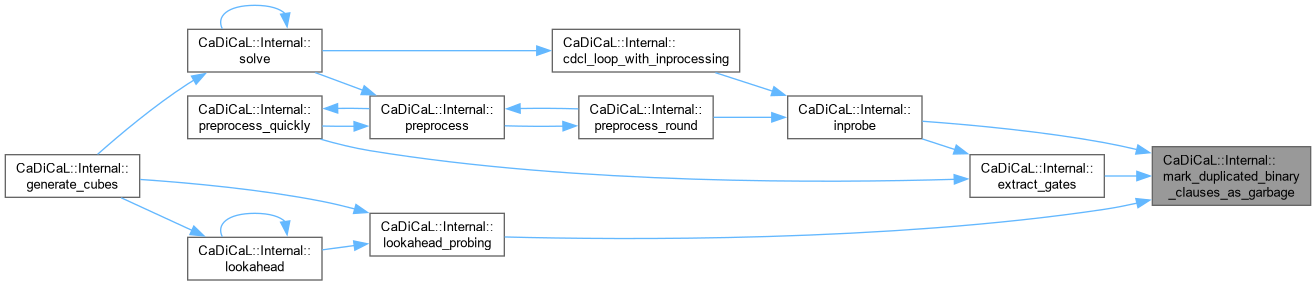
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::mark_duplicated_binary_clauses_as_garbage | ( | ) |
Definition at line 24 of file cadical_deduplicate.cpp.
|
inline |
Definition at line 1064 of file internal.hpp.
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::mark_eliminated | ( | int | lit | ) |
Definition at line 38 of file cadical_flags.cpp.
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::mark_eliminated_clauses_as_garbage | ( | Eliminator & | eliminator, |
| int | pivot, | ||
| bool & | deleted_binary_clause ) |
Definition at line 616 of file cadical_elim.cpp.
|
inline |
Definition at line 1043 of file internal.hpp.
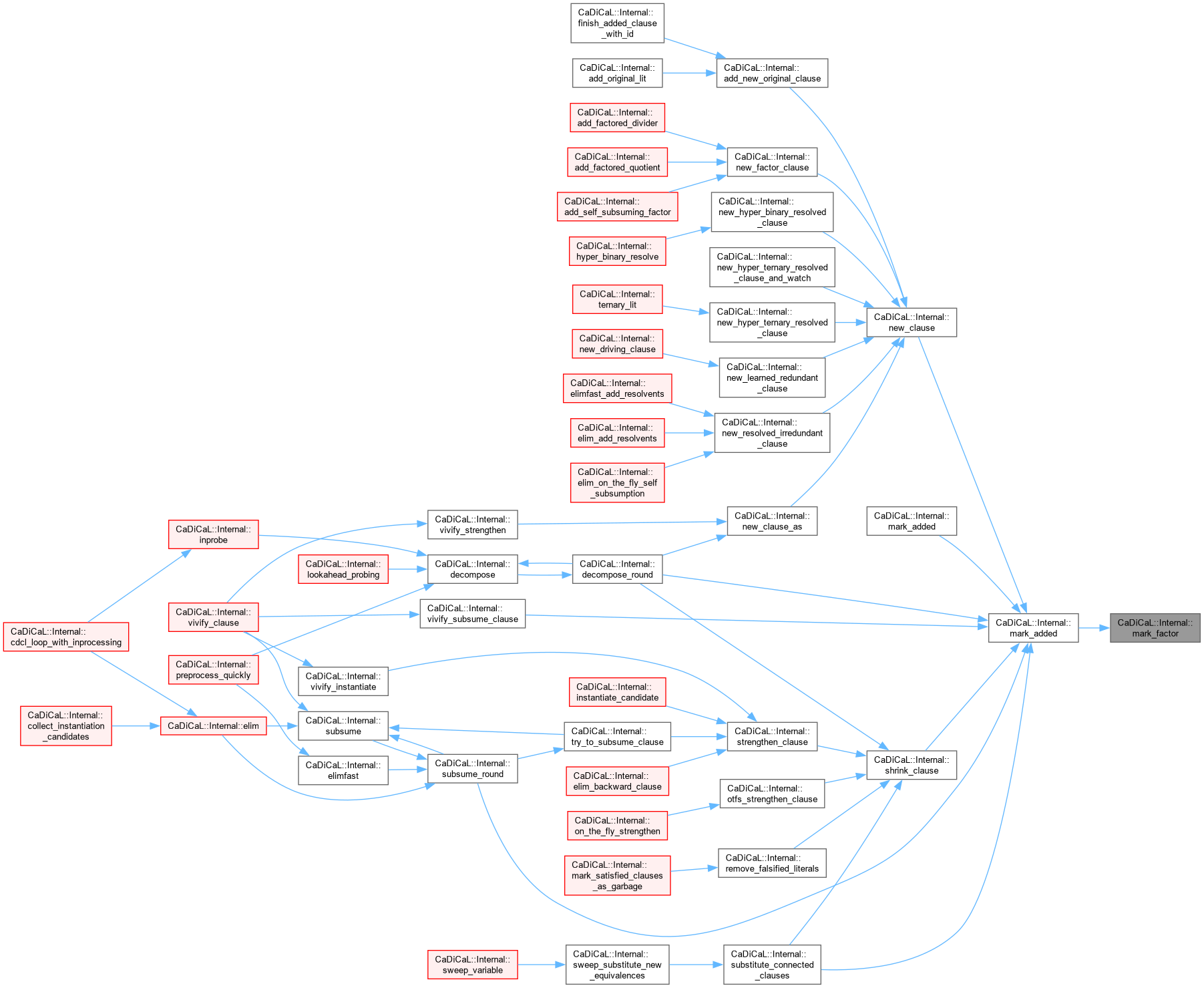
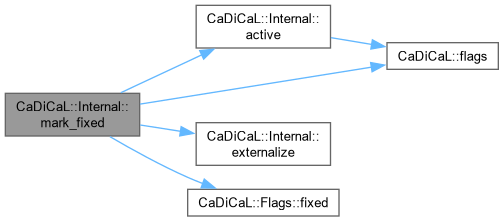
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::mark_fixed | ( | int | lit | ) |
Definition at line 9 of file cadical_flags.cpp.
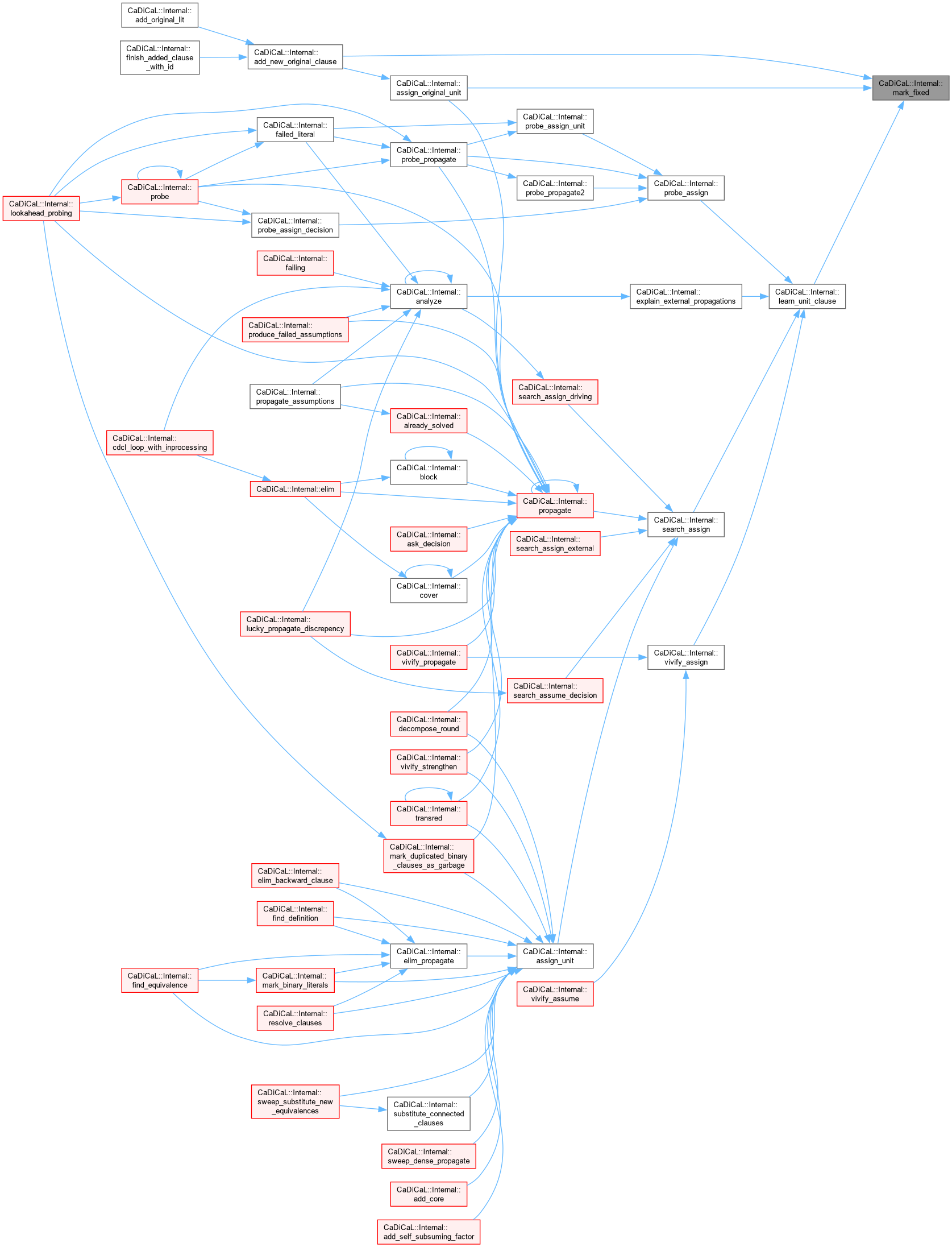
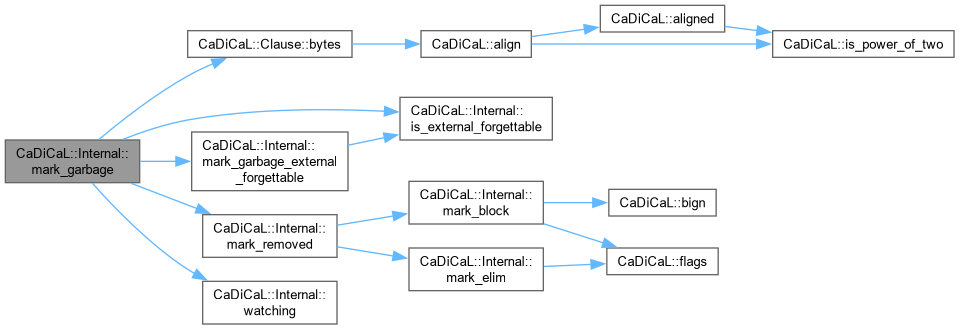
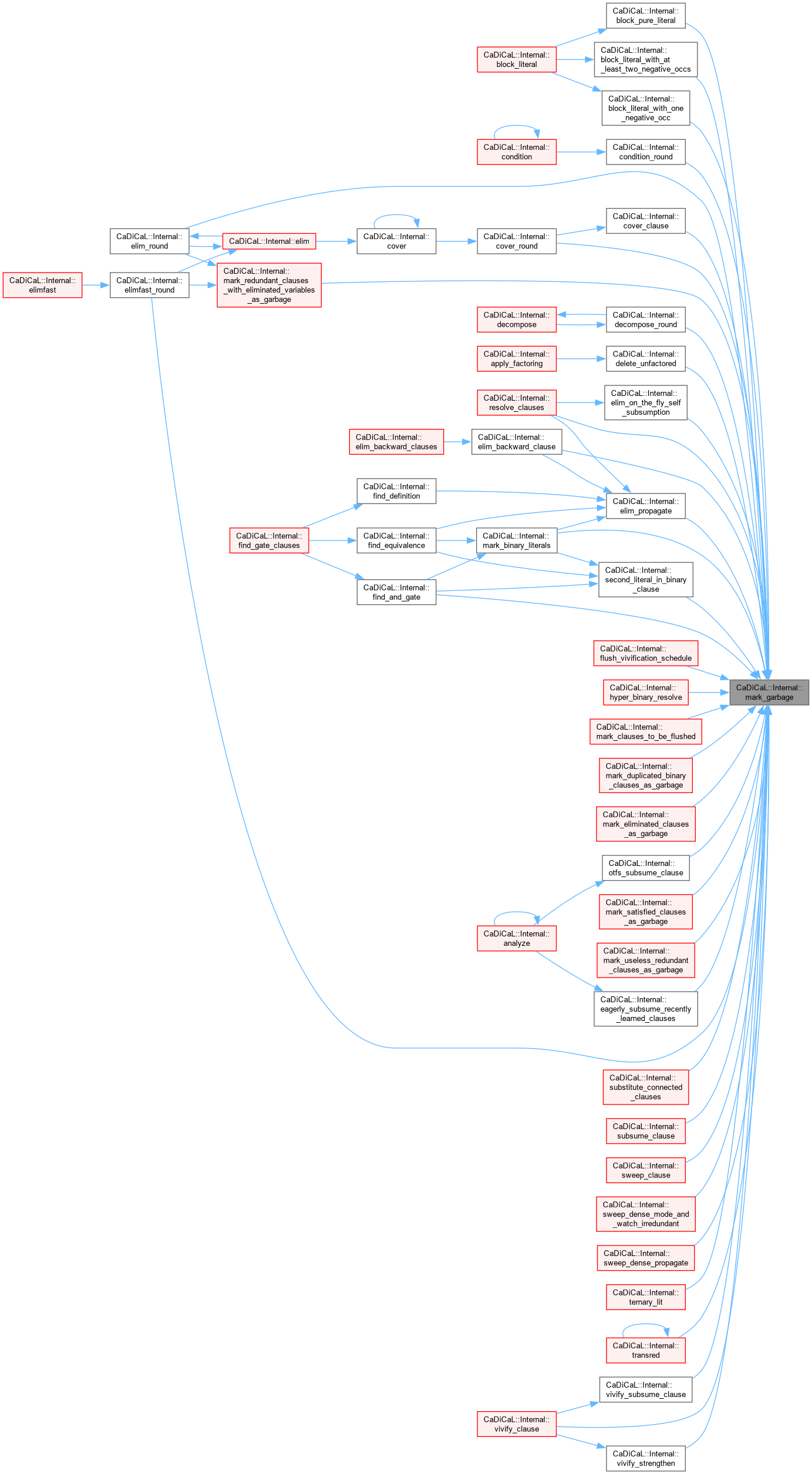
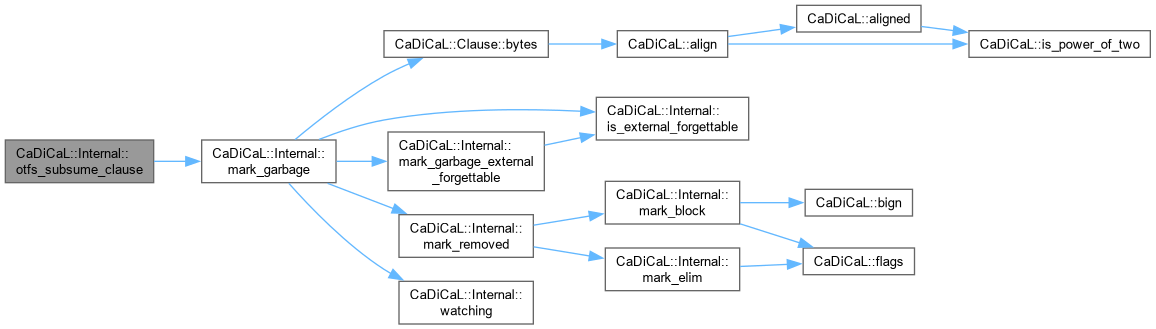
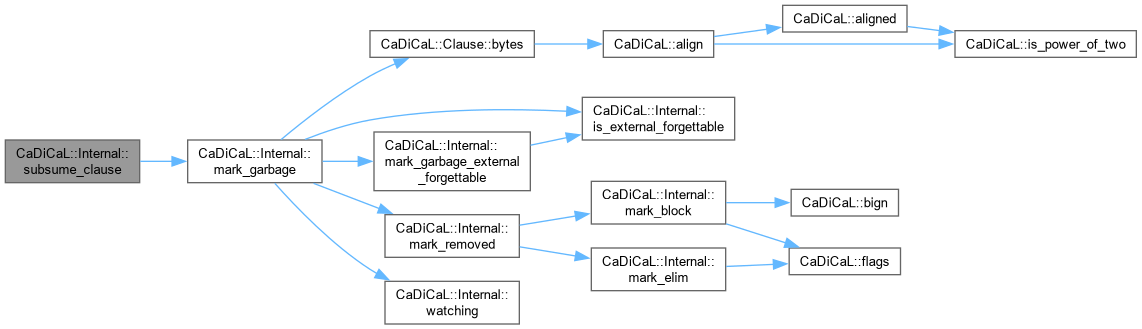
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::mark_garbage | ( | Clause * | c | ) |
Definition at line 301 of file cadical_clause.cpp.
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::mark_garbage_external_forgettable | ( | int64_t | id | ) |
Definition at line 1070 of file cadical_external_propagate.cpp.
|
inline |
Definition at line 134 of file cadical_condition.cpp.
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::mark_incomplete | ( | Sweeper & | sweeper | ) |
Definition at line 1805 of file cadical_sweep.cpp.
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::mark_pure | ( | int | lit | ) |
Definition at line 52 of file cadical_flags.cpp.
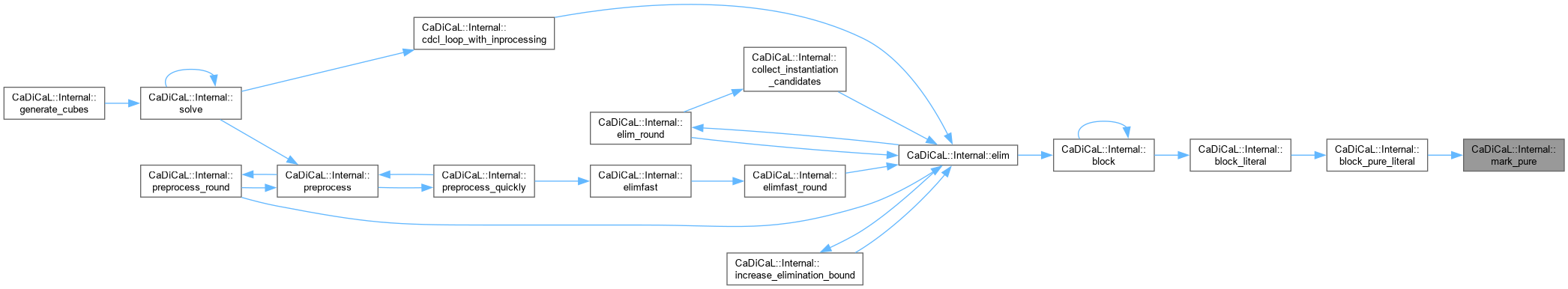
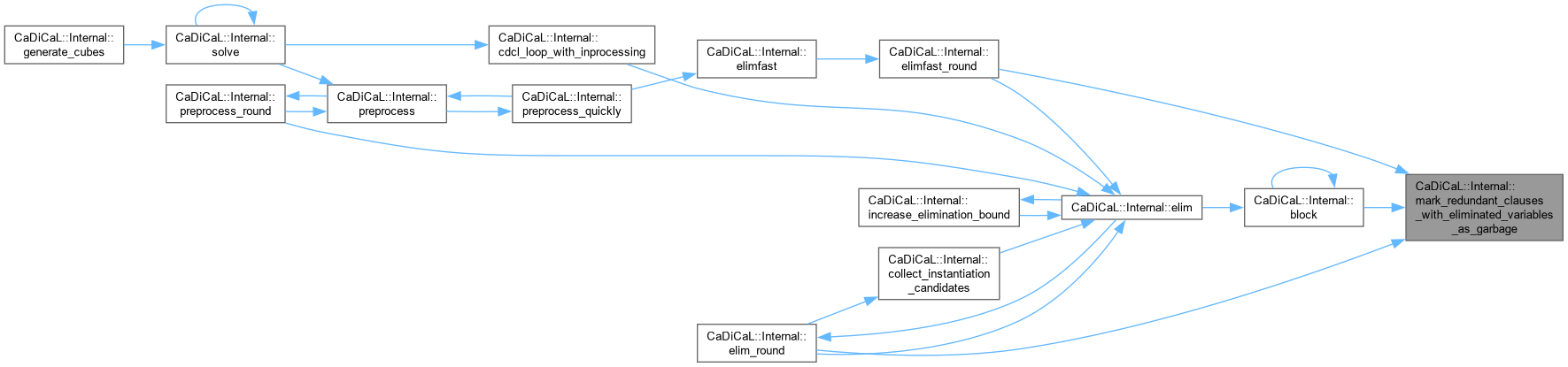
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::mark_redundant_clauses_with_eliminated_variables_as_garbage | ( | ) |
Definition at line 741 of file cadical_elim.cpp.
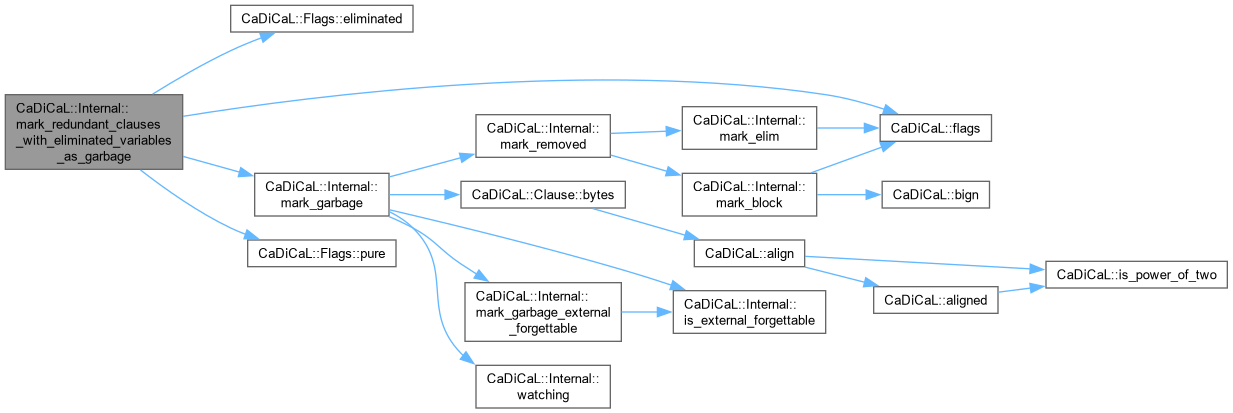
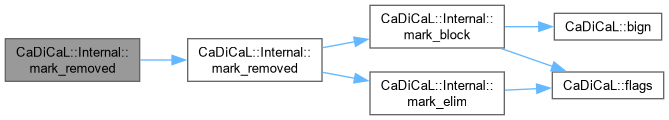
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::mark_removed | ( | Clause * | c, |
| int | except = 0 ) |
Definition at line 46 of file cadical_clause.cpp.
|
inline |
Definition at line 1081 of file internal.hpp.

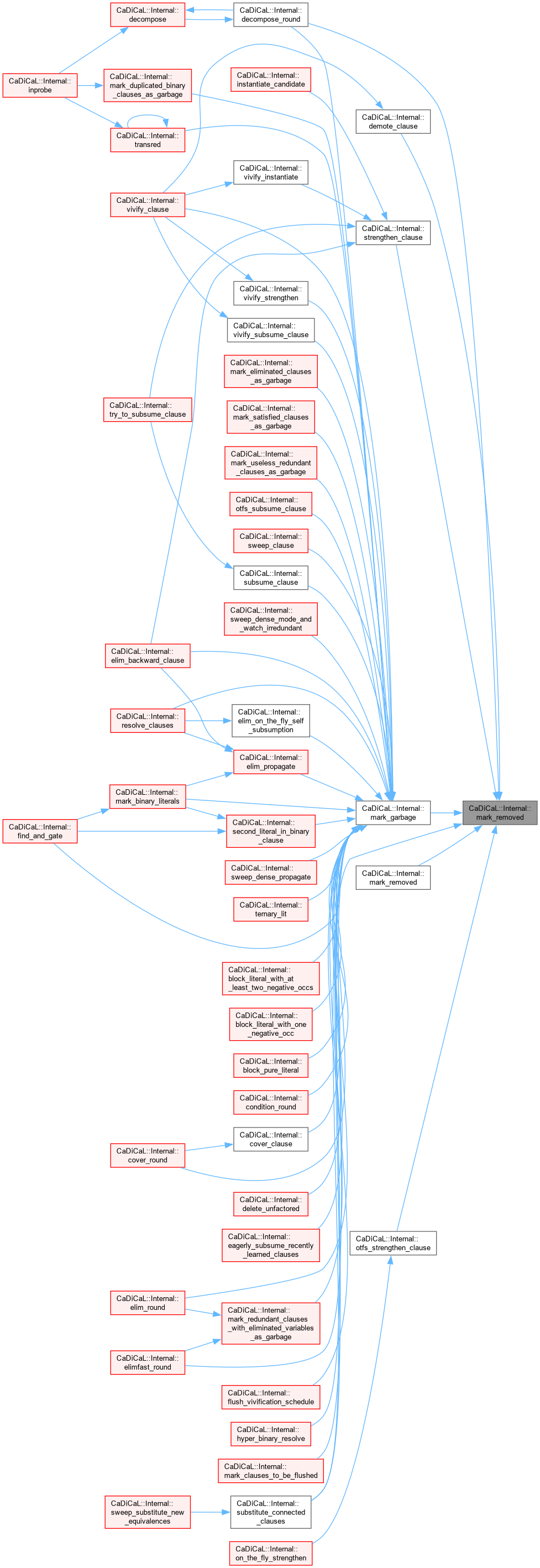
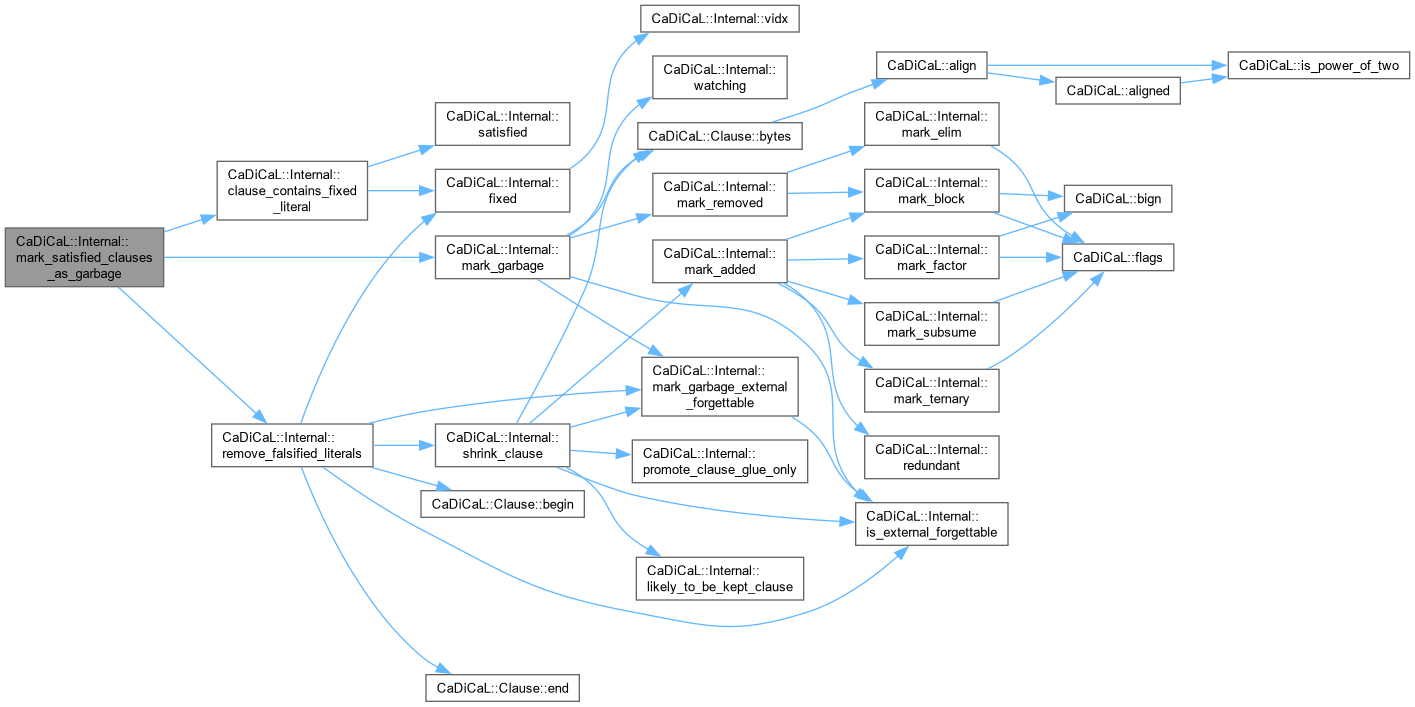
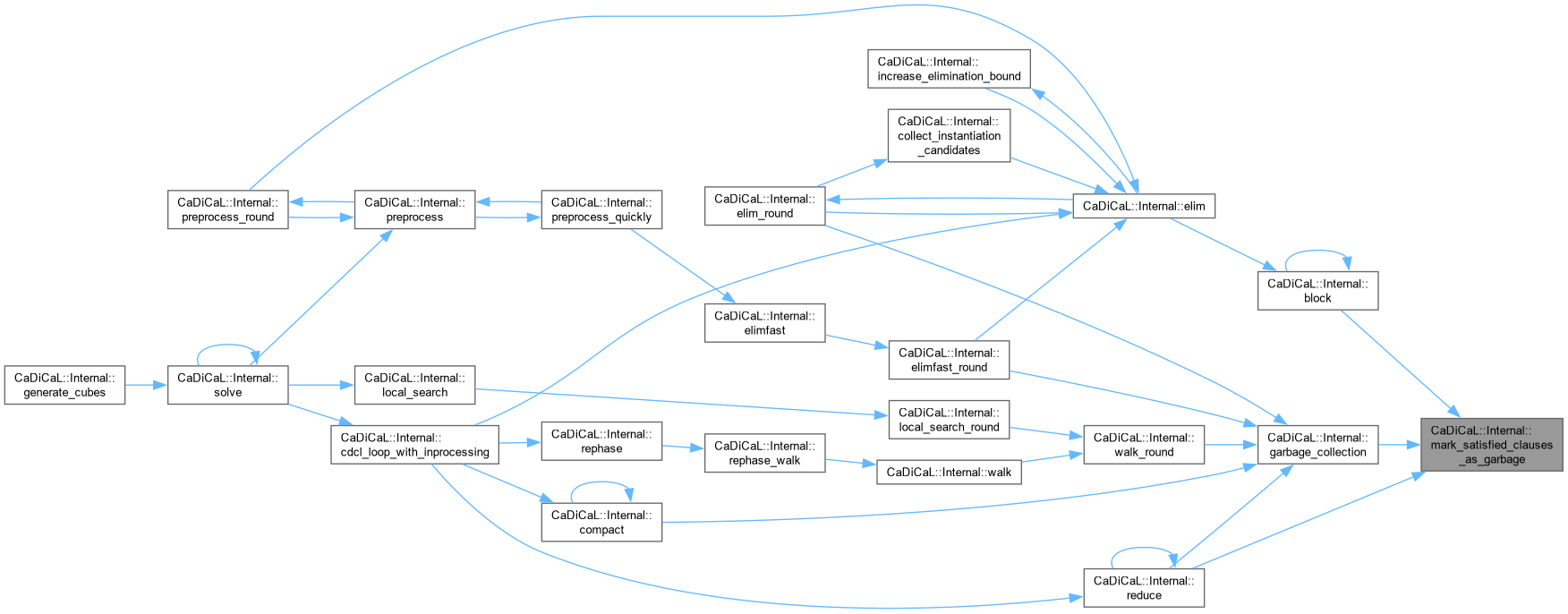
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::mark_satisfied_clauses_as_garbage | ( | ) |
Definition at line 77 of file cadical_collect.cpp.
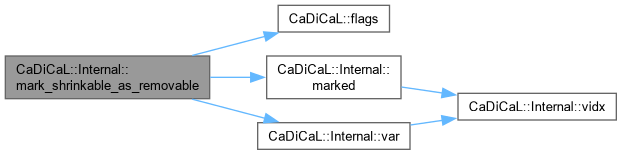
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::mark_shrinkable_as_removable | ( | int | blevel, |
| std::vector< int >::size_type | minimized_start ) |
Definition at line 26 of file cadical_shrink.cpp.
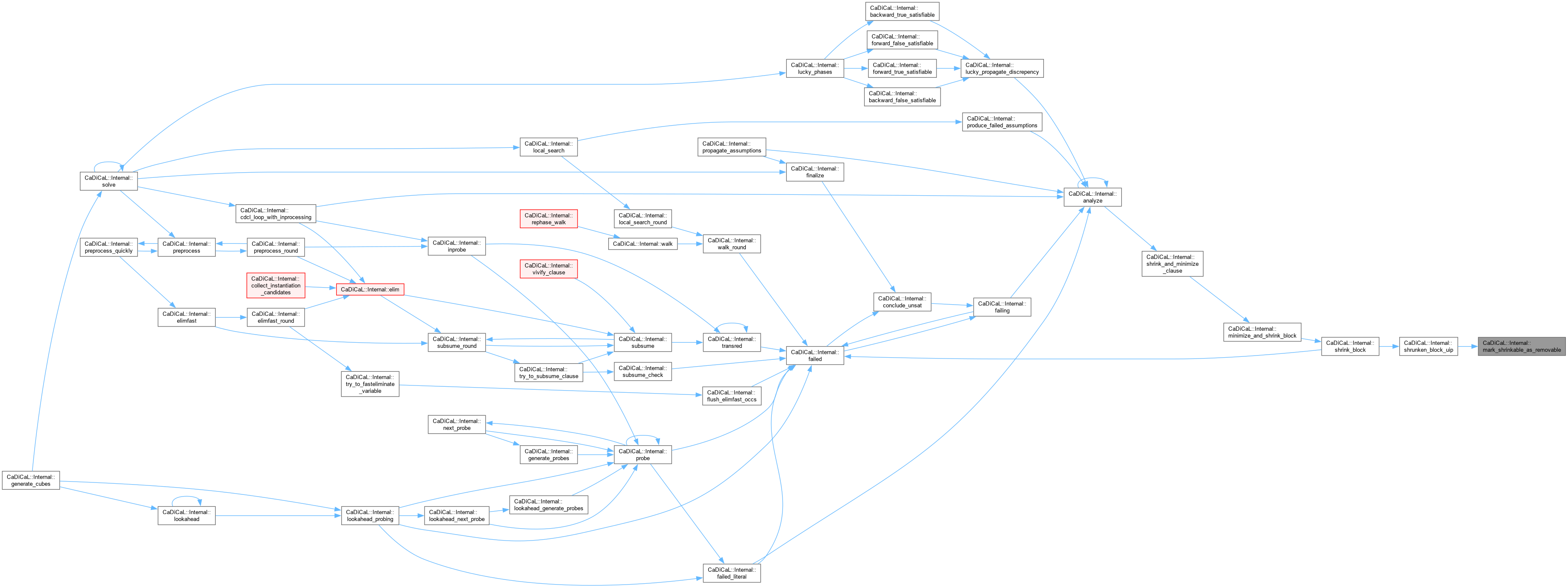
|
inline |
Definition at line 1103 of file internal.hpp.
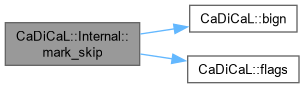
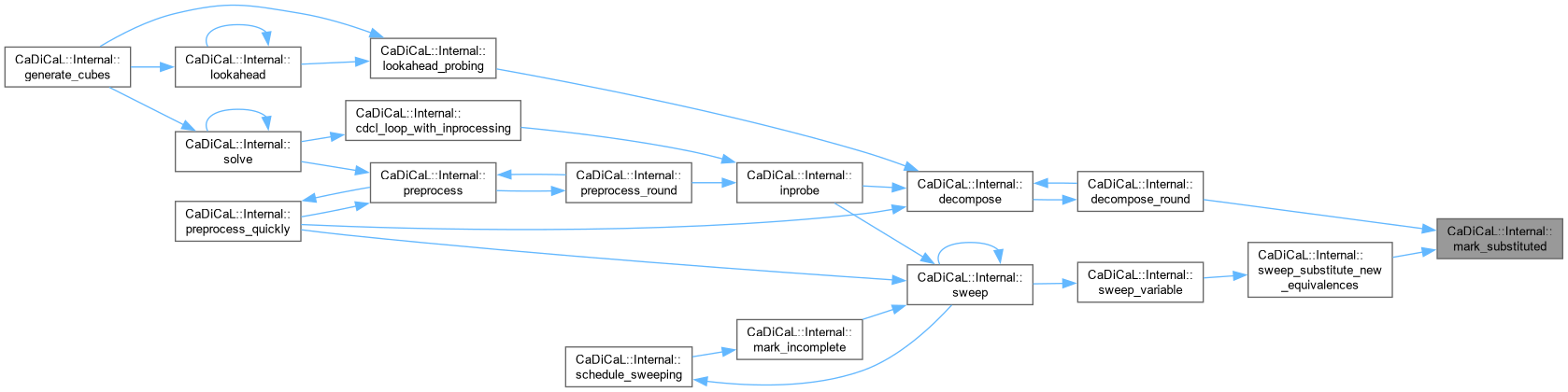
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::mark_substituted | ( | int | lit | ) |
Definition at line 66 of file cadical_flags.cpp.
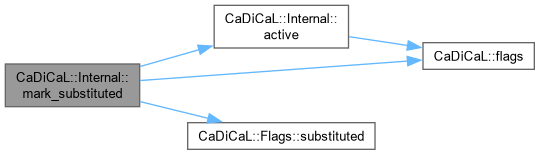
|
inline |
Definition at line 1027 of file internal.hpp.
|
inline |
Definition at line 1035 of file internal.hpp.
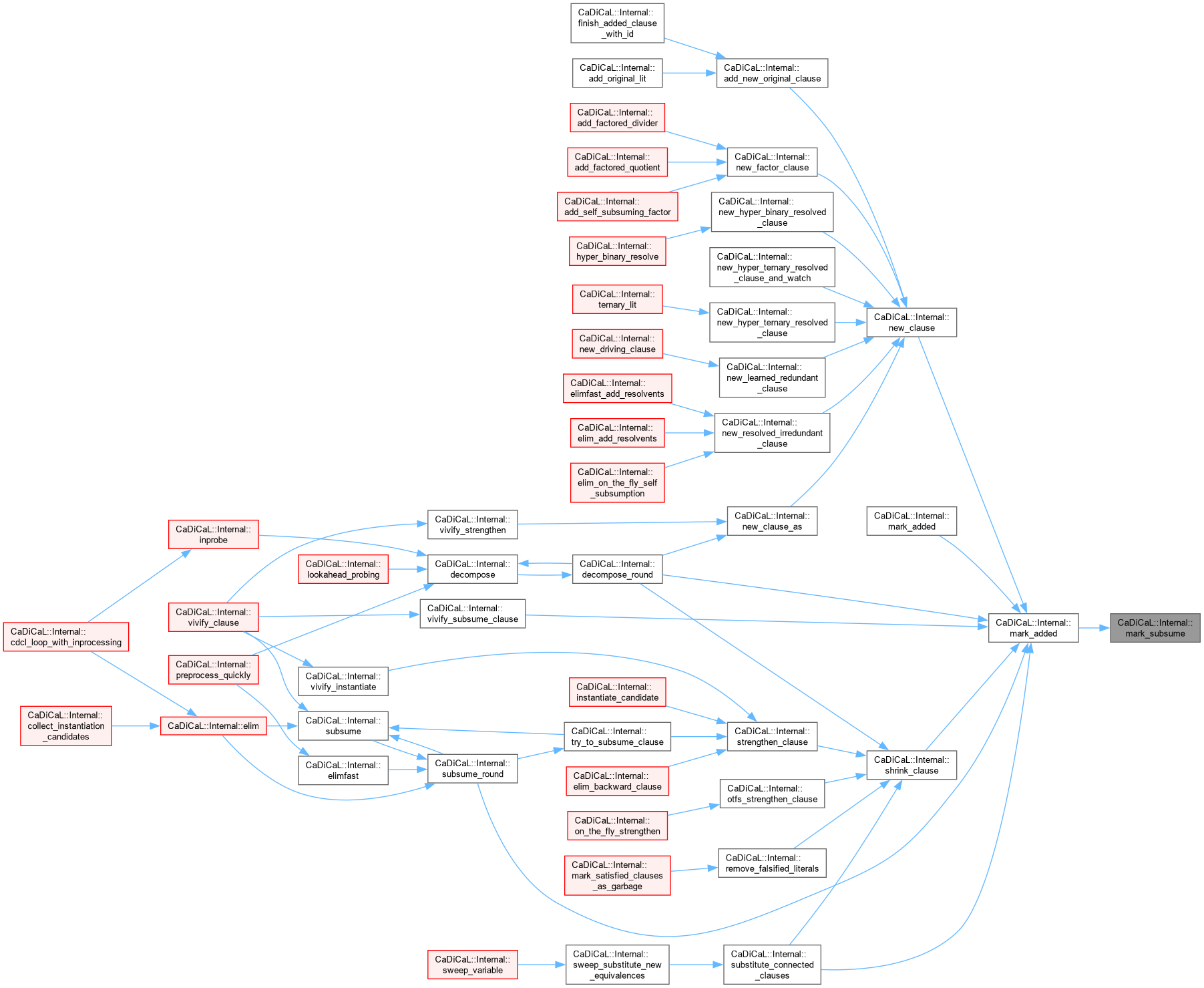
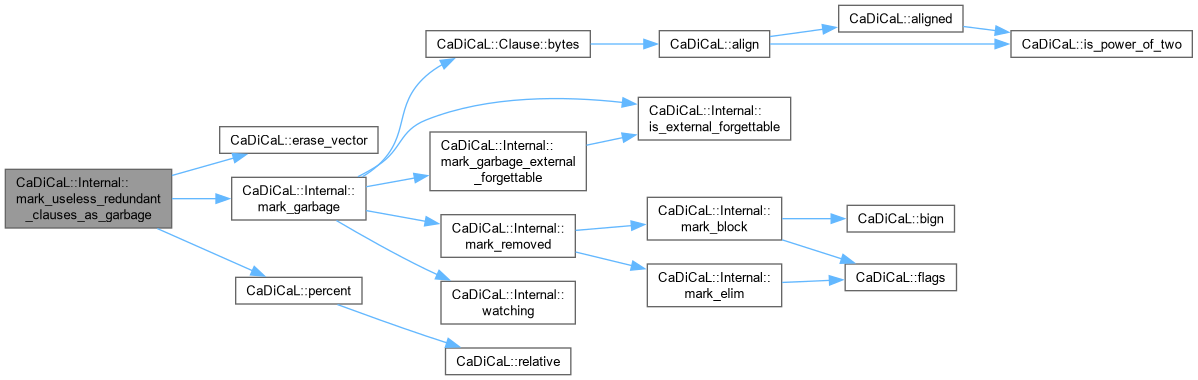
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::mark_useless_redundant_clauses_as_garbage | ( | ) |
Definition at line 92 of file cadical_reduce.cpp.

|
inline |
|
inline |
Definition at line 555 of file internal.hpp.
|
inline |
|
inline |
|
inline |
|
inline |
|
inline |
|
inline |
Definition at line 580 of file internal.hpp.

Definition at line 476 of file cadical_gates.cpp.
|
inline |
Definition at line 1585 of file internal.hpp.

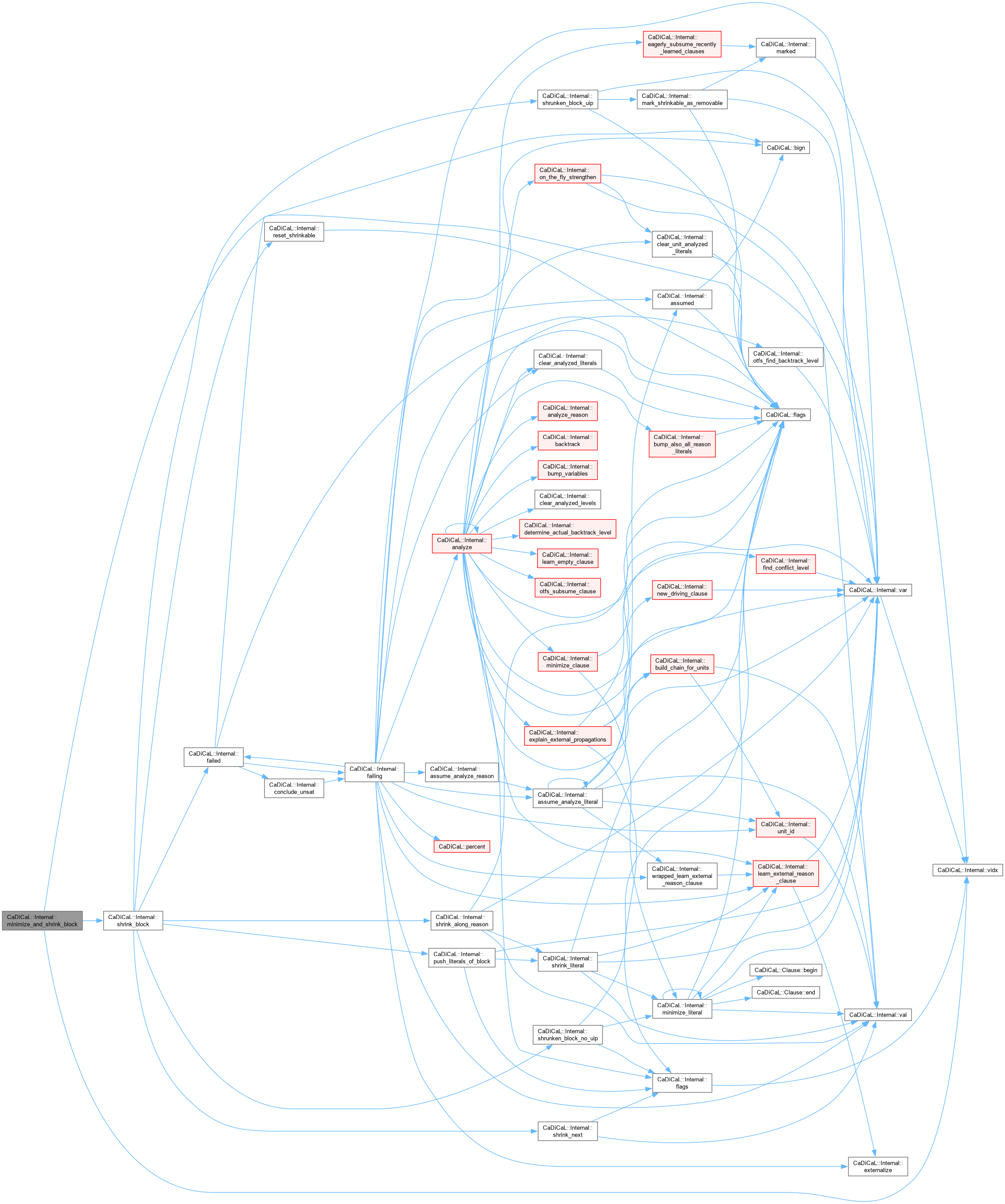
| std::vector< int >::reverse_iterator CaDiCaL::Internal::minimize_and_shrink_block | ( | std::vector< int >::reverse_iterator & | , |
| unsigned int & | , | ||
| unsigned int & | , | ||
| const int | ) |
Definition at line 371 of file cadical_shrink.cpp.
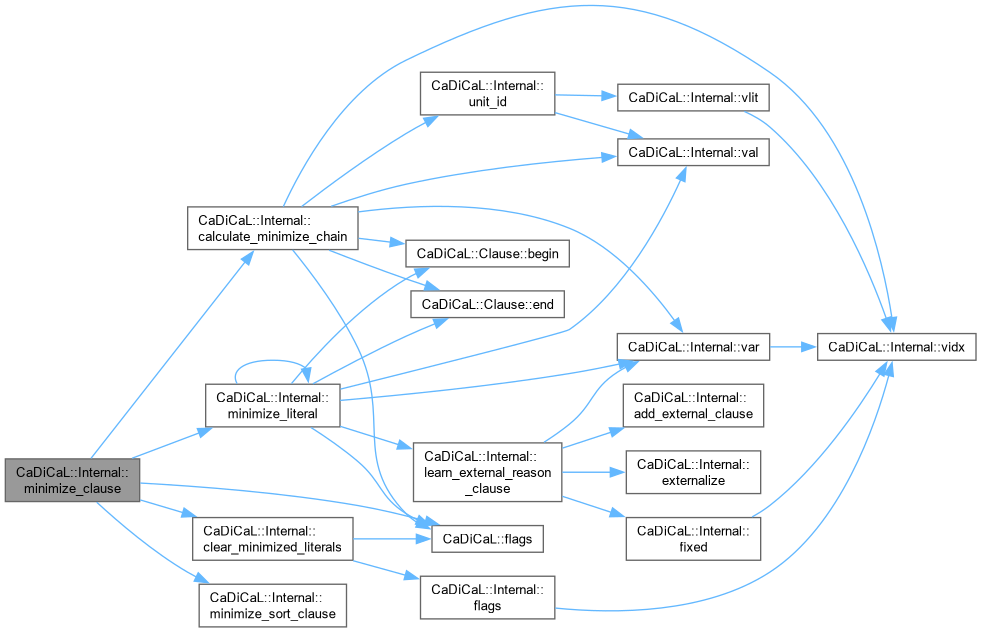
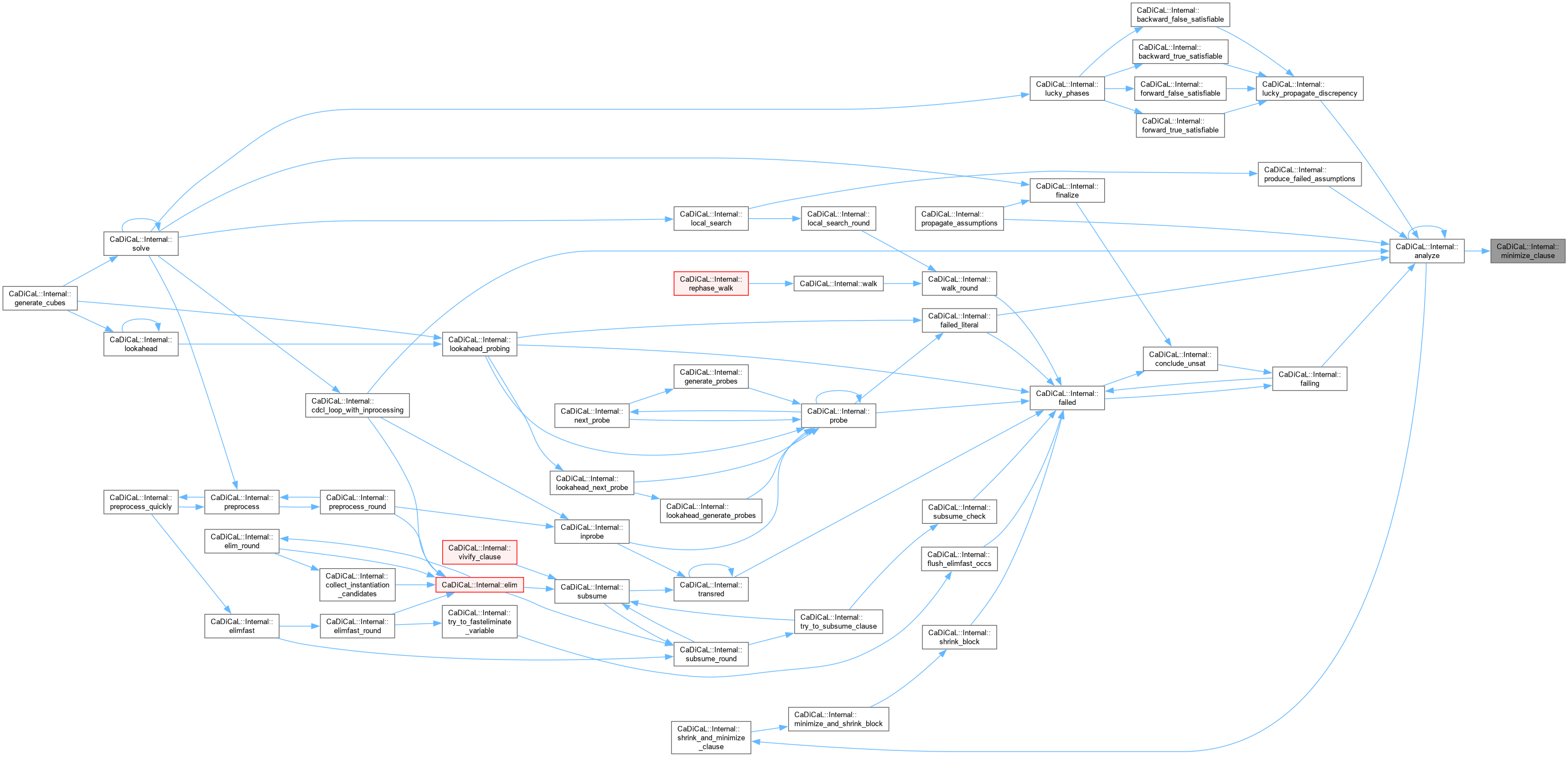
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::minimize_clause | ( | ) |
Definition at line 114 of file cadical_minimize.cpp.
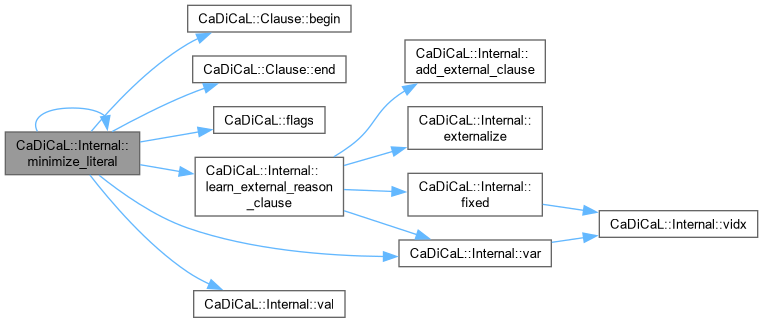
| bool CaDiCaL::Internal::minimize_literal | ( | int | lit, |
| int | depth = 0 ) |
Definition at line 21 of file cadical_minimize.cpp.
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::minimize_sort_clause | ( | ) |
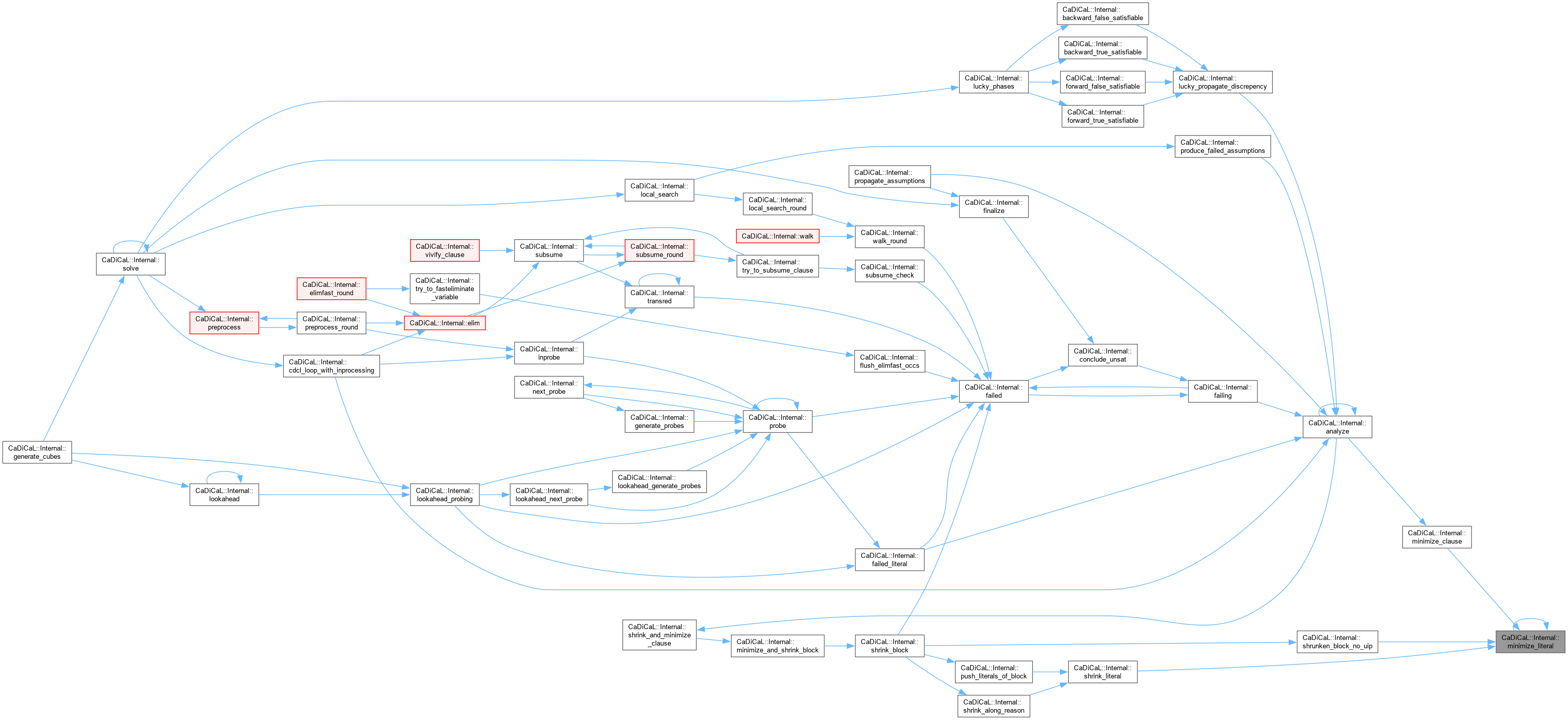
| int CaDiCaL::Internal::most_occurring_literal | ( | ) |
Definition at line 51 of file cadical_lookahead.cpp.
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::move_literals_to_watch | ( | ) |
Definition at line 404 of file cadical_external_propagate.cpp.


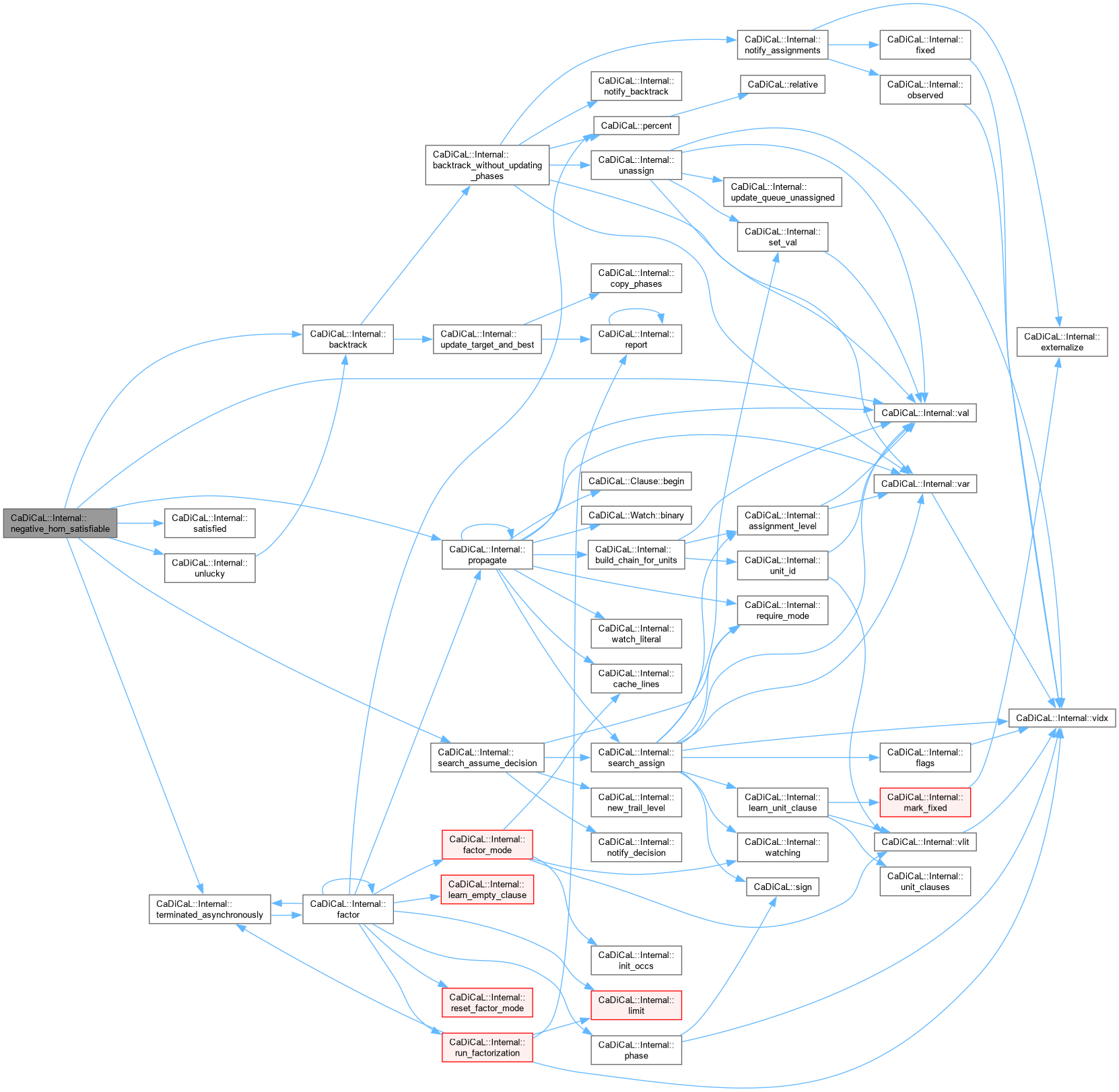
| int CaDiCaL::Internal::negative_horn_satisfiable | ( | ) |
Definition at line 323 of file cadical_lucky.cpp.
Definition at line 82 of file cadical_clause.cpp.
Definition at line 622 of file cadical_clause.cpp.
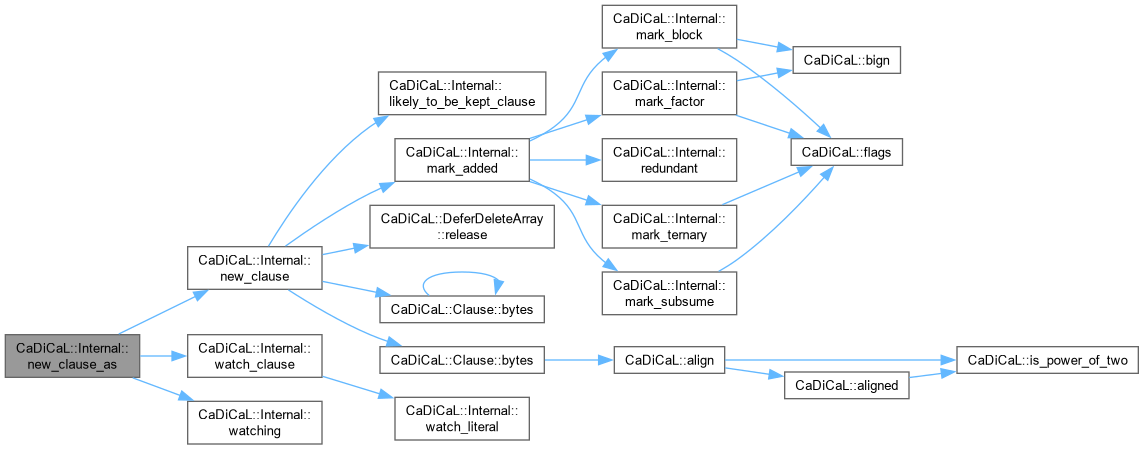
Definition at line 506 of file cadical_analyze.cpp.
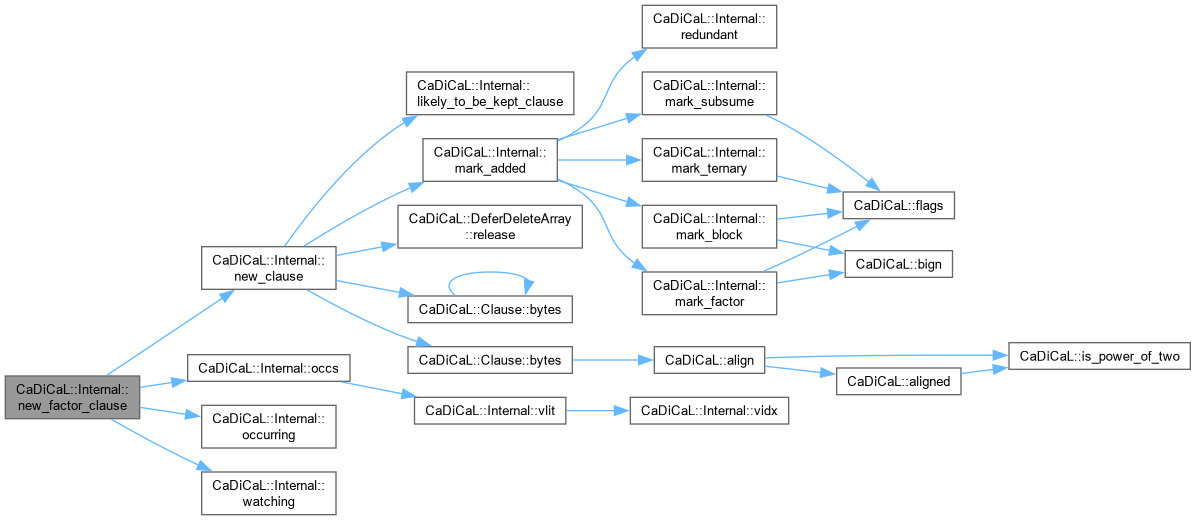
| Clause * CaDiCaL::Internal::new_factor_clause | ( | ) |
Definition at line 585 of file cadical_clause.cpp.
Definition at line 561 of file cadical_clause.cpp.
Definition at line 574 of file cadical_clause.cpp.
| Clause * CaDiCaL::Internal::new_hyper_ternary_resolved_clause_and_watch | ( | bool | red, |
| bool | full_watching ) |
Definition at line 604 of file cadical_clause.cpp.
| Clause * CaDiCaL::Internal::new_learned_redundant_clause | ( | int | glue | ) |
Definition at line 542 of file cadical_clause.cpp.
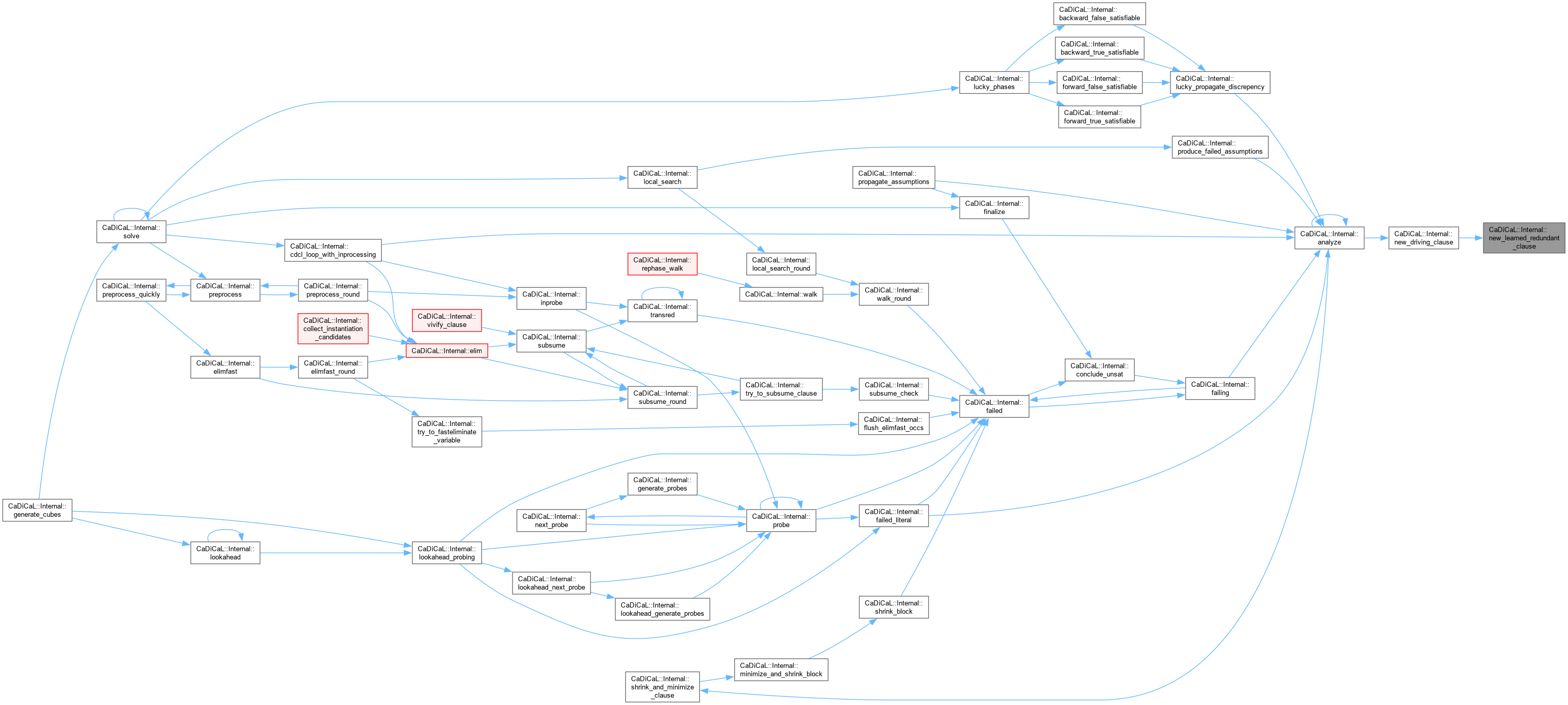
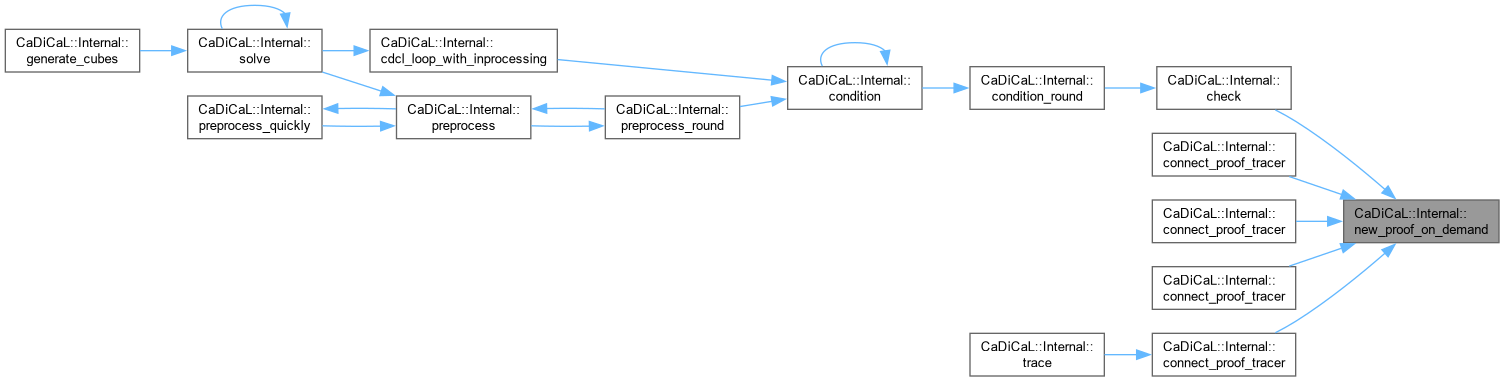
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::new_proof_on_demand | ( | ) |
Definition at line 15 of file cadical_proof.cpp.
Definition at line 149 of file cadical_factor.cpp.
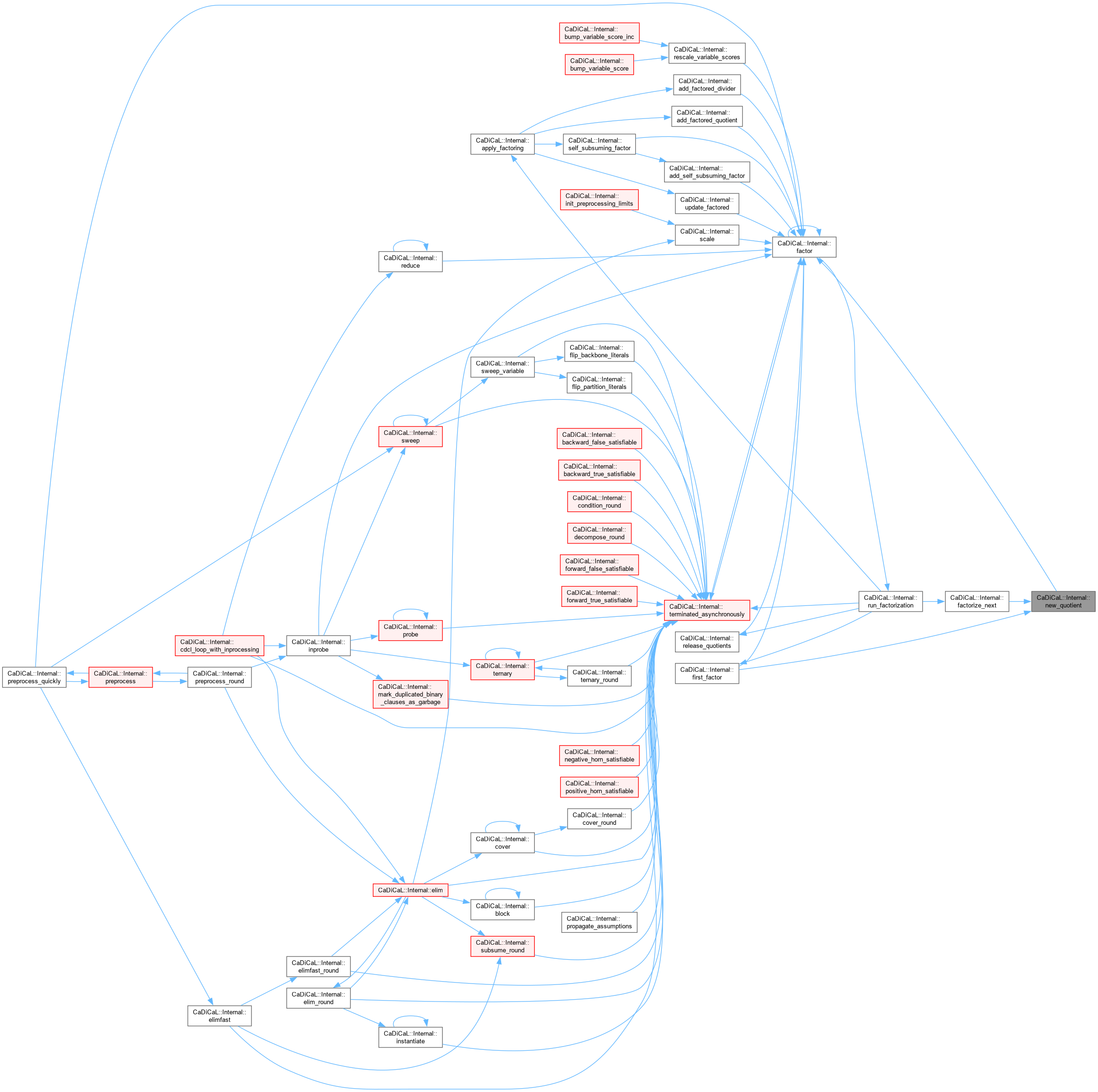
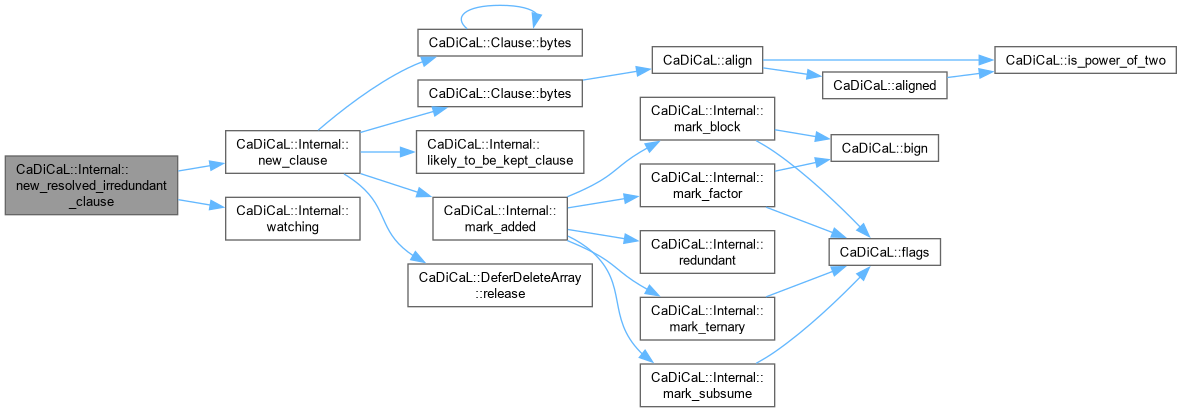
| Clause * CaDiCaL::Internal::new_resolved_irredundant_clause | ( | ) |
Definition at line 637 of file cadical_clause.cpp.
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::new_trail_level | ( | int | lit | ) |
| int CaDiCaL::Internal::next_decision_variable | ( | ) |
Definition at line 44 of file cadical_decide.cpp.
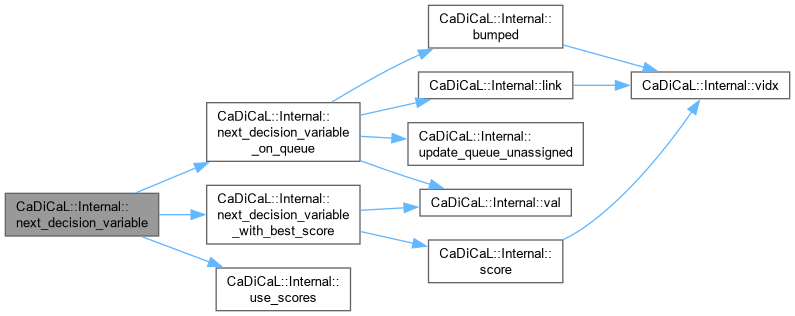
| int CaDiCaL::Internal::next_decision_variable_on_queue | ( | ) |
Definition at line 16 of file cadical_decide.cpp.
| int CaDiCaL::Internal::next_decision_variable_with_best_score | ( | ) |
Definition at line 32 of file cadical_decide.cpp.

| int CaDiCaL::Internal::next_factor | ( | Factoring & | factoring, |
| unsigned * | next_count_ptr ) |
Definition at line 253 of file cadical_factor.cpp.
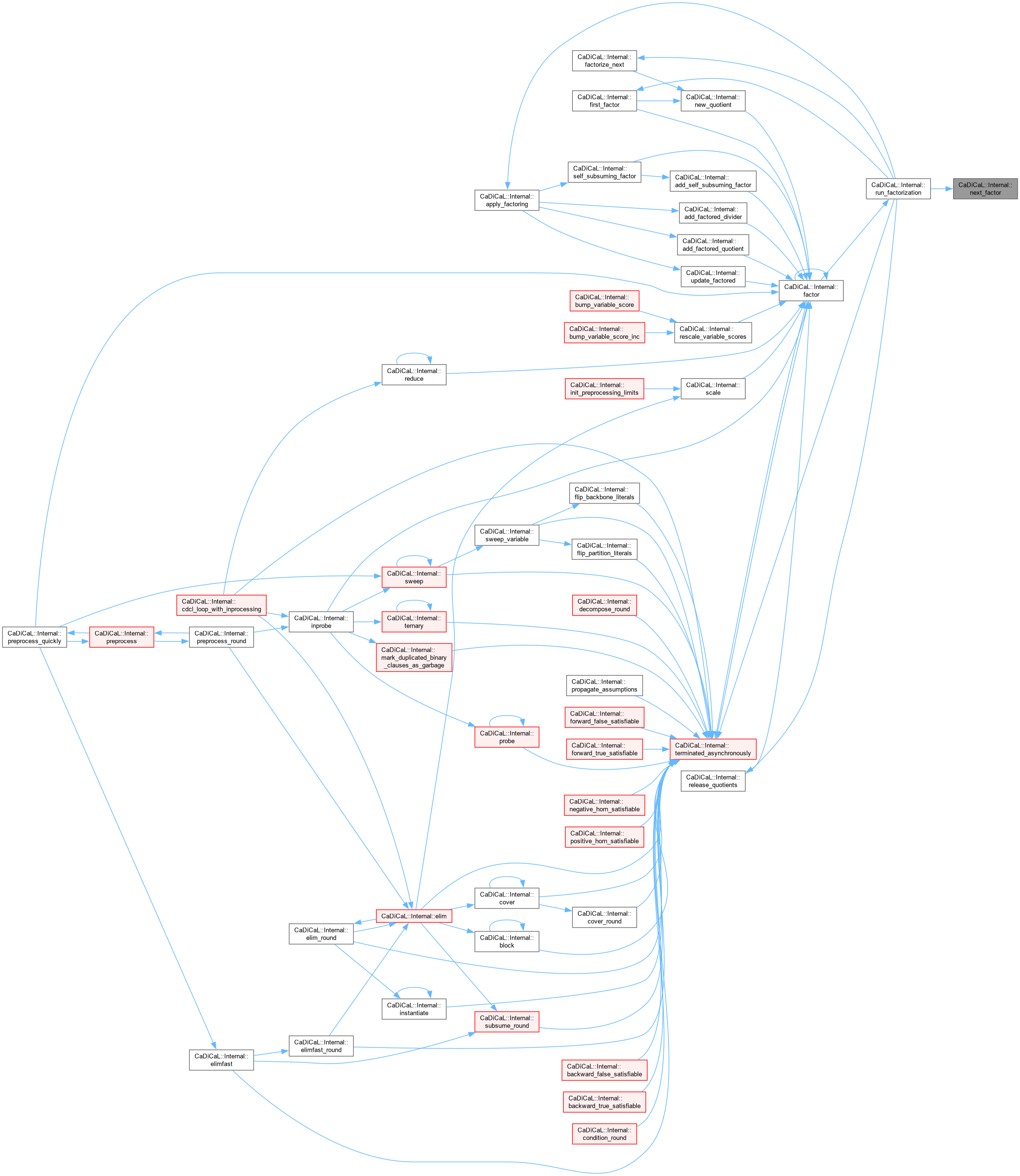
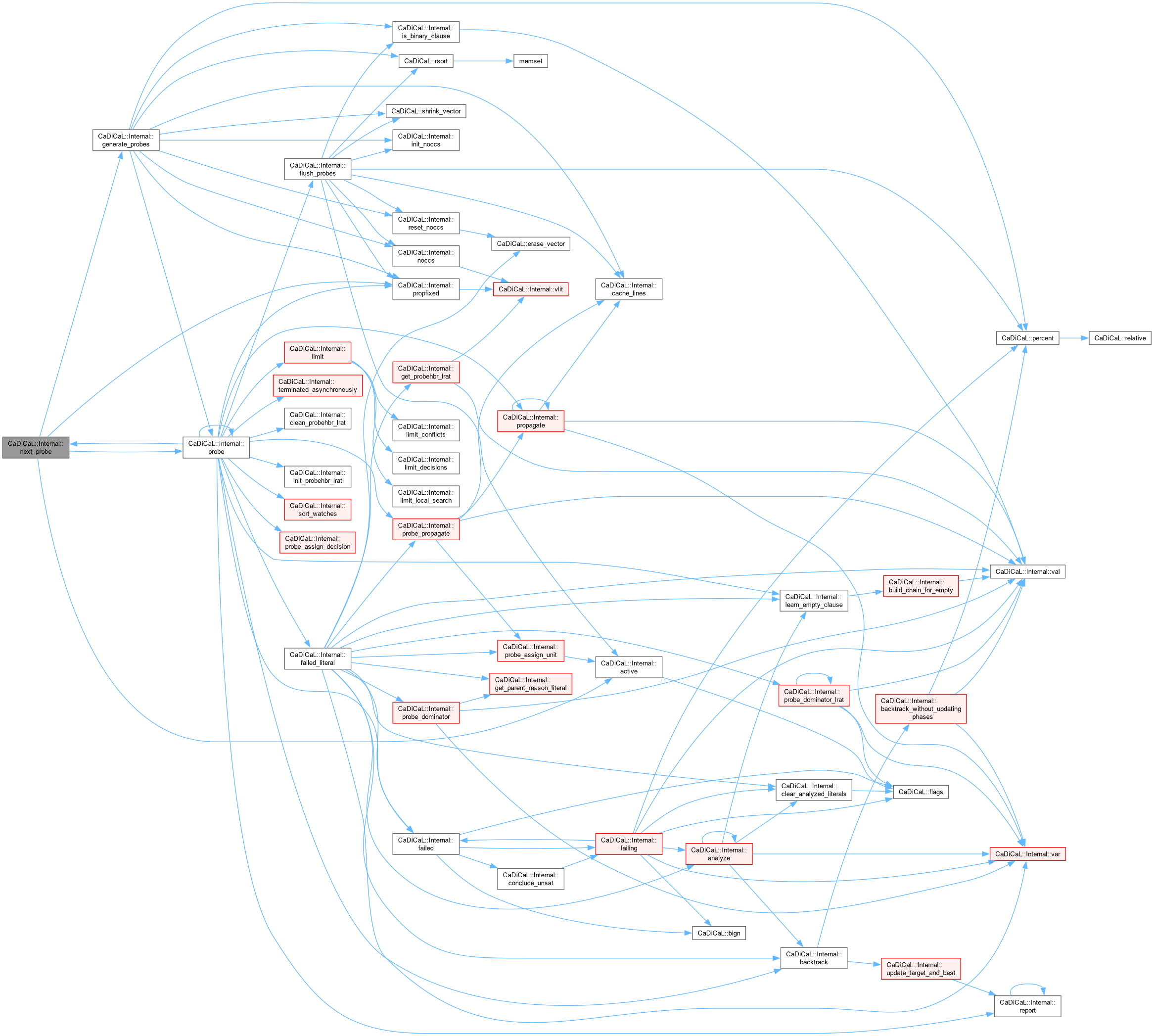
| int CaDiCaL::Internal::next_probe | ( | ) |
Definition at line 753 of file cadical_probe.cpp.
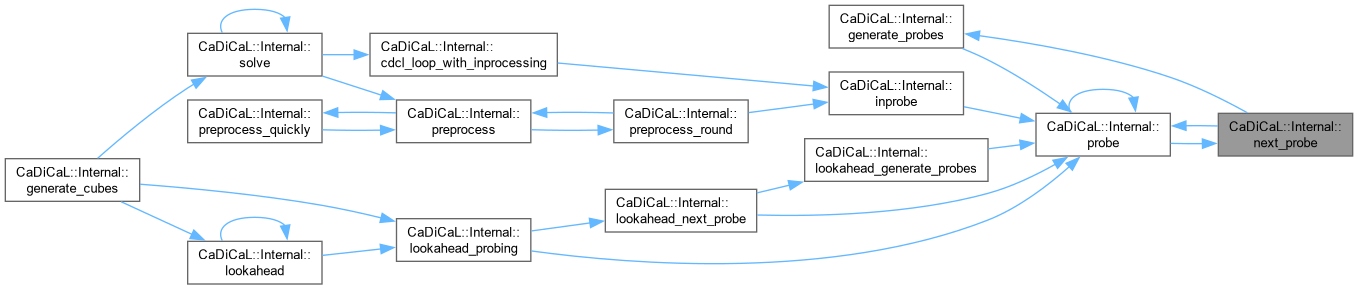
| int CaDiCaL::Internal::next_scheduled | ( | Sweeper & | sweeper | ) |
Definition at line 1008 of file cadical_sweep.cpp.
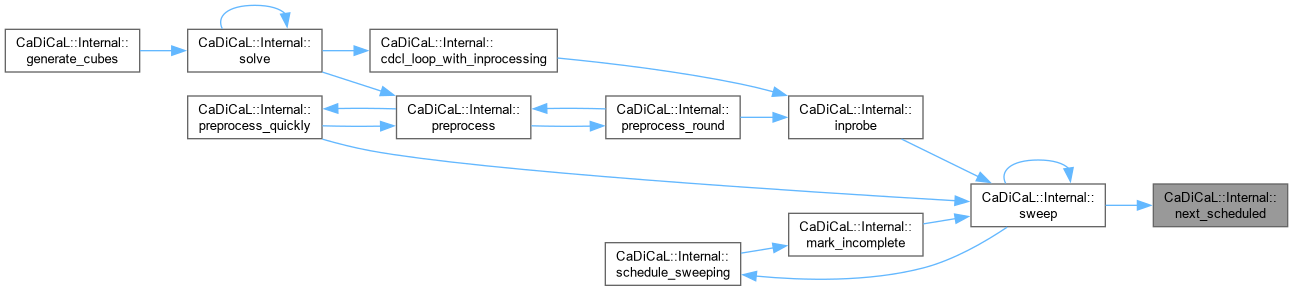
|
inline |
Definition at line 466 of file internal.hpp.

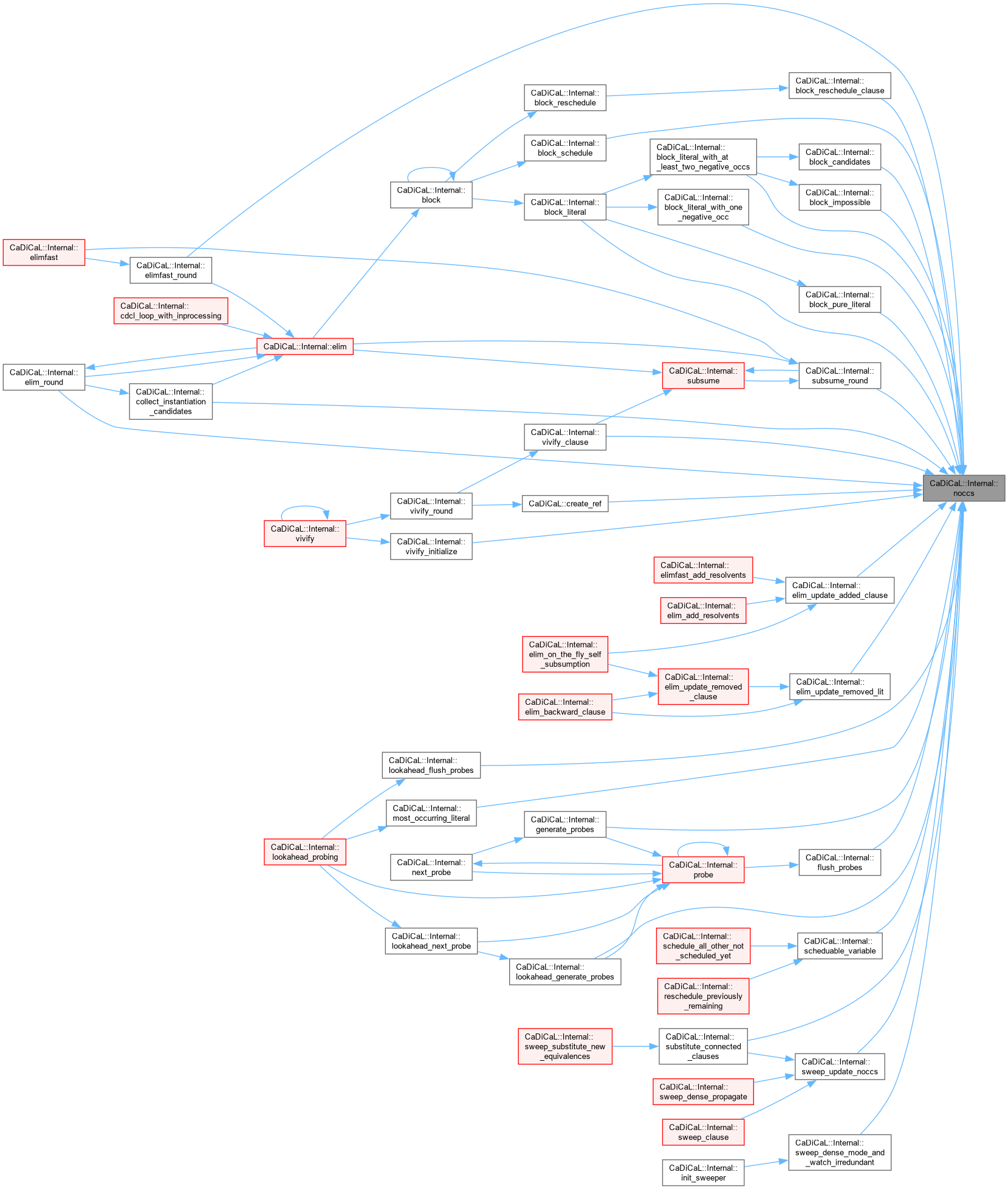
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::notify_assignments | ( | ) |
Definition at line 932 of file cadical_external_propagate.cpp.
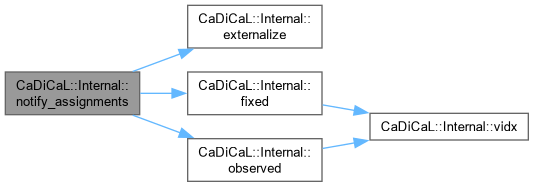
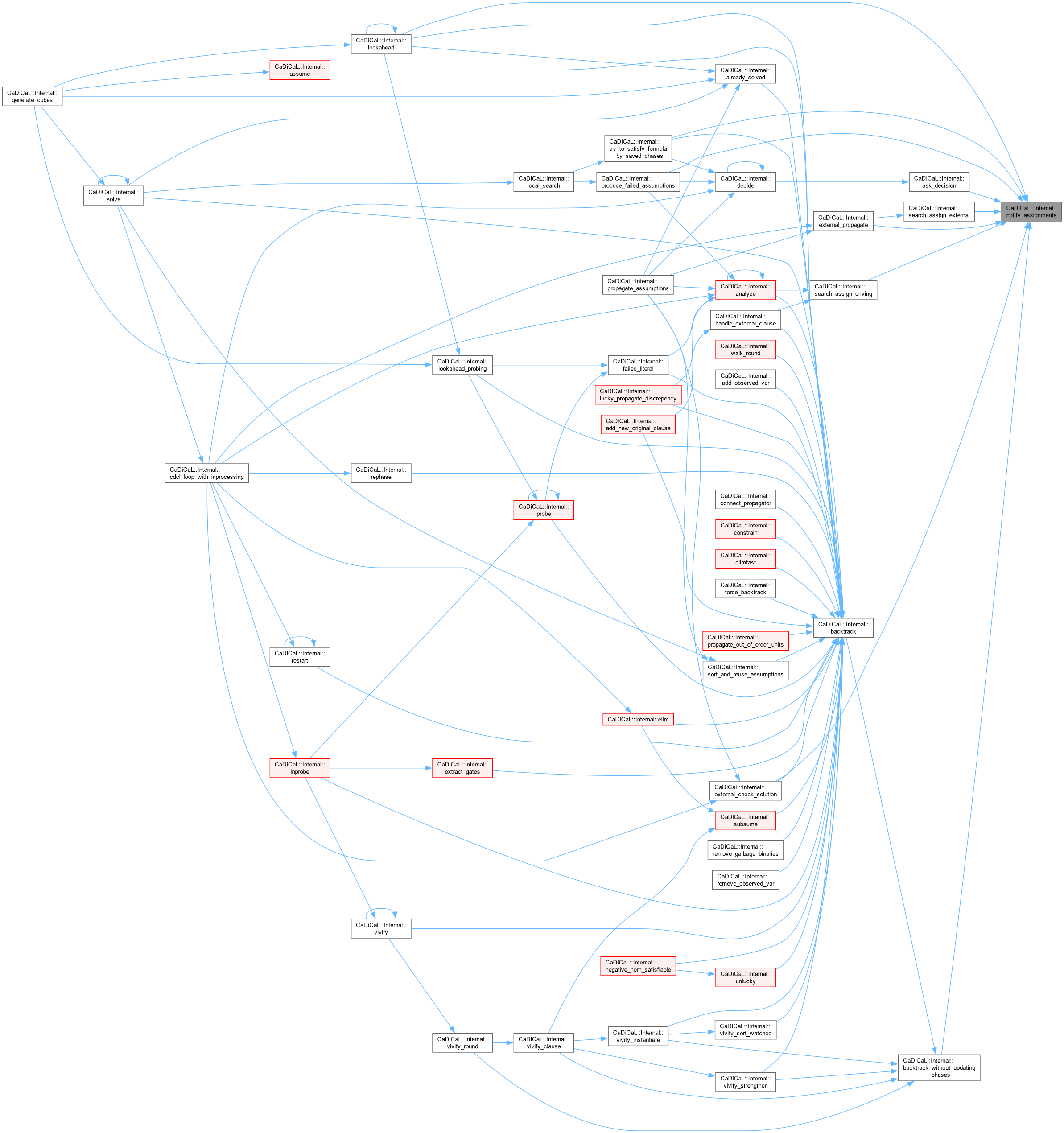
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::notify_backtrack | ( | size_t | new_level | ) |
Definition at line 987 of file cadical_external_propagate.cpp.
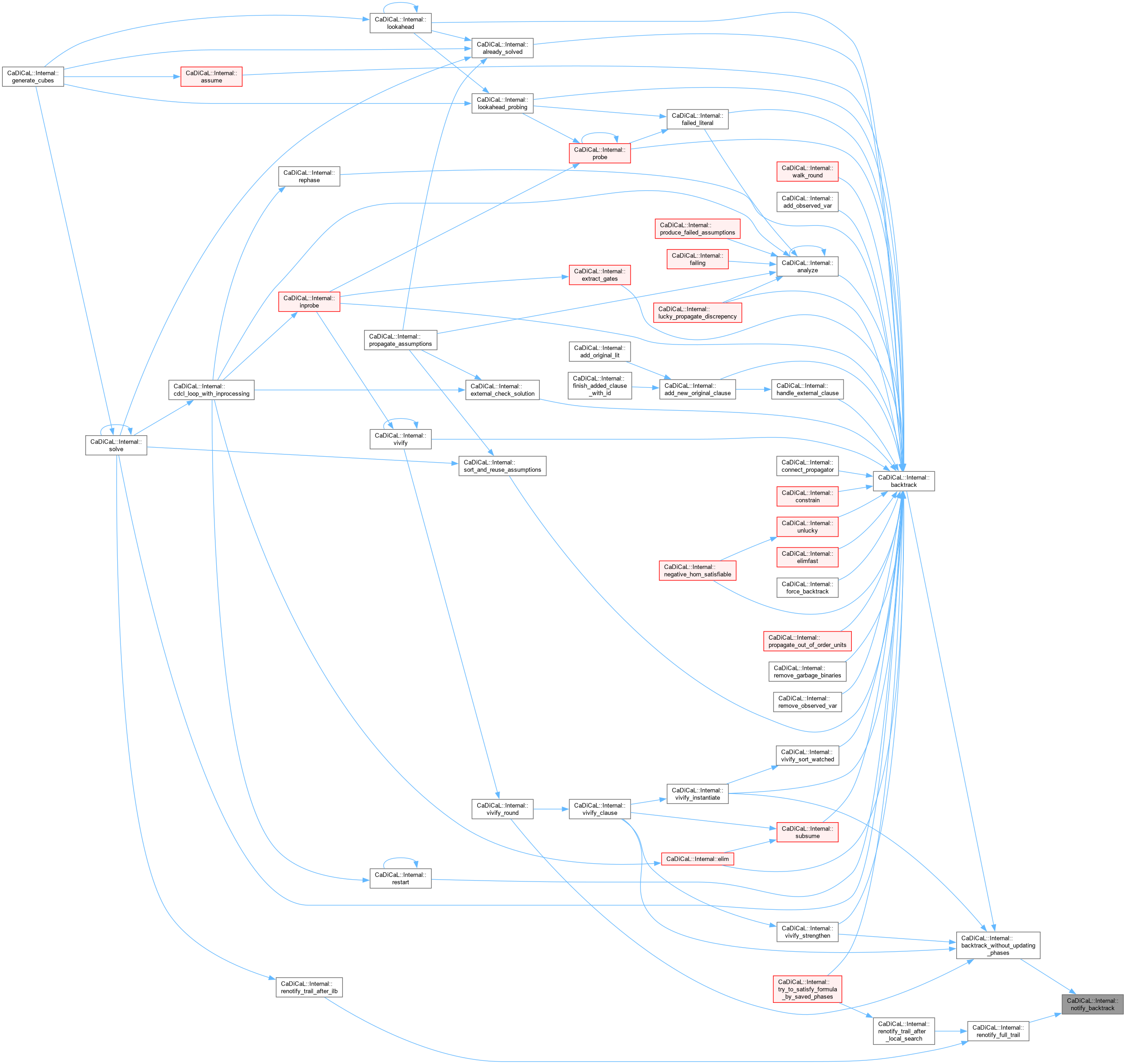
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::notify_decision | ( | ) |
Definition at line 977 of file cadical_external_propagate.cpp.
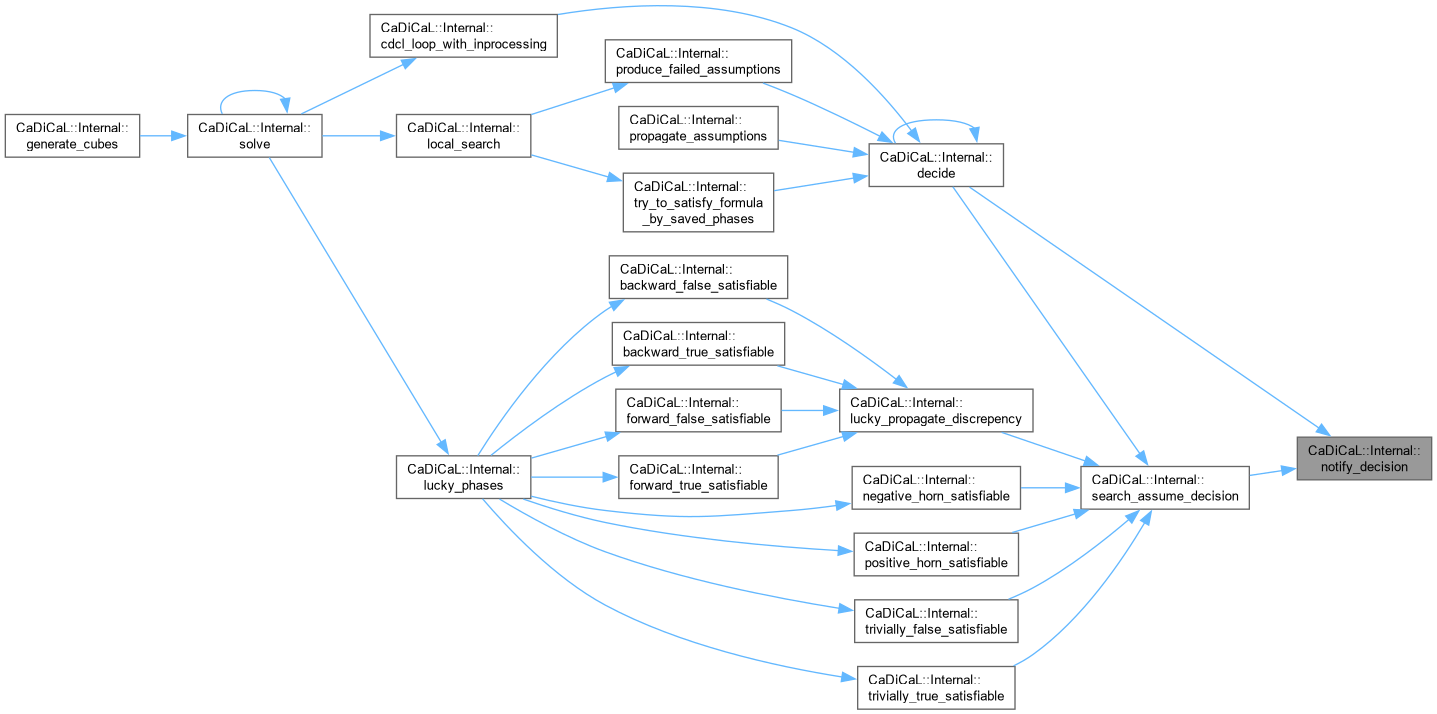
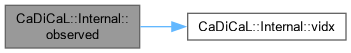
| bool CaDiCaL::Internal::observed | ( | int | ilit | ) | const |
Definition at line 72 of file cadical_external_propagate.cpp.
|
inline |
|
inline |
Definition at line 773 of file cadical_analyze.cpp.
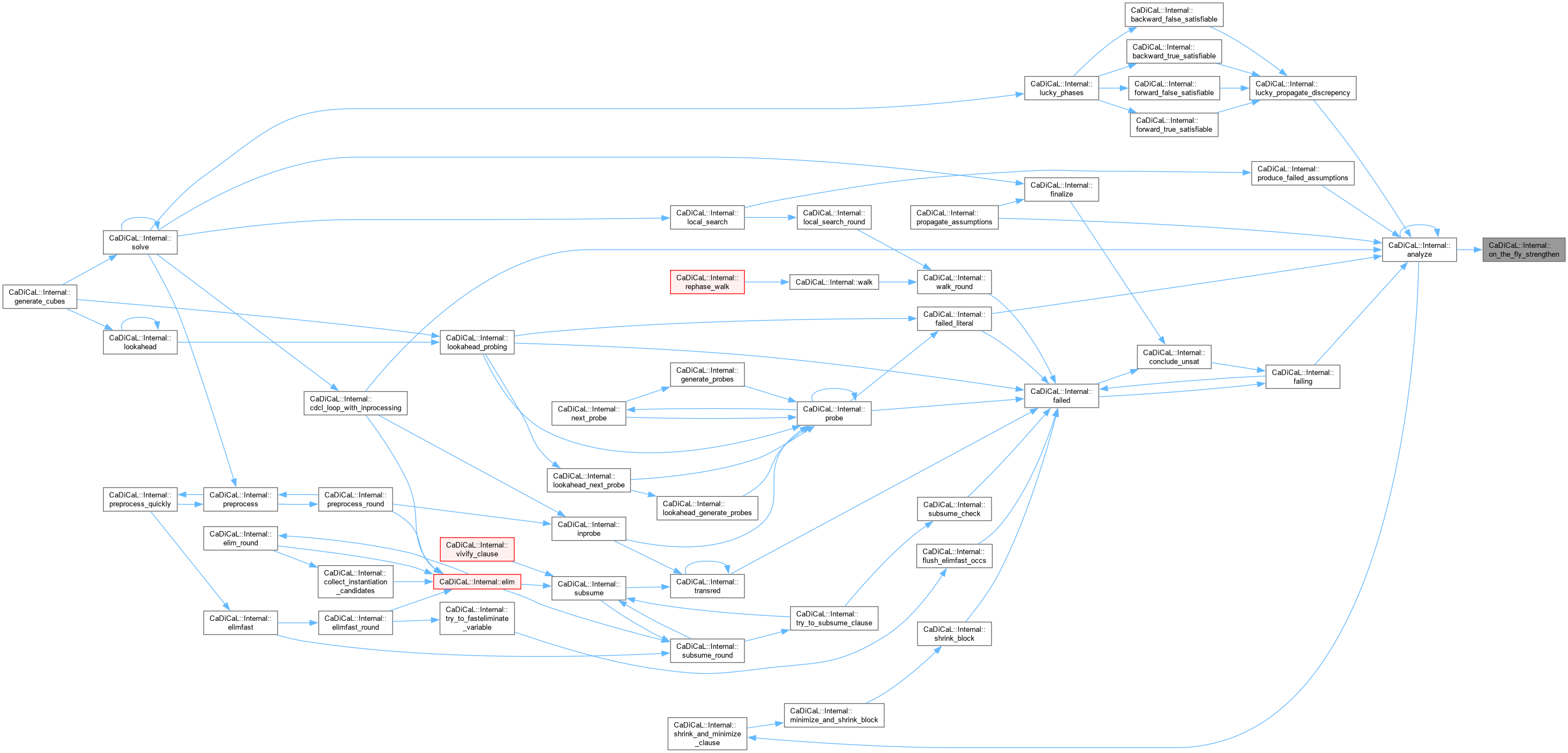
|
inline |
Definition at line 551 of file cadical_analyze.cpp.

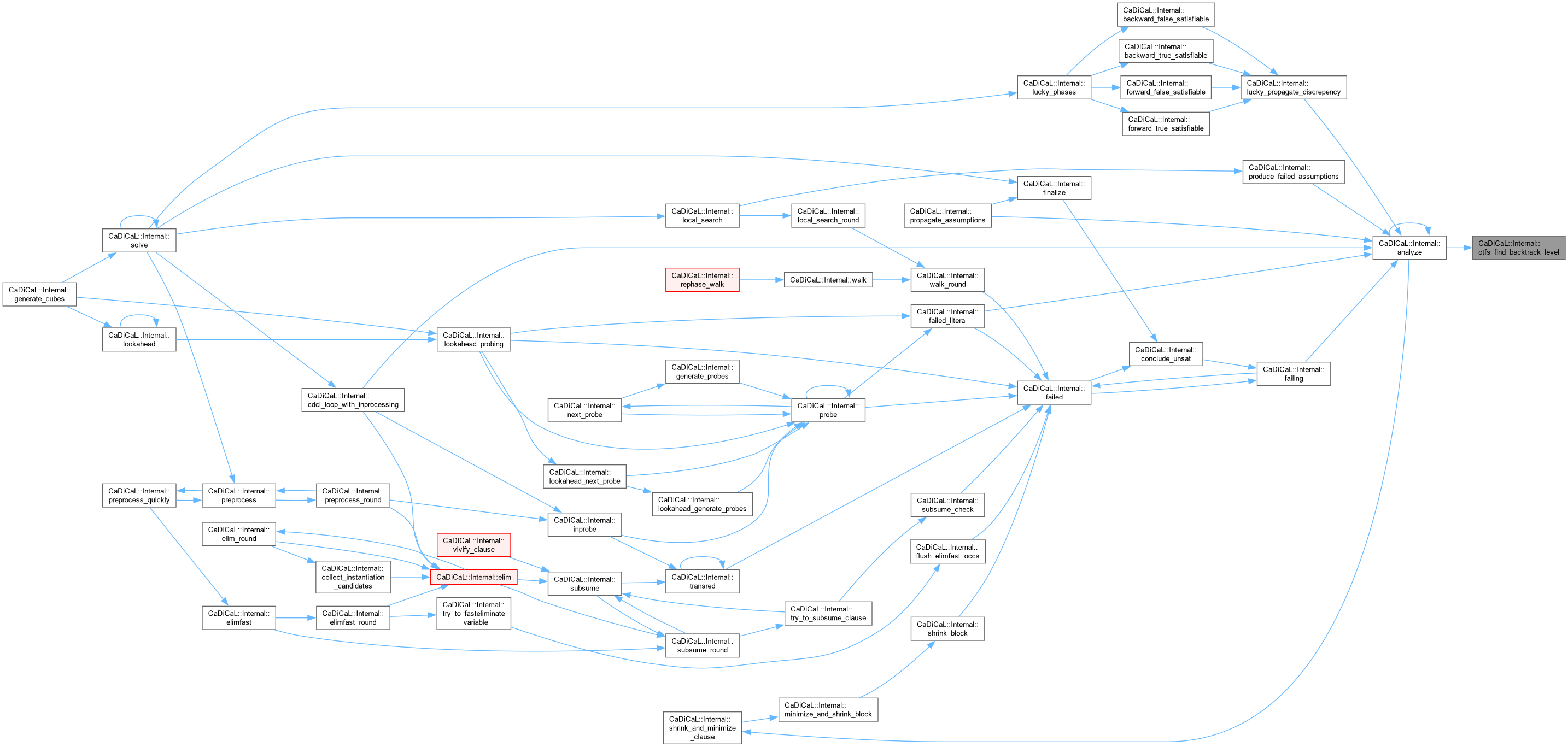
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::otfs_strengthen_clause | ( | Clause * | c, |
| int | lit, | ||
| int | new_size, | ||
| const std::vector< int > & | old ) |
Definition at line 903 of file cadical_analyze.cpp.
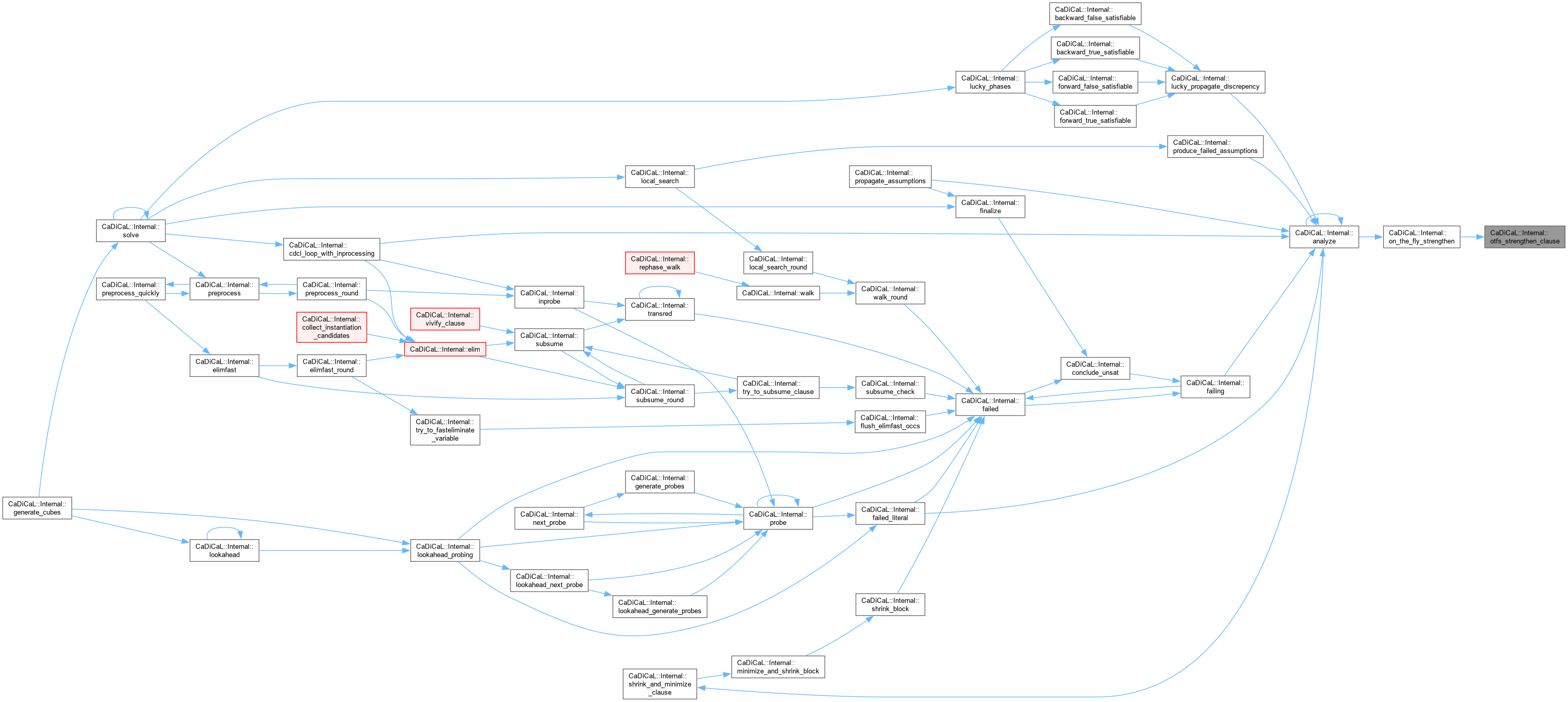
Definition at line 871 of file cadical_analyze.cpp.
| const char * CaDiCaL::Internal::parse_dimacs | ( | FILE * | ) |
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::phase | ( | int | lit | ) |
Definition at line 23 of file cadical_phases.cpp.
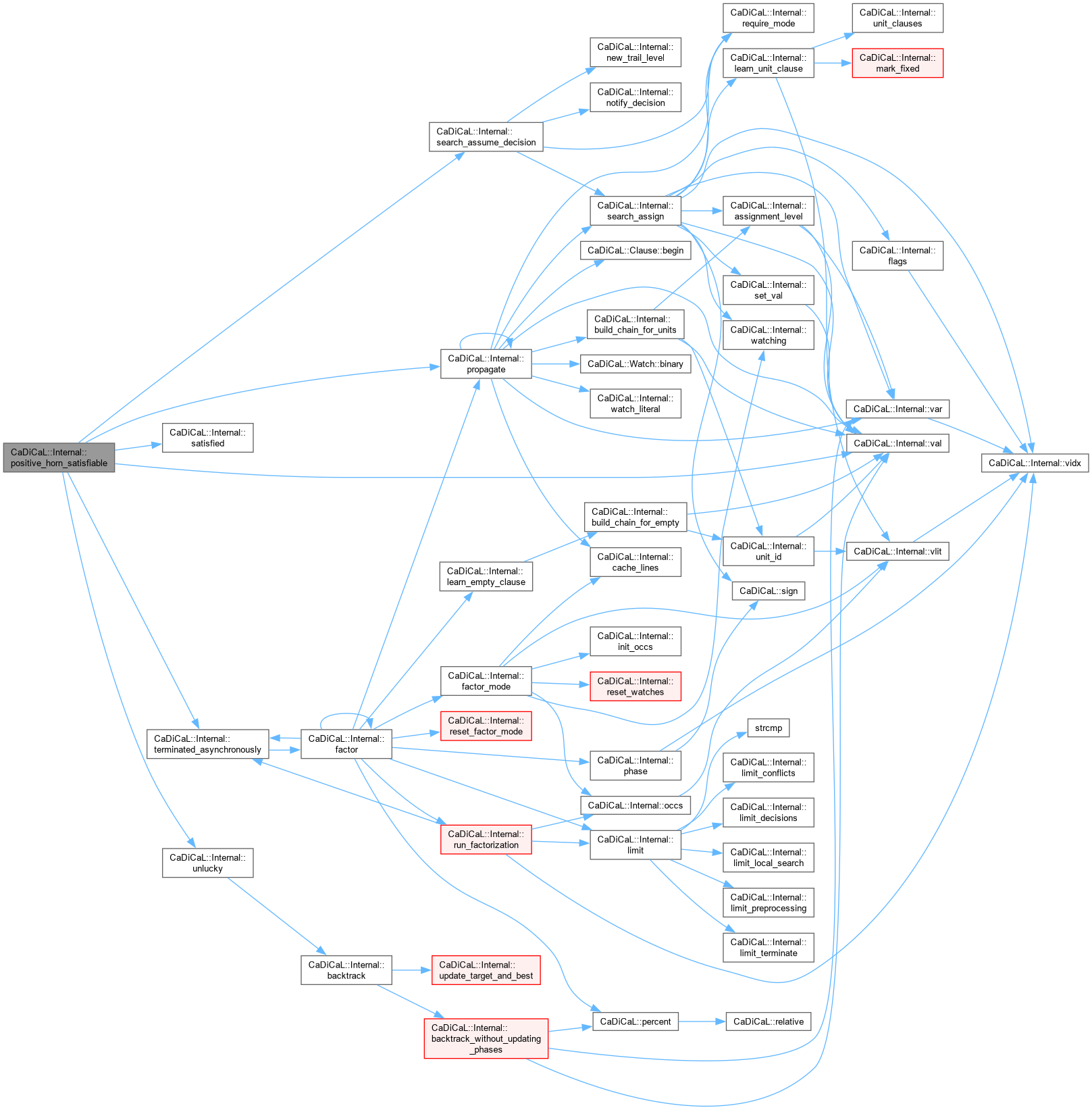
| int CaDiCaL::Internal::positive_horn_satisfiable | ( | ) |
Definition at line 264 of file cadical_lucky.cpp.
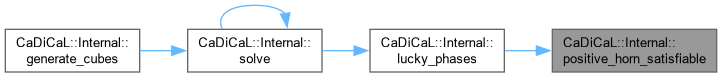
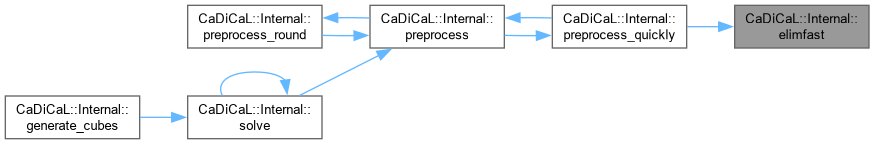
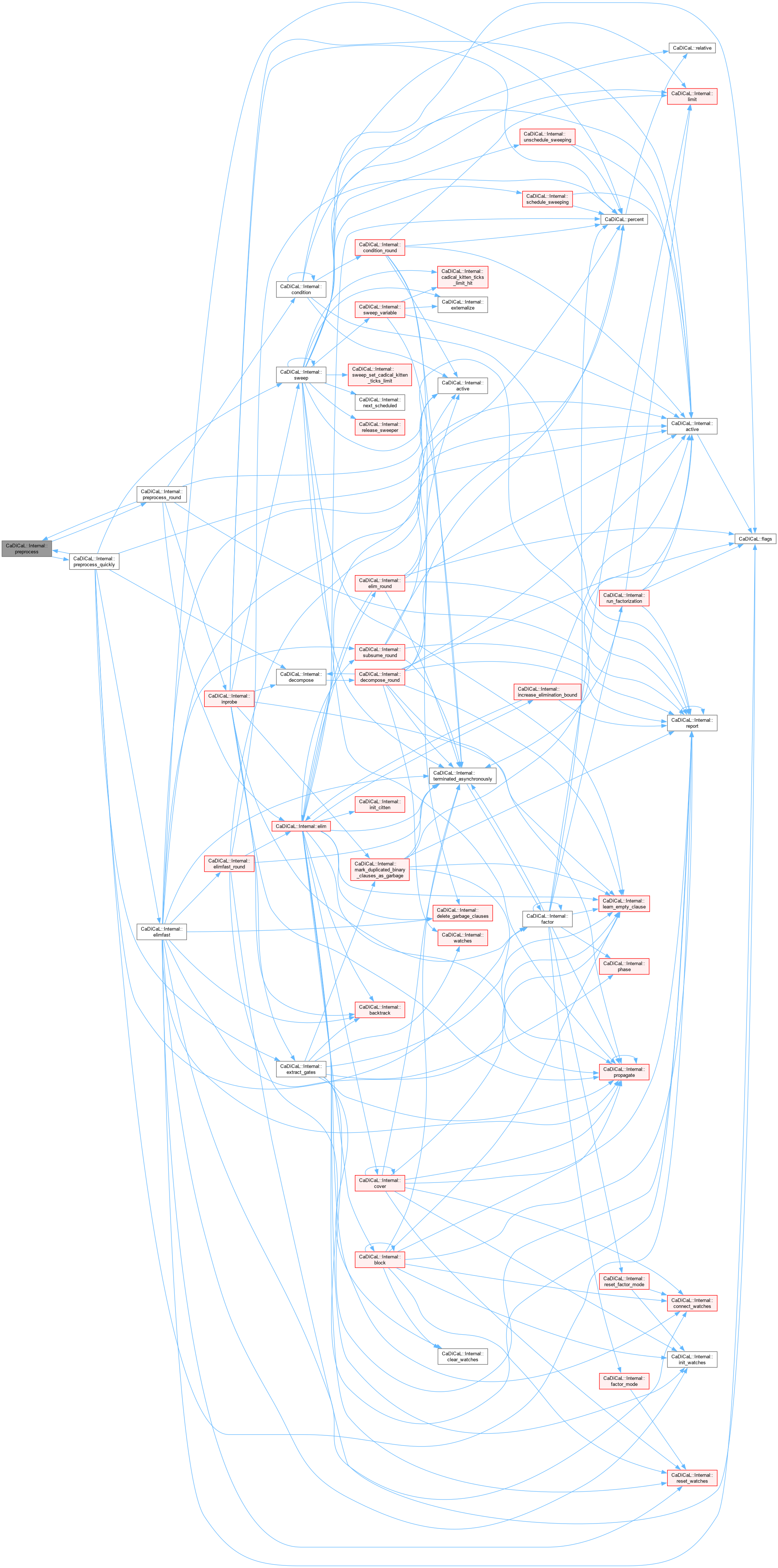
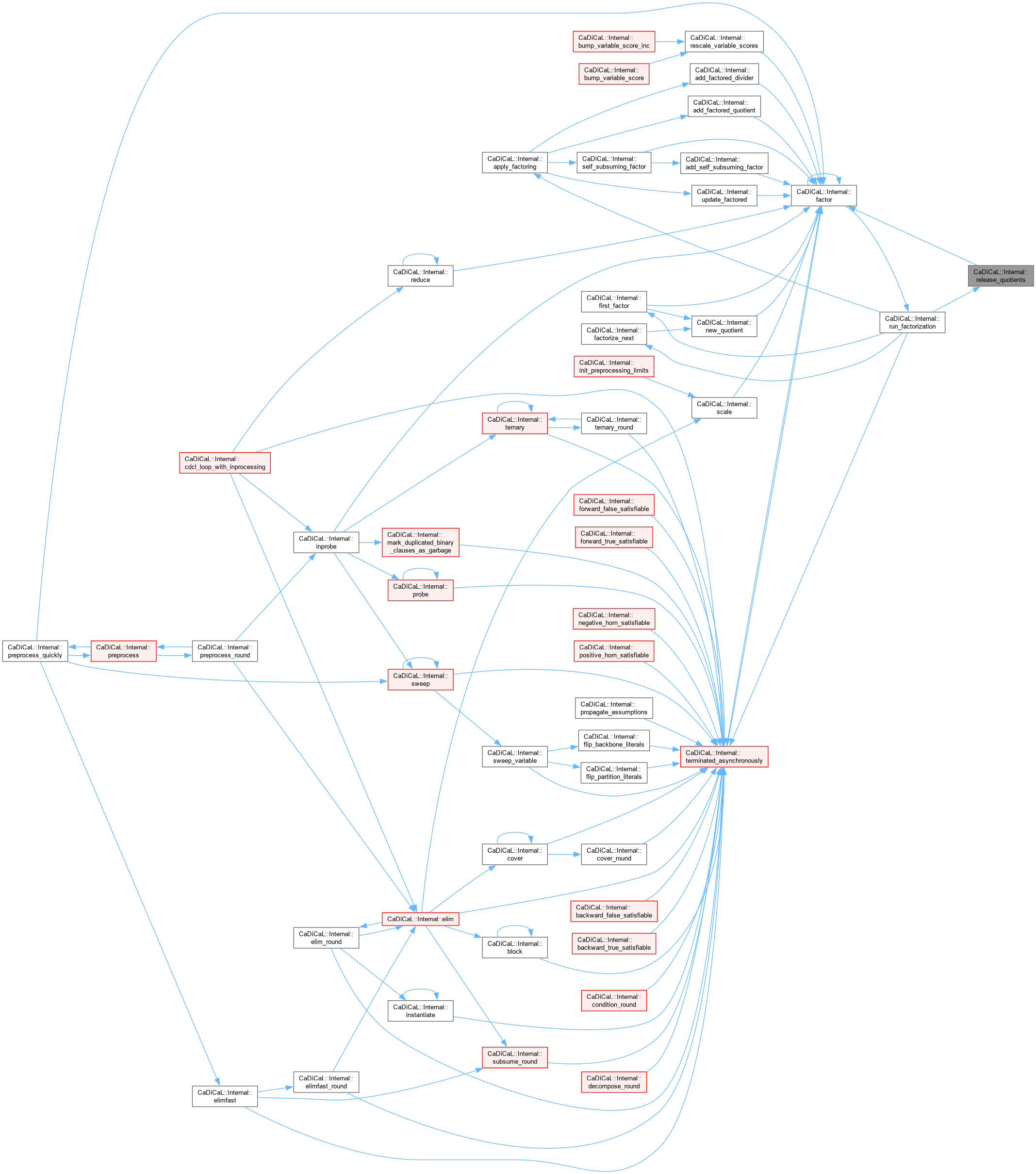
| int CaDiCaL::Internal::preprocess | ( | ) |
Definition at line 740 of file cadical_internal.cpp.
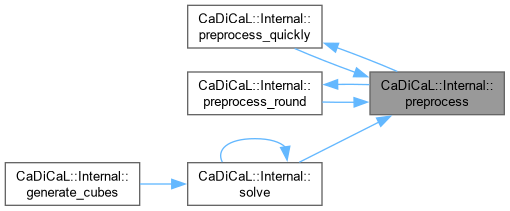
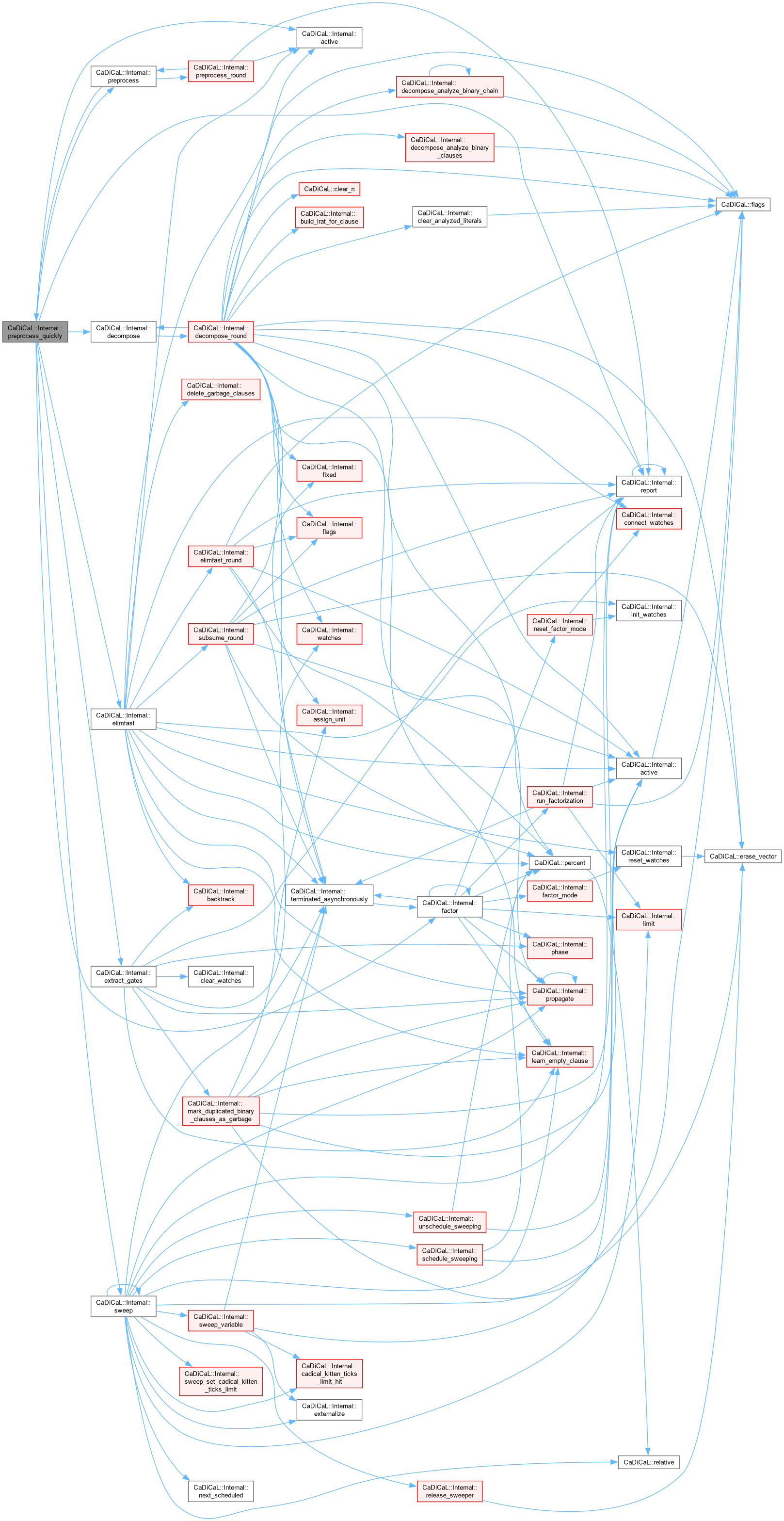
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::preprocess_quickly | ( | ) |
Definition at line 696 of file cadical_internal.cpp.
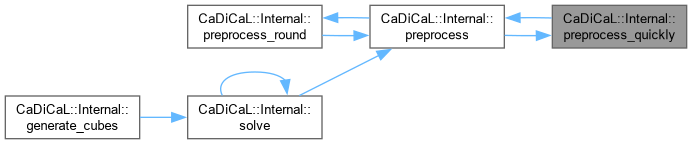
| bool CaDiCaL::Internal::preprocess_round | ( | int | round | ) |
Definition at line 649 of file cadical_internal.cpp.
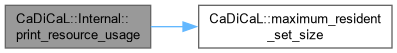
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::print_resource_usage | ( | ) |
Definition at line 756 of file cadical_stats.cpp.
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::print_statistics | ( | ) |
Definition at line 1098 of file cadical_internal.cpp.
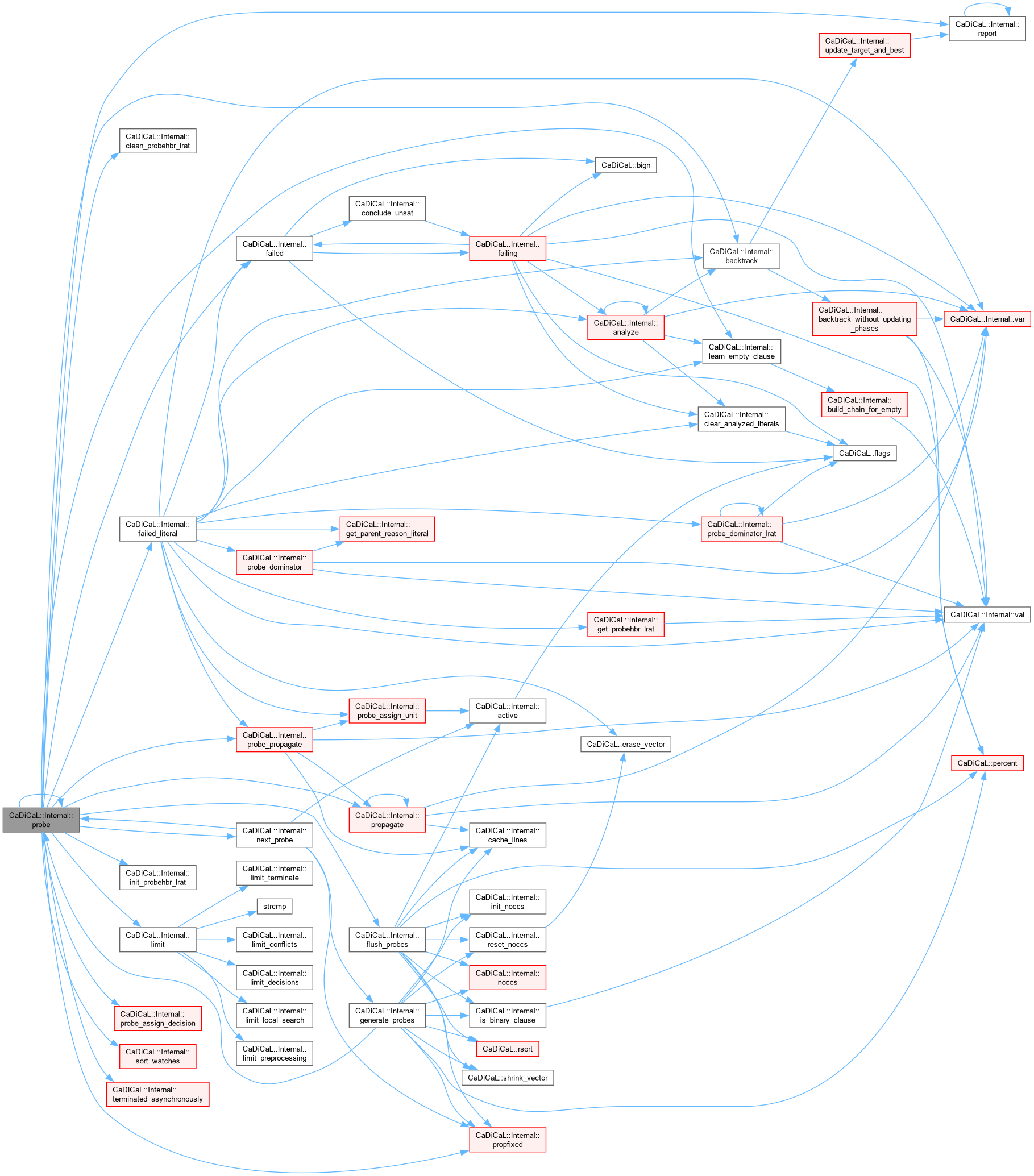
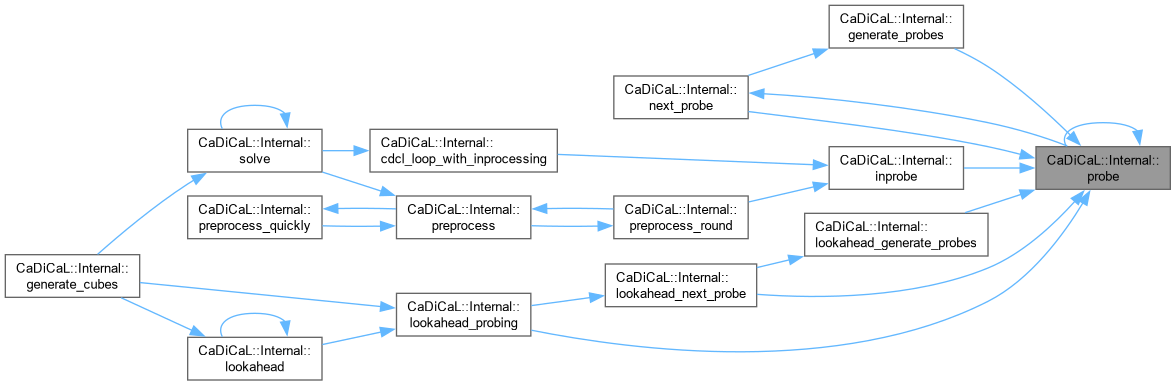
| bool CaDiCaL::Internal::probe | ( | ) |
Definition at line 791 of file cadical_probe.cpp.
|
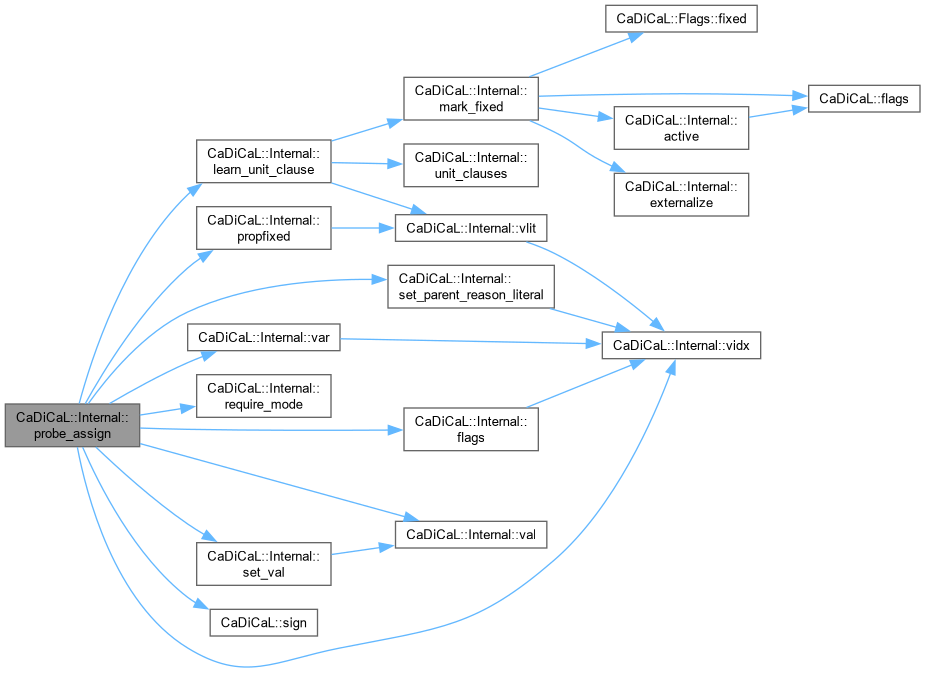
inline |
Definition at line 296 of file cadical_probe.cpp.
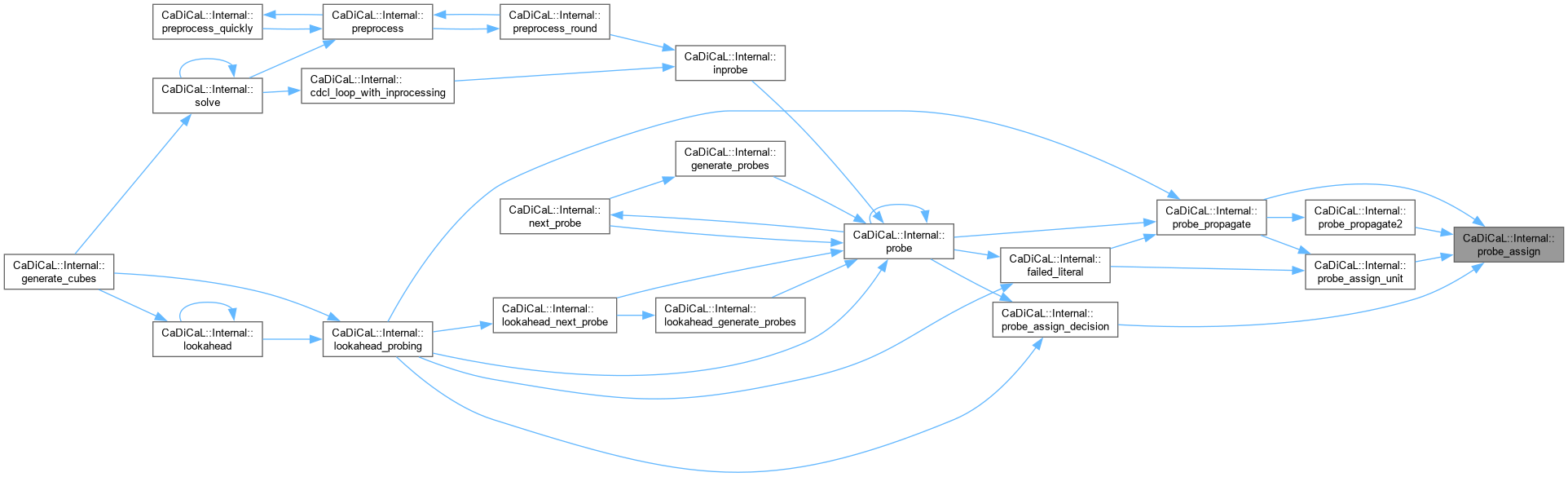
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::probe_assign_decision | ( | int | lit | ) |
Definition at line 336 of file cadical_probe.cpp.
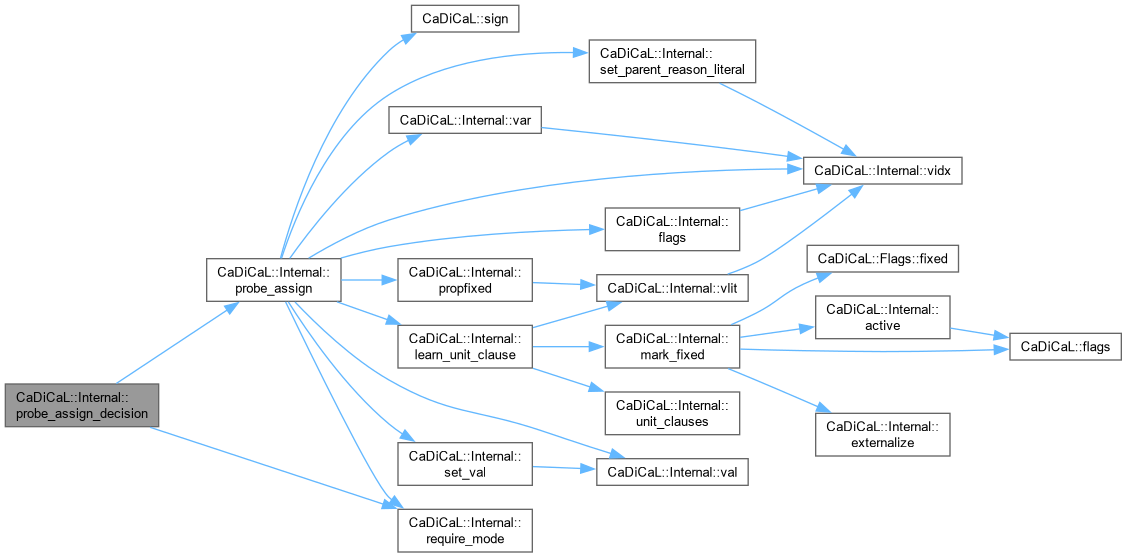
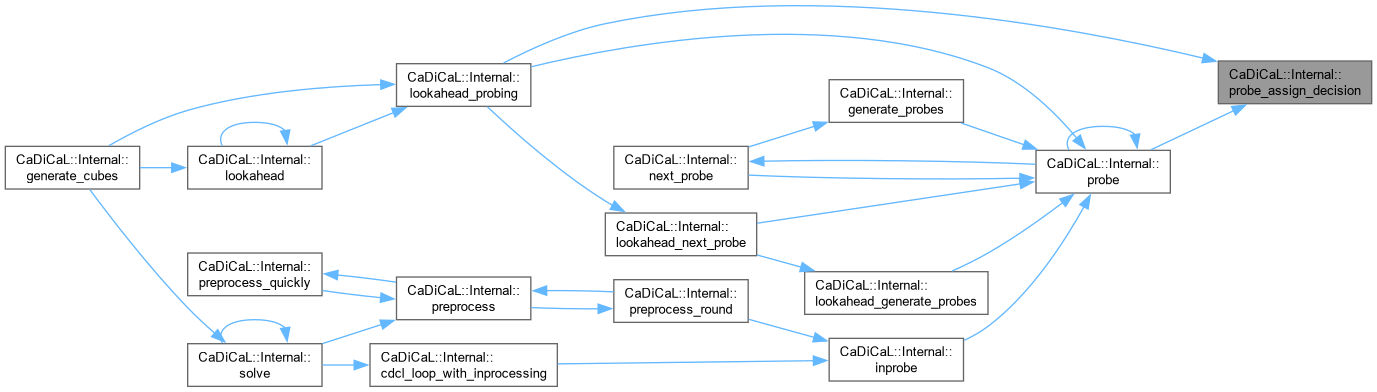
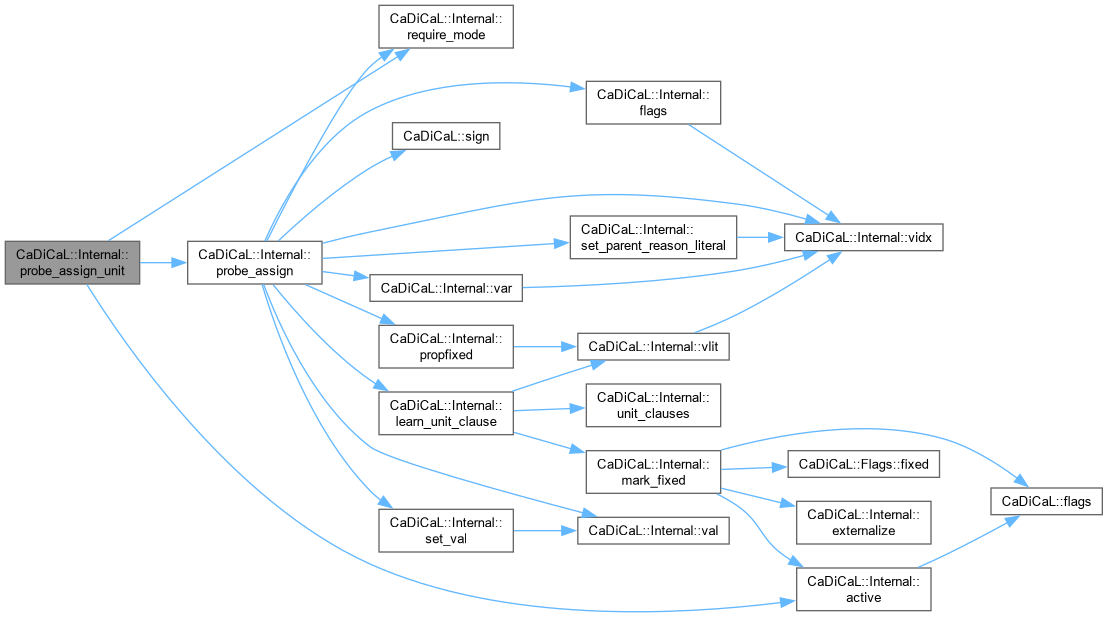
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::probe_assign_unit | ( | int | lit | ) |
Definition at line 345 of file cadical_probe.cpp.
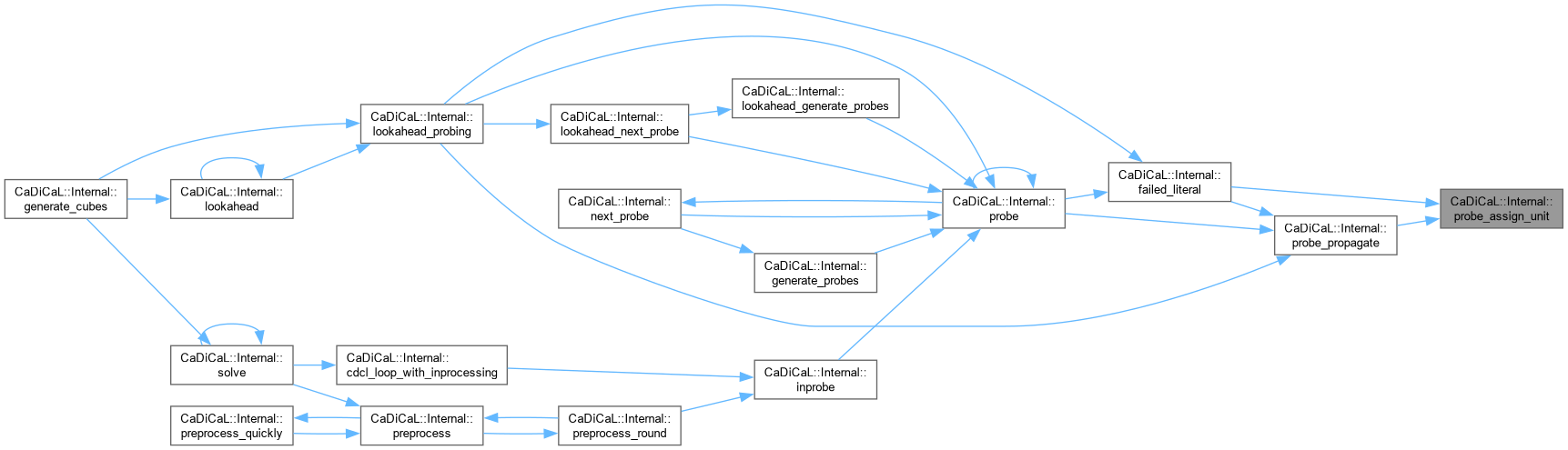
| int CaDiCaL::Internal::probe_dominator | ( | int | a, |
| int | b ) |
Definition at line 154 of file cadical_probe.cpp.
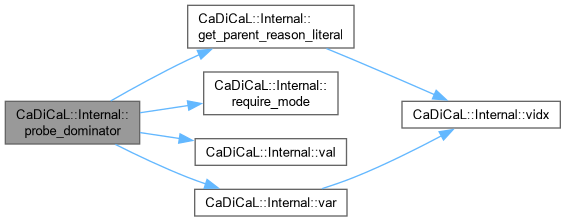
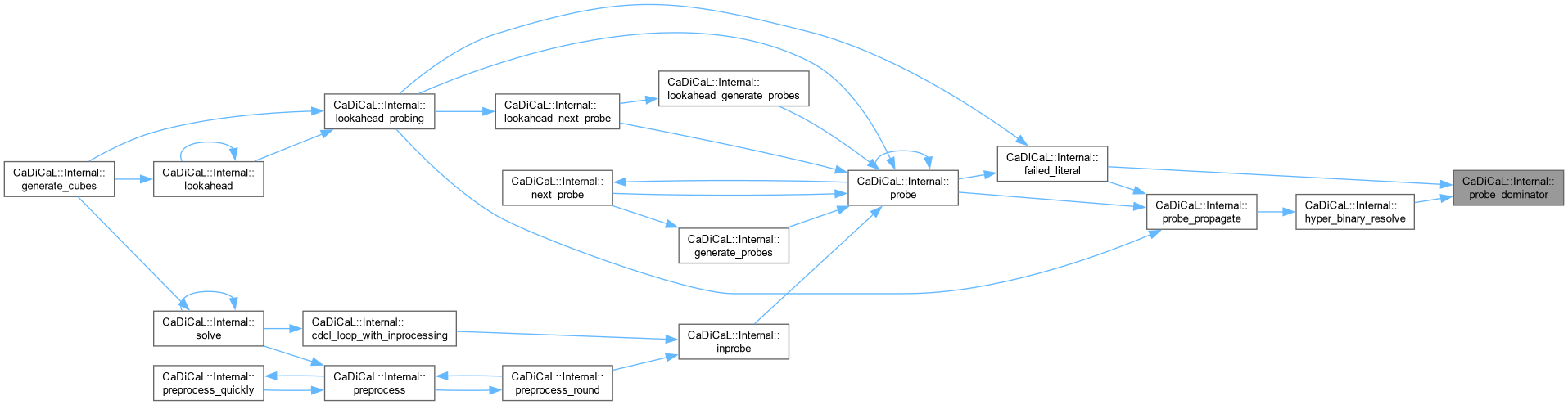
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::probe_dominator_lrat | ( | int | dom, |
| Clause * | reason ) |
Definition at line 117 of file cadical_probe.cpp.
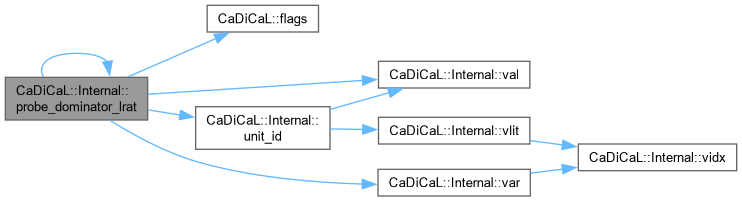
|
inline |
Definition at line 356 of file cadical_probe.cpp.
| bool CaDiCaL::Internal::probe_propagate | ( | ) |
Definition at line 416 of file cadical_probe.cpp.
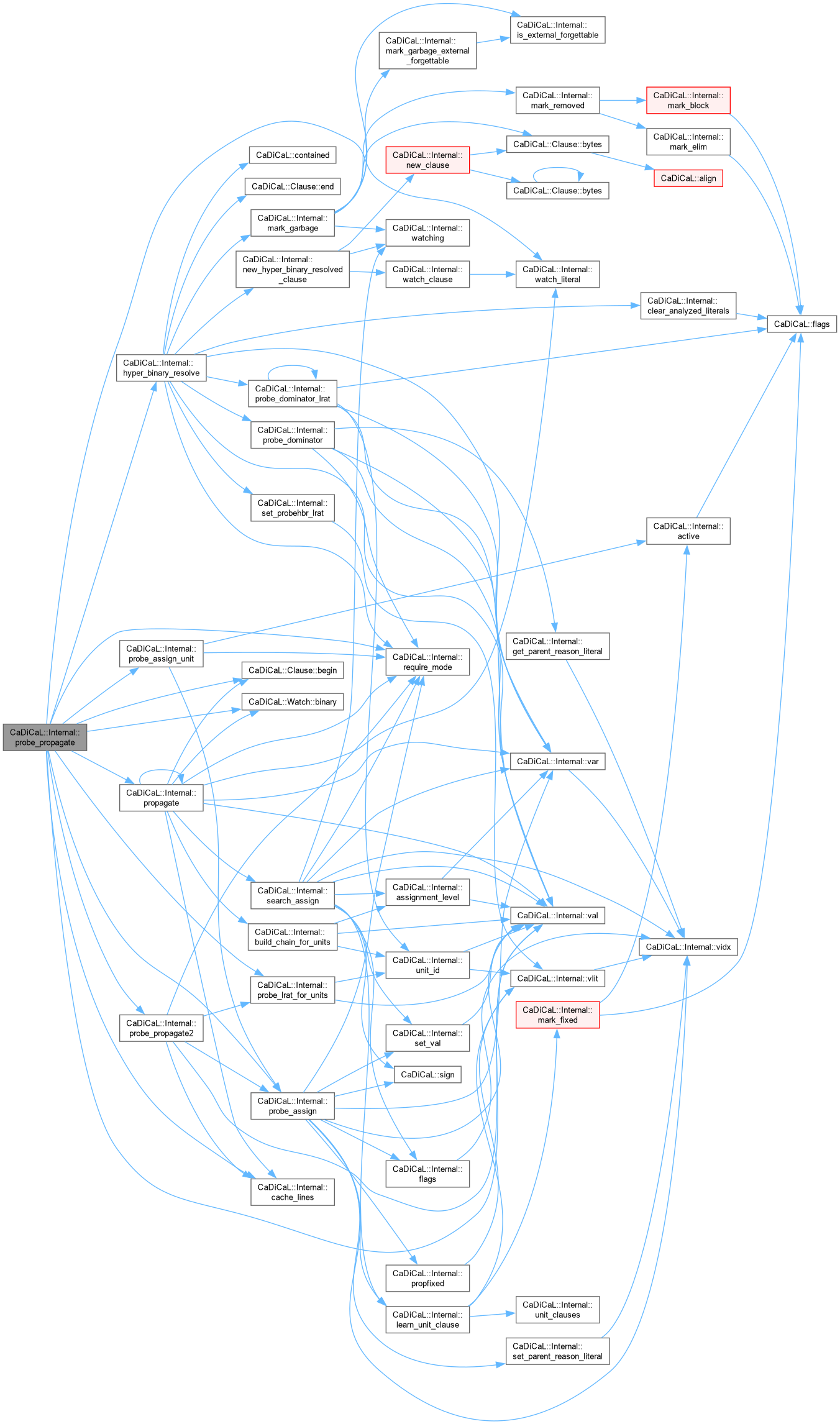
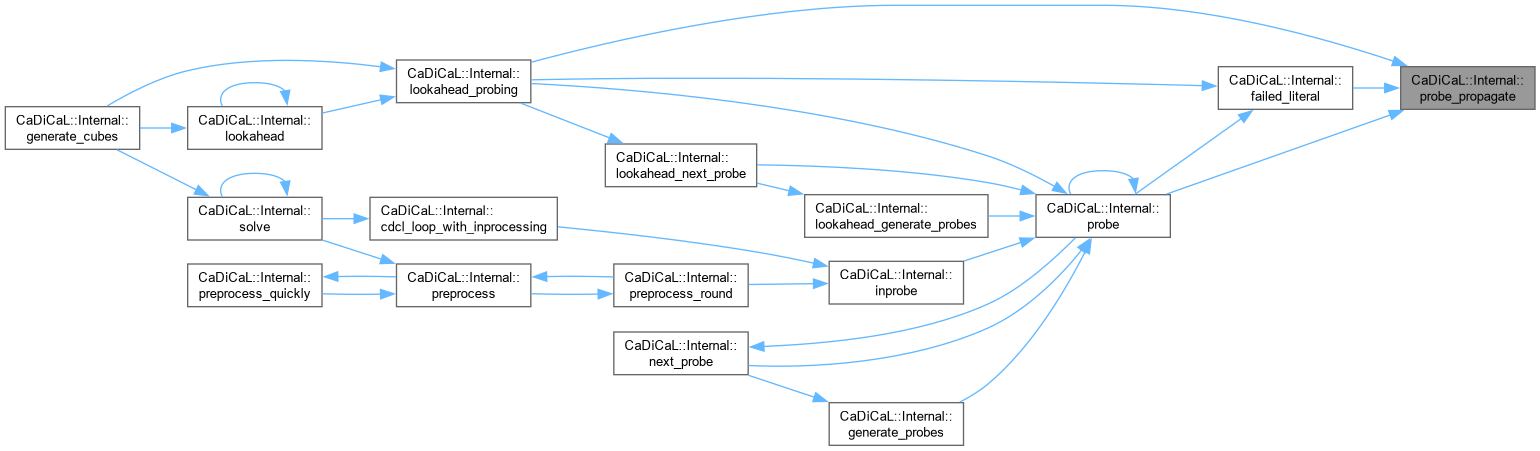
|
inline |
Definition at line 387 of file cadical_probe.cpp.
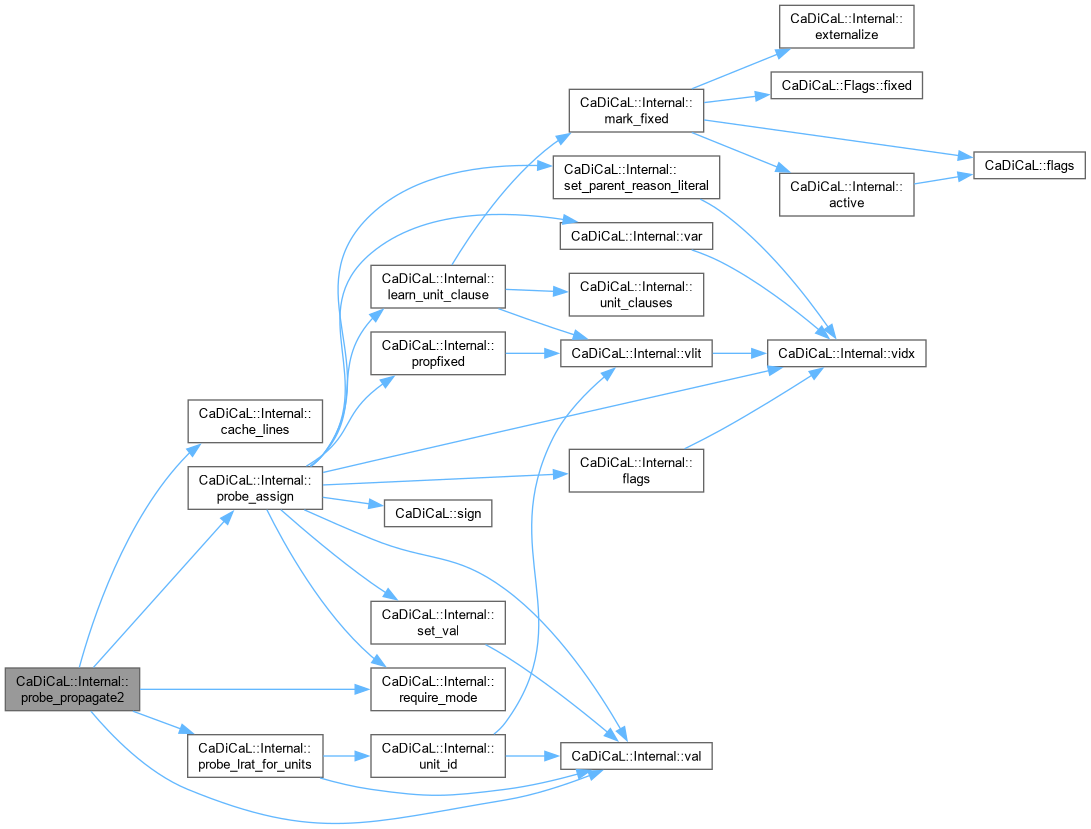
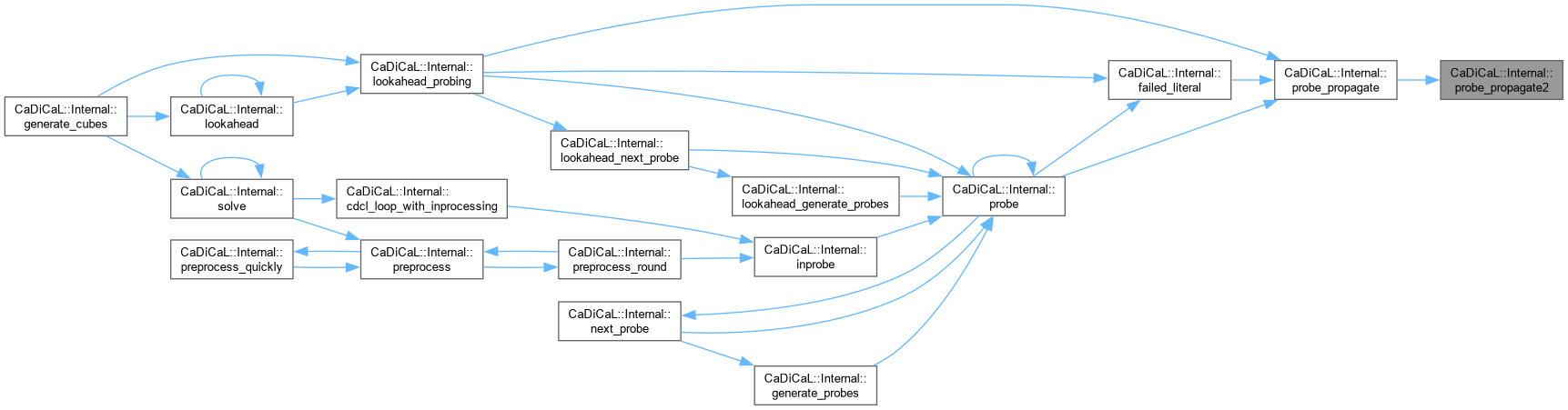
| double CaDiCaL::Internal::process_time | ( | ) | const |
Definition at line 105 of file cadical_resources.cpp.

| void CaDiCaL::Internal::produce_failed_assumptions | ( | ) |
Definition at line 796 of file cadical_internal.cpp.
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::promote_clause | ( | Clause * | c, |
| int | new_glue ) |
Definition at line 152 of file cadical_clause.cpp.
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::promote_clause_glue_only | ( | Clause * | c, |
| int | new_glue ) |
Definition at line 179 of file cadical_clause.cpp.
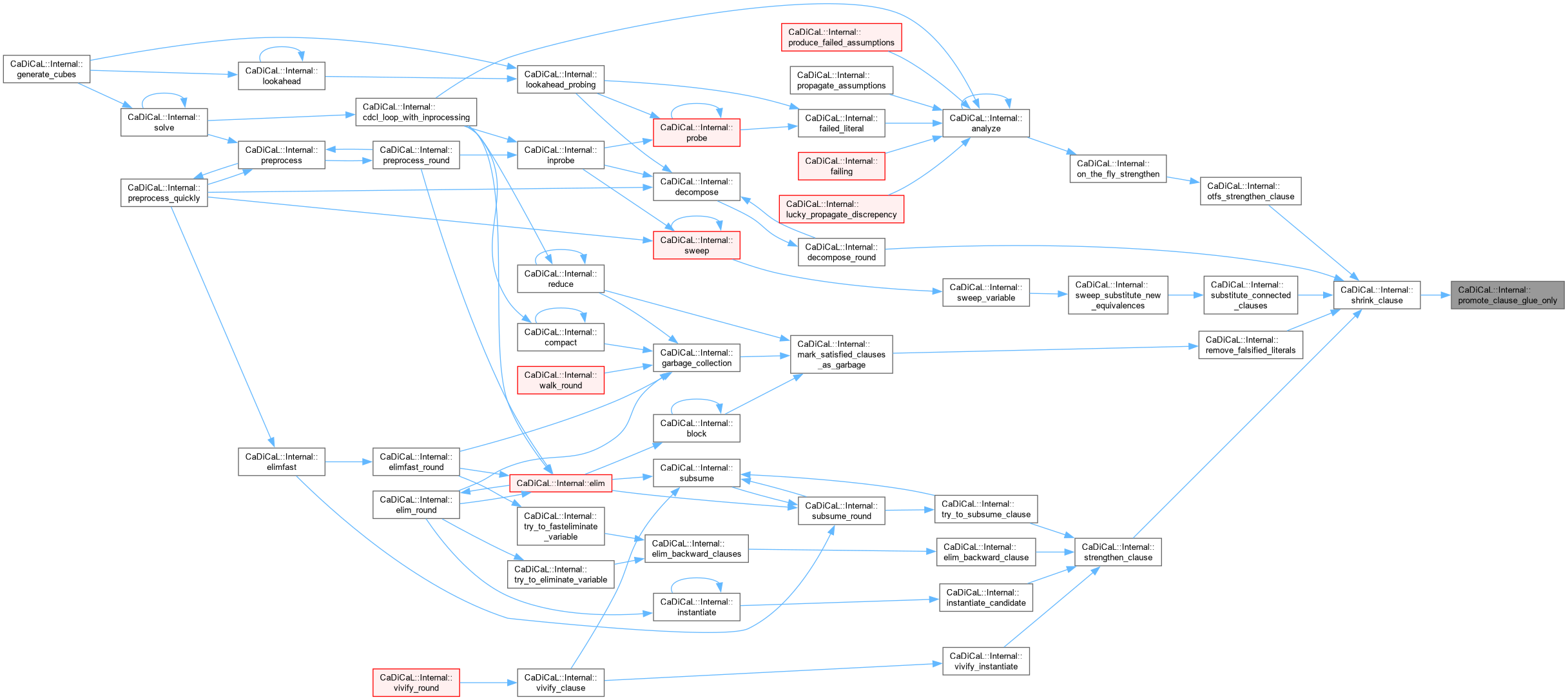
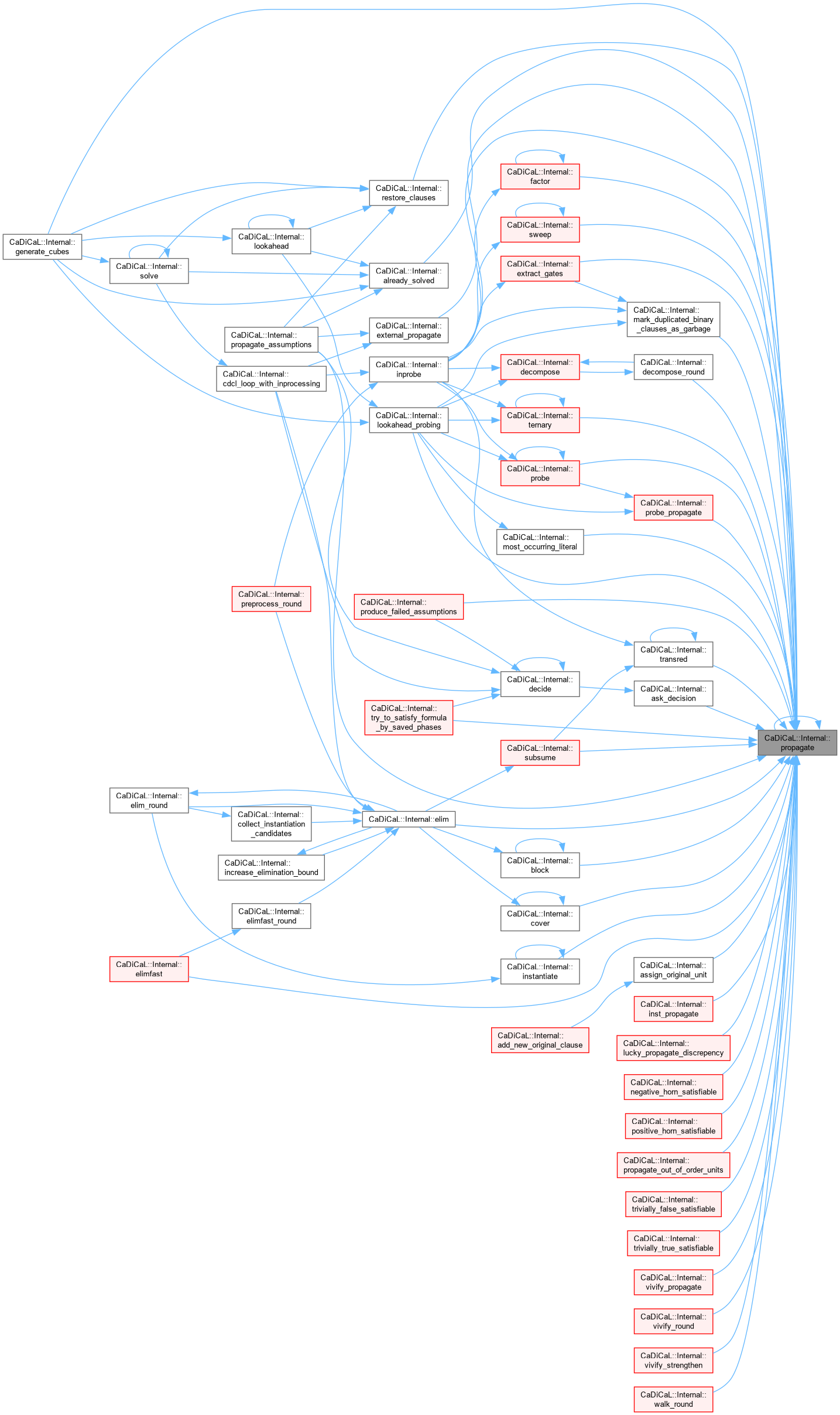
| bool CaDiCaL::Internal::propagate | ( | ) |
Definition at line 232 of file cadical_propagate.cpp.
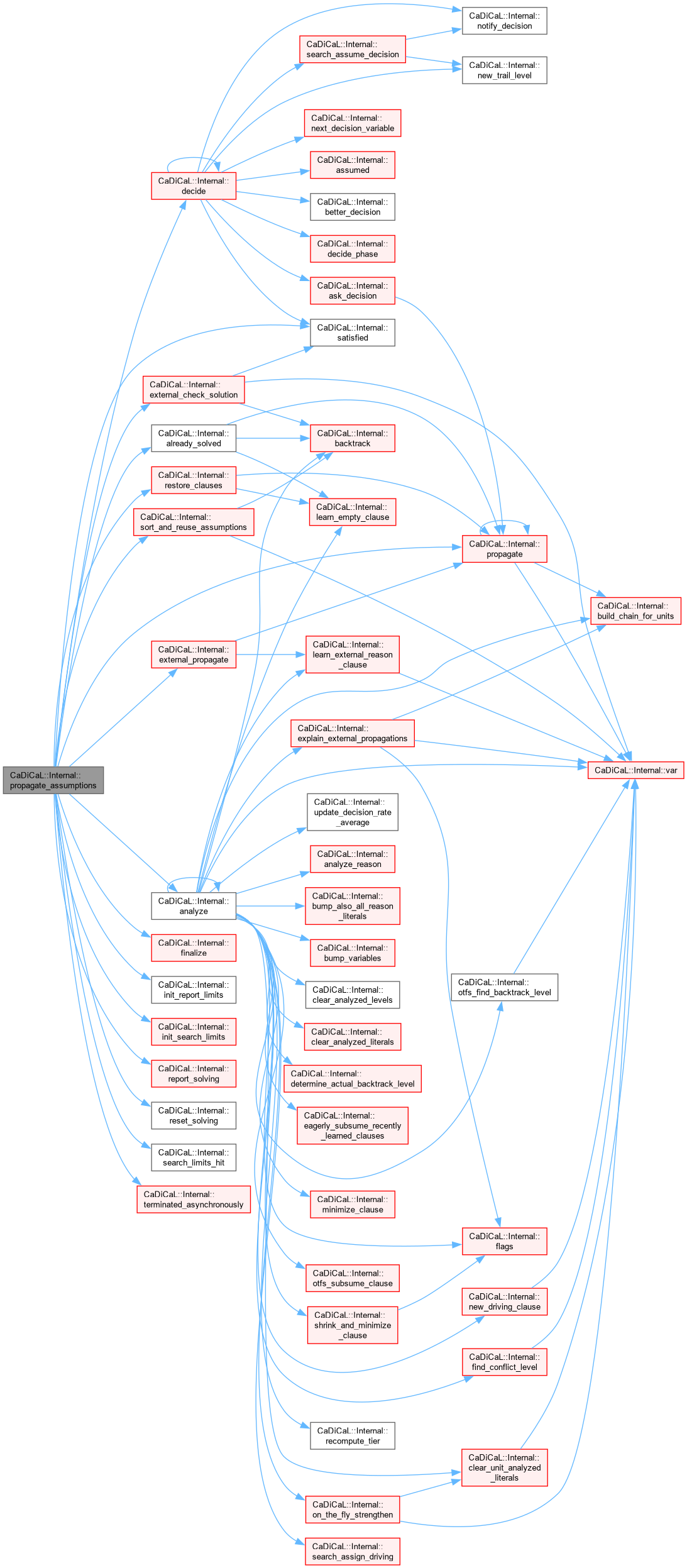
| int CaDiCaL::Internal::propagate_assumptions | ( | ) |
Definition at line 347 of file cadical_internal.cpp.
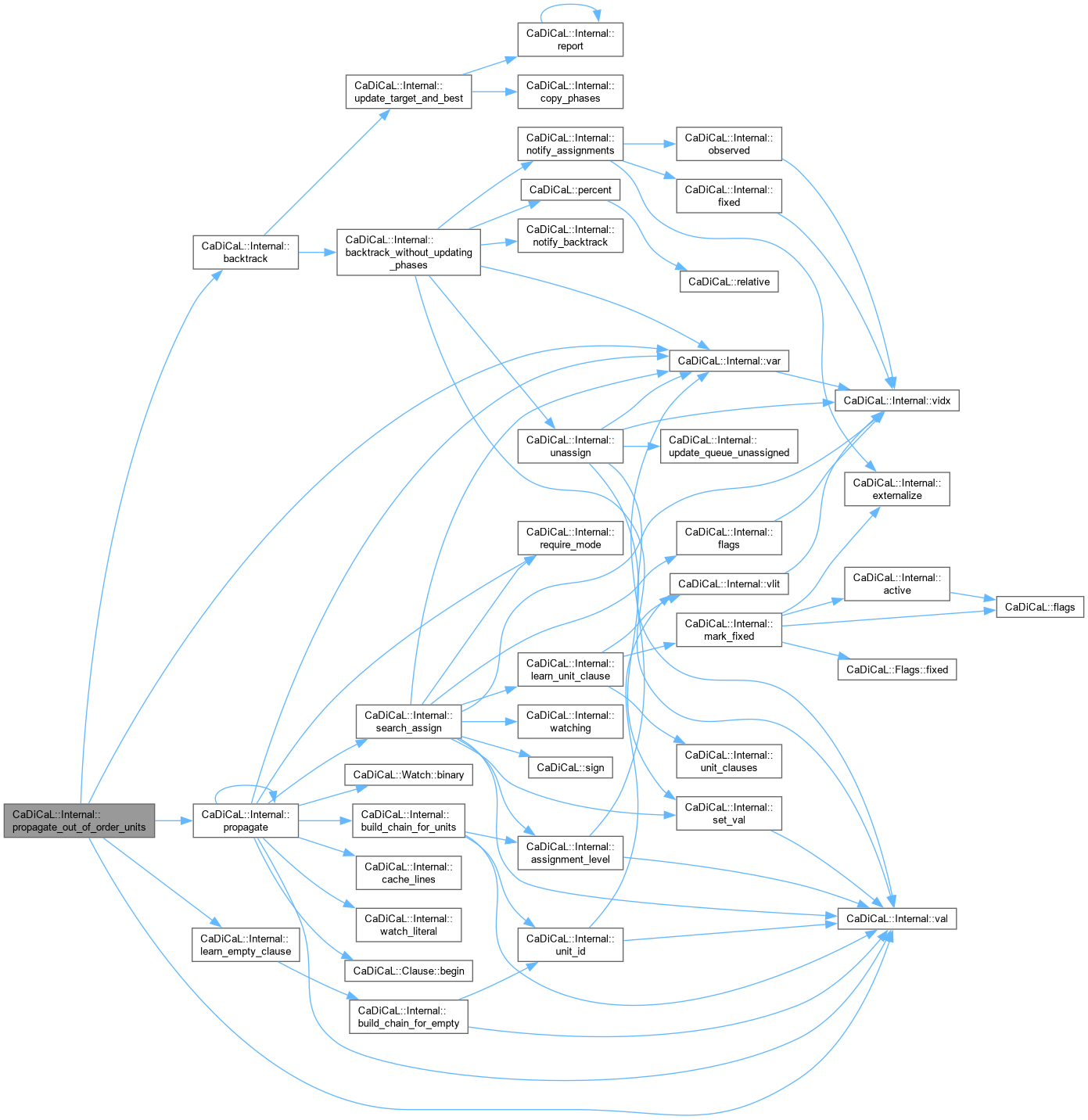
| bool CaDiCaL::Internal::propagate_out_of_order_units | ( | ) |
Definition at line 176 of file cadical_reduce.cpp.

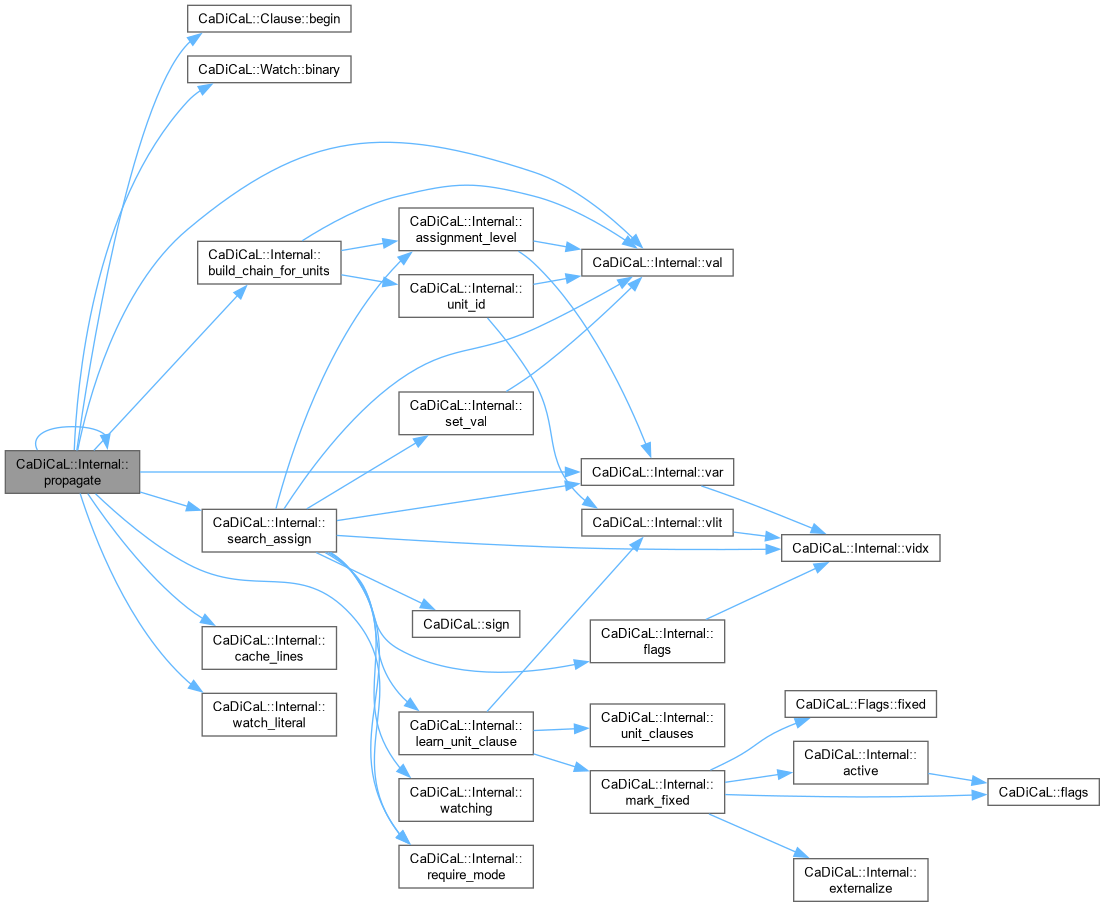
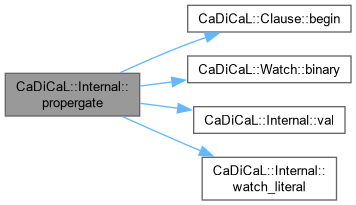
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::propergate | ( | ) |
Definition at line 502 of file cadical_propagate.cpp.
|
inline |
Definition at line 456 of file internal.hpp.

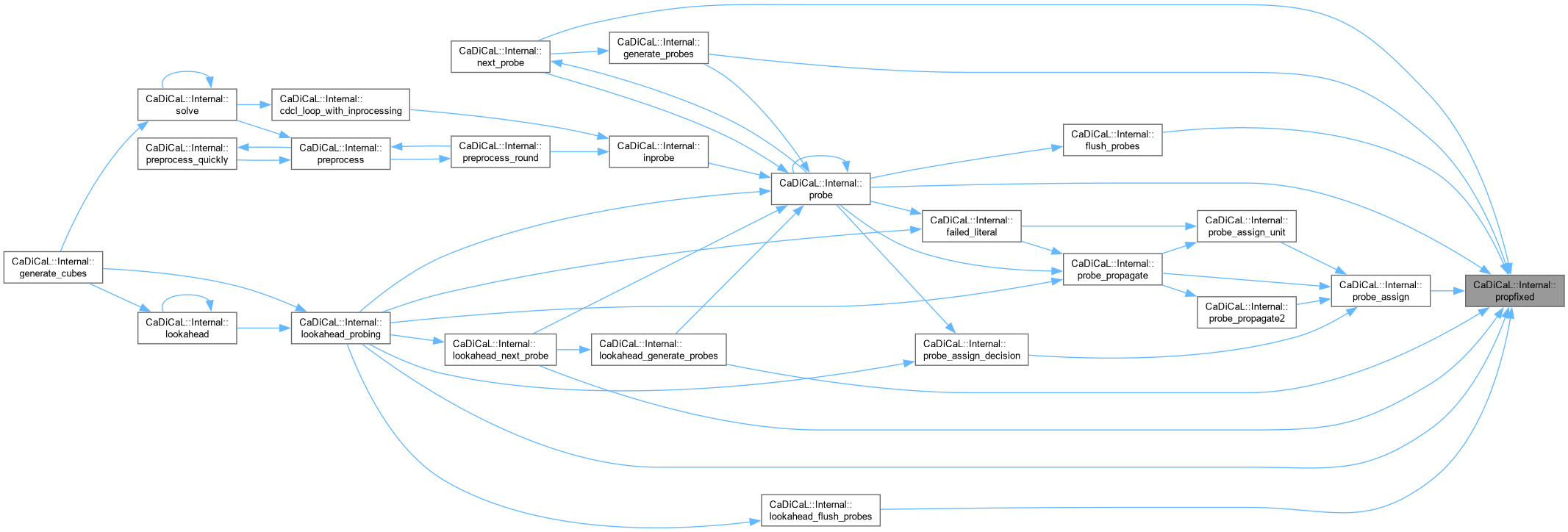
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::protect_reasons | ( | ) |
Definition at line 107 of file cadical_collect.cpp.
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::push_literals_of_block | ( | const std::vector< int >::reverse_iterator & | rbegin_block, |
| const std::vector< int >::reverse_iterator & | rend_block, | ||
| int | blevel, | ||
| unsigned | max_trail ) |
Definition at line 185 of file cadical_shrink.cpp.
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::reactivate | ( | int | lit | ) |
Definition at line 93 of file cadical_flags.cpp.

| double CaDiCaL::Internal::real_time | ( | ) | const |
Definition at line 101 of file cadical_resources.cpp.
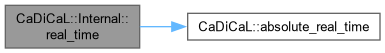

| int CaDiCaL::Internal::recompute_glue | ( | Clause * | c | ) |
Definition at line 210 of file cadical_analyze.cpp.

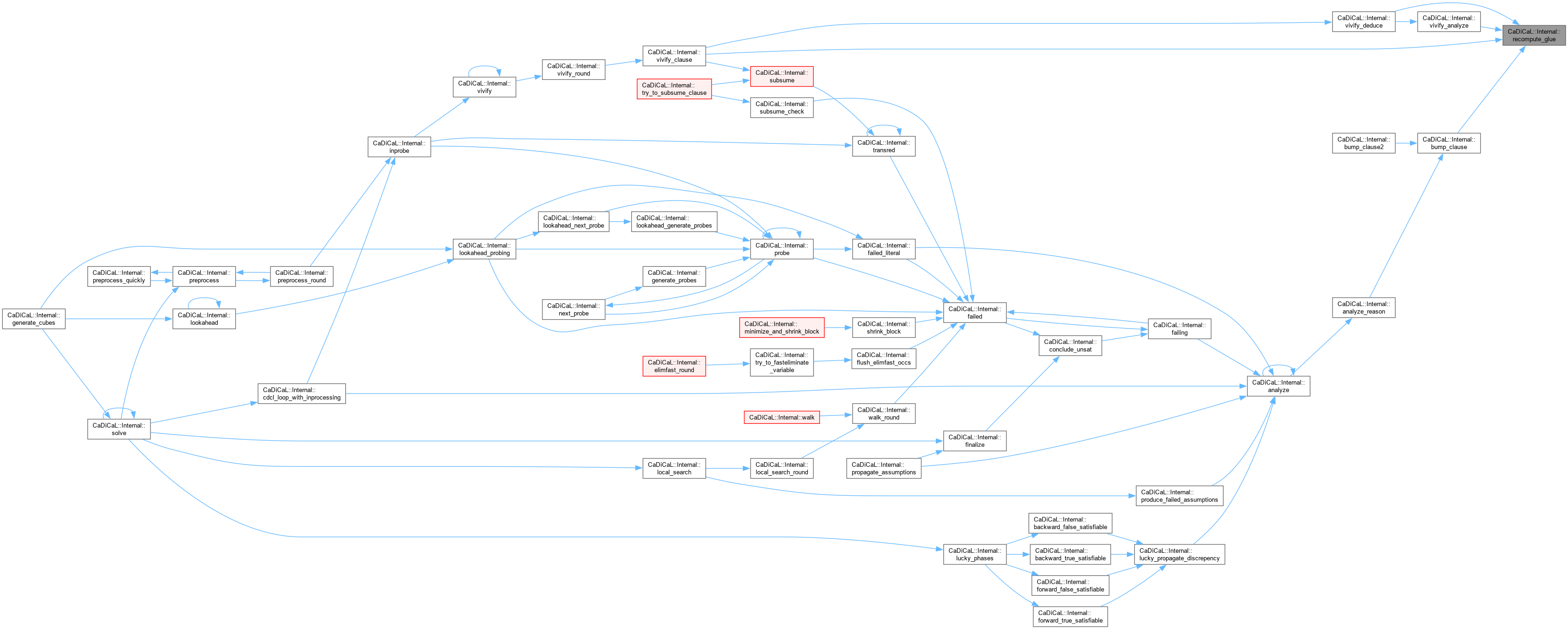
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::recompute_tier | ( | ) |
Definition at line 9 of file cadical_tier.cpp.
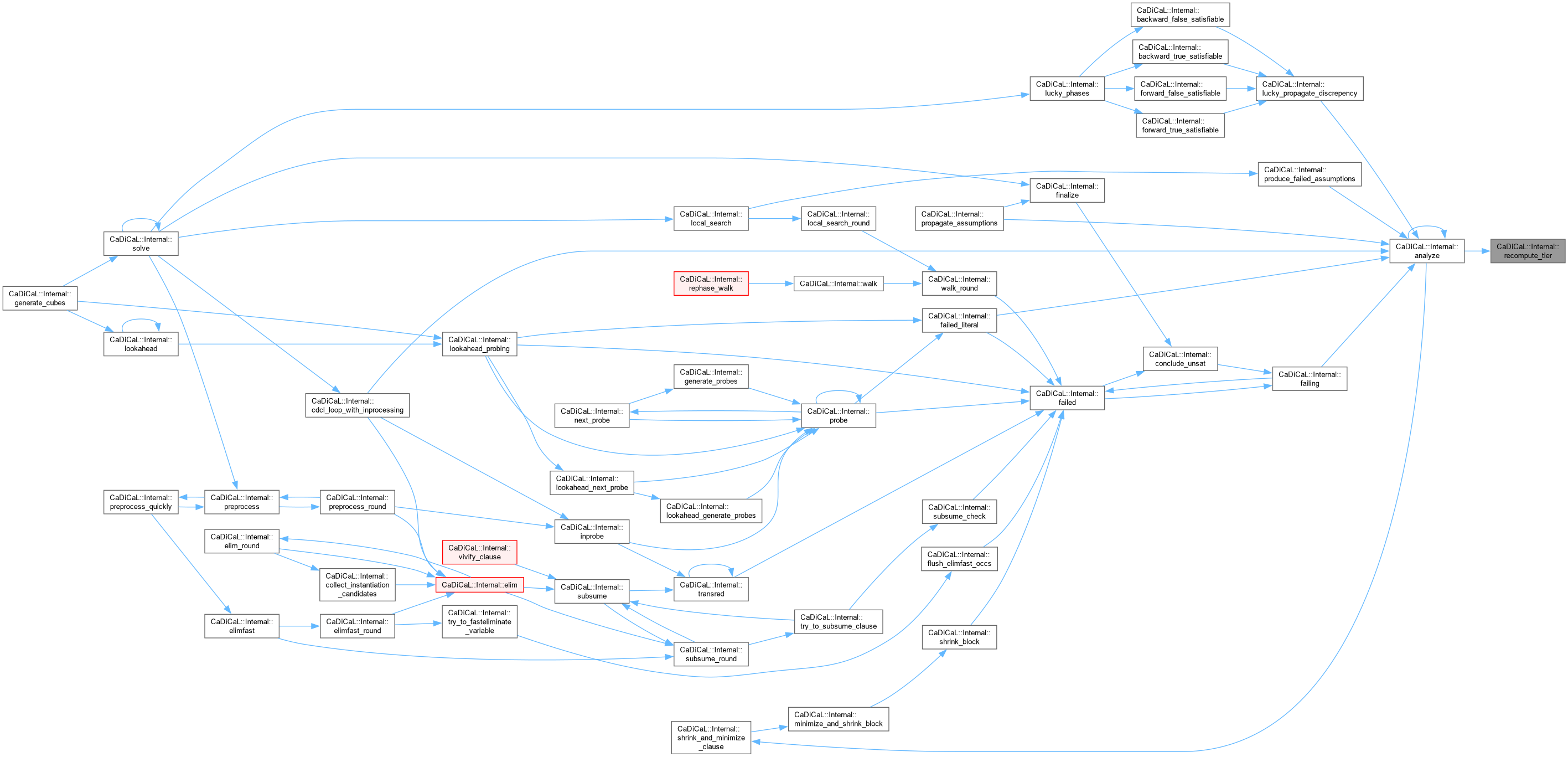
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::reduce | ( | ) |
Definition at line 217 of file cadical_reduce.cpp.
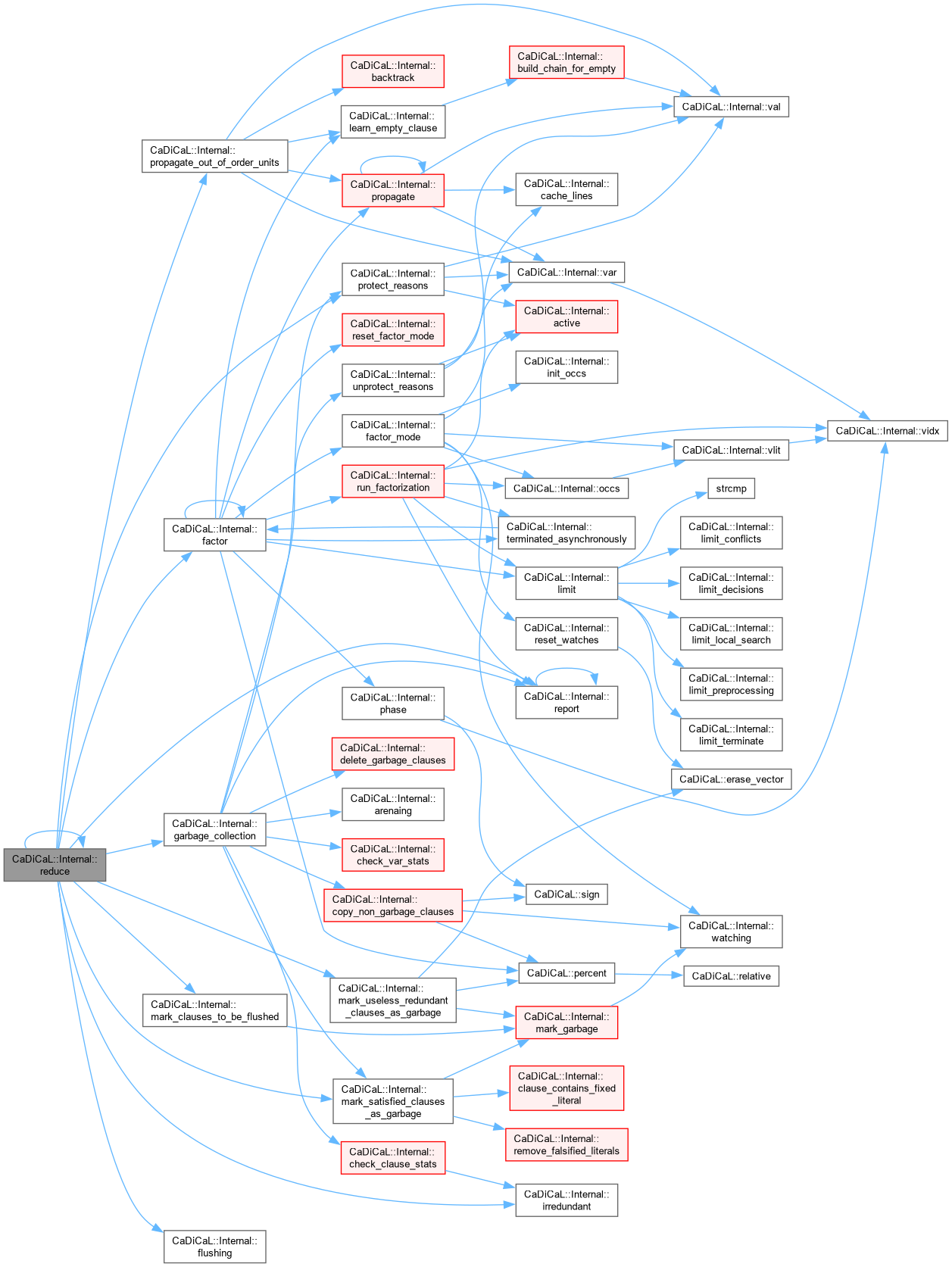
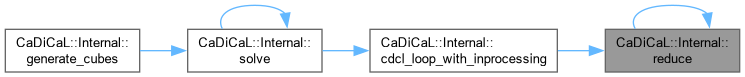
| bool CaDiCaL::Internal::reducing | ( | ) |
|
inline |
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::release_quotients | ( | Factoring & | factoring | ) |
Definition at line 173 of file cadical_factor.cpp.
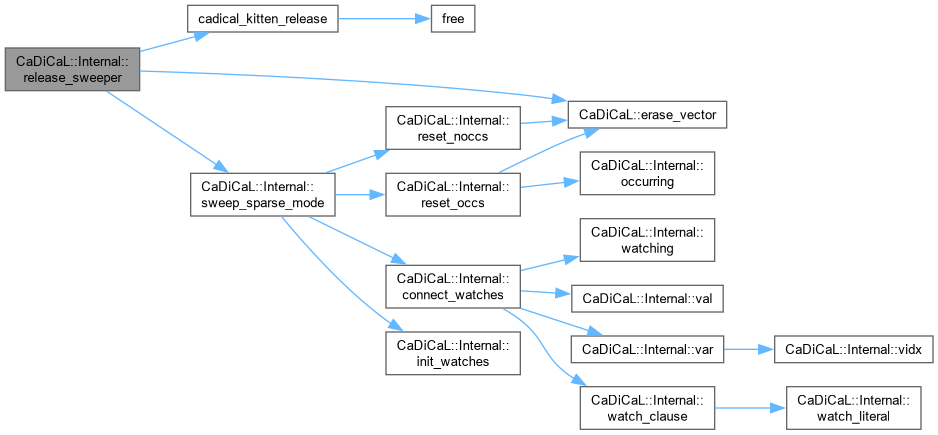
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::release_sweeper | ( | Sweeper & | sweeper | ) |
Definition at line 275 of file cadical_sweep.cpp.
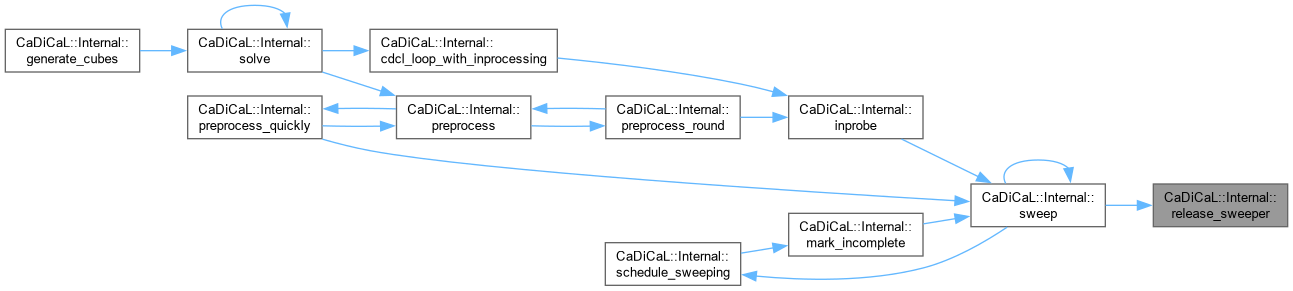
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::remove_falsified_literals | ( | Clause * | c | ) |
Definition at line 44 of file cadical_collect.cpp.
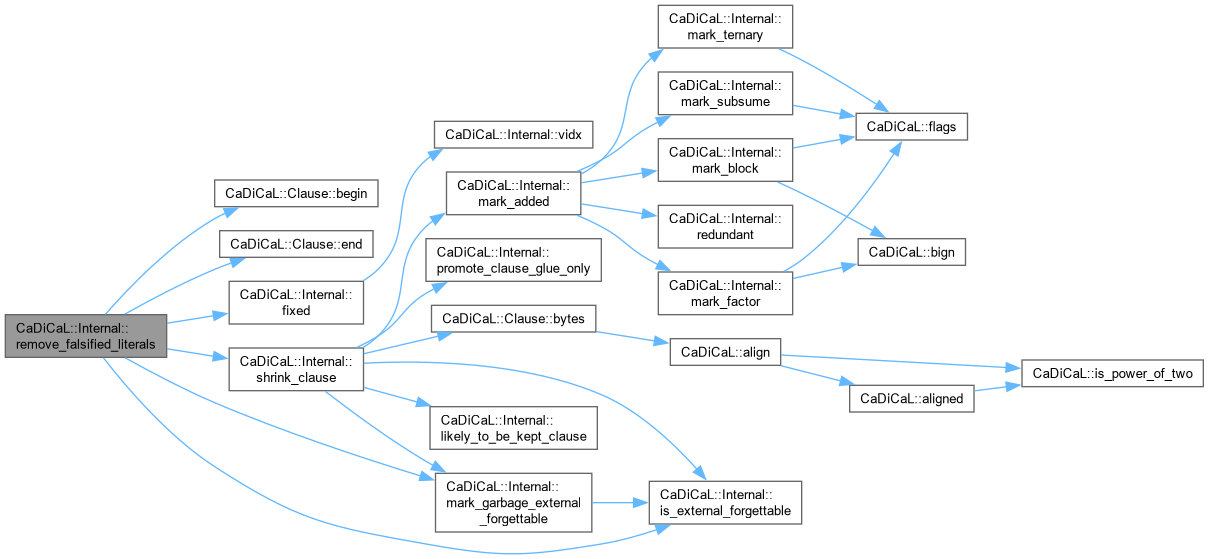
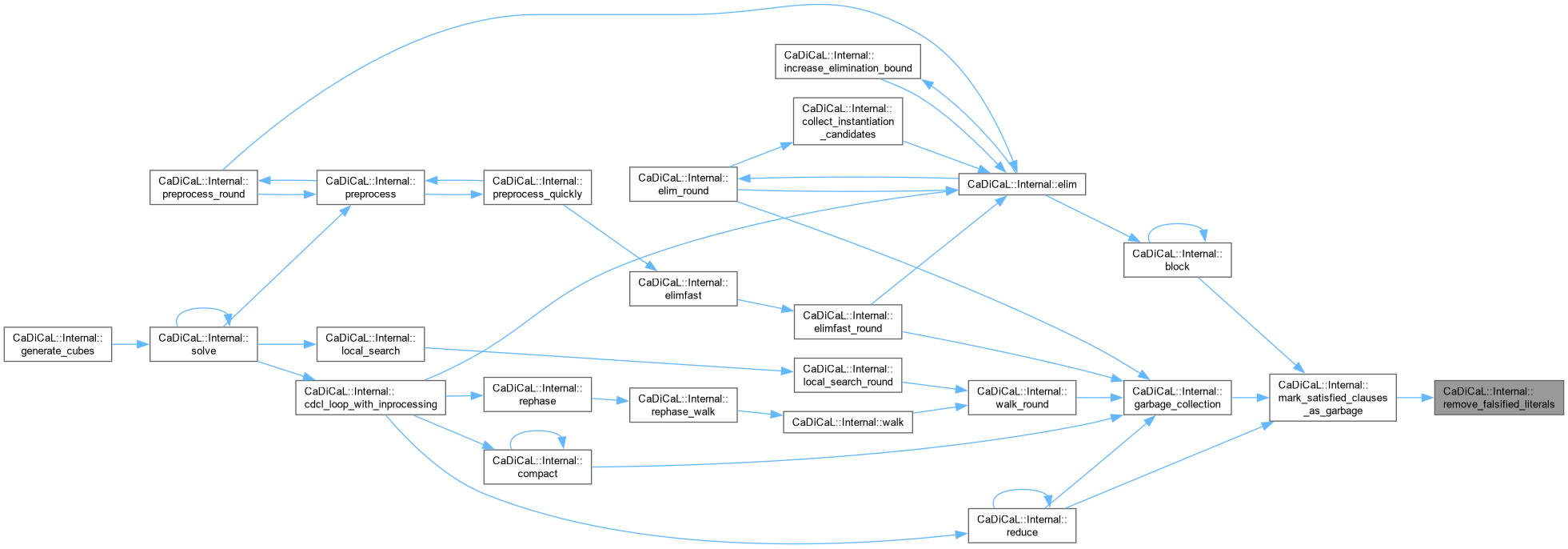
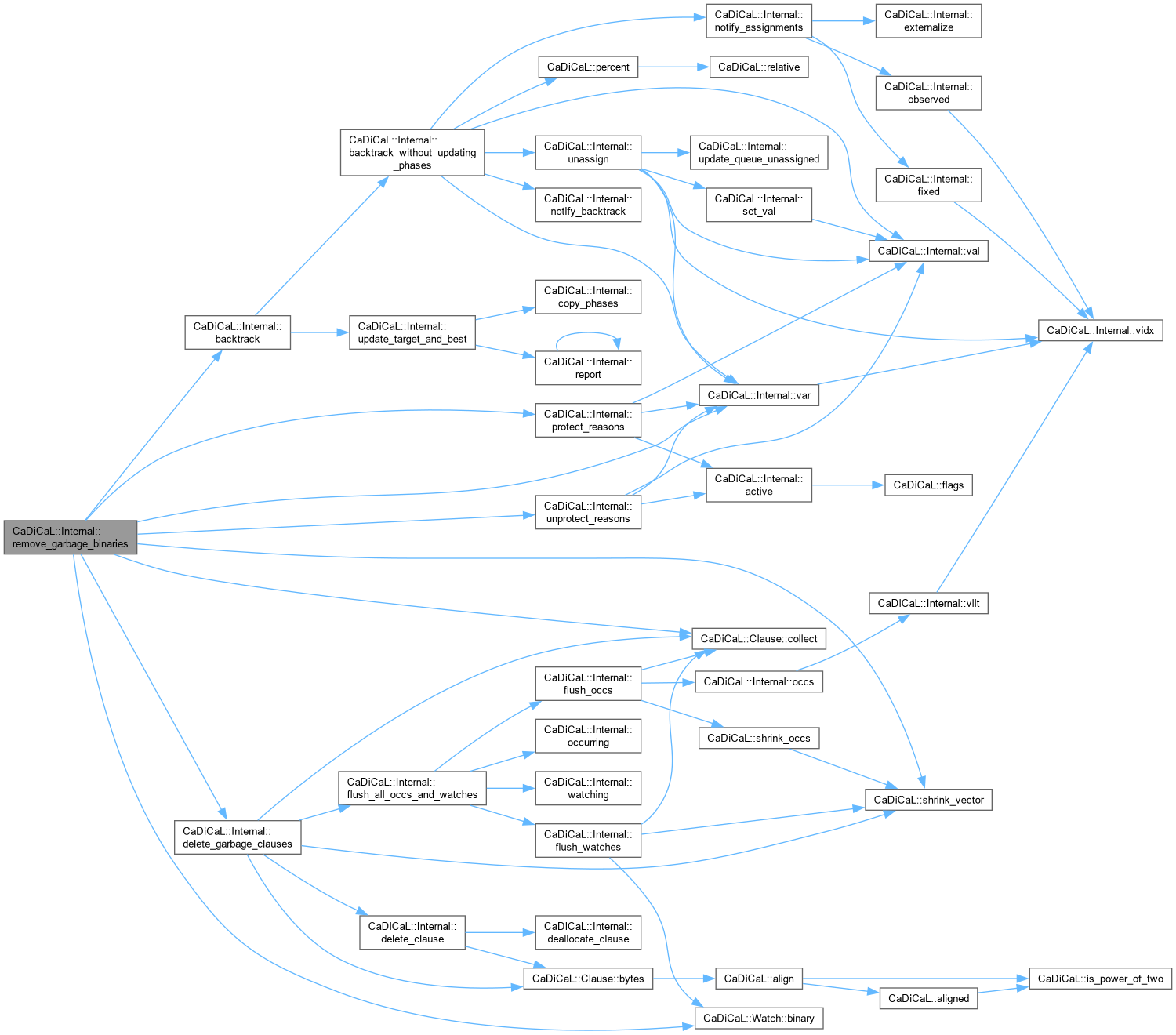
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::remove_garbage_binaries | ( | ) |
Definition at line 477 of file cadical_collect.cpp.
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::remove_observed_var | ( | int | ilit | ) |
Definition at line 45 of file cadical_external_propagate.cpp.
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::renotify_full_trail | ( | ) |
Definition at line 130 of file cadical_external_propagate.cpp.
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::renotify_trail_after_ilb | ( | ) |
Definition at line 101 of file cadical_external_propagate.cpp.

| void CaDiCaL::Internal::renotify_trail_after_local_search | ( | ) |
Definition at line 114 of file cadical_external_propagate.cpp.

| void CaDiCaL::Internal::rephase | ( | ) |
Definition at line 108 of file cadical_rephase.cpp.
| char CaDiCaL::Internal::rephase_best | ( | ) |
Definition at line 85 of file cadical_rephase.cpp.

| char CaDiCaL::Internal::rephase_flipping | ( | ) |
| char CaDiCaL::Internal::rephase_inverted | ( | ) |
Definition at line 49 of file cadical_rephase.cpp.

| char CaDiCaL::Internal::rephase_original | ( | ) |
Definition at line 37 of file cadical_rephase.cpp.

| char CaDiCaL::Internal::rephase_random | ( | ) |
Definition at line 72 of file cadical_rephase.cpp.


| char CaDiCaL::Internal::rephase_walk | ( | ) |
Definition at line 98 of file cadical_rephase.cpp.

| bool CaDiCaL::Internal::rephasing | ( | ) |
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::report | ( | char | type, |
| int | verbose_level = 0 ) |
Definition at line 296 of file cadical_report.cpp.

| void CaDiCaL::Internal::report_solving | ( | int | res | ) |
Definition at line 959 of file cadical_internal.cpp.
|
inline |
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::rescale_variable_scores | ( | ) |
Definition at line 89 of file cadical_analyze.cpp.
| unsigned CaDiCaL::Internal::reschedule_previously_remaining | ( | Sweeper & | sweeper | ) |
Definition at line 1773 of file cadical_sweep.cpp.
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::reserve_ids | ( | int | number | ) |
Definition at line 233 of file cadical_internal.cpp.
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::reset_assumptions | ( | ) |
Definition at line 502 of file cadical_assume.cpp.


| void CaDiCaL::Internal::reset_bins | ( | ) |
Definition at line 20 of file cadical_bins.cpp.
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::reset_citten | ( | ) |
Definition at line 1011 of file cadical_elim.cpp.

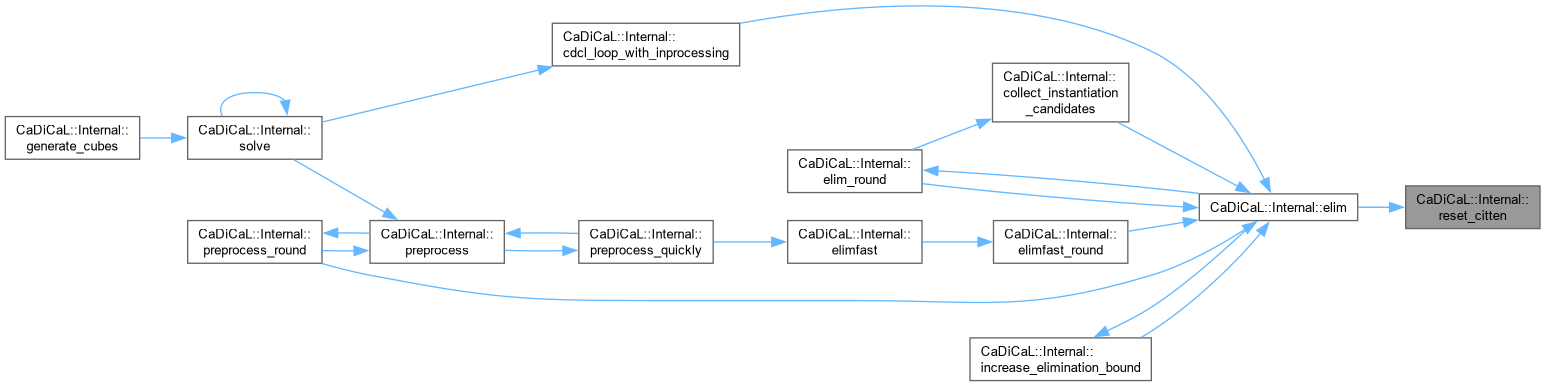
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::reset_concluded | ( | ) |
Definition at line 485 of file cadical_assume.cpp.
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::reset_constraint | ( | ) |
Definition at line 59 of file cadical_constrain.cpp.


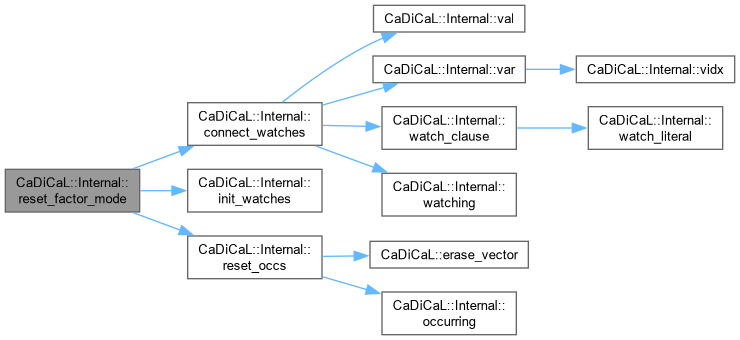
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::reset_factor_mode | ( | ) |
Definition at line 111 of file cadical_factor.cpp.
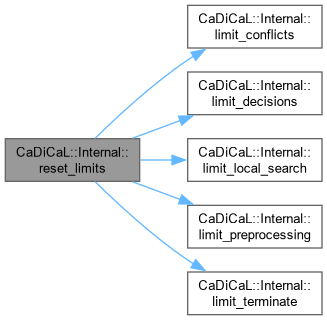
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::reset_limits | ( | ) |
Definition at line 124 of file cadical_limit.cpp.
|
inline |
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::reset_noccs | ( | ) |
Definition at line 50 of file cadical_occs.cpp.
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::reset_occs | ( | ) |
Definition at line 19 of file cadical_occs.cpp.
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::reset_shrinkable | ( | ) |
Definition at line 10 of file cadical_shrink.cpp.
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::reset_solving | ( | ) |
Definition at line 968 of file cadical_internal.cpp.
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::reset_subsume_bits | ( | ) |
Definition at line 9 of file cadical_var.cpp.
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::reset_watches | ( | ) |
Definition at line 21 of file cadical_watch.cpp.
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::resize_factoring | ( | Factoring & | factoring, |
| int | lit ) |
Definition at line 472 of file cadical_factor.cpp.
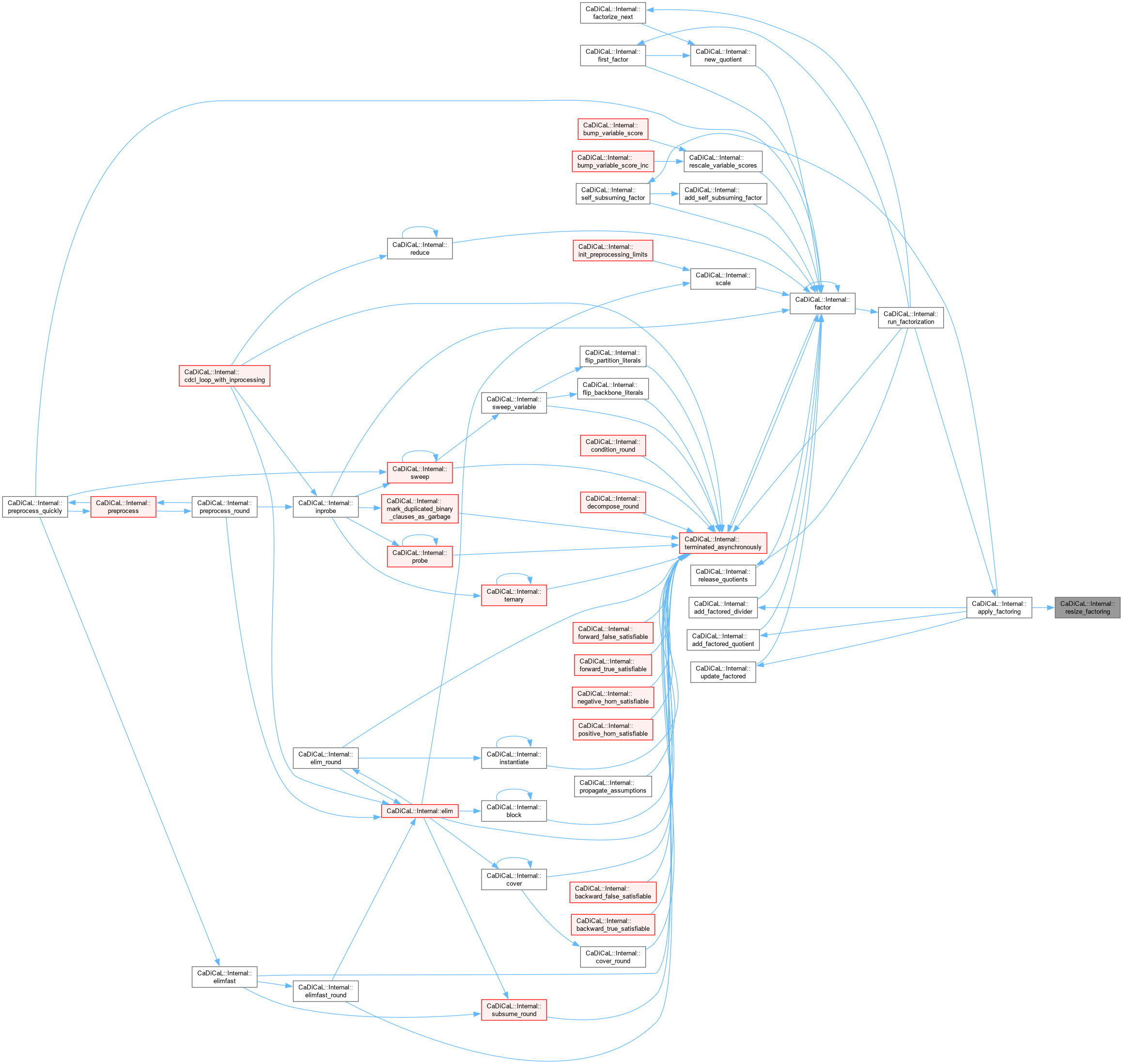
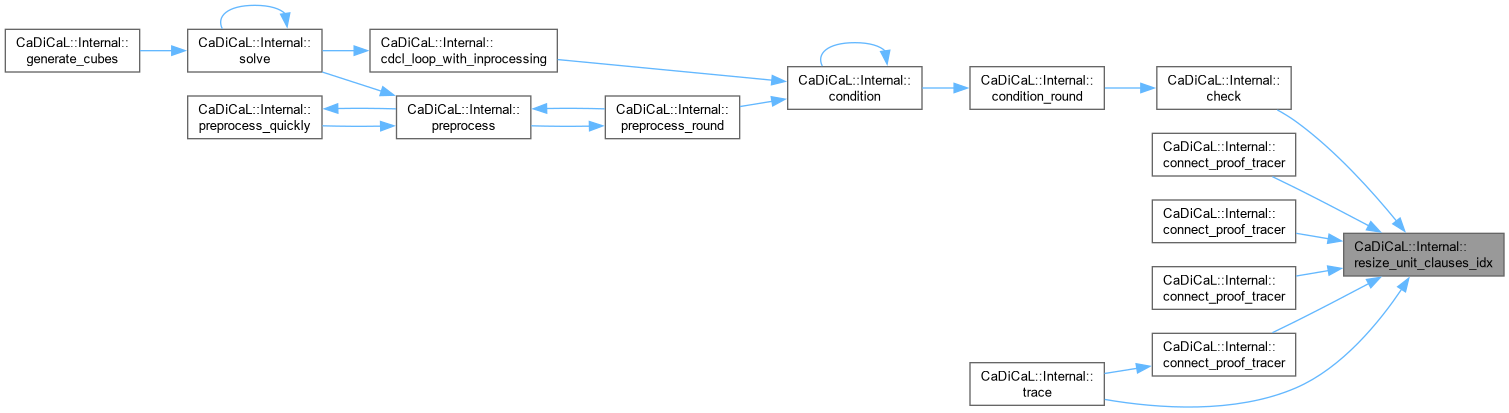
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::resize_unit_clauses_idx | ( | ) |
Definition at line 22 of file cadical_proof.cpp.
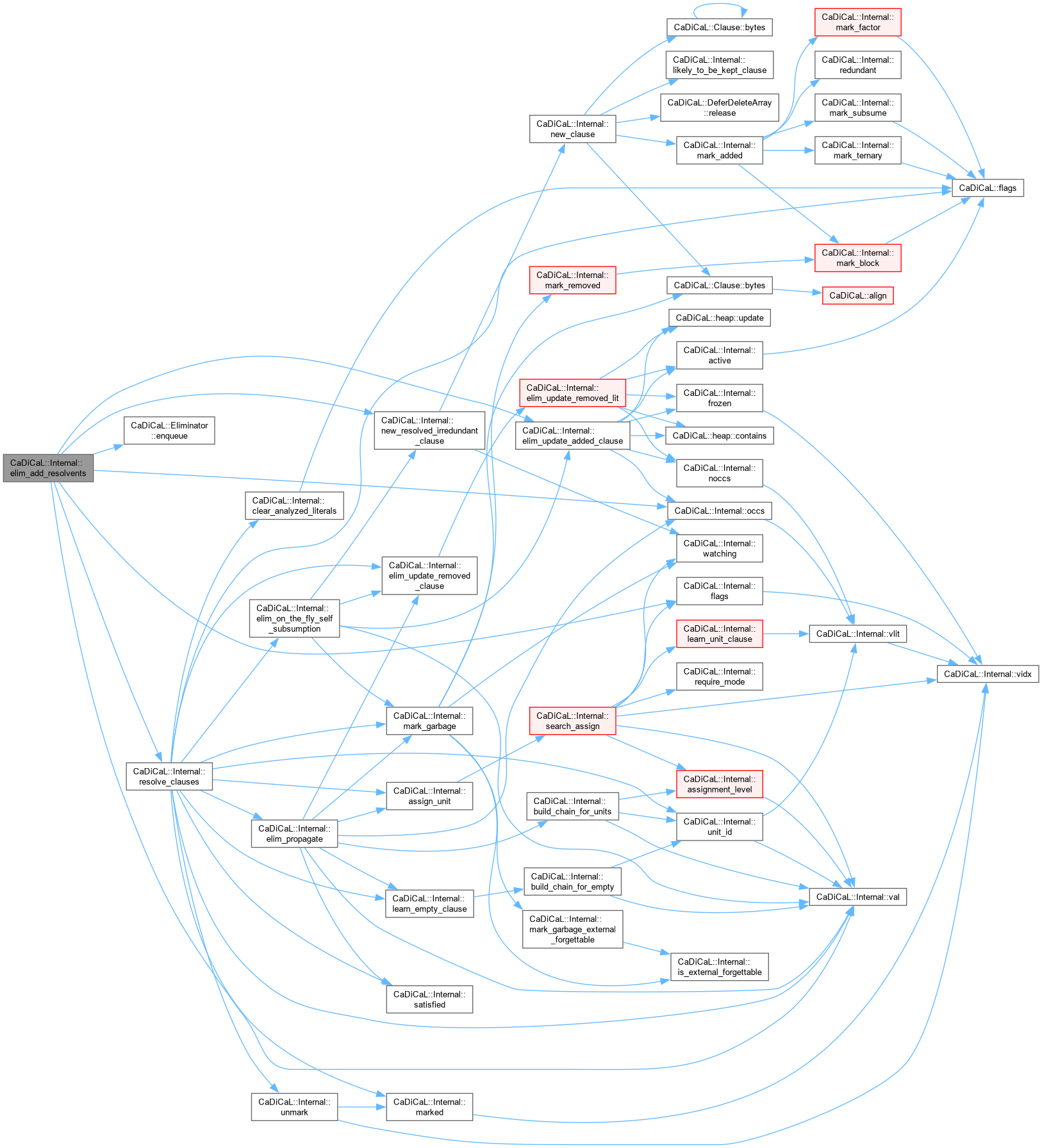
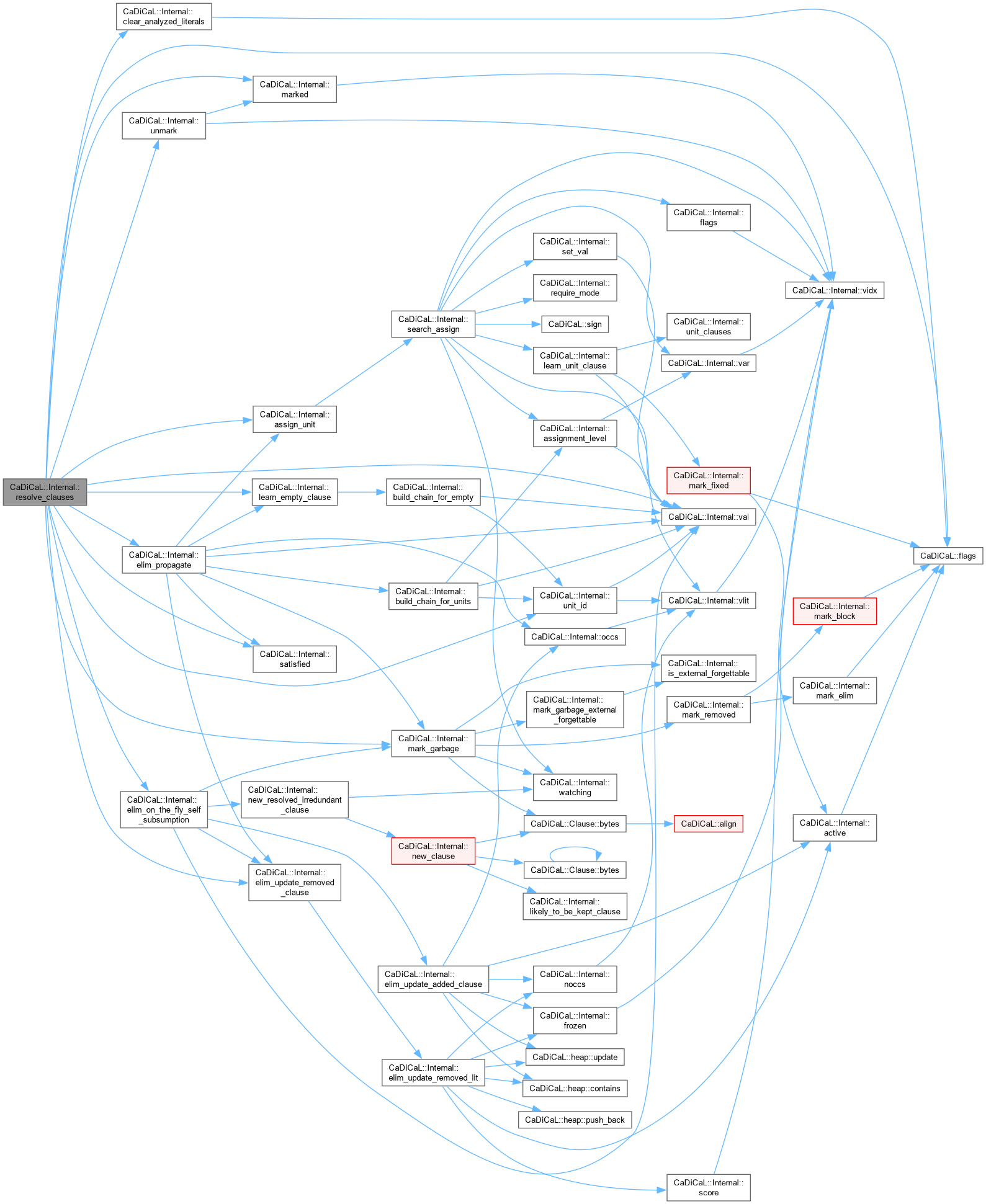
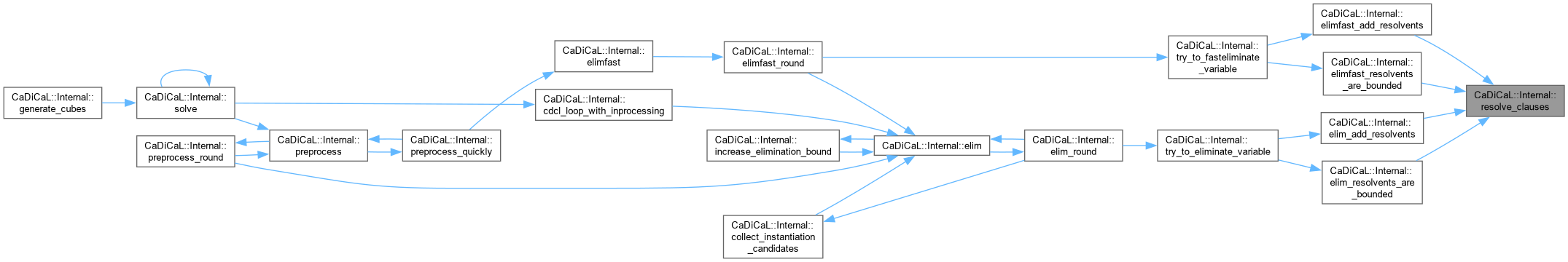
| bool CaDiCaL::Internal::resolve_clauses | ( | Eliminator & | eliminator, |
| Clause * | c, | ||
| int | pivot, | ||
| Clause * | d, | ||
| bool | propagate_eagerly ) |
Definition at line 269 of file cadical_elim.cpp.
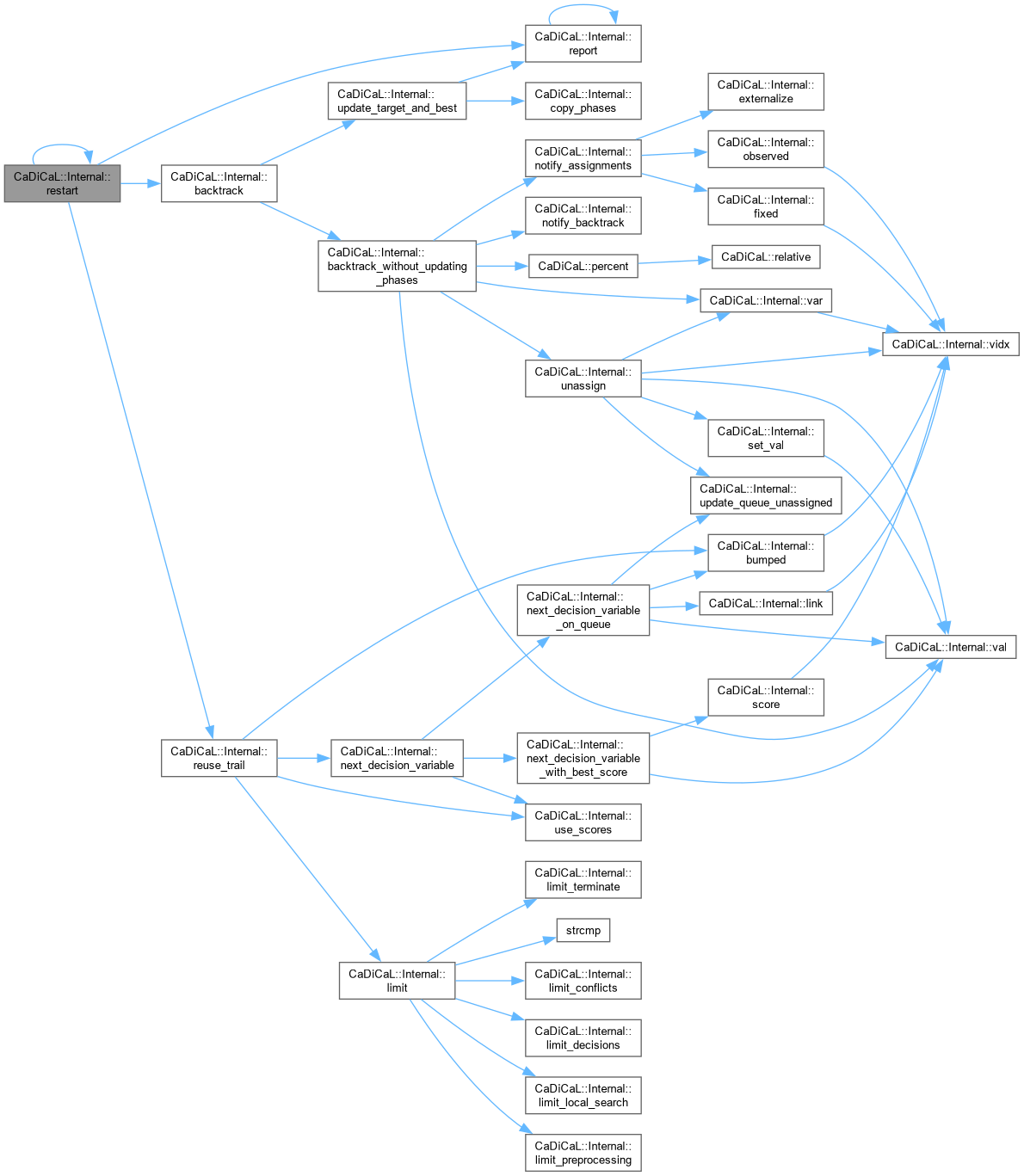
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::restart | ( | ) |
Definition at line 147 of file cadical_restart.cpp.
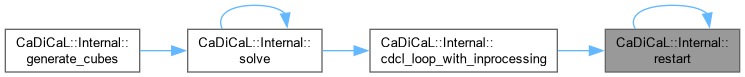
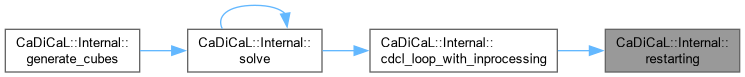
| bool CaDiCaL::Internal::restarting | ( | ) |
Definition at line 89 of file cadical_restart.cpp.
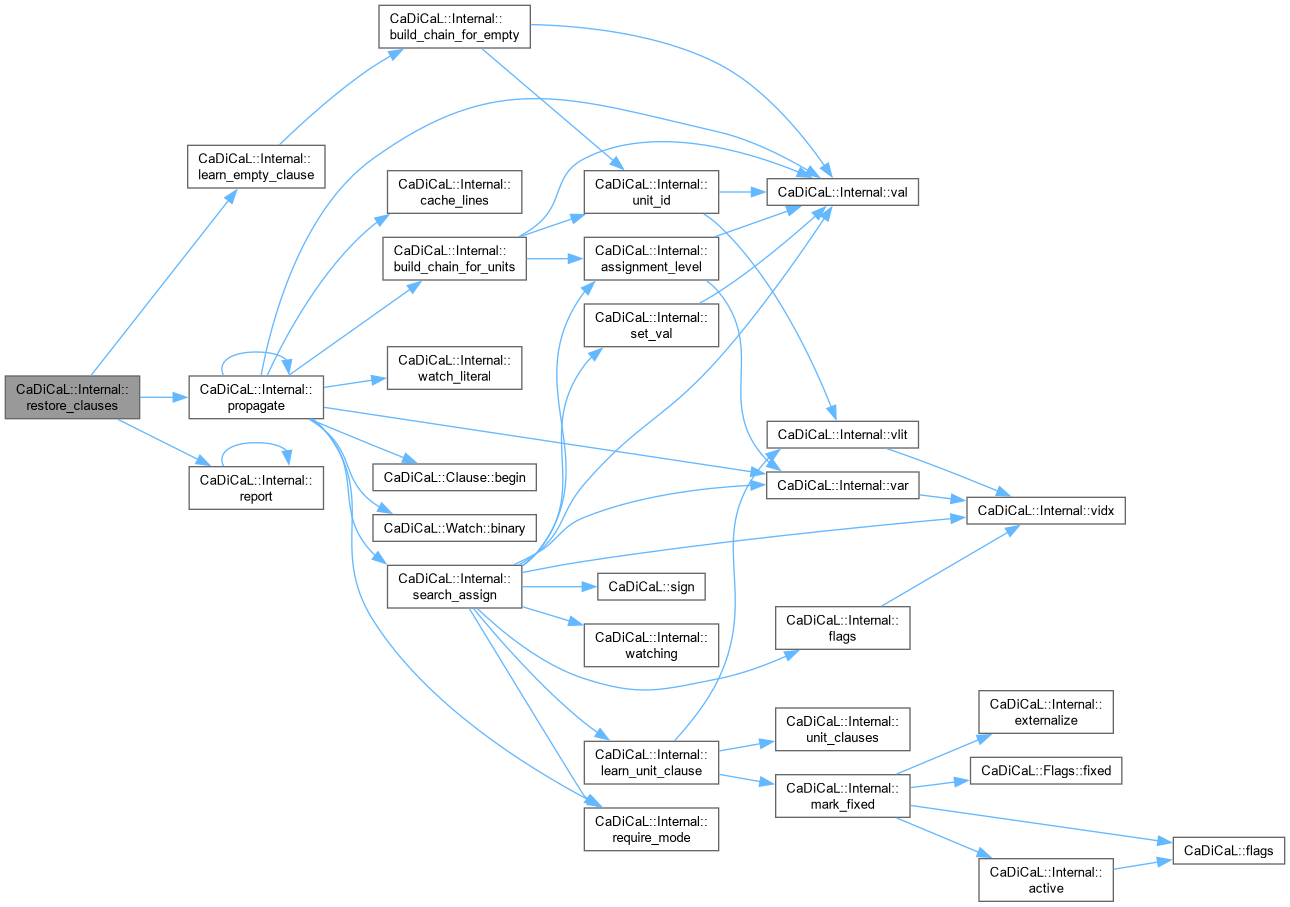
| int CaDiCaL::Internal::restore_clauses | ( | ) |
Definition at line 985 of file cadical_internal.cpp.
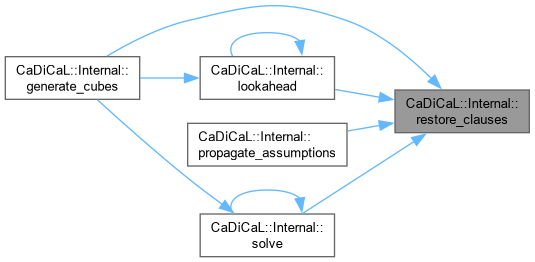
| int CaDiCaL::Internal::reuse_trail | ( | ) |
Definition at line 110 of file cadical_restart.cpp.
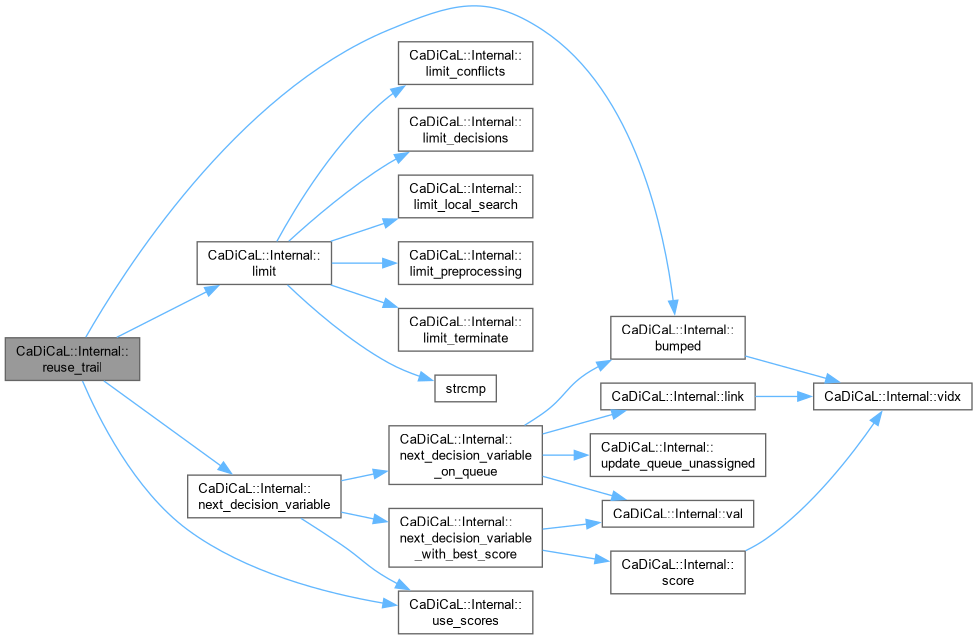

| bool CaDiCaL::Internal::run_factorization | ( | int64_t | limit | ) |
Definition at line 772 of file cadical_factor.cpp.
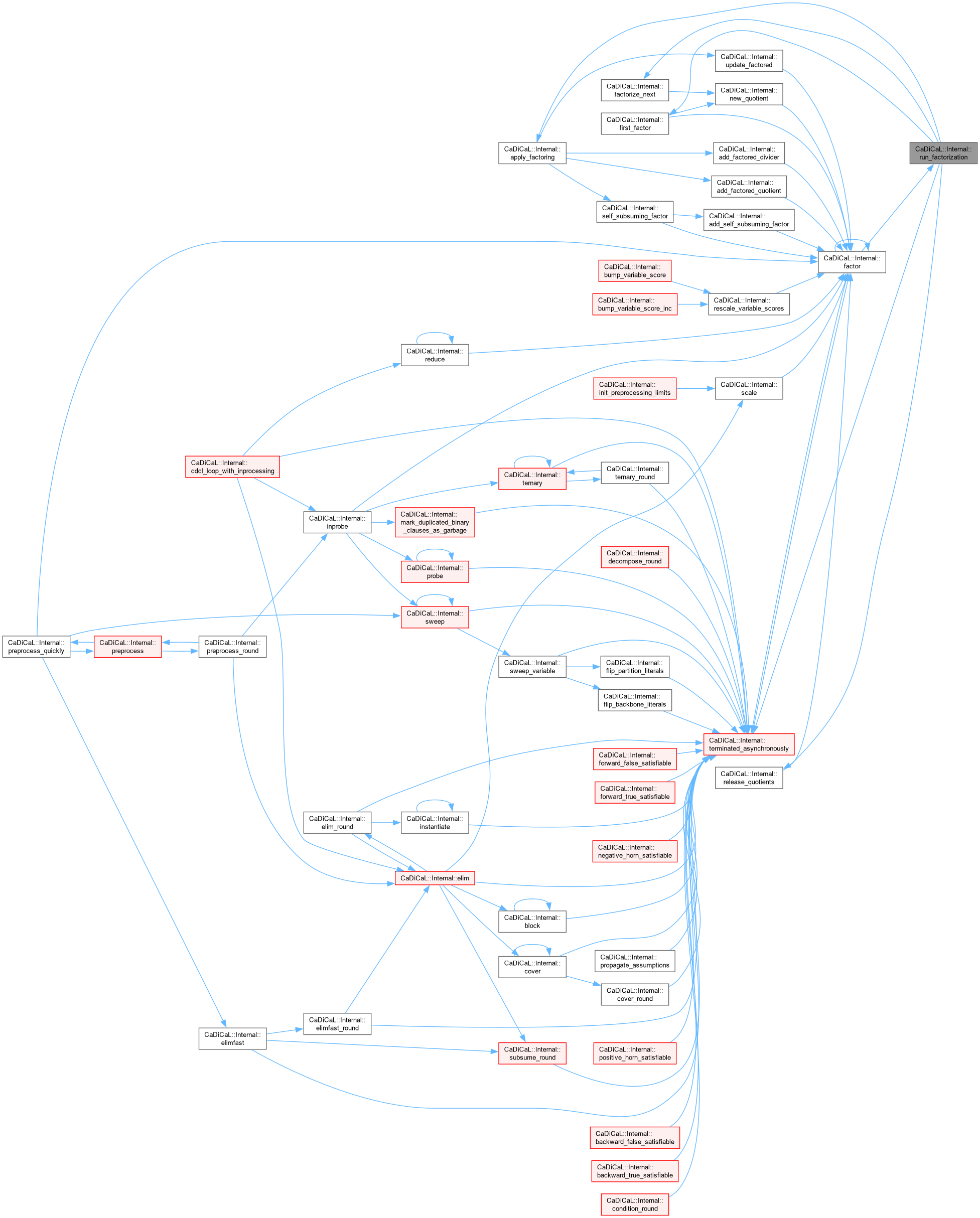
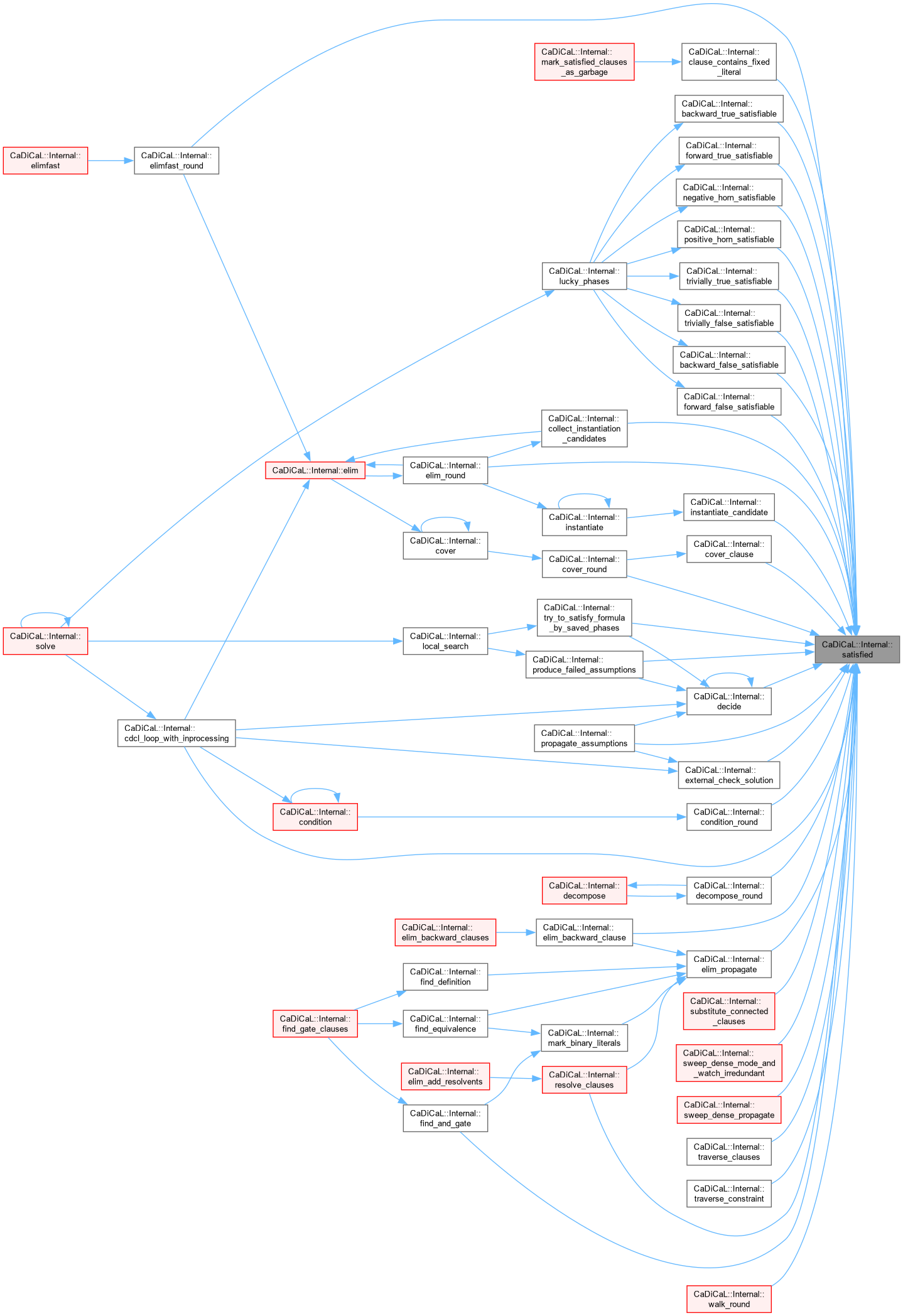
| bool CaDiCaL::Internal::satisfied | ( | ) |
Definition at line 102 of file cadical_decide.cpp.
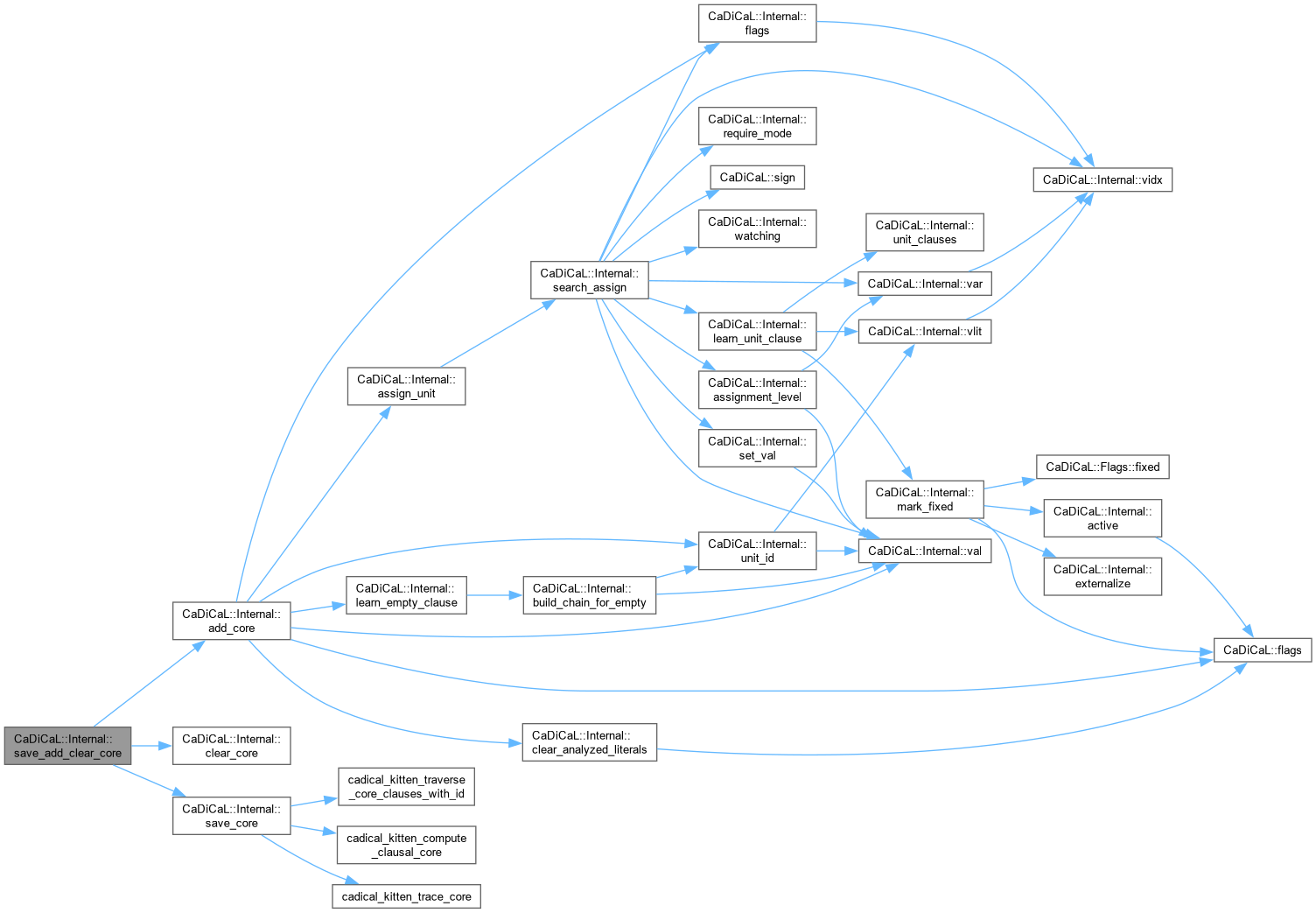
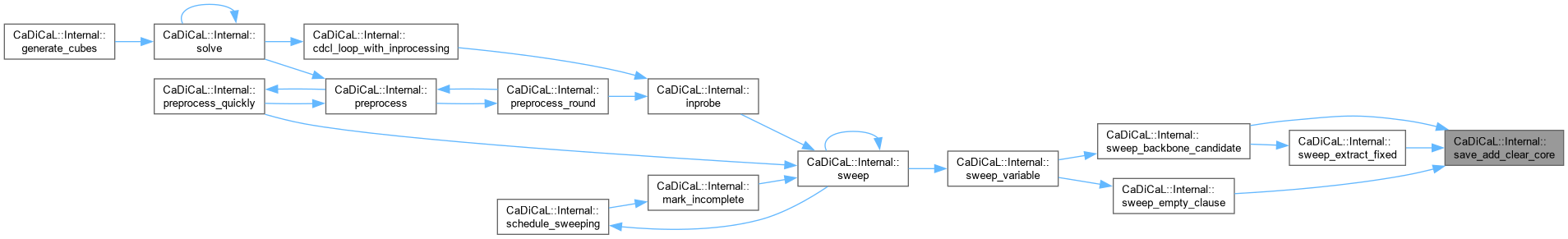
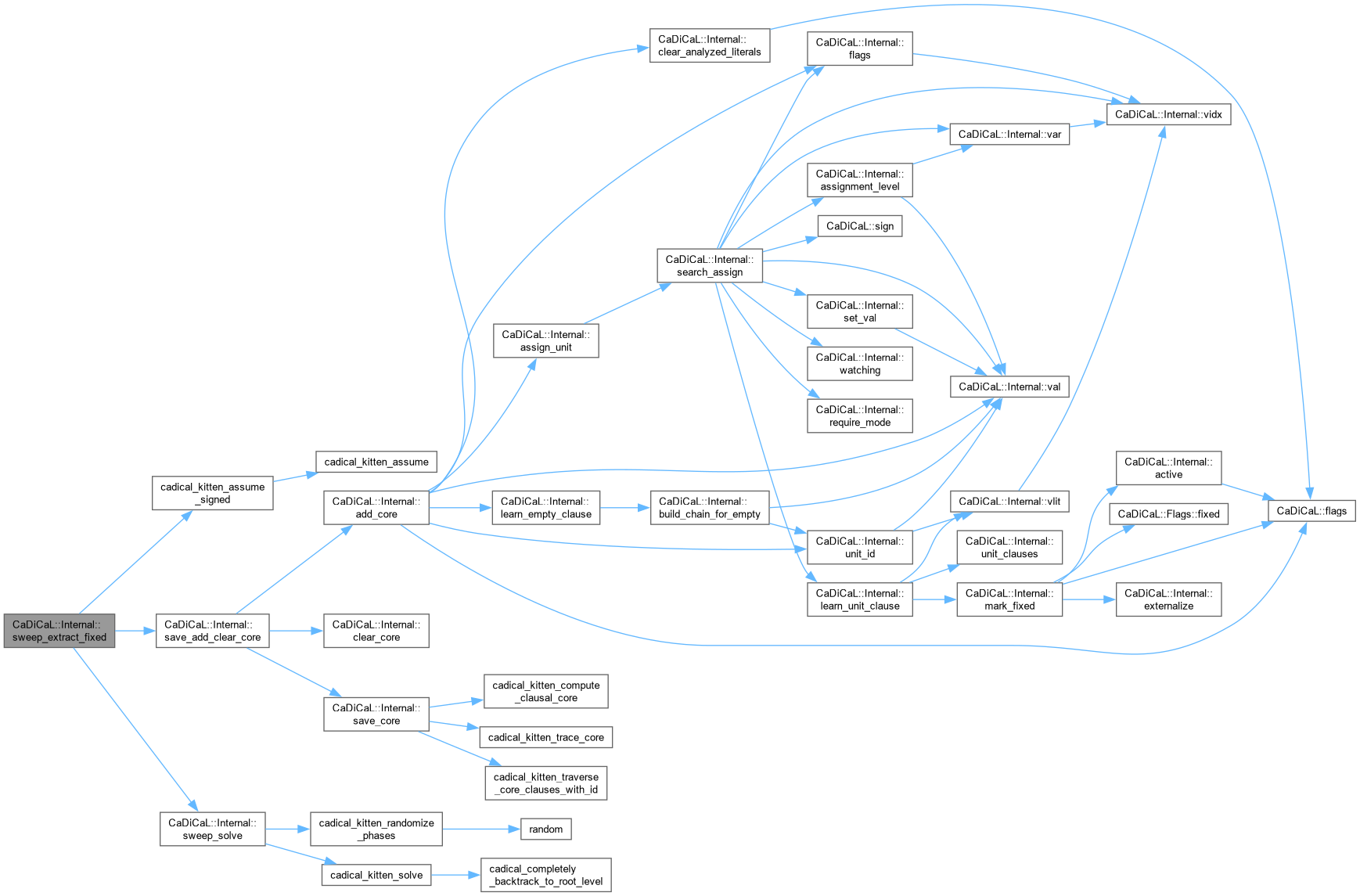
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::save_add_clear_core | ( | Sweeper & | sweeper | ) |
Definition at line 626 of file cadical_sweep.cpp.
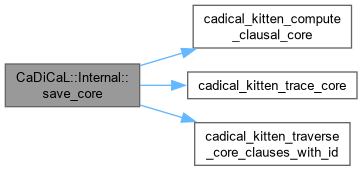
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::save_core | ( | Sweeper & | sweeper, |
| unsigned | core ) |
Definition at line 599 of file cadical_sweep.cpp.
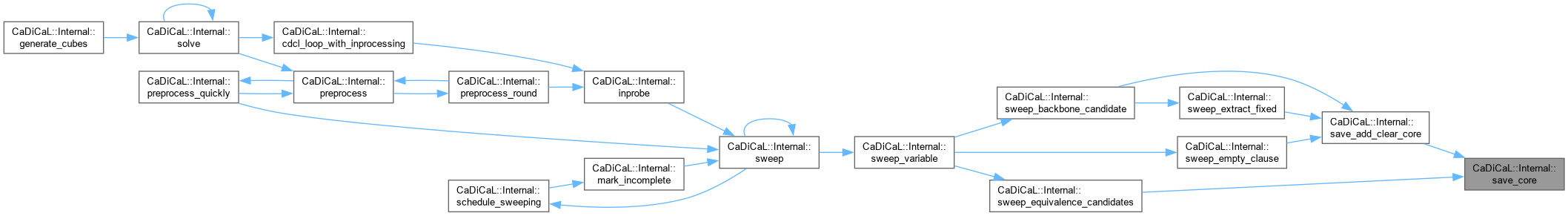
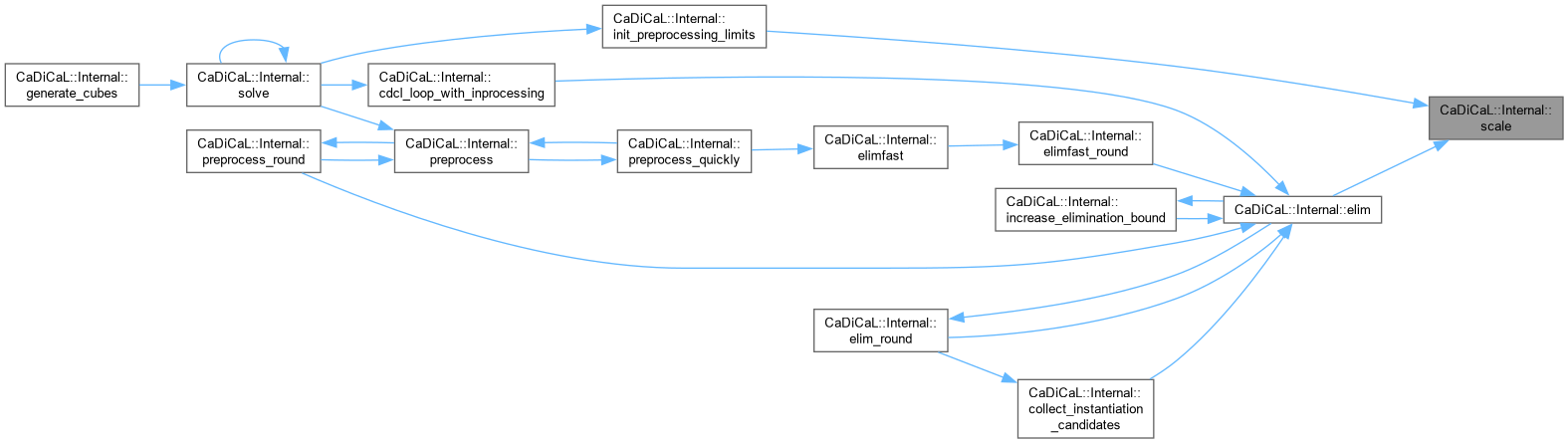
| double CaDiCaL::Internal::scale | ( | double | v | ) | const |
Definition at line 13 of file cadical_limit.cpp.
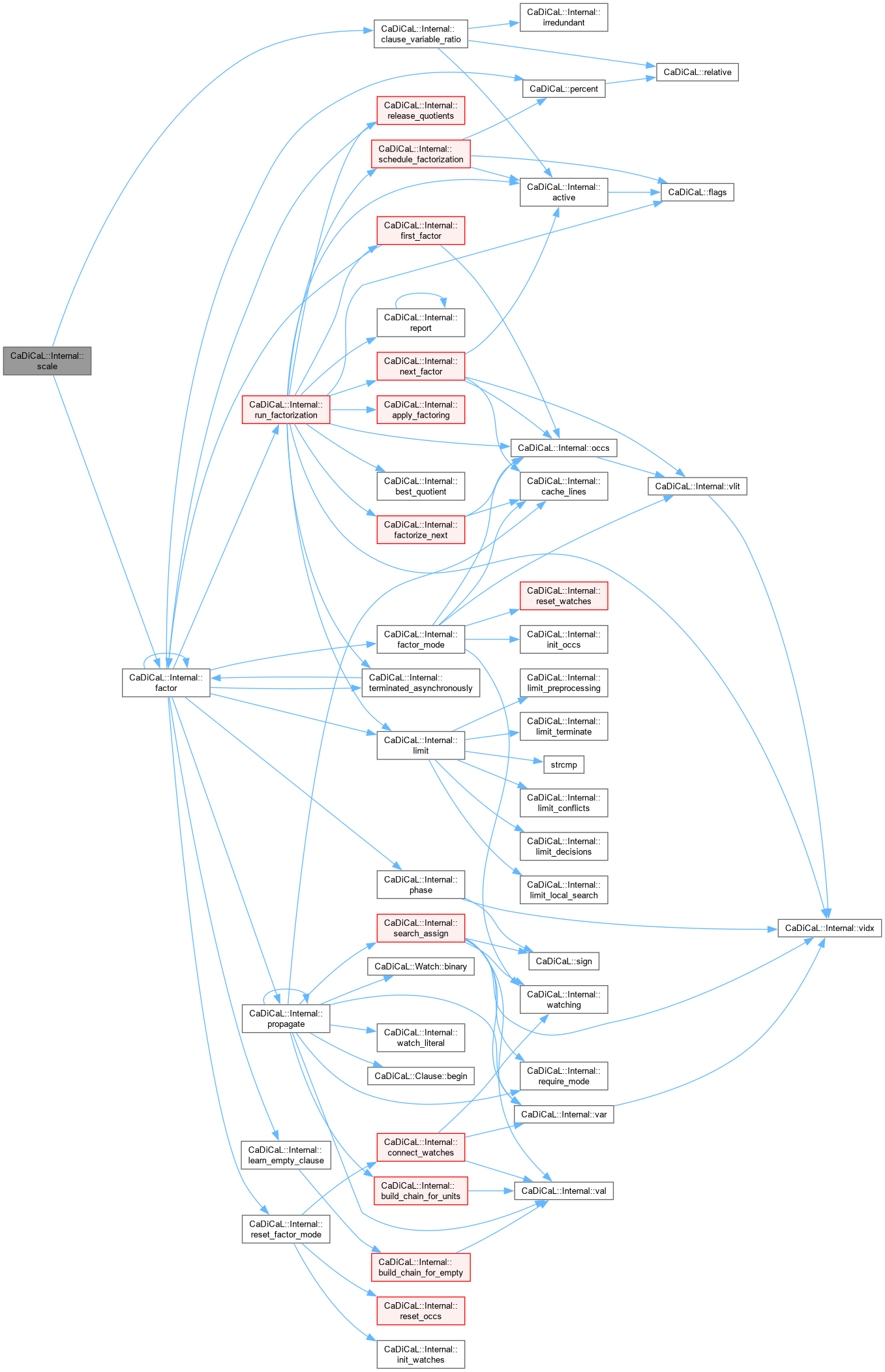
Definition at line 1726 of file cadical_sweep.cpp.

| unsigned CaDiCaL::Internal::schedule_all_other_not_scheduled_yet | ( | Sweeper & | sweeper | ) |
Definition at line 1745 of file cadical_sweep.cpp.
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::schedule_factorization | ( | Factoring & | factoring | ) |
Definition at line 753 of file cadical_factor.cpp.
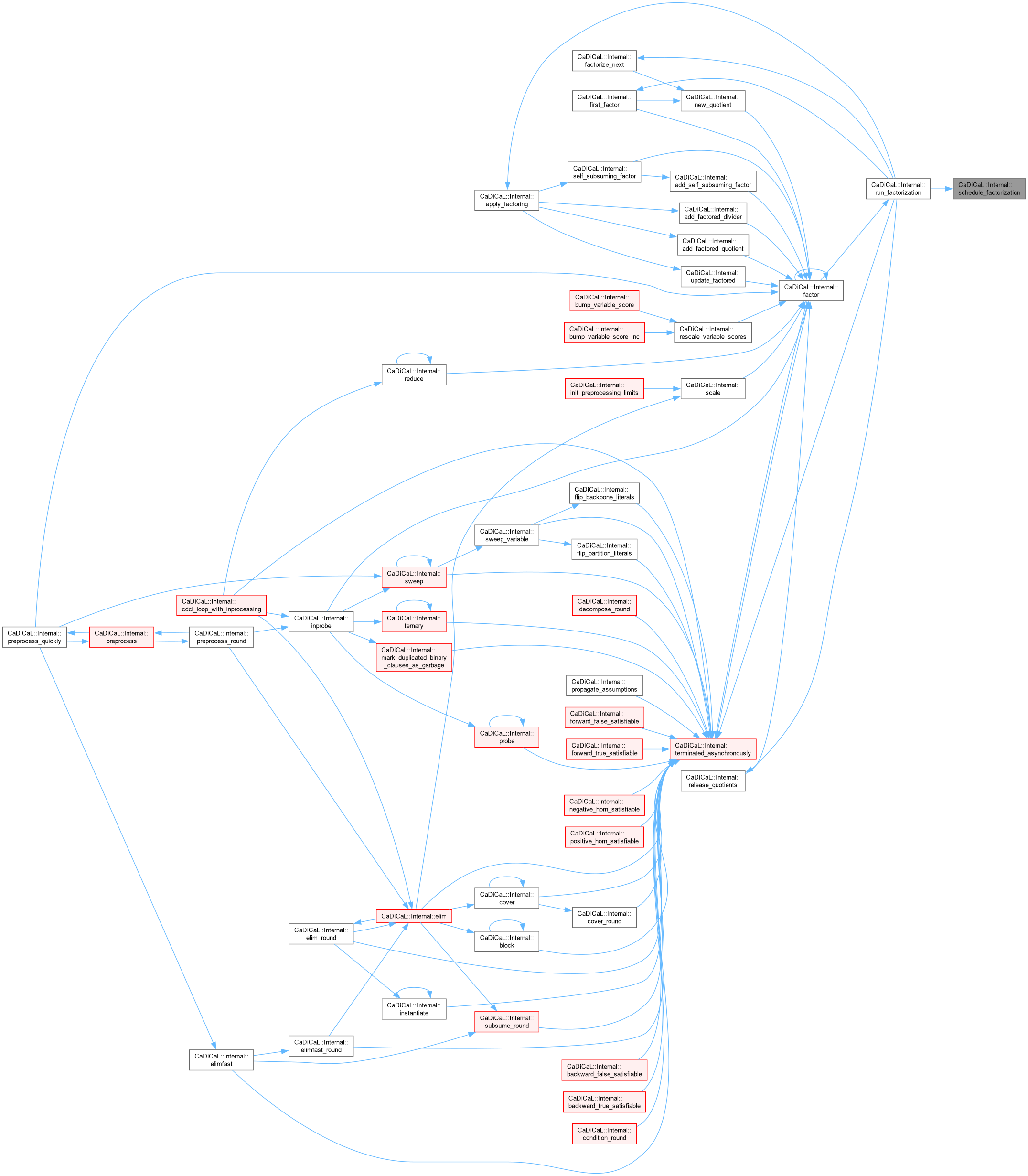
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::schedule_inner | ( | Sweeper & | sweeper, |
| int | idx ) |
Definition at line 946 of file cadical_sweep.cpp.

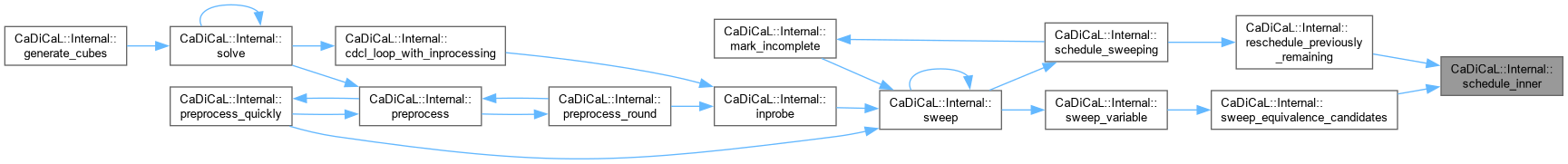
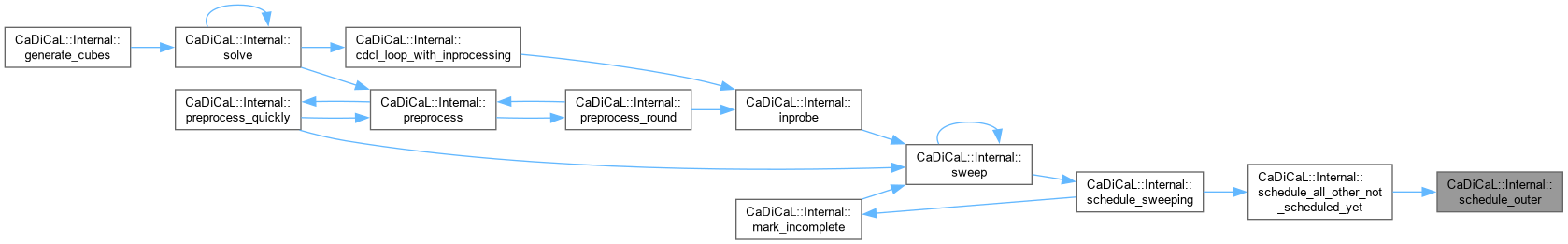
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::schedule_outer | ( | Sweeper & | sweeper, |
| int | idx ) |
Definition at line 991 of file cadical_sweep.cpp.
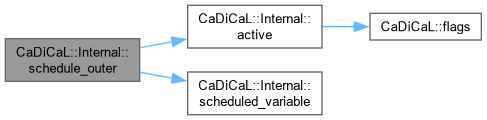
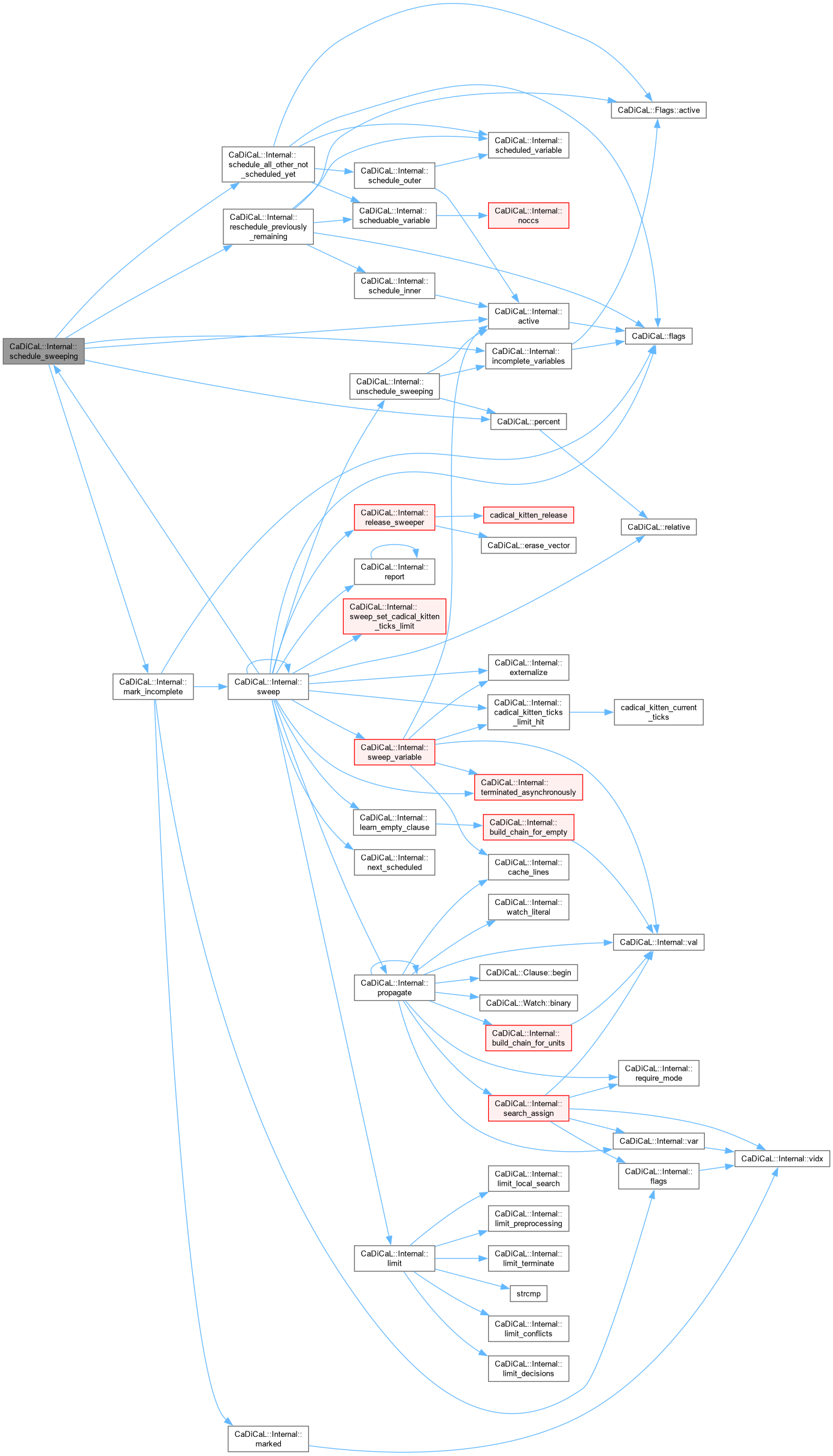
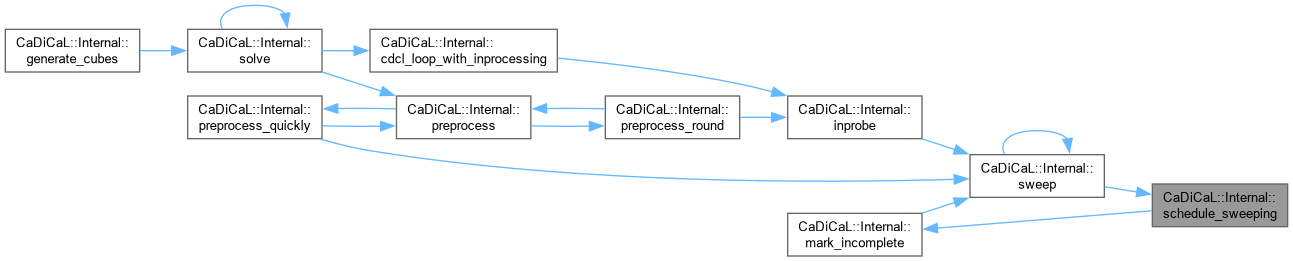
| unsigned CaDiCaL::Internal::schedule_sweeping | ( | Sweeper & | sweeper | ) |
Definition at line 1822 of file cadical_sweep.cpp.
|
inline |
Definition at line 457 of file internal.hpp.
|
inline |
Definition at line 106 of file cadical_propagate.cpp.
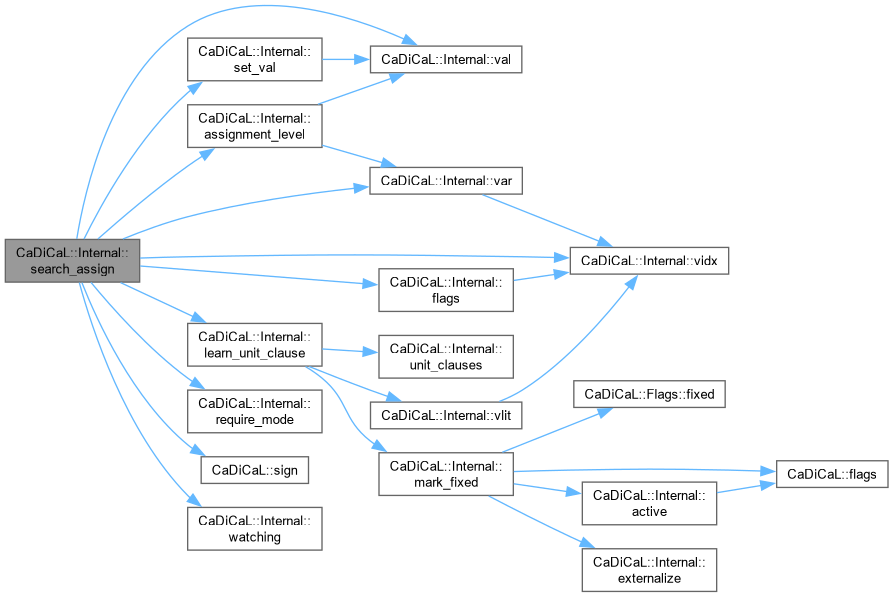
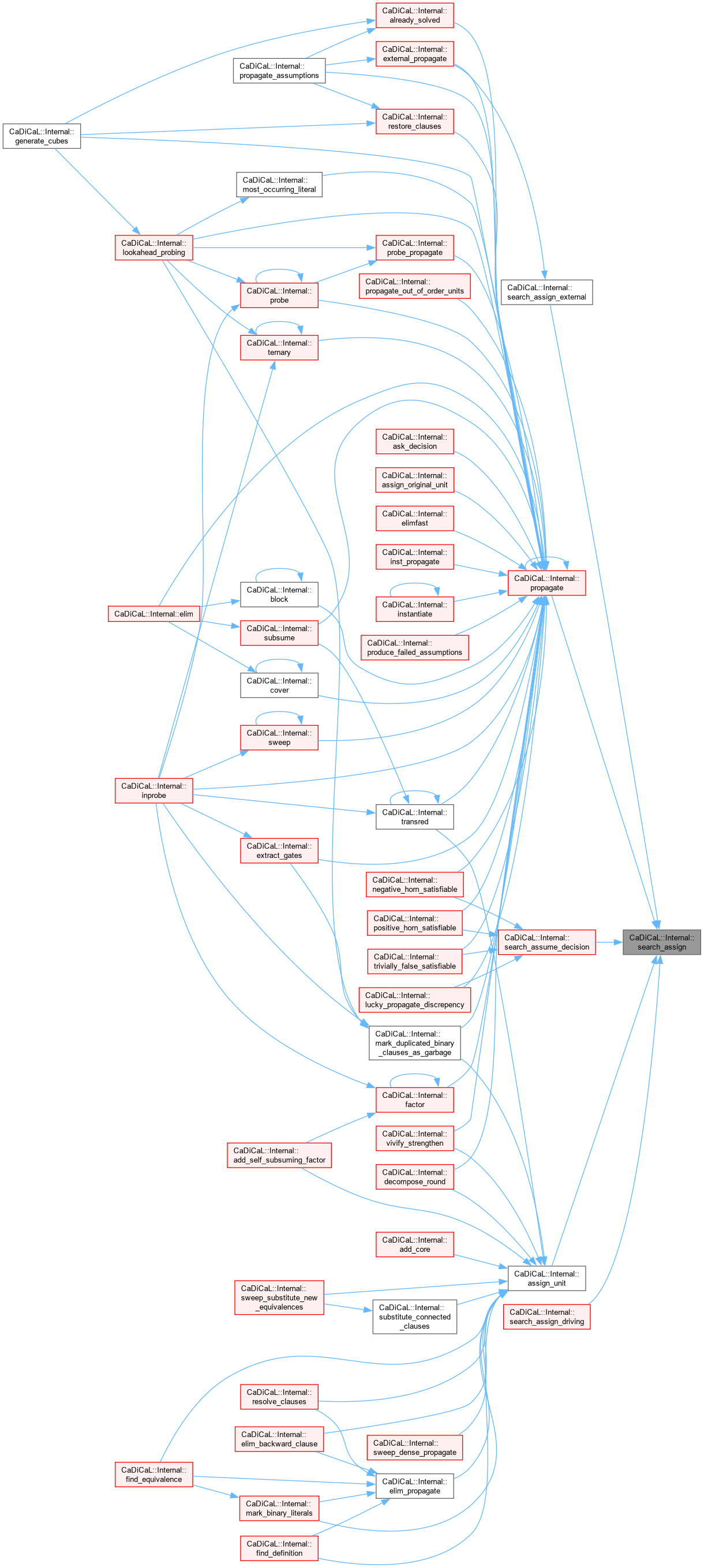
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::search_assign_driving | ( | int | lit, |
| Clause * | reason ) |
Definition at line 201 of file cadical_propagate.cpp.
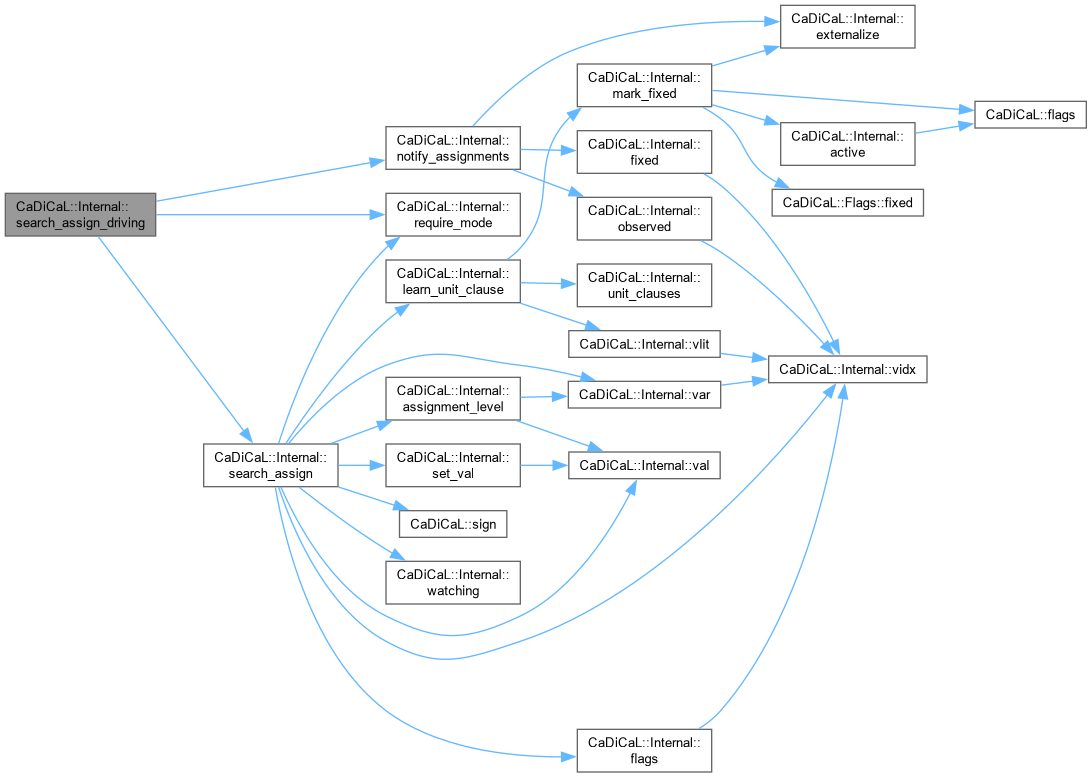
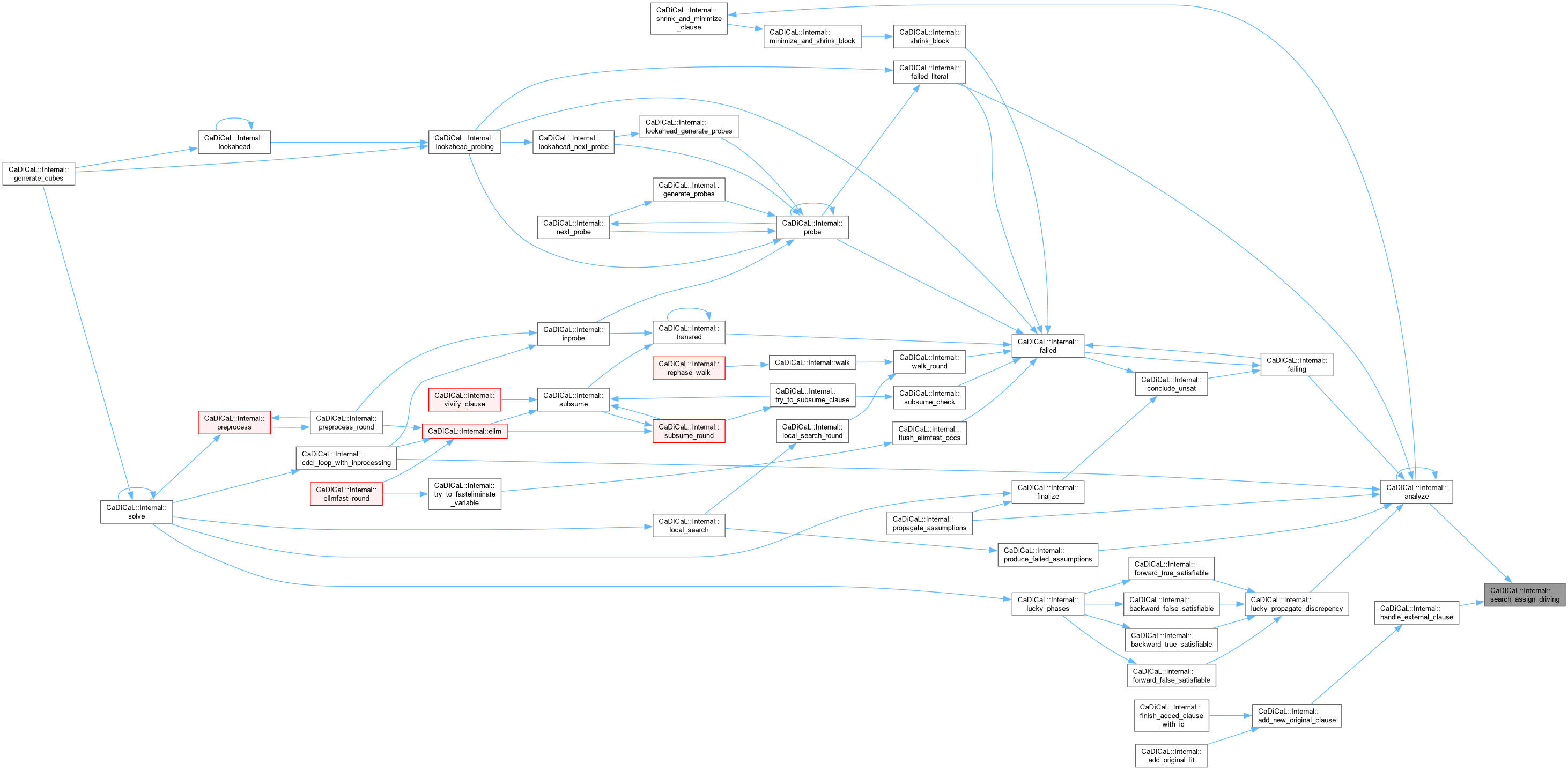
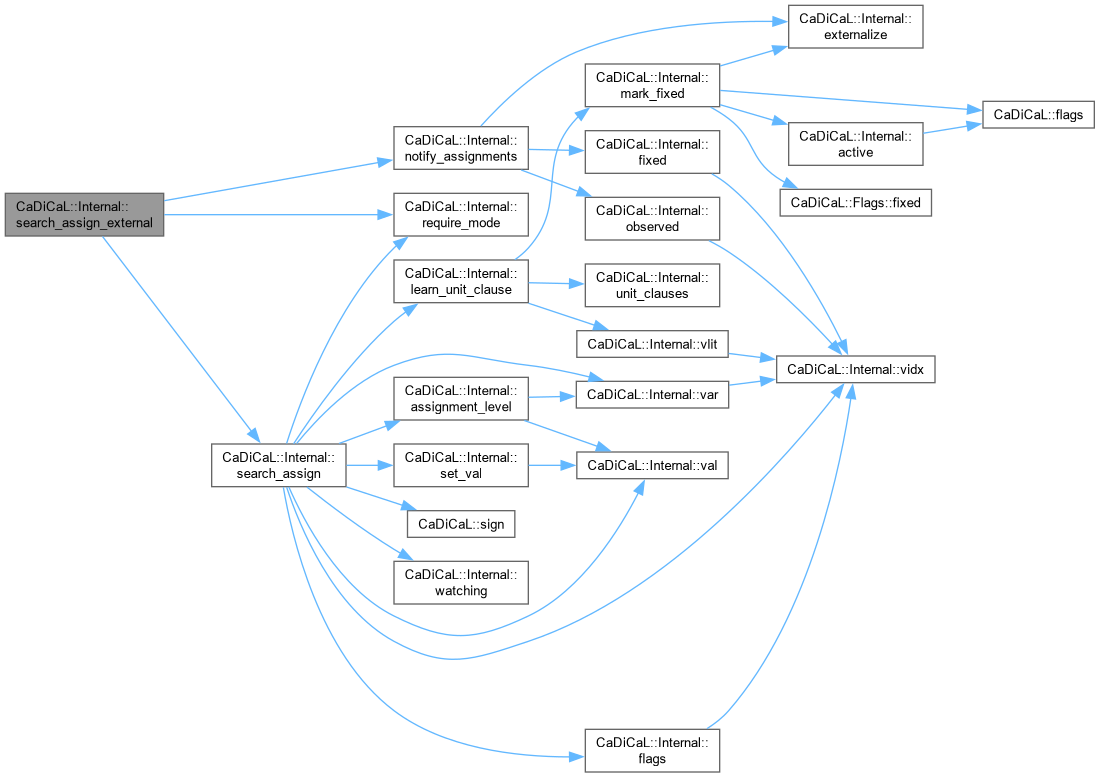
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::search_assign_external | ( | int | lit | ) |
Definition at line 207 of file cadical_propagate.cpp.

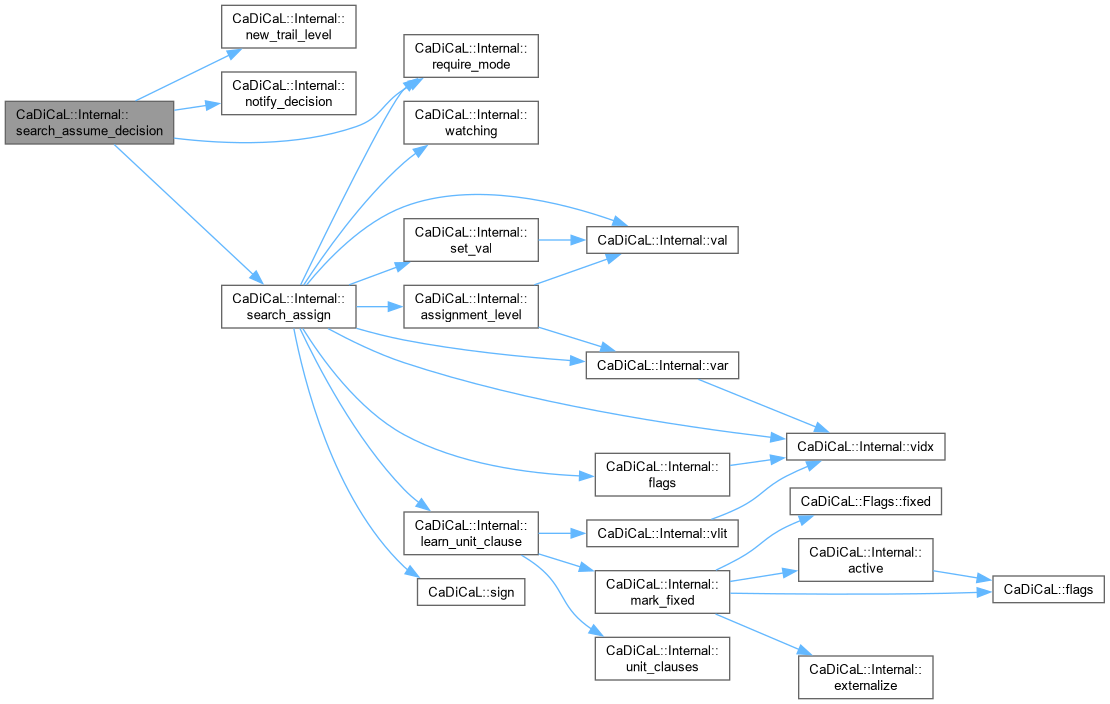
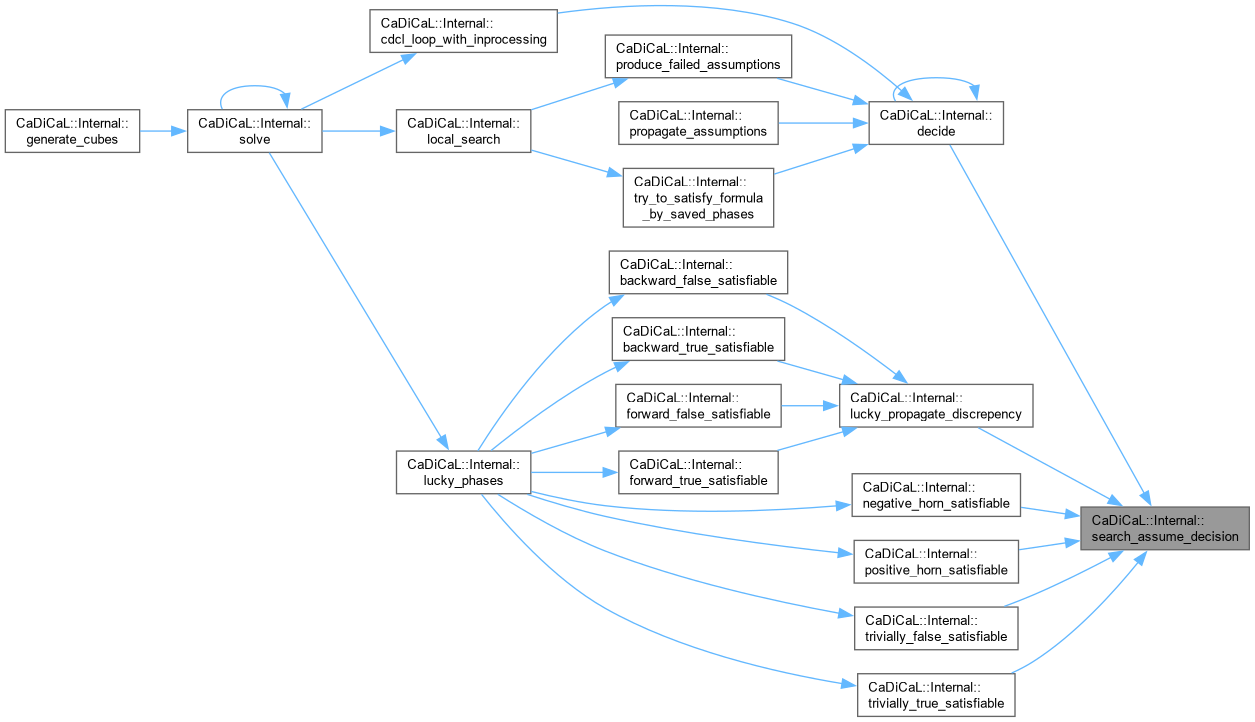
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::search_assume_decision | ( | int | decision | ) |
Definition at line 192 of file cadical_propagate.cpp.
|
inline |
Definition at line 1843 of file internal.hpp.
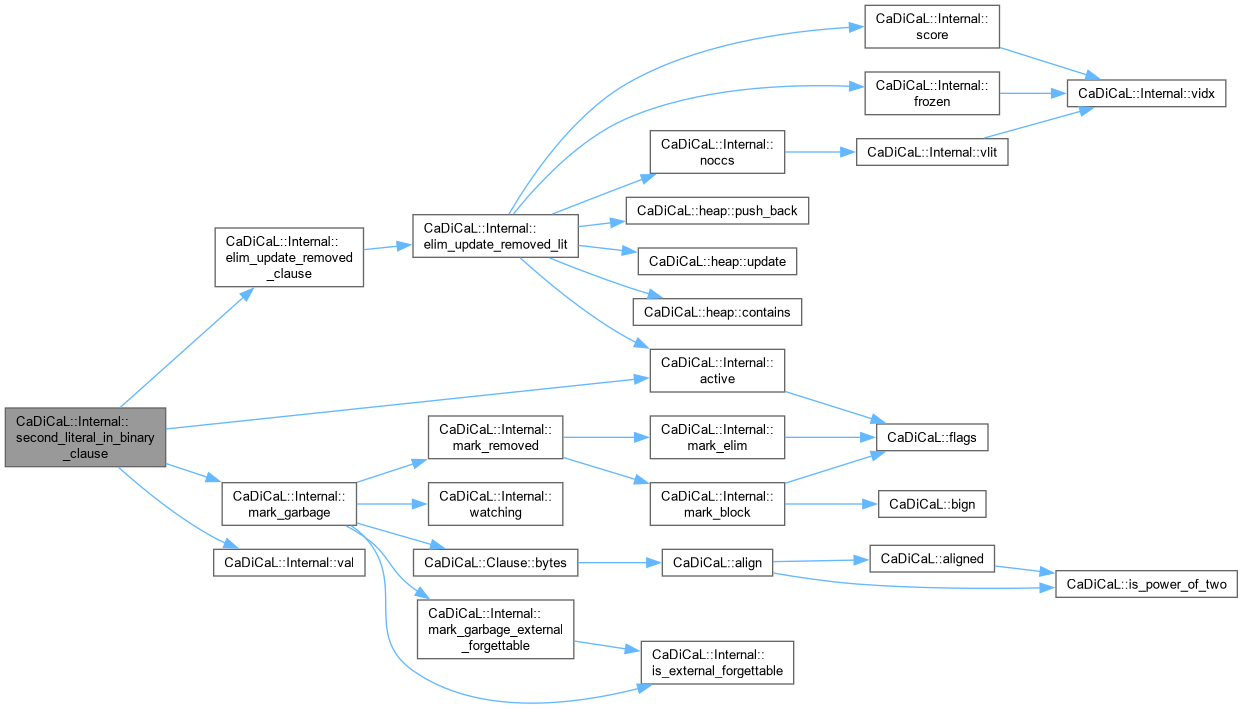
| int CaDiCaL::Internal::second_literal_in_binary_clause | ( | Eliminator & | eliminator, |
| Clause * | c, | ||
| int | first ) |
Definition at line 24 of file cadical_gates.cpp.
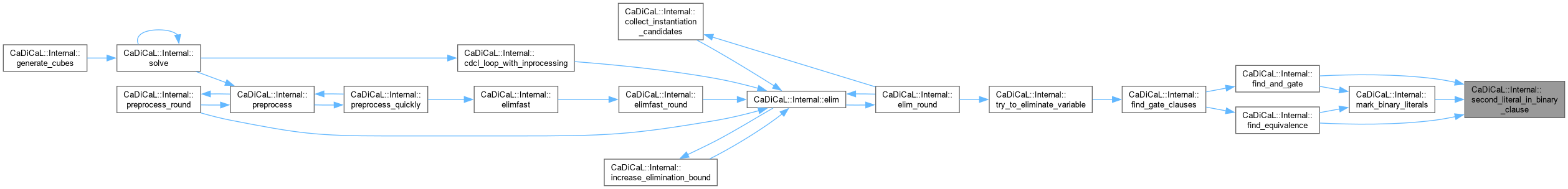
| int CaDiCaL::Internal::second_literal_in_binary_clause_lrat | ( | Clause * | c, |
| int | first ) |
Definition at line 63 of file cadical_gates.cpp.
Definition at line 566 of file cadical_factor.cpp.
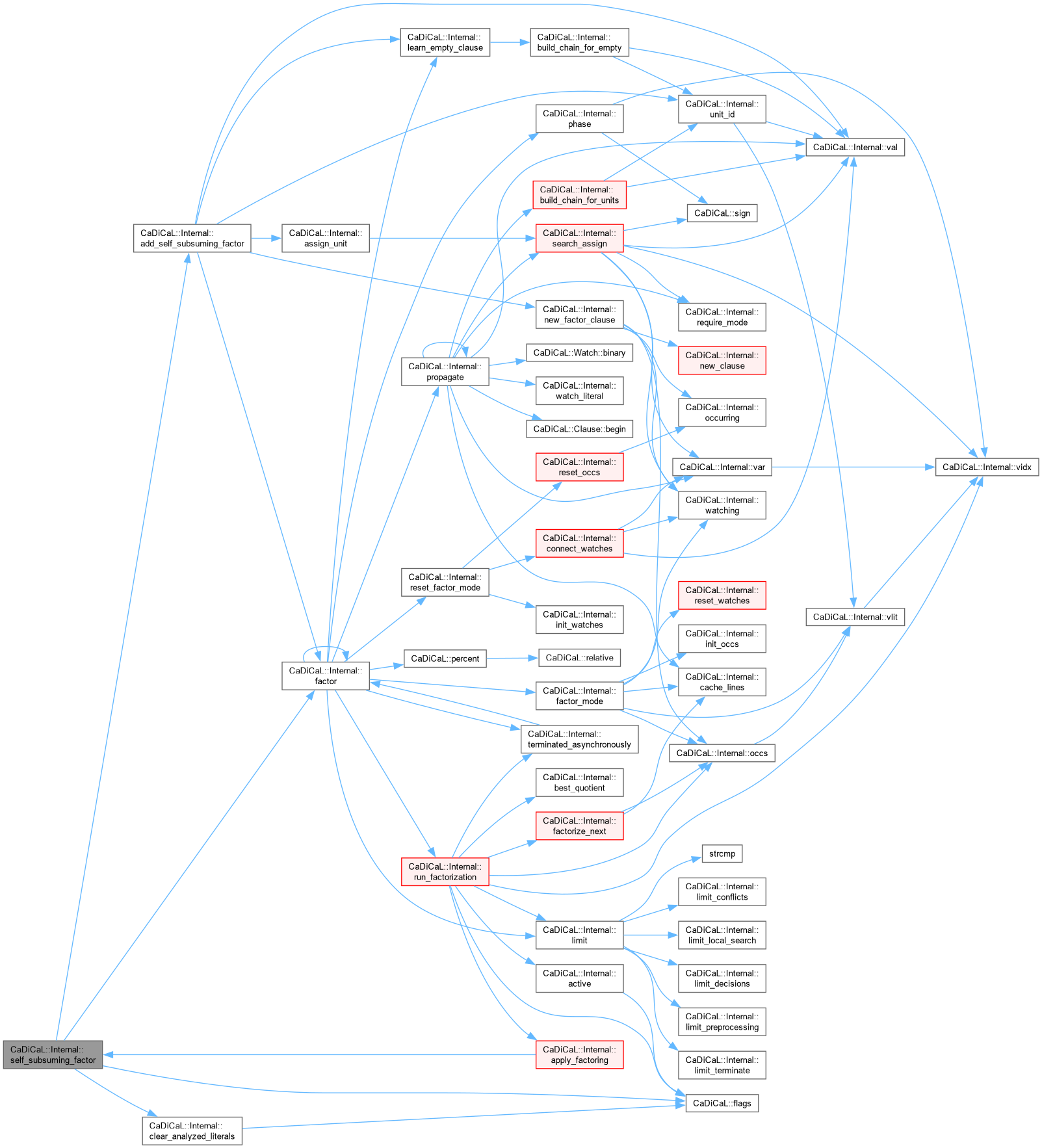
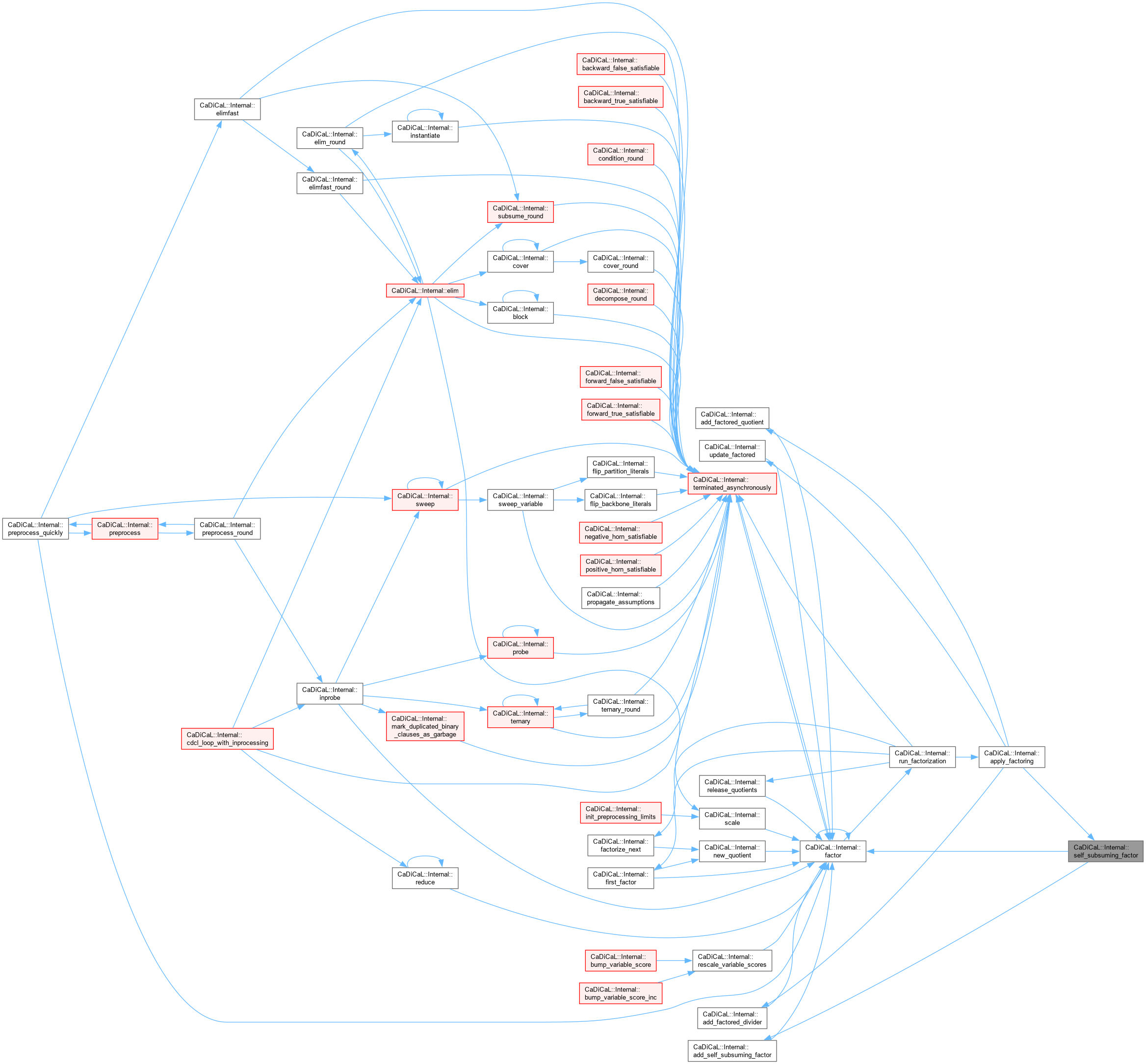
|
inline |
|
inline |
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::set_probehbr_lrat | ( | int | lit, |
| int | uip ) |
Definition at line 104 of file cadical_probe.cpp.

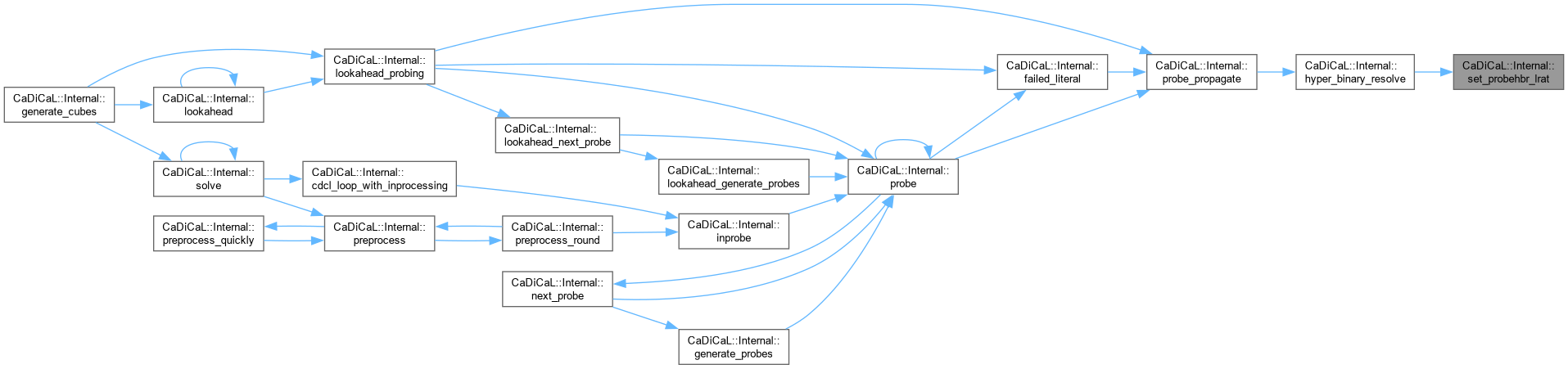
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::set_tainted_literal | ( | ) |
Definition at line 81 of file cadical_external_propagate.cpp.

|
inline |
Definition at line 1528 of file internal.hpp.
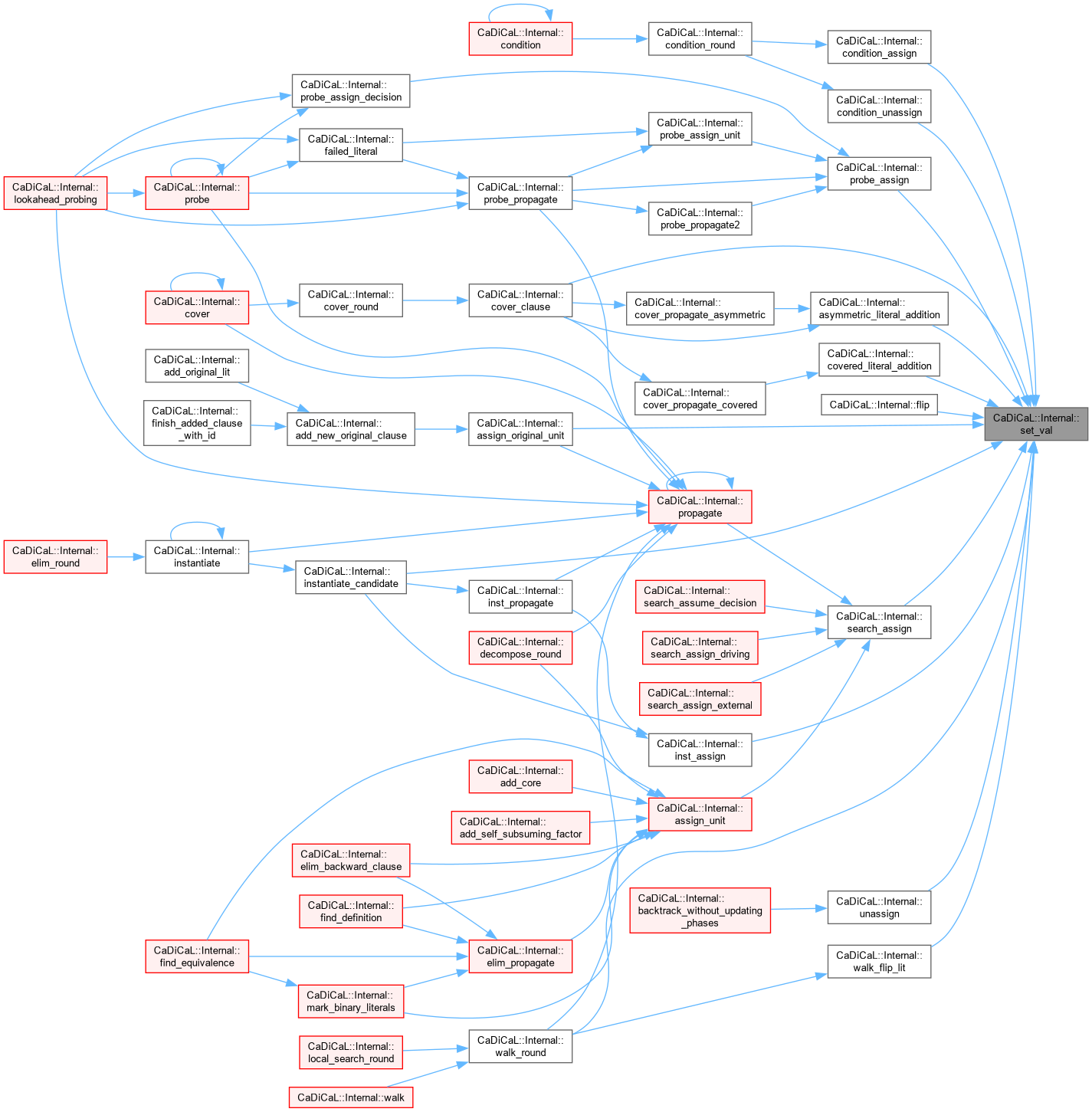
|
inline |
Definition at line 540 of file internal.hpp.


|
inline |
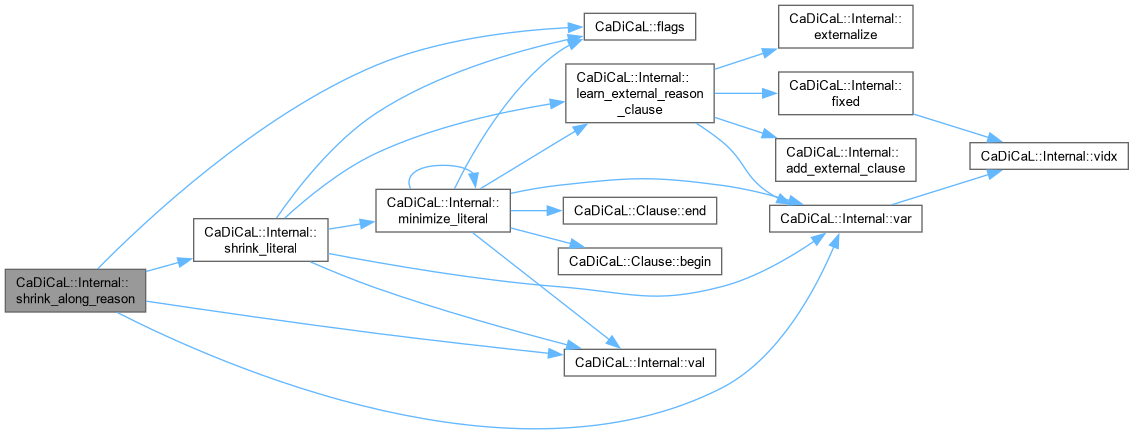
Definition at line 234 of file cadical_shrink.cpp.
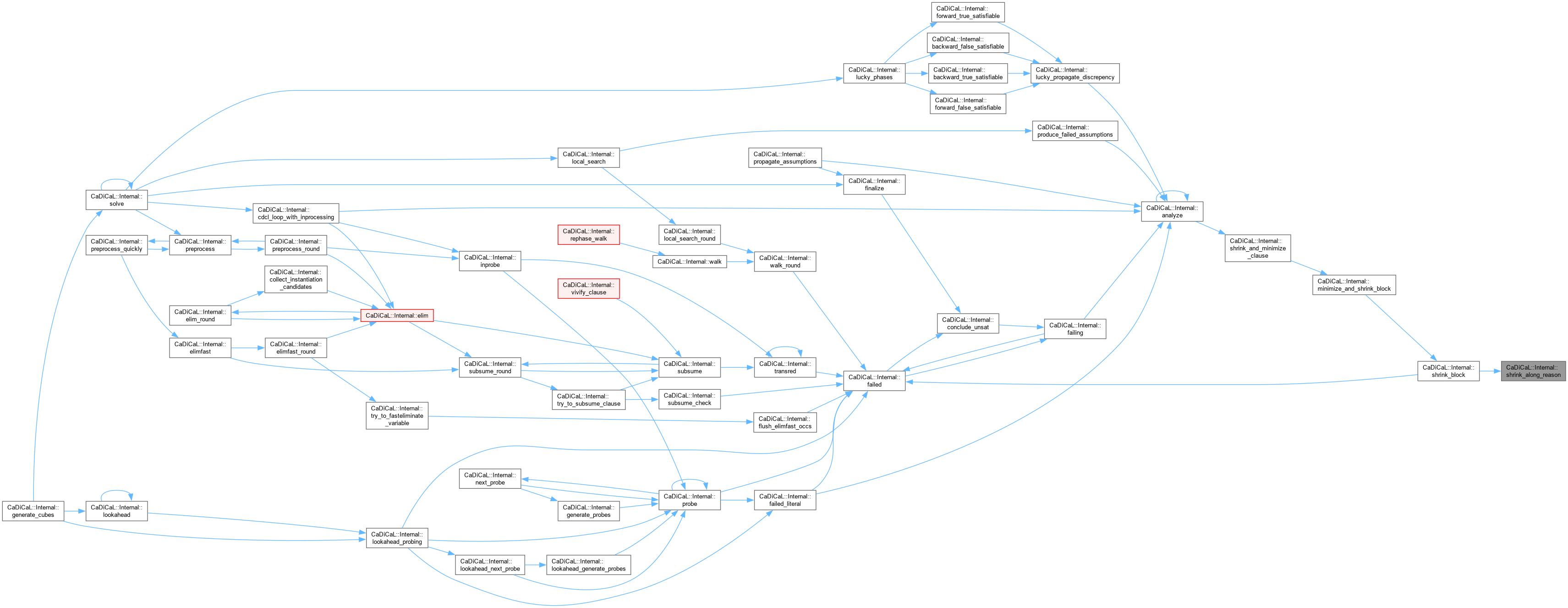
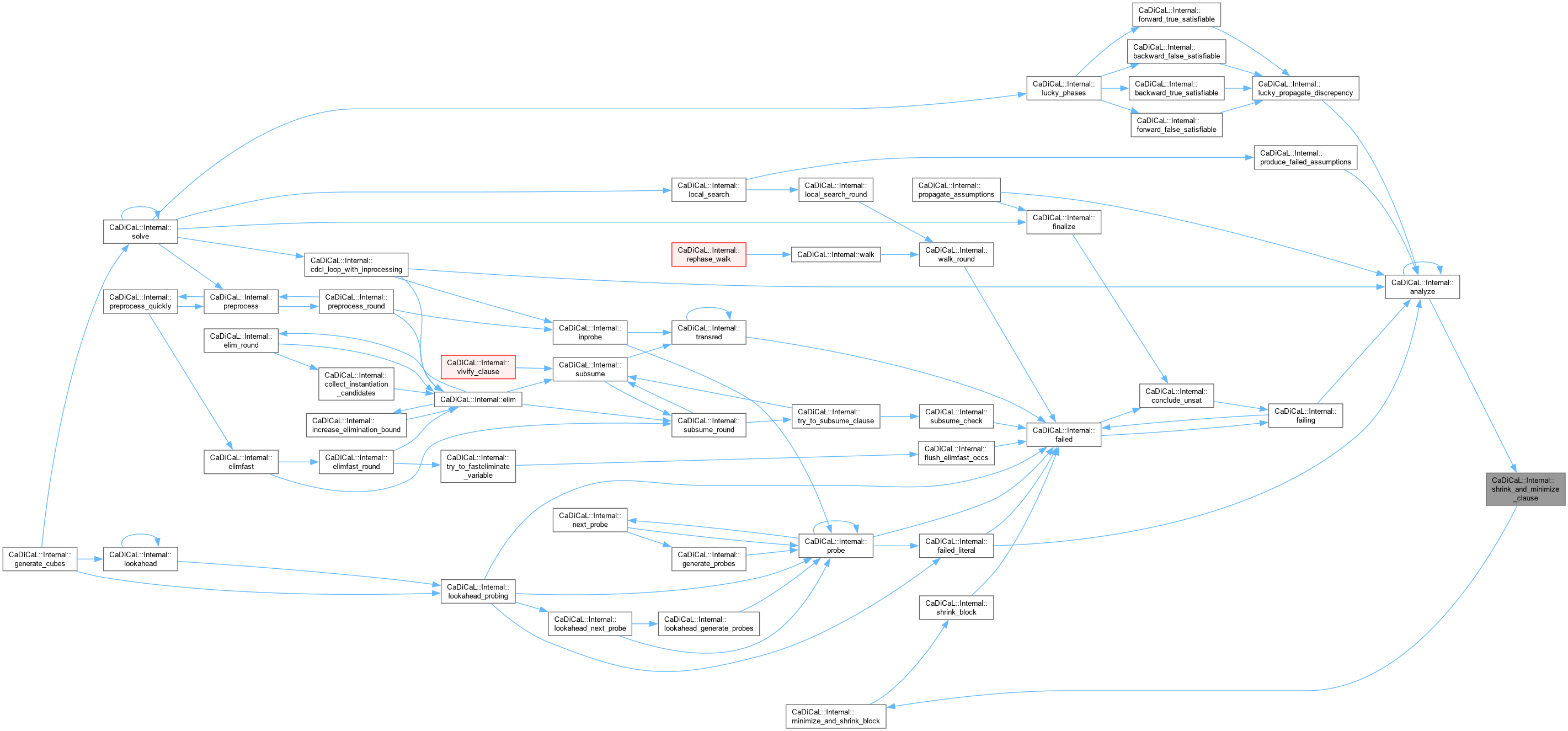
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::shrink_and_minimize_clause | ( | ) |
Definition at line 430 of file cadical_shrink.cpp.
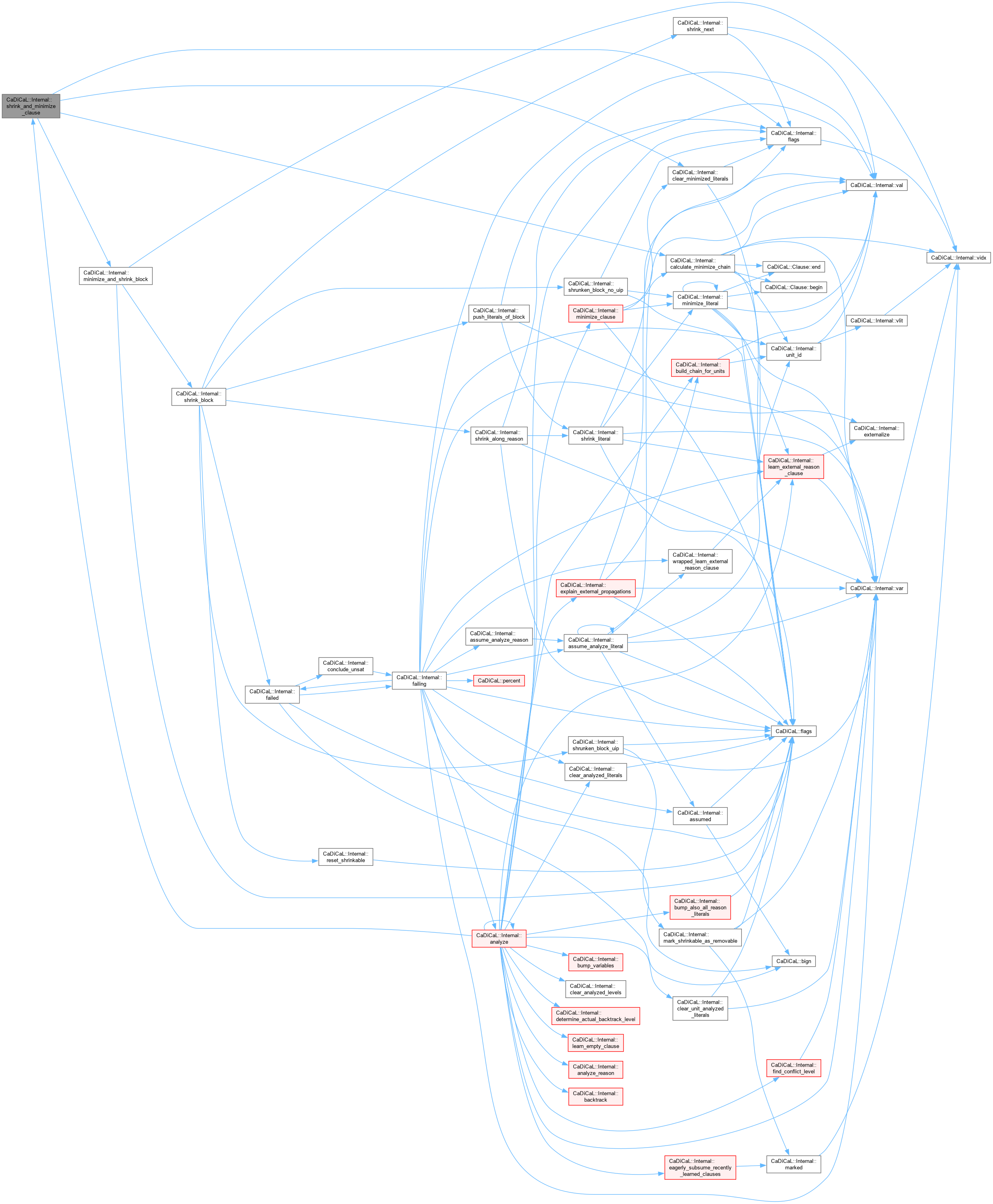
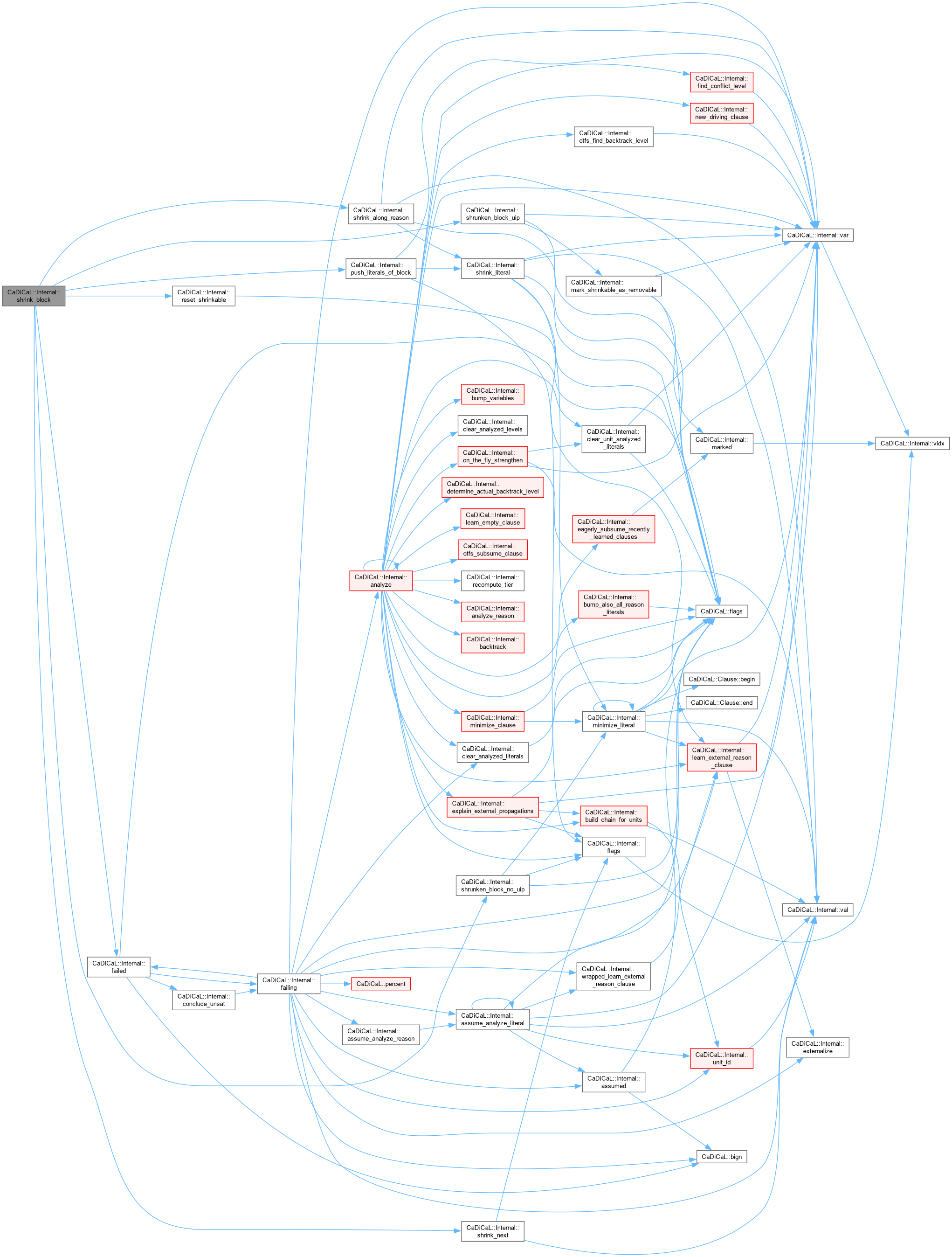
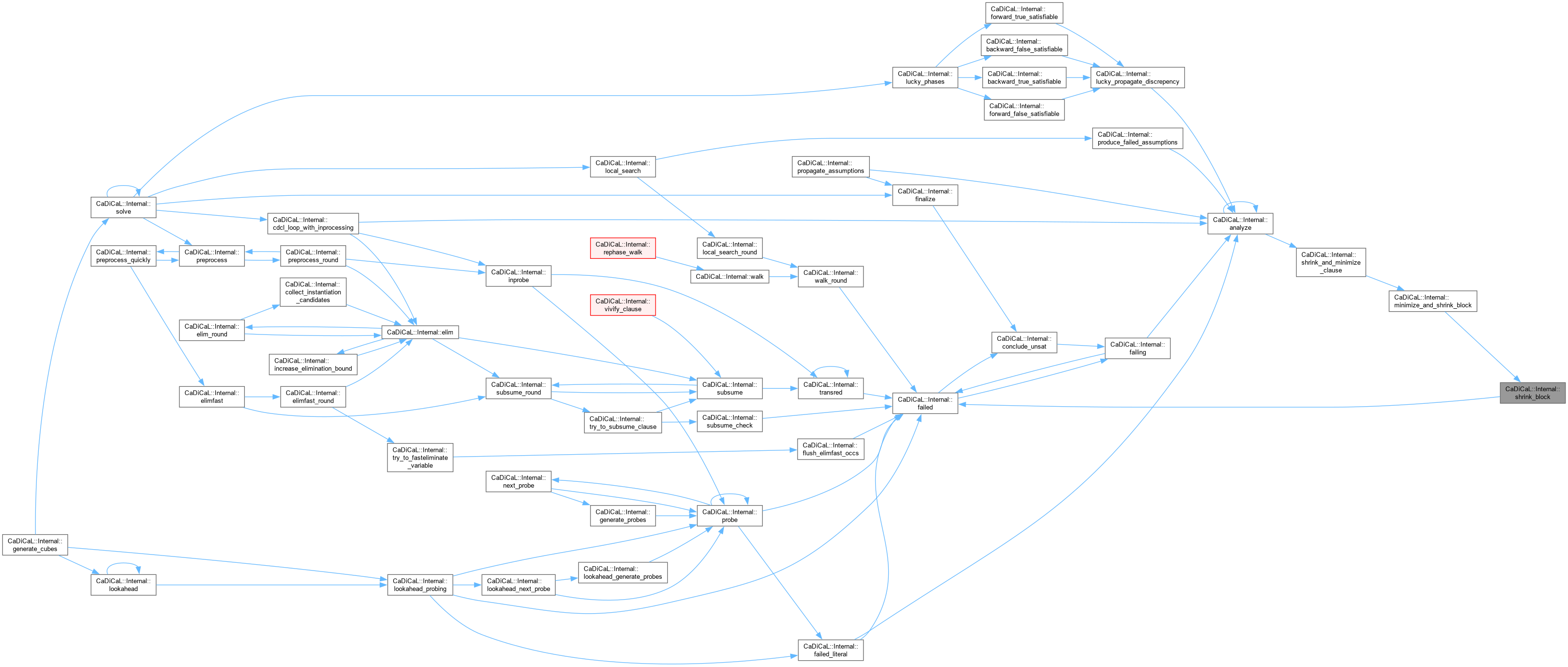
| unsigned CaDiCaL::Internal::shrink_block | ( | std::vector< int >::reverse_iterator & | rbegin_lits, |
| std::vector< int >::reverse_iterator & | rend_block, | ||
| int | blevel, | ||
| unsigned & | open, | ||
| unsigned & | block_minimized, | ||
| const int | uip0, | ||
| unsigned | max_trail ) |
Definition at line 275 of file cadical_shrink.cpp.
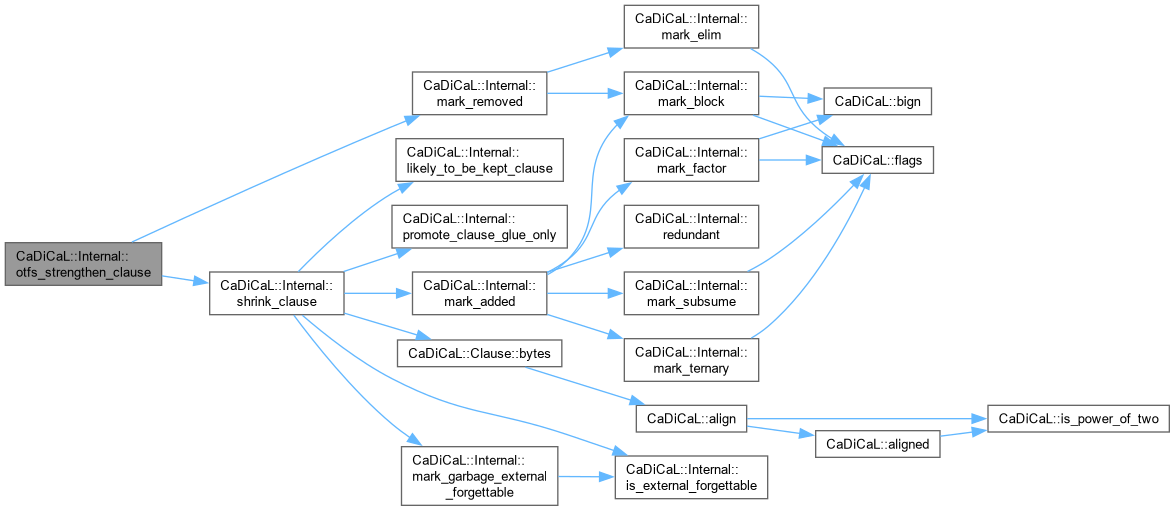
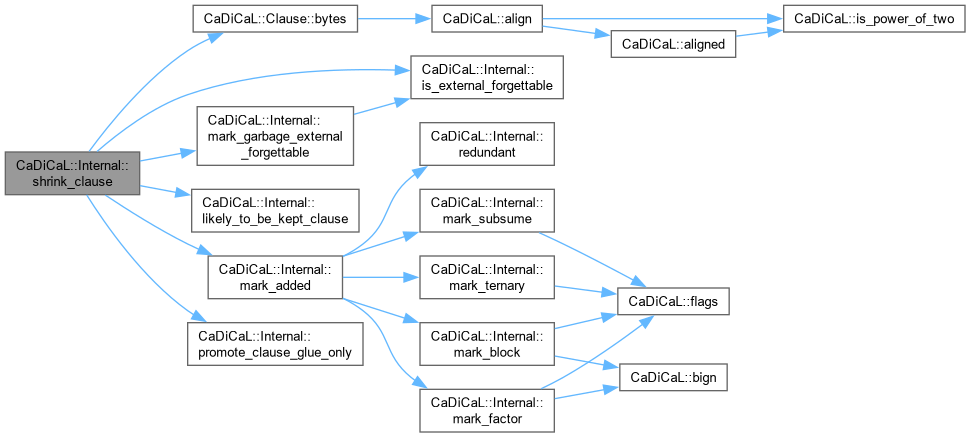
| size_t CaDiCaL::Internal::shrink_clause | ( | Clause * | c, |
| int | new_size ) |
Definition at line 213 of file cadical_clause.cpp.
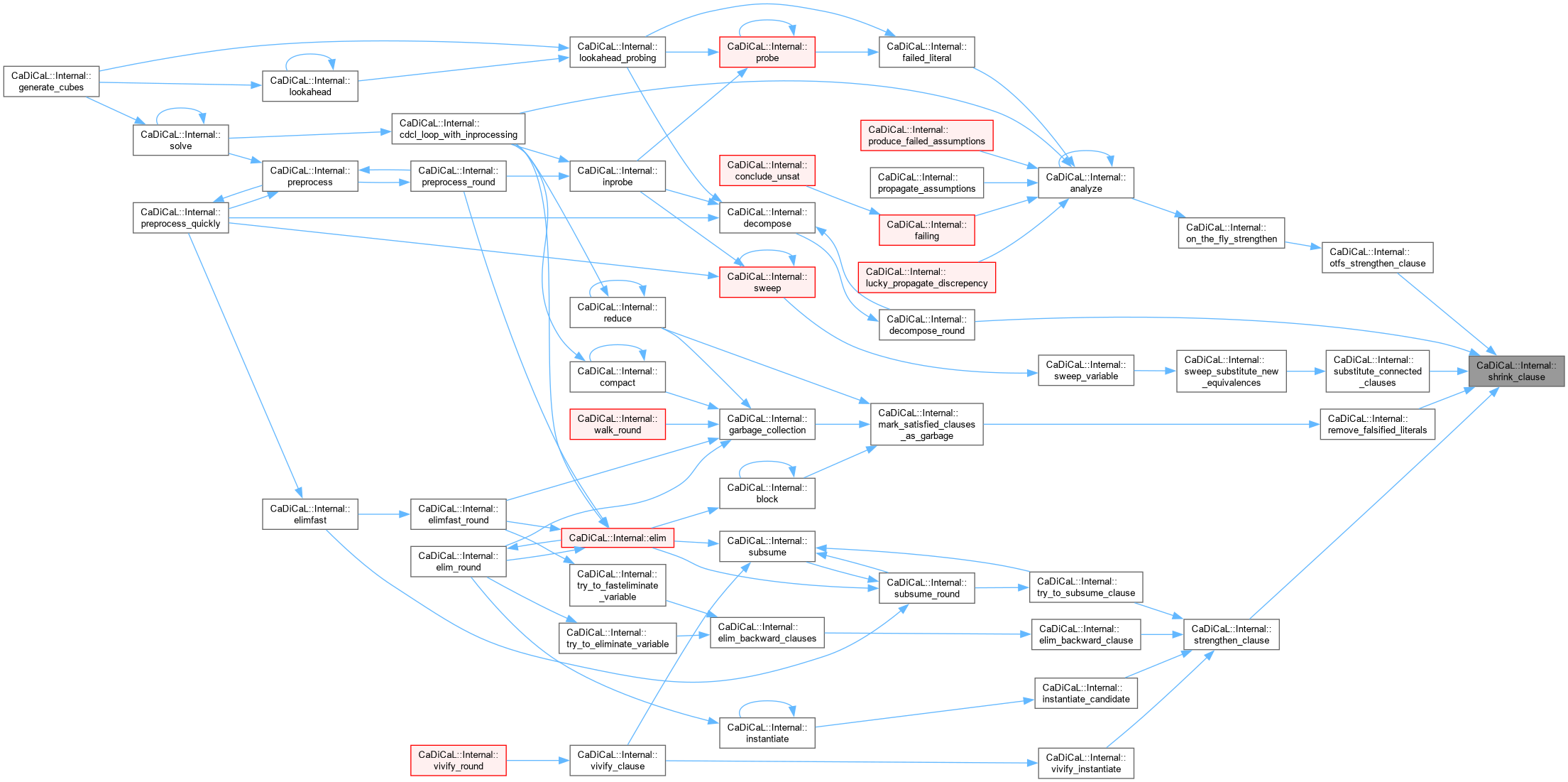
|
inline |
Definition at line 70 of file cadical_shrink.cpp.
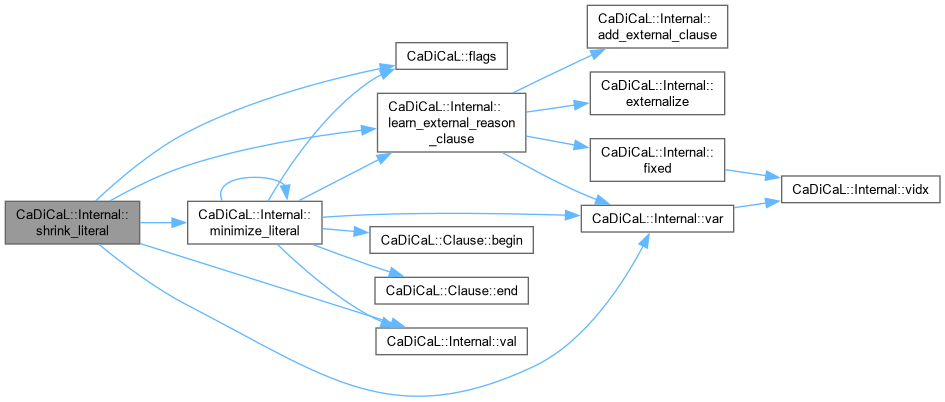
|
inline |
Definition at line 203 of file cadical_shrink.cpp.

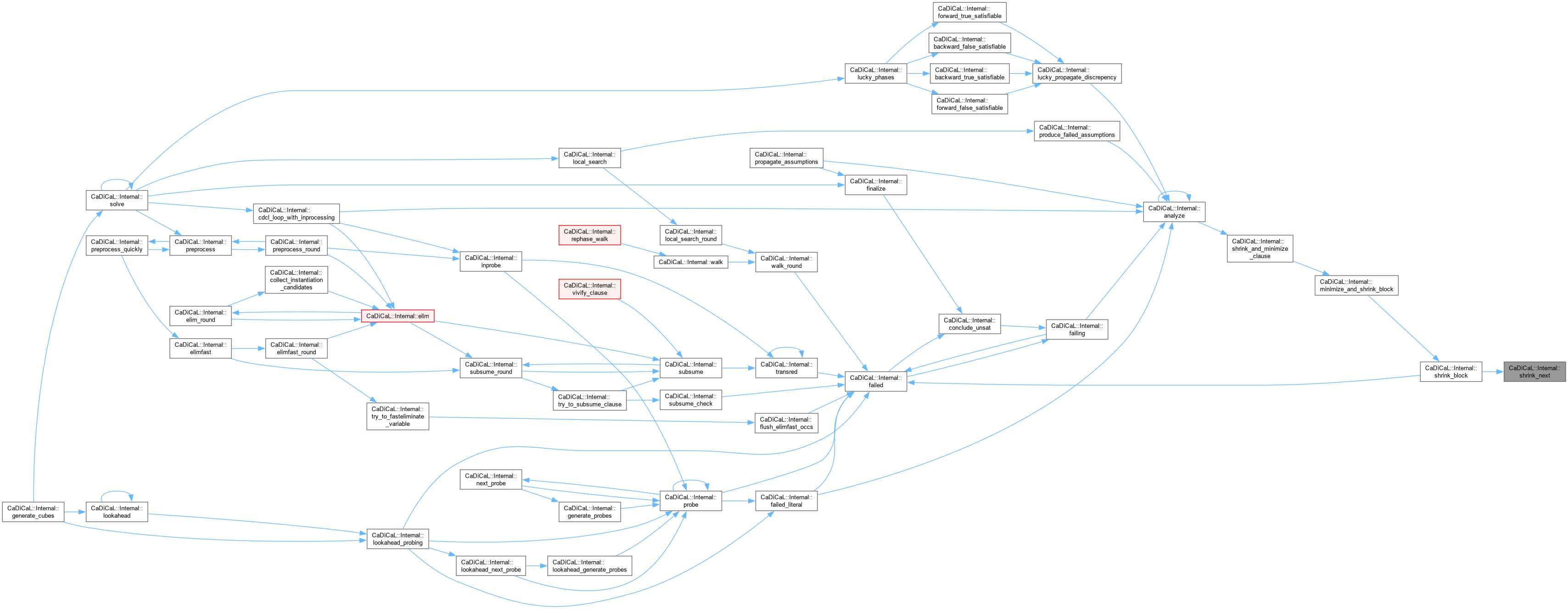
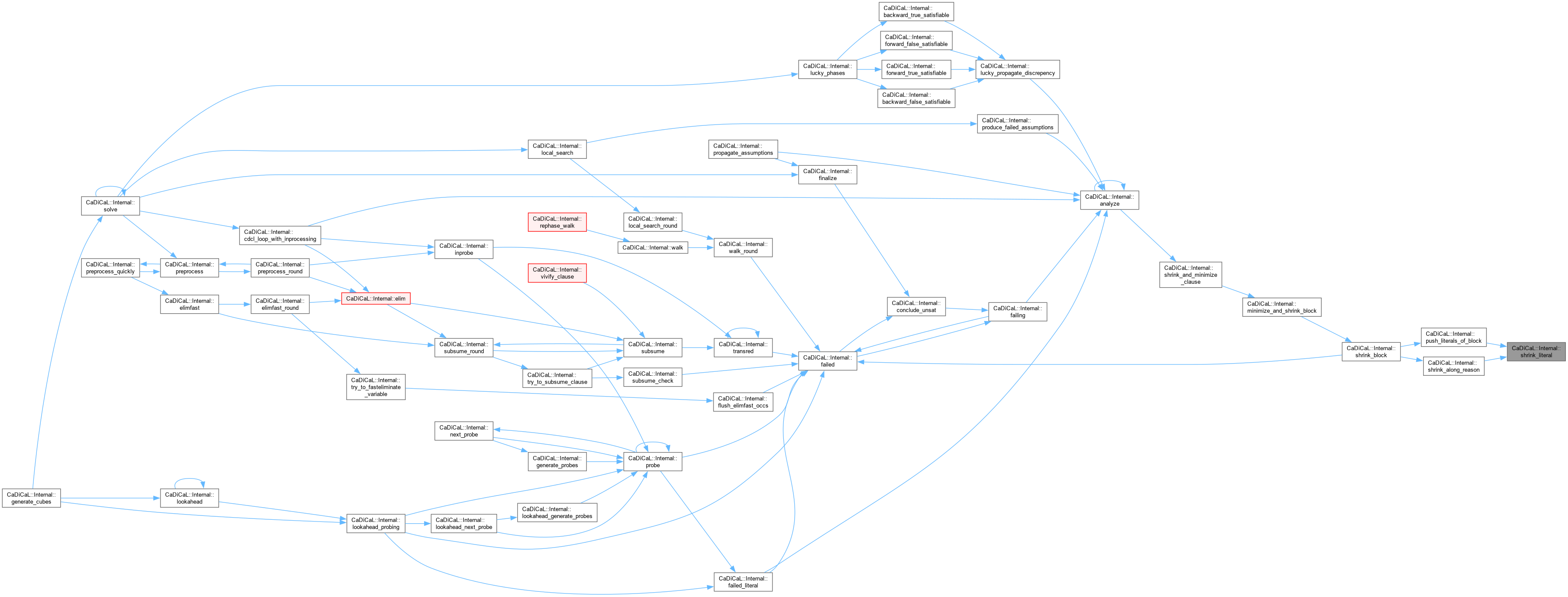
|
inline |
Definition at line 161 of file cadical_shrink.cpp.
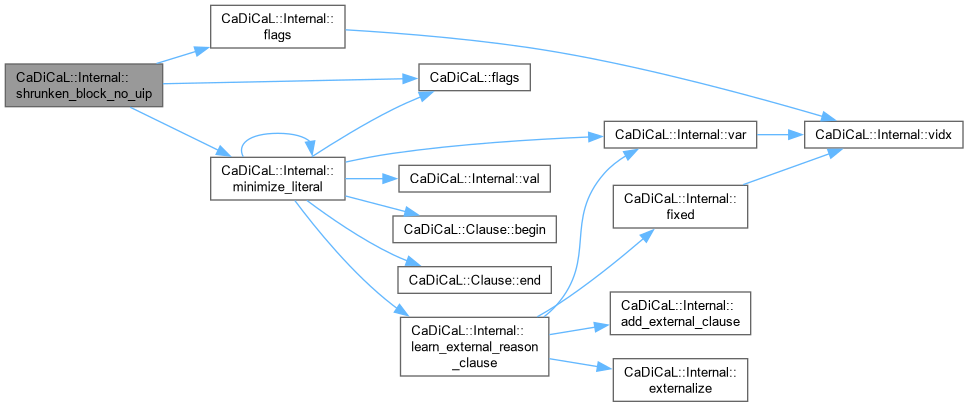
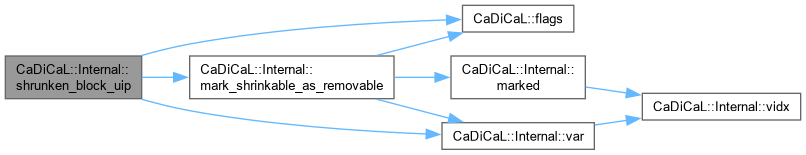
| unsigned CaDiCaL::Internal::shrunken_block_uip | ( | int | uip, |
| int | blevel, | ||
| std::vector< int >::reverse_iterator & | rbegin_block, | ||
| std::vector< int >::reverse_iterator & | rend_block, | ||
| std::vector< int >::size_type | minimized_start, | ||
| const int | uip0 ) |
Definition at line 124 of file cadical_shrink.cpp.
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::shuffle_queue | ( | ) |
Definition at line 64 of file cadical_queue.cpp.


| void CaDiCaL::Internal::shuffle_scores | ( | ) |
Definition at line 22 of file cadical_score.cpp.


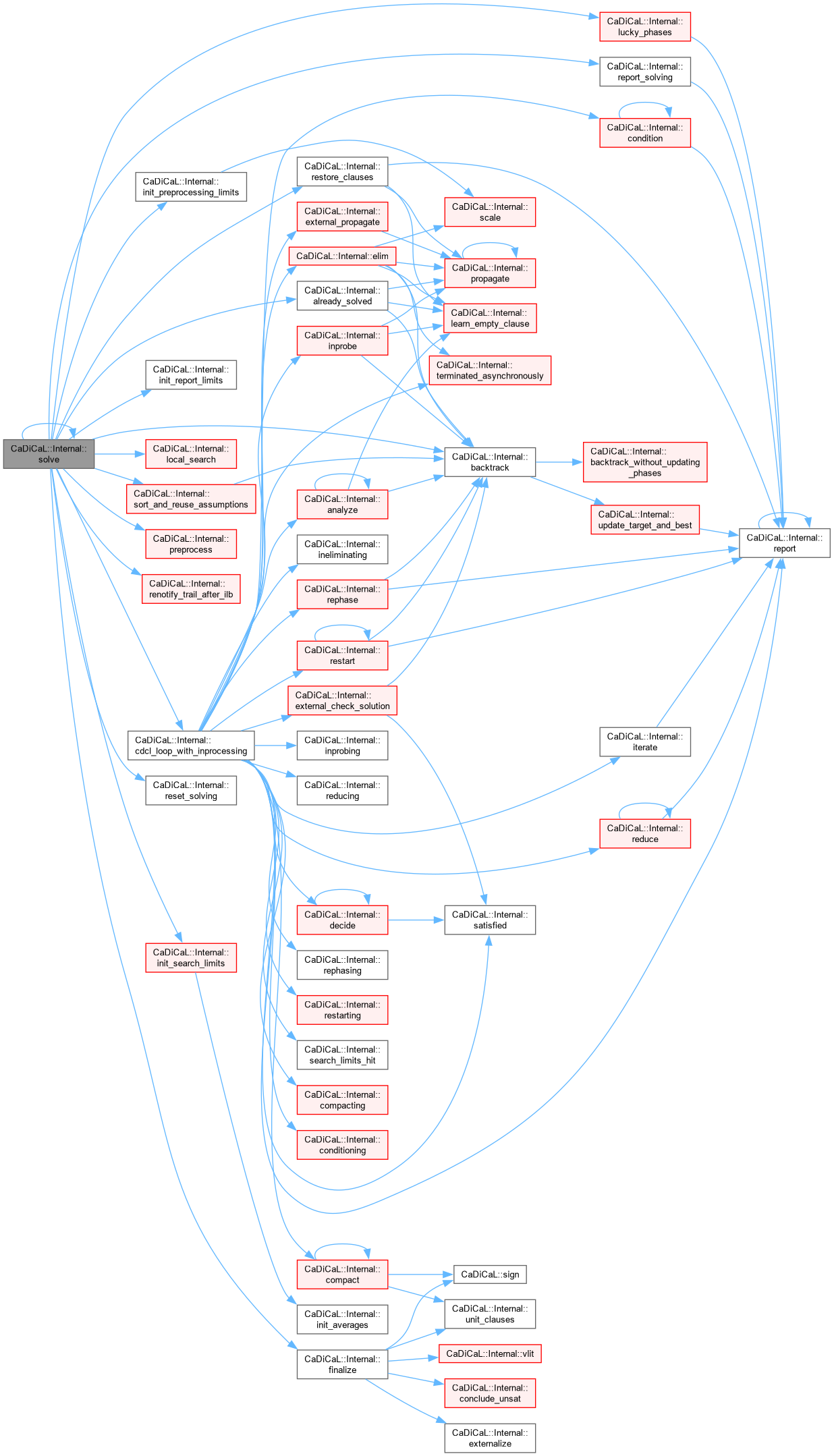
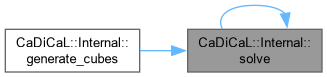
Definition at line 884 of file cadical_internal.cpp.
| double CaDiCaL::Internal::solve_time | ( | ) |
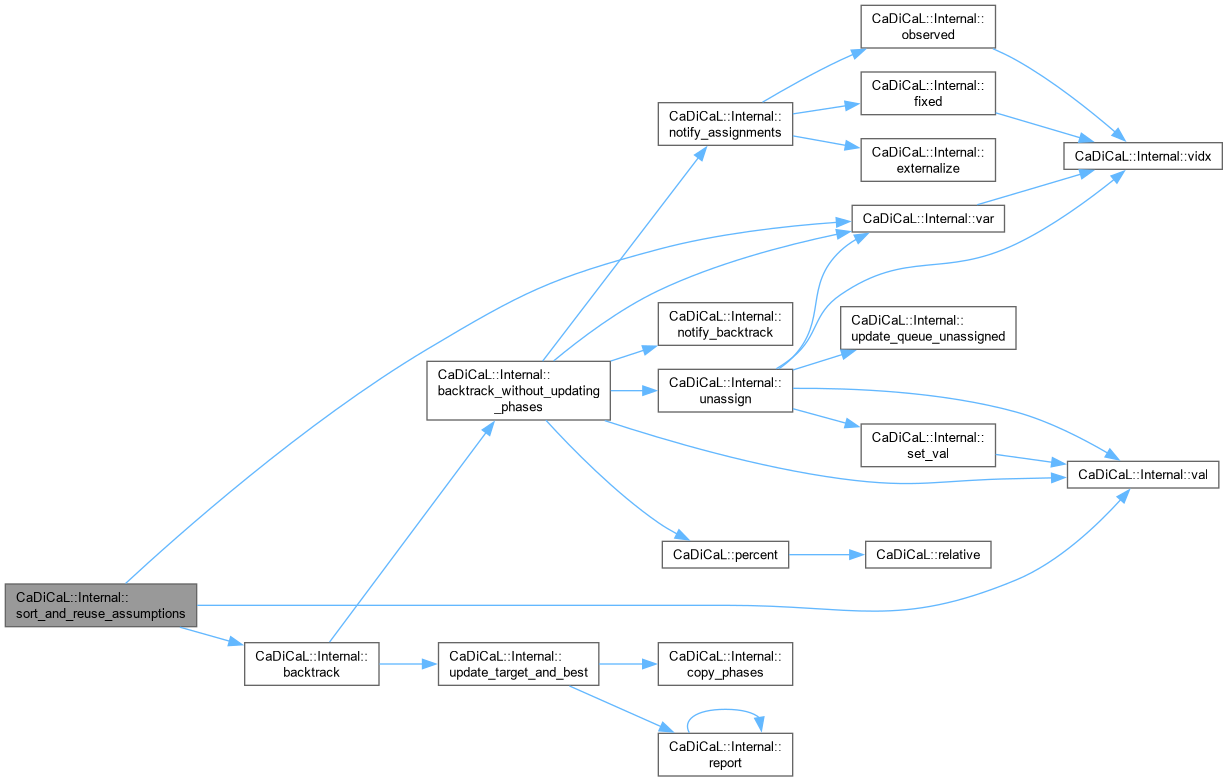
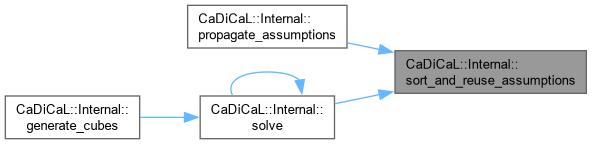
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::sort_and_reuse_assumptions | ( | ) |
Definition at line 554 of file cadical_assume.cpp.
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::sort_watches | ( | ) |
Definition at line 103 of file cadical_watch.cpp.
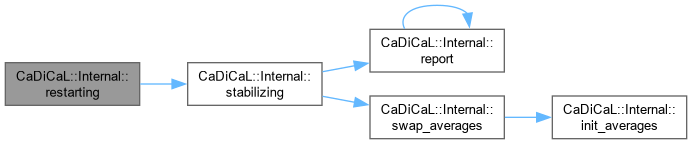
| bool CaDiCaL::Internal::stabilizing | ( | ) |
Definition at line 22 of file cadical_restart.cpp.

| void CaDiCaL::Internal::strengthen_clause | ( | Clause * | c, |
| int | lit ) |
Definition at line 160 of file cadical_subsume.cpp.
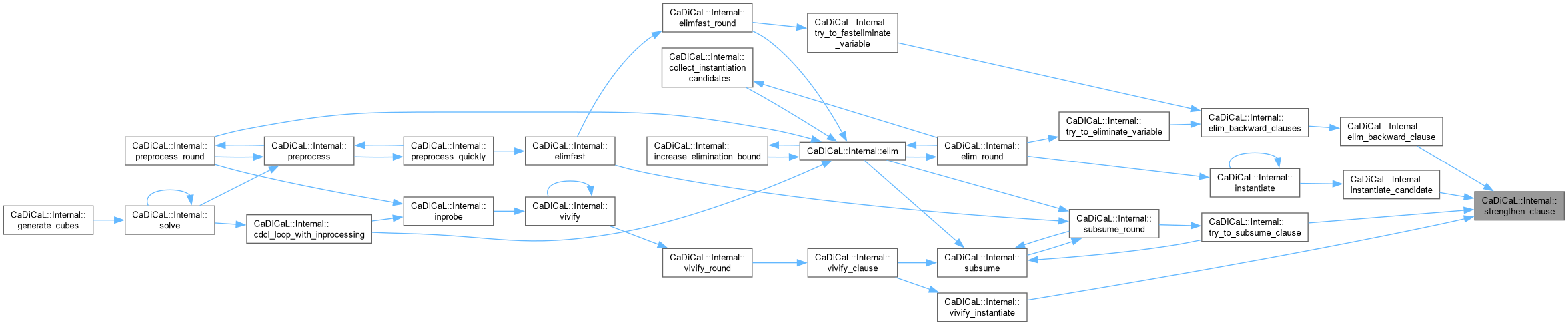
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::substitute_connected_clauses | ( | Sweeper & | sweeper, |
| int | lit, | ||
| int | other, | ||
| int64_t | id ) |
Definition at line 1051 of file cadical_sweep.cpp.
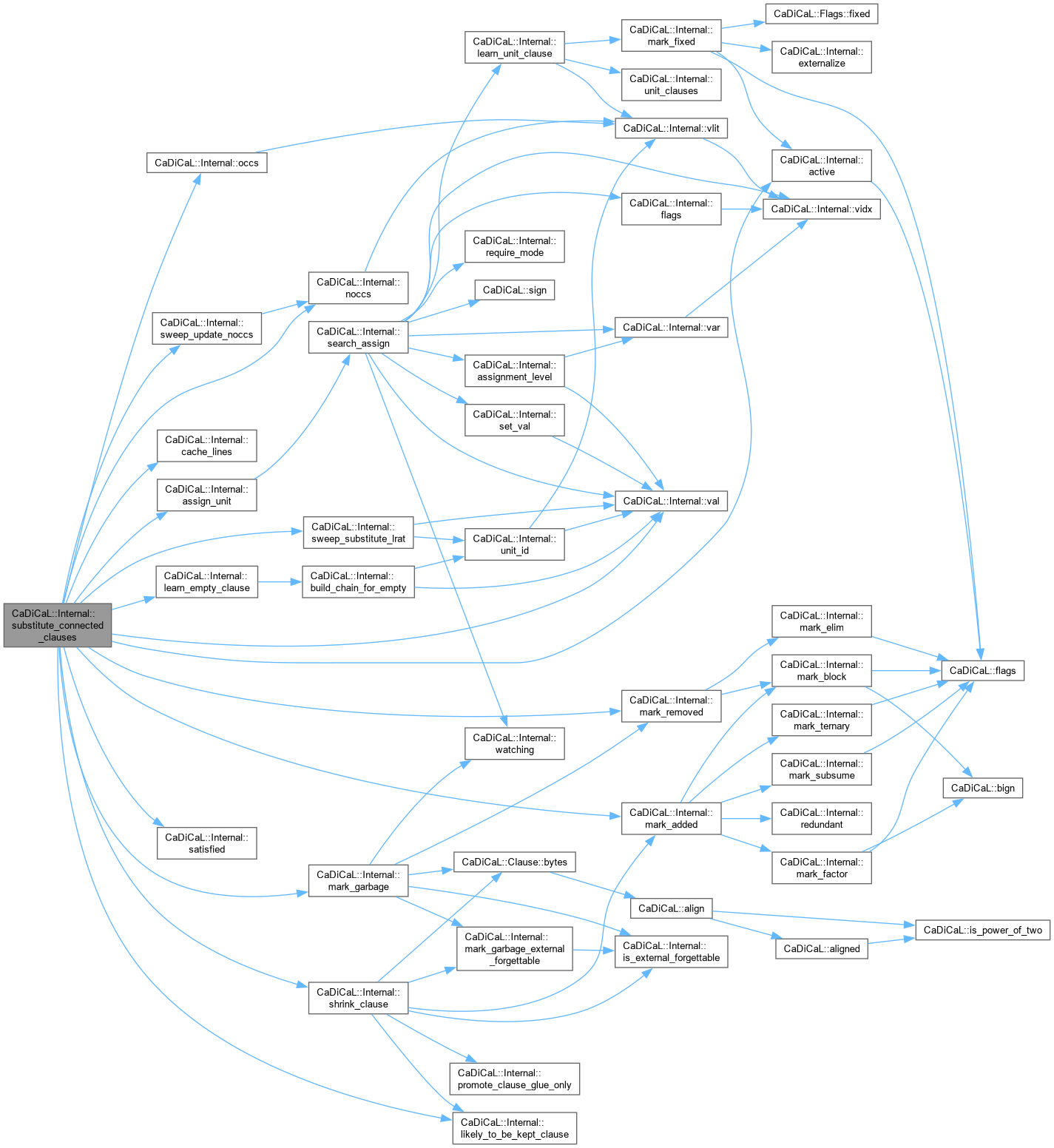
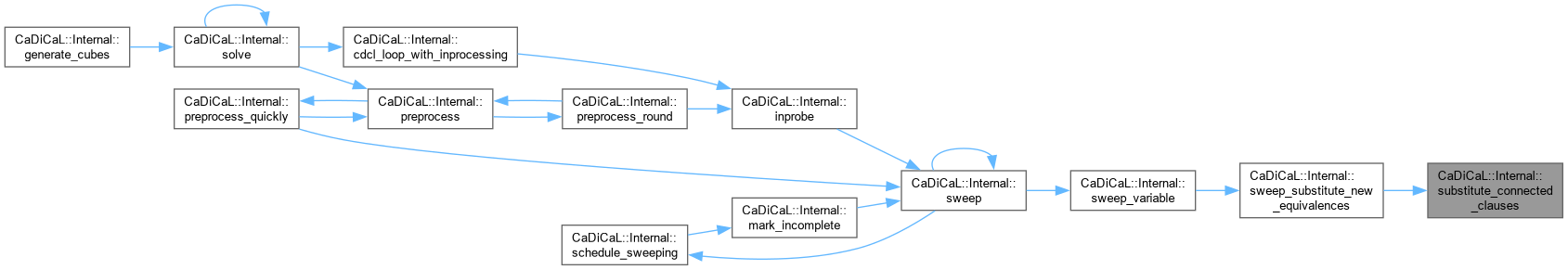
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::subsume | ( | ) |
Definition at line 611 of file cadical_subsume.cpp.
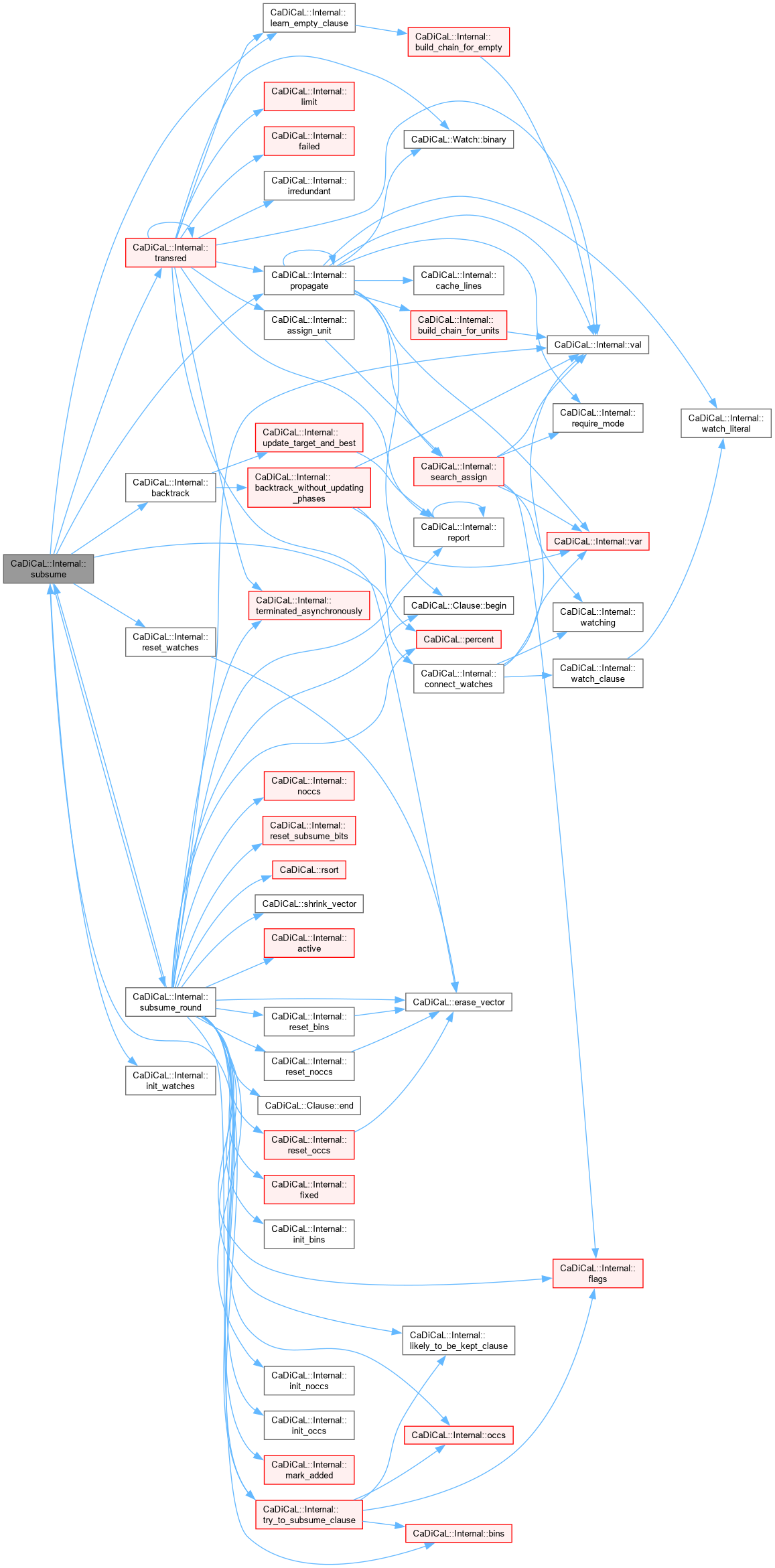
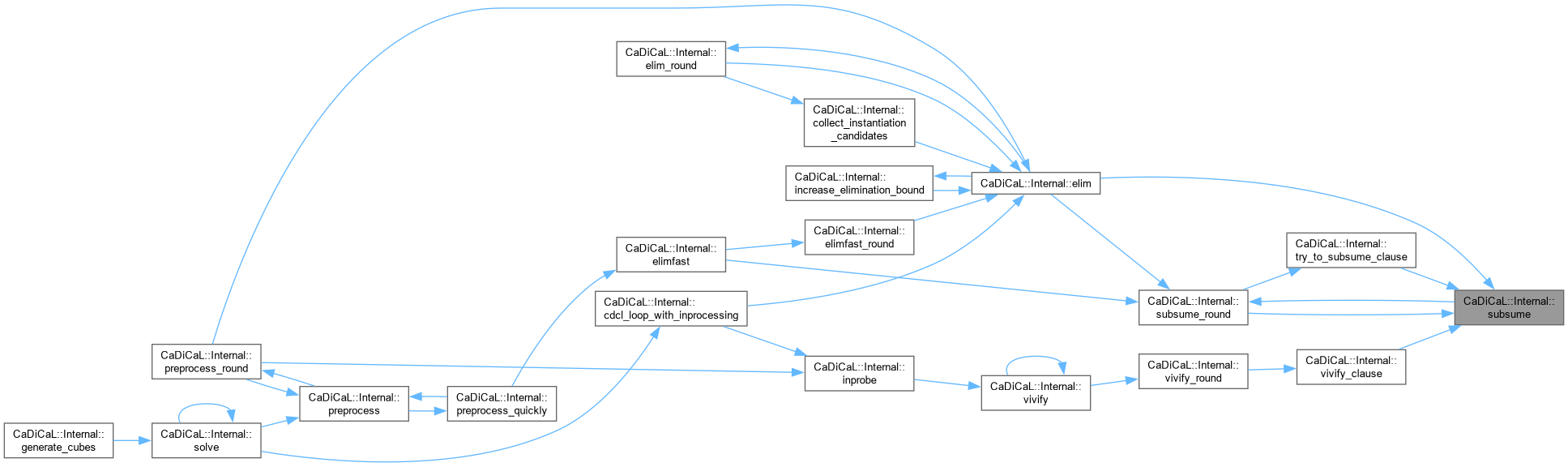
Definition at line 78 of file cadical_subsume.cpp.
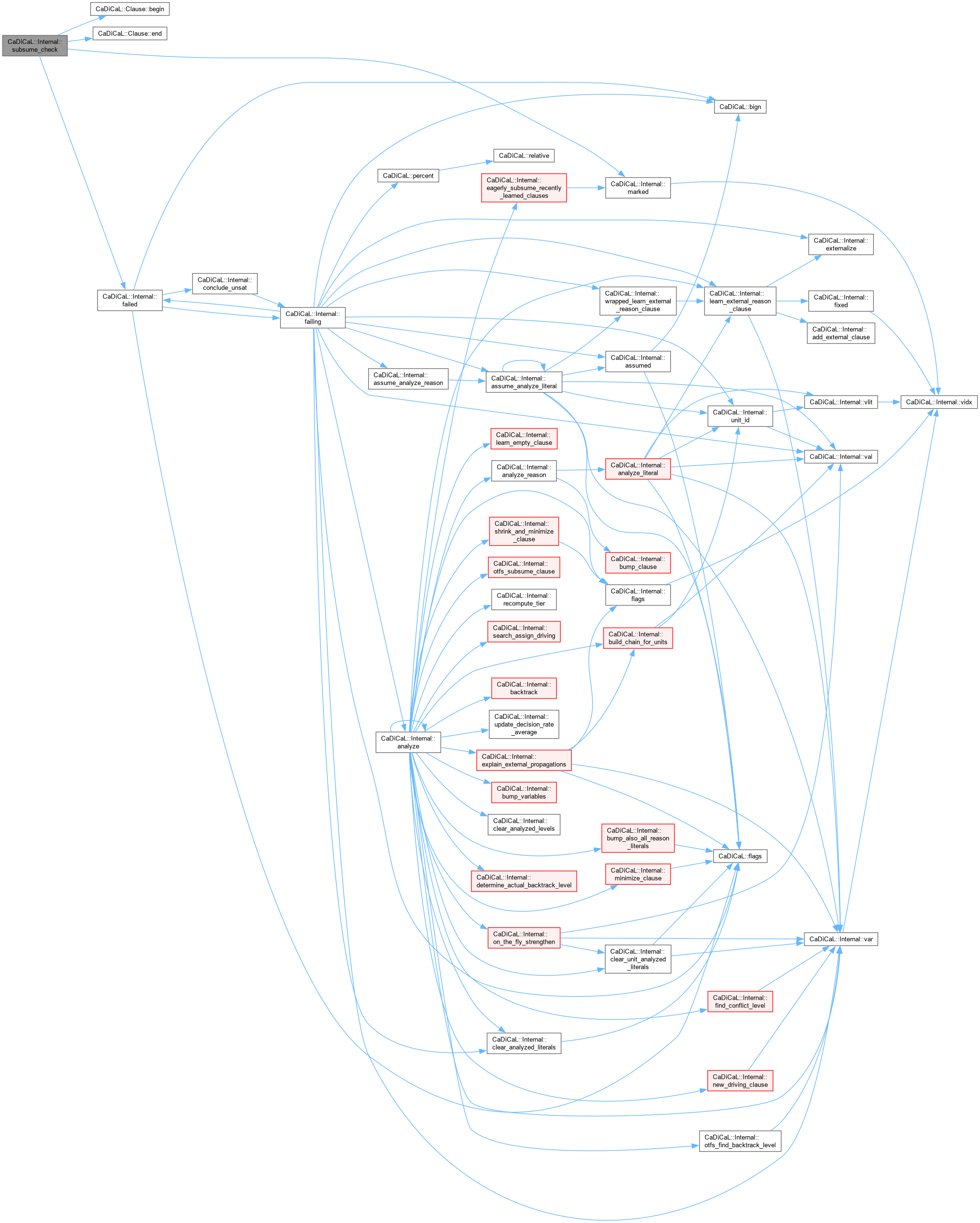
Definition at line 129 of file cadical_subsume.cpp.
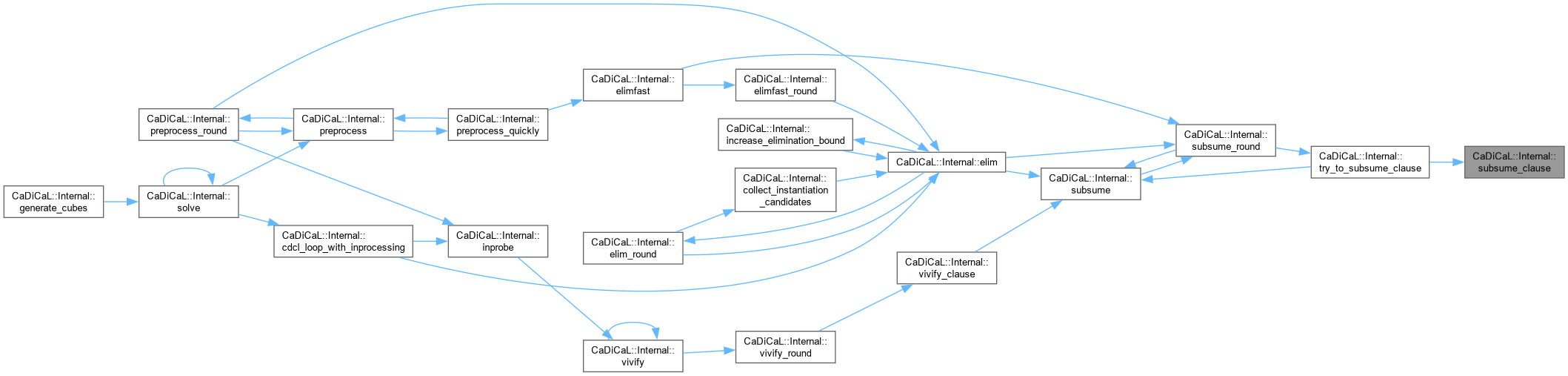
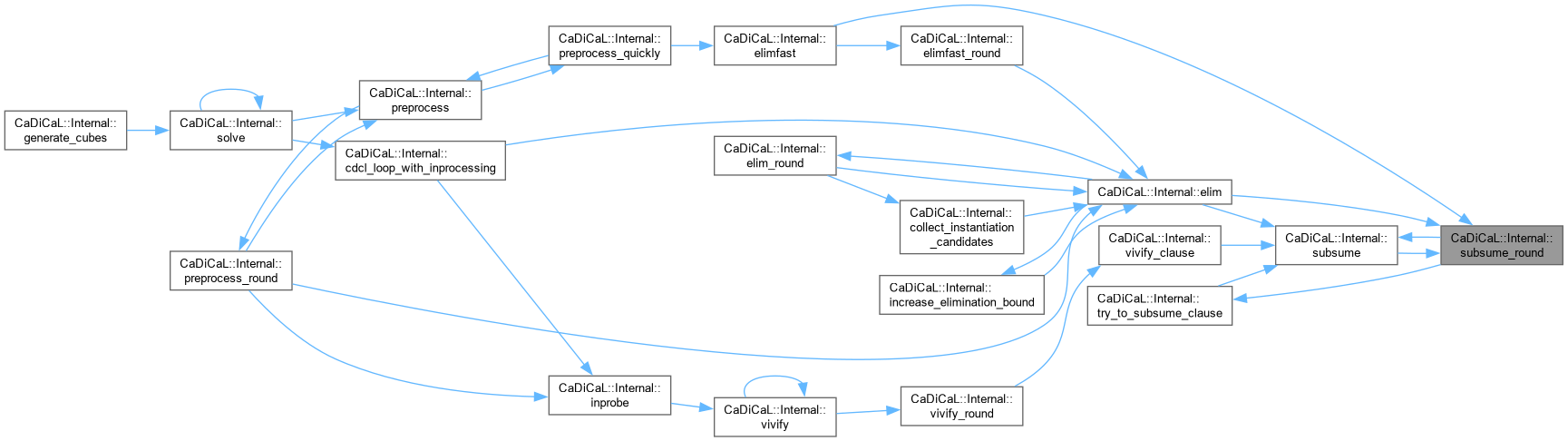
| bool CaDiCaL::Internal::subsume_round | ( | ) |
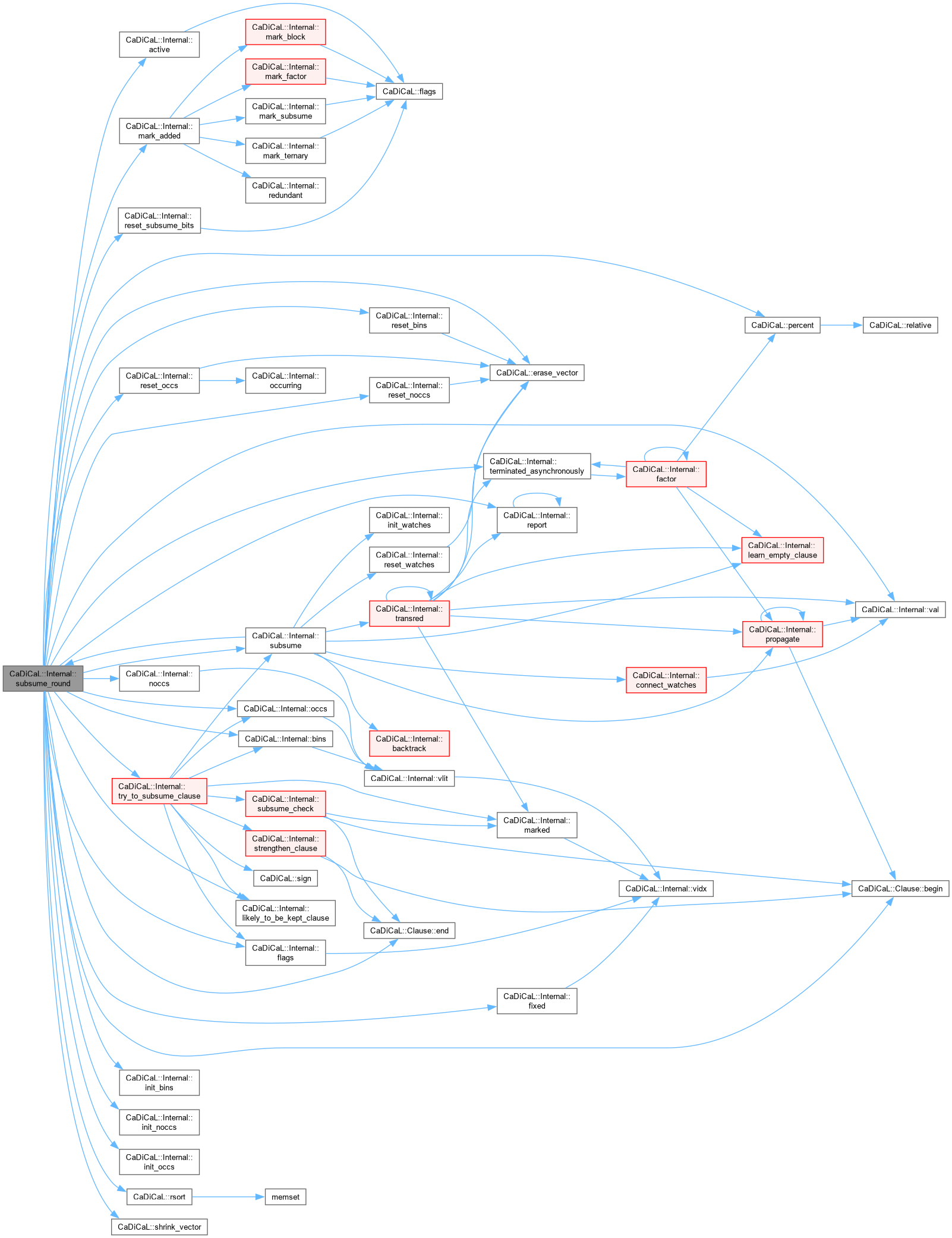
Definition at line 340 of file cadical_subsume.cpp.
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::swap_averages | ( | ) |
Definition at line 28 of file cadical_averages.cpp.
| bool CaDiCaL::Internal::sweep | ( | ) |
Definition at line 1875 of file cadical_sweep.cpp.
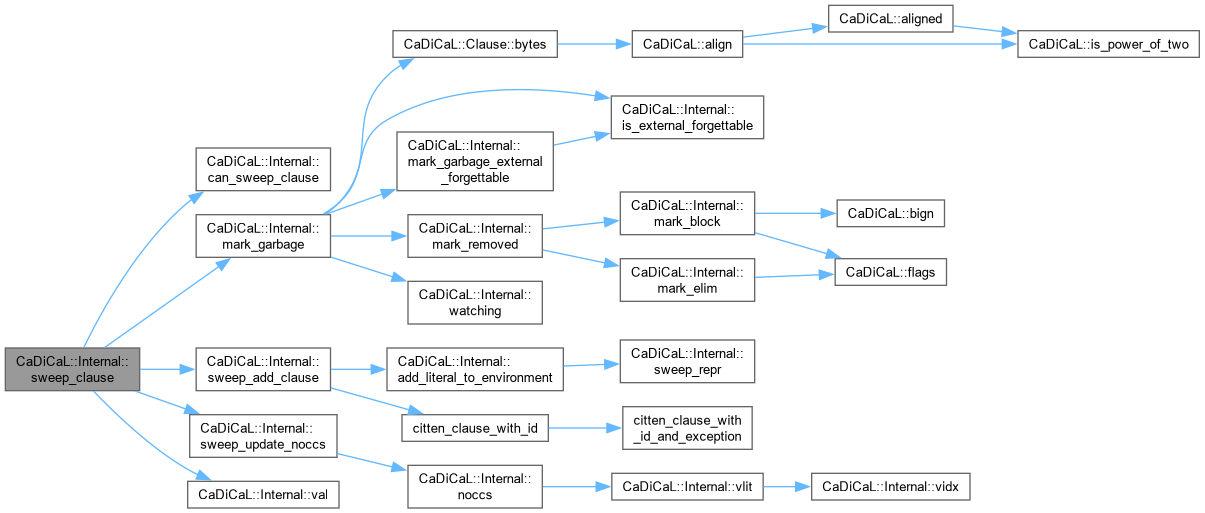
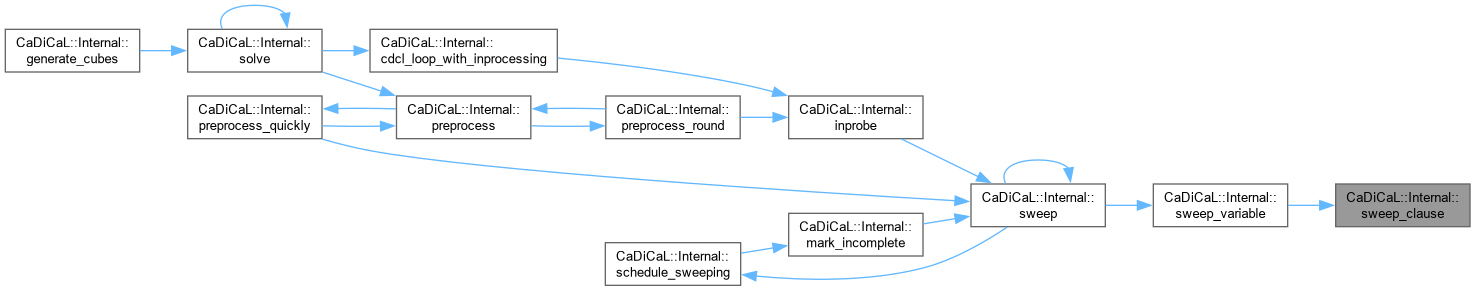
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::sweep_add_clause | ( | Sweeper & | sweeper, |
| unsigned | depth ) |
Definition at line 358 of file cadical_sweep.cpp.

Definition at line 843 of file cadical_sweep.cpp.
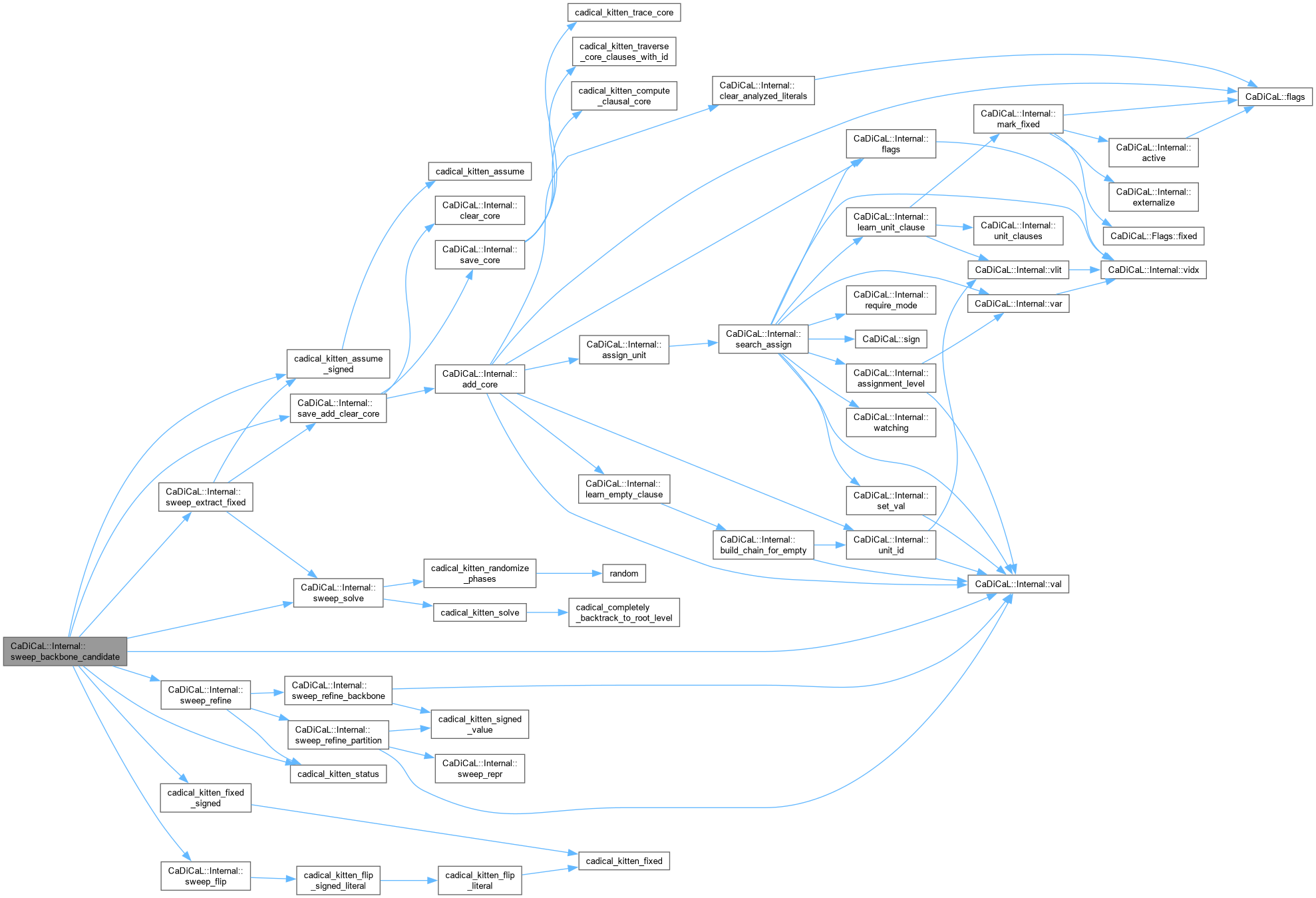
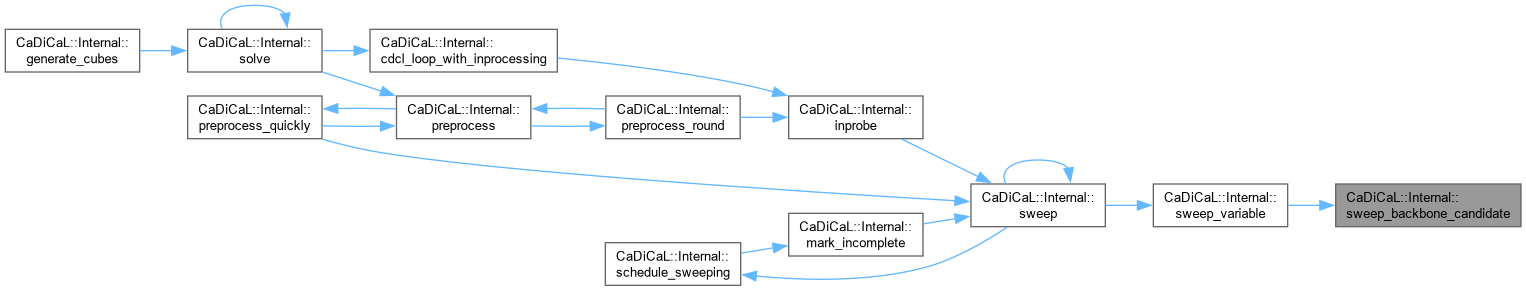
Definition at line 370 of file cadical_sweep.cpp.
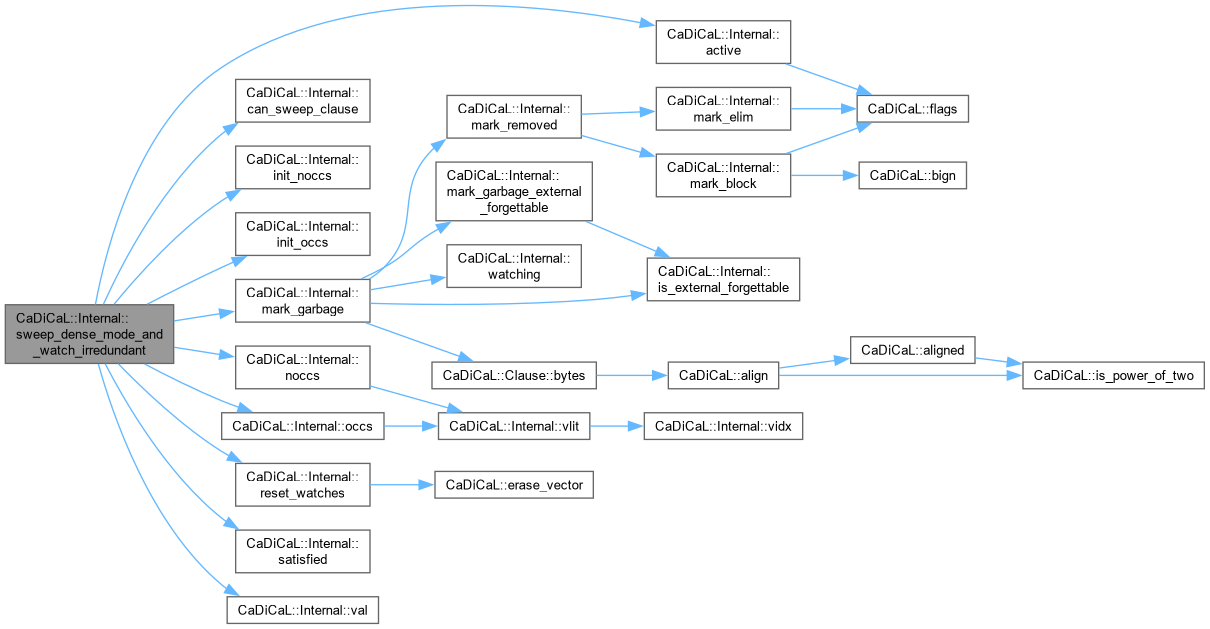
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::sweep_dense_mode_and_watch_irredundant | ( | ) |
Definition at line 77 of file cadical_sweep.cpp.
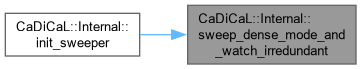
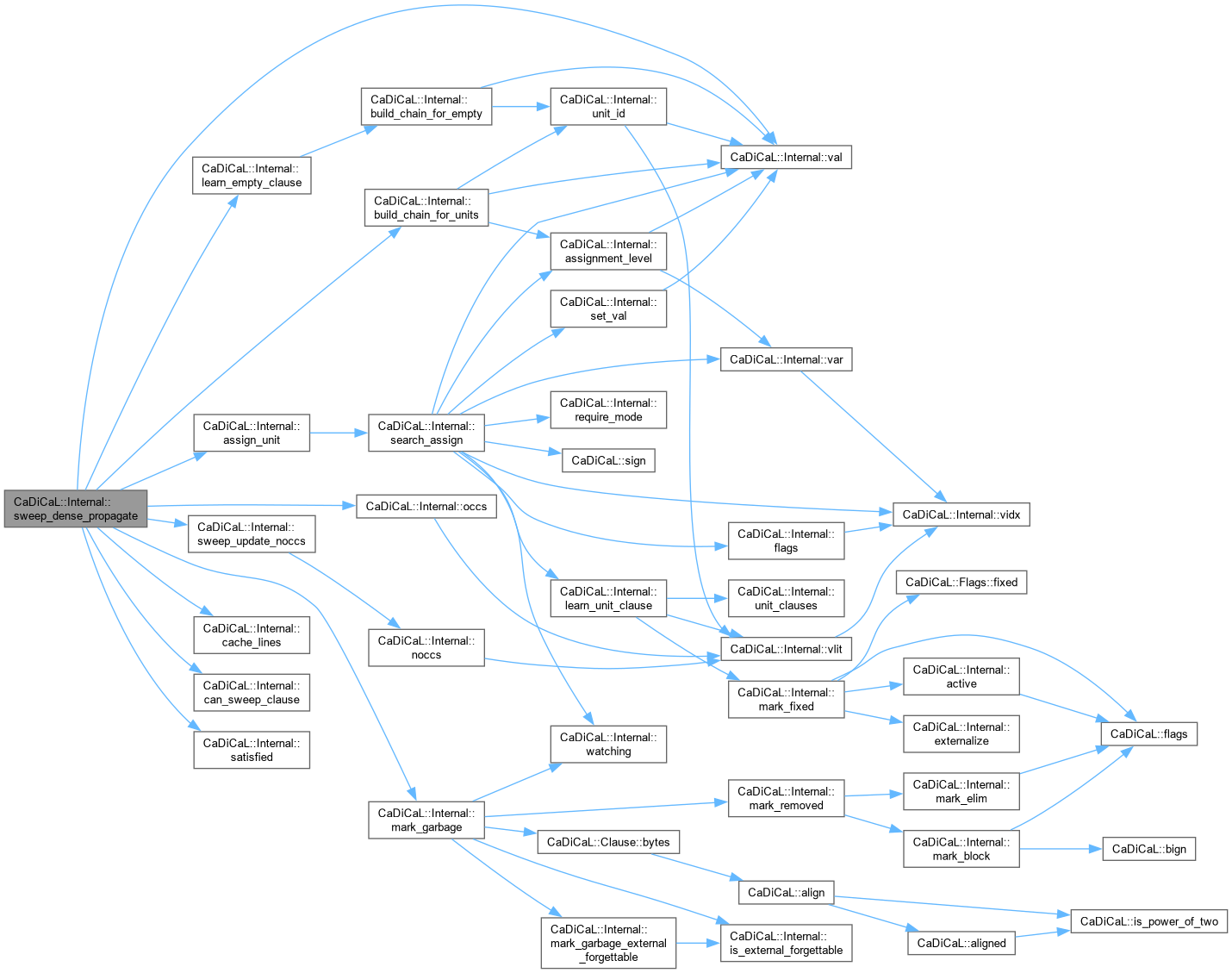
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::sweep_dense_propagate | ( | Sweeper & | sweeper | ) |
Definition at line 133 of file cadical_sweep.cpp.
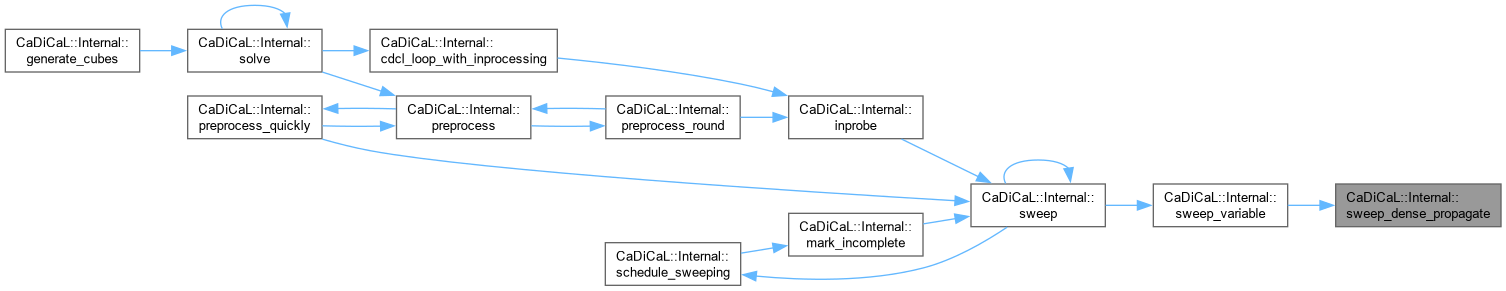
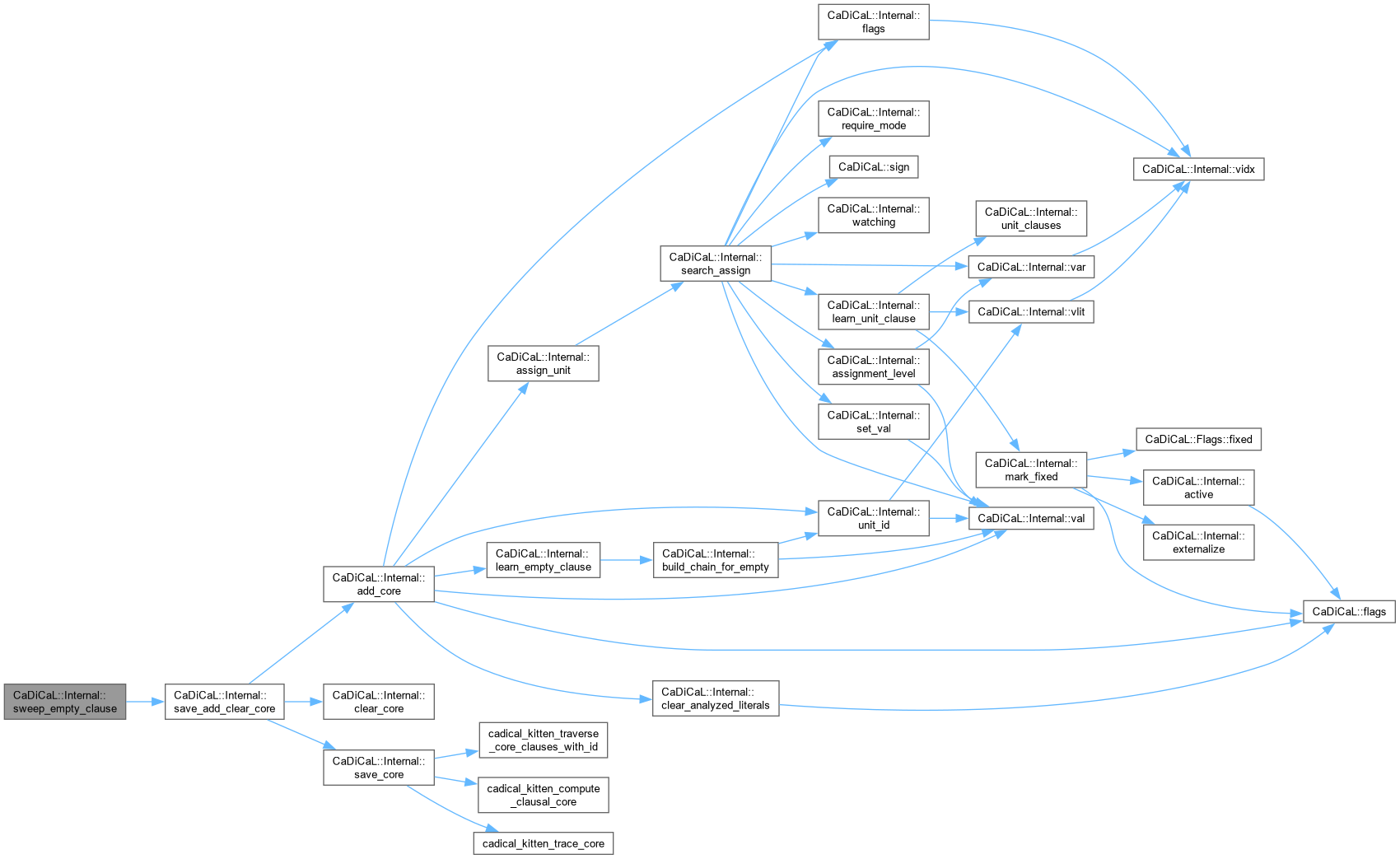
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::sweep_empty_clause | ( | Sweeper & | sweeper | ) |
Definition at line 654 of file cadical_sweep.cpp.
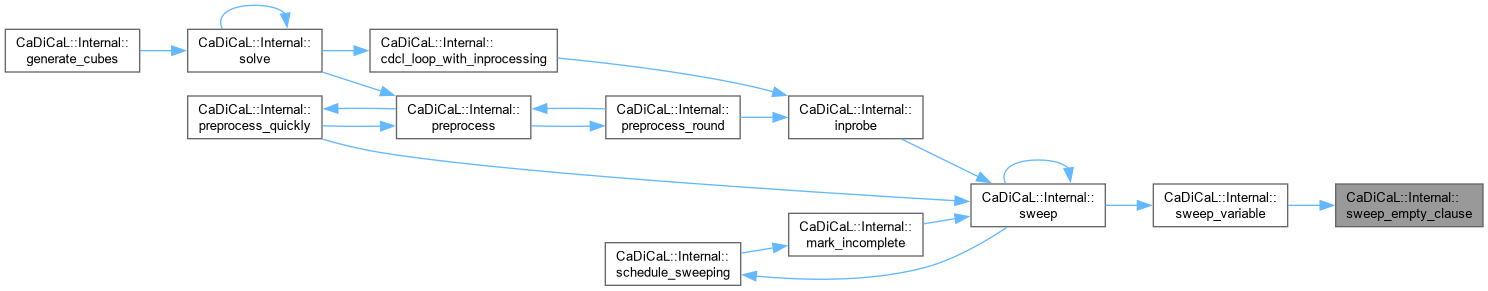
Definition at line 1341 of file cadical_sweep.cpp.
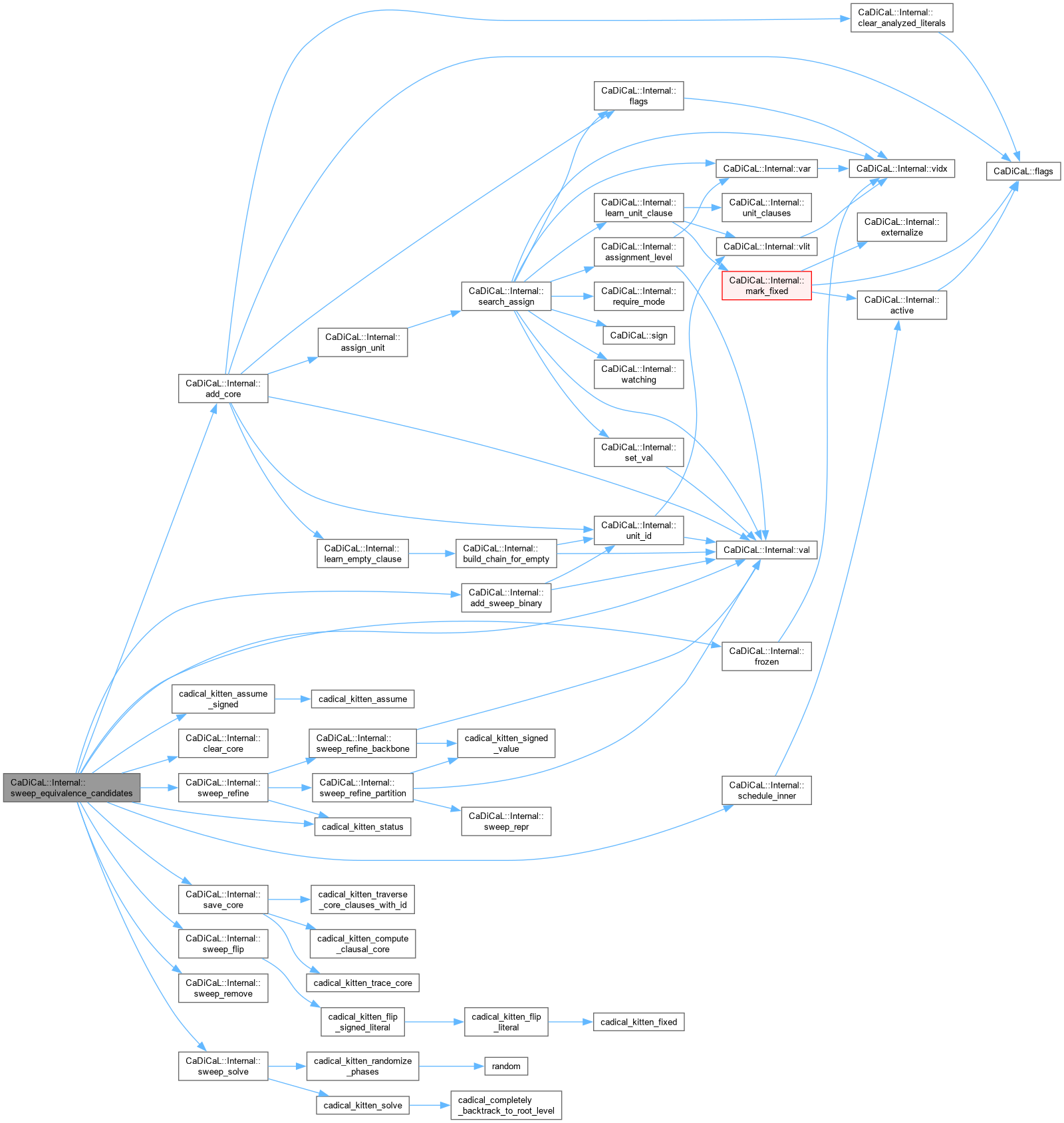
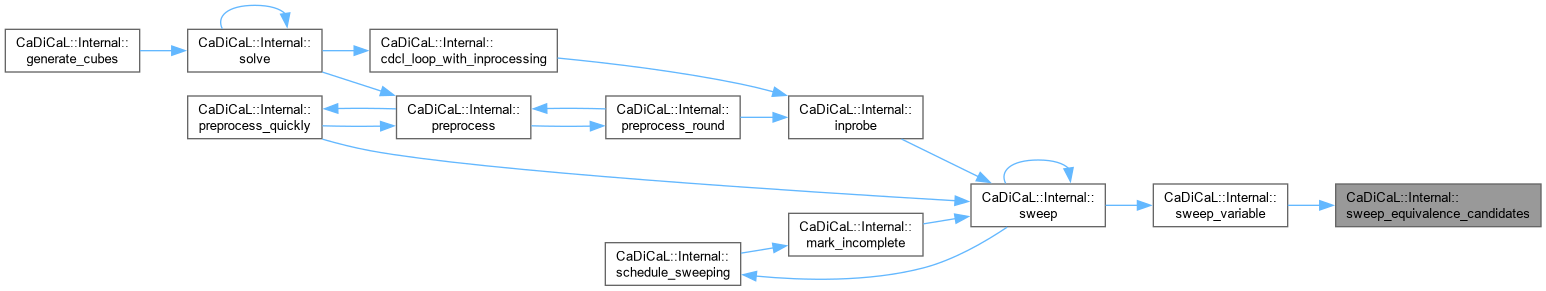
Definition at line 827 of file cadical_sweep.cpp.
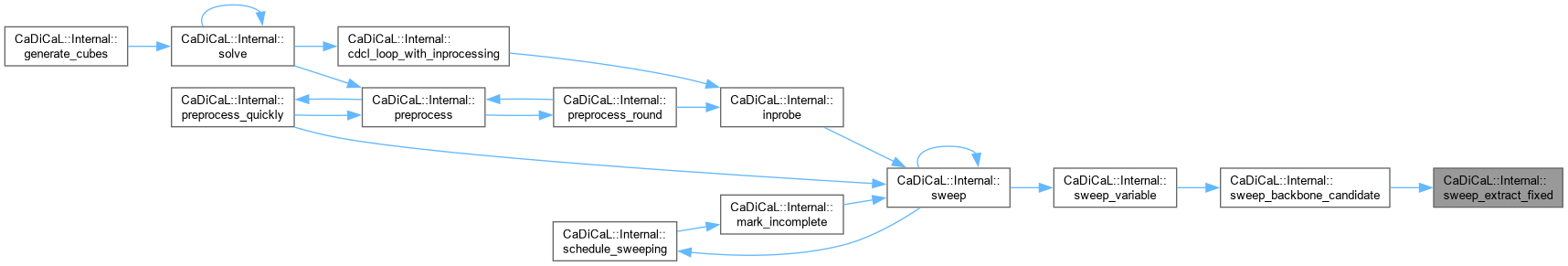
| bool CaDiCaL::Internal::sweep_flip | ( | int | lit | ) |
Definition at line 37 of file cadical_sweep.cpp.

| int CaDiCaL::Internal::sweep_flip_and_implicant | ( | int | lit | ) |
Definition at line 44 of file cadical_sweep.cpp.

| void CaDiCaL::Internal::sweep_refine | ( | Sweeper & | sweeper | ) |
Definition at line 762 of file cadical_sweep.cpp.
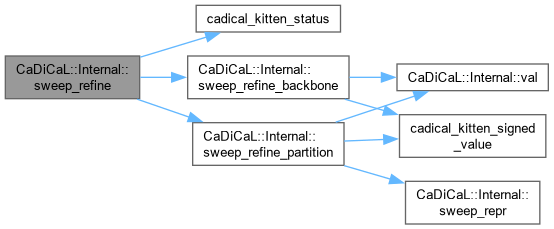
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::sweep_refine_backbone | ( | Sweeper & | sweeper | ) |
Definition at line 745 of file cadical_sweep.cpp.
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::sweep_refine_partition | ( | Sweeper & | sweeper | ) |
Definition at line 660 of file cadical_sweep.cpp.
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::sweep_remove | ( | Sweeper & | sweeper, |
| int | lit ) |
Definition at line 1242 of file cadical_sweep.cpp.
| int CaDiCaL::Internal::sweep_repr | ( | Sweeper & | sweeper, |
| int | lit ) |
Definition at line 319 of file cadical_sweep.cpp.
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::sweep_set_cadical_kitten_ticks_limit | ( | Sweeper & | sweeper | ) |
Definition at line 51 of file cadical_sweep.cpp.
| int CaDiCaL::Internal::sweep_solve | ( | ) |
Definition at line 24 of file cadical_sweep.cpp.

| void CaDiCaL::Internal::sweep_sparse_mode | ( | ) |
Definition at line 125 of file cadical_sweep.cpp.
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::sweep_substitute_lrat | ( | Clause * | c, |
| int64_t | id ) |
Definition at line 1030 of file cadical_sweep.cpp.
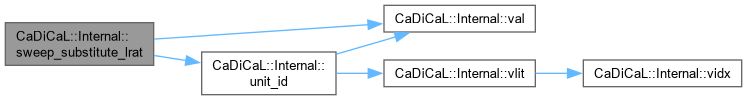
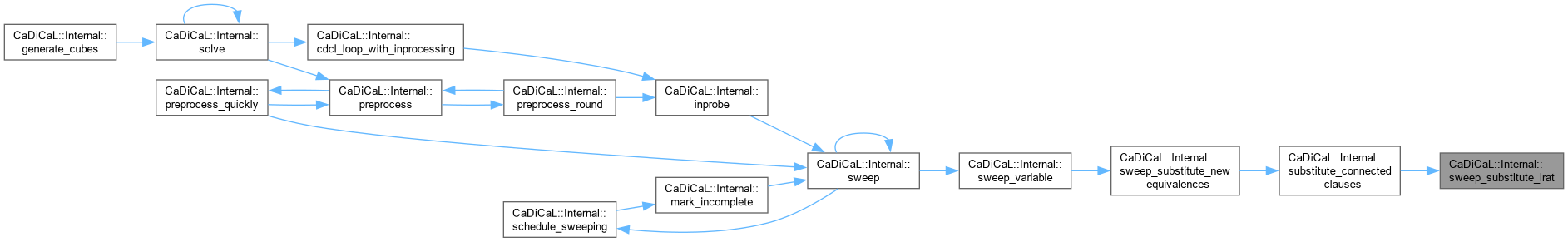
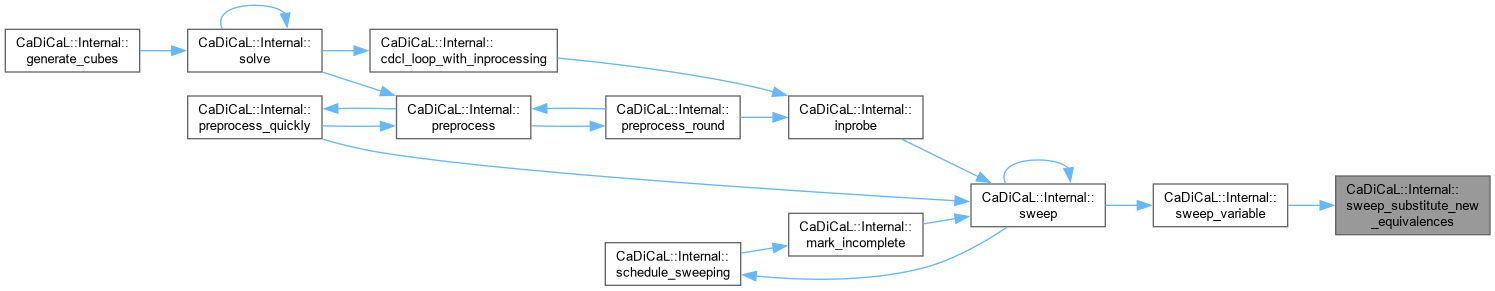
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::sweep_substitute_new_equivalences | ( | Sweeper & | sweeper | ) |
Definition at line 1181 of file cadical_sweep.cpp.
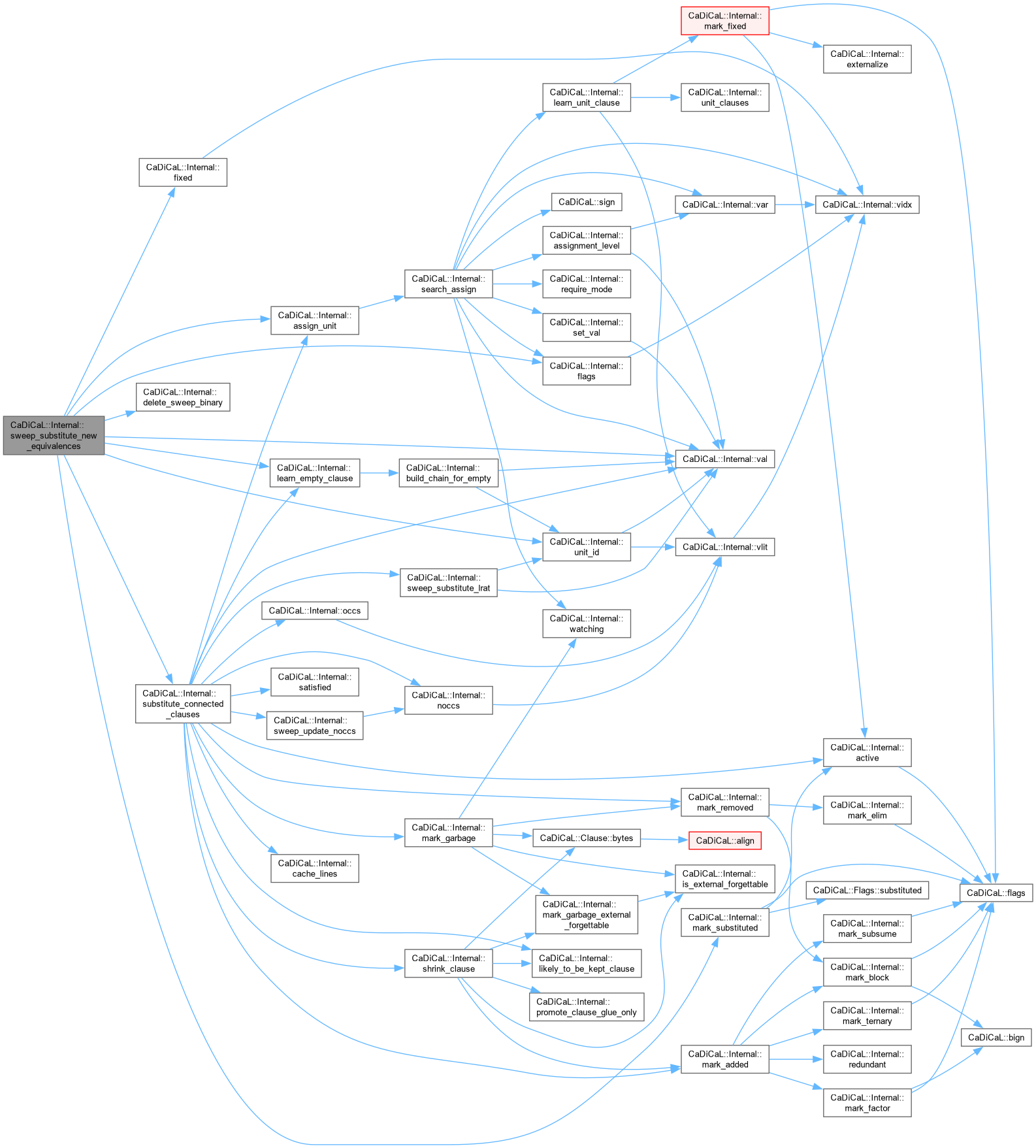
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::sweep_update_noccs | ( | Clause * | c | ) |
Definition at line 60 of file cadical_sweep.cpp.

Definition at line 1514 of file cadical_sweep.cpp.
|
inline |
Definition at line 878 of file internal.hpp.
|
inline |
Definition at line 1789 of file internal.hpp.
| bool CaDiCaL::Internal::terminating_asked | ( | ) |
Definition at line 267 of file cadical_lookahead.cpp.
| bool CaDiCaL::Internal::ternary | ( | ) |
Definition at line 361 of file cadical_ternary.cpp.
| bool CaDiCaL::Internal::ternary_find_binary_clause | ( | int | a, |
| int | b ) |
Definition at line 29 of file cadical_ternary.cpp.
| bool CaDiCaL::Internal::ternary_find_ternary_clause | ( | int | a, |
| int | b, | ||
| int | c ) |
Definition at line 55 of file cadical_ternary.cpp.
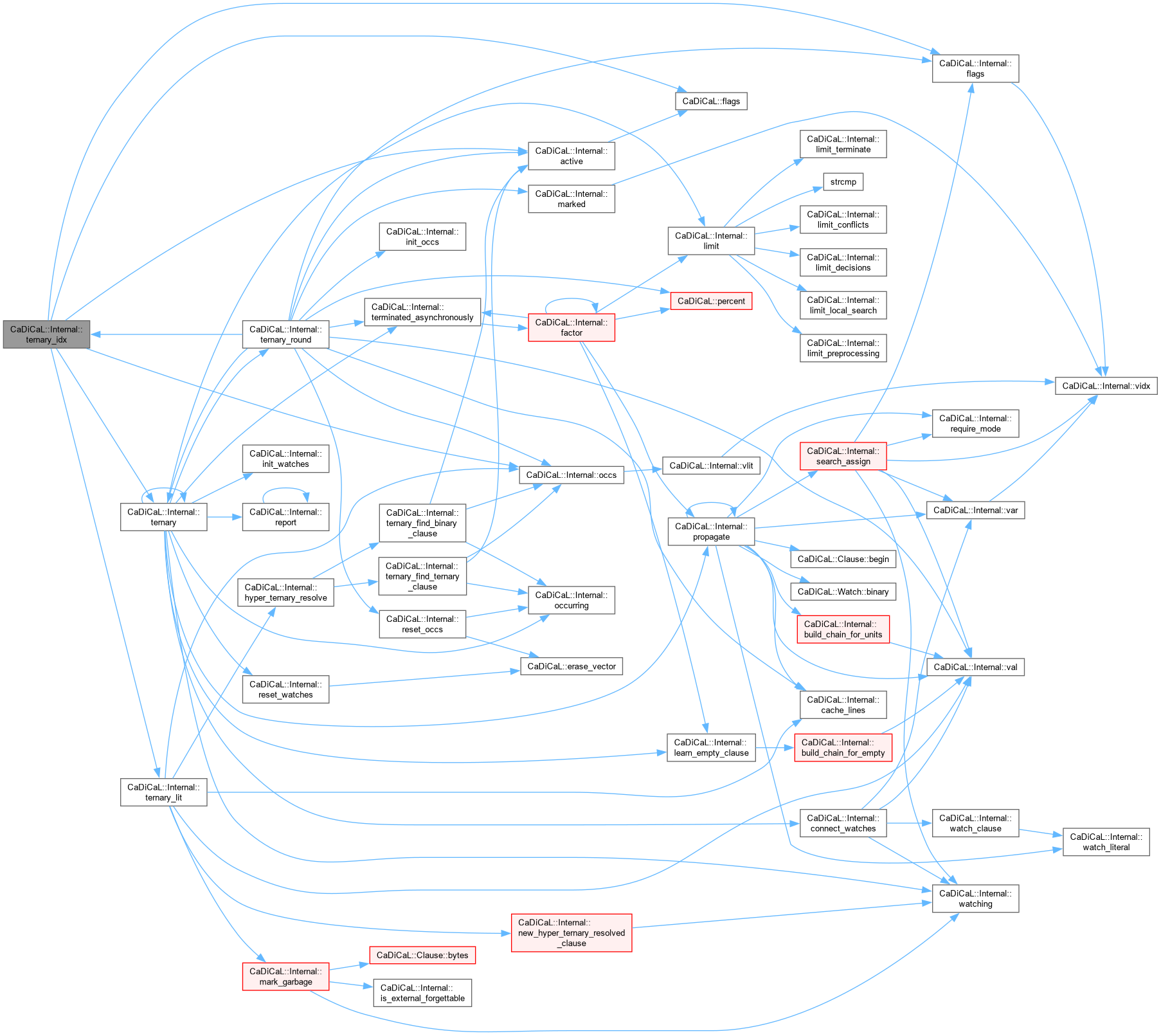
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::ternary_idx | ( | int | idx, |
| int64_t & | steps, | ||
| int64_t & | htrs ) |
Definition at line 241 of file cadical_ternary.cpp.
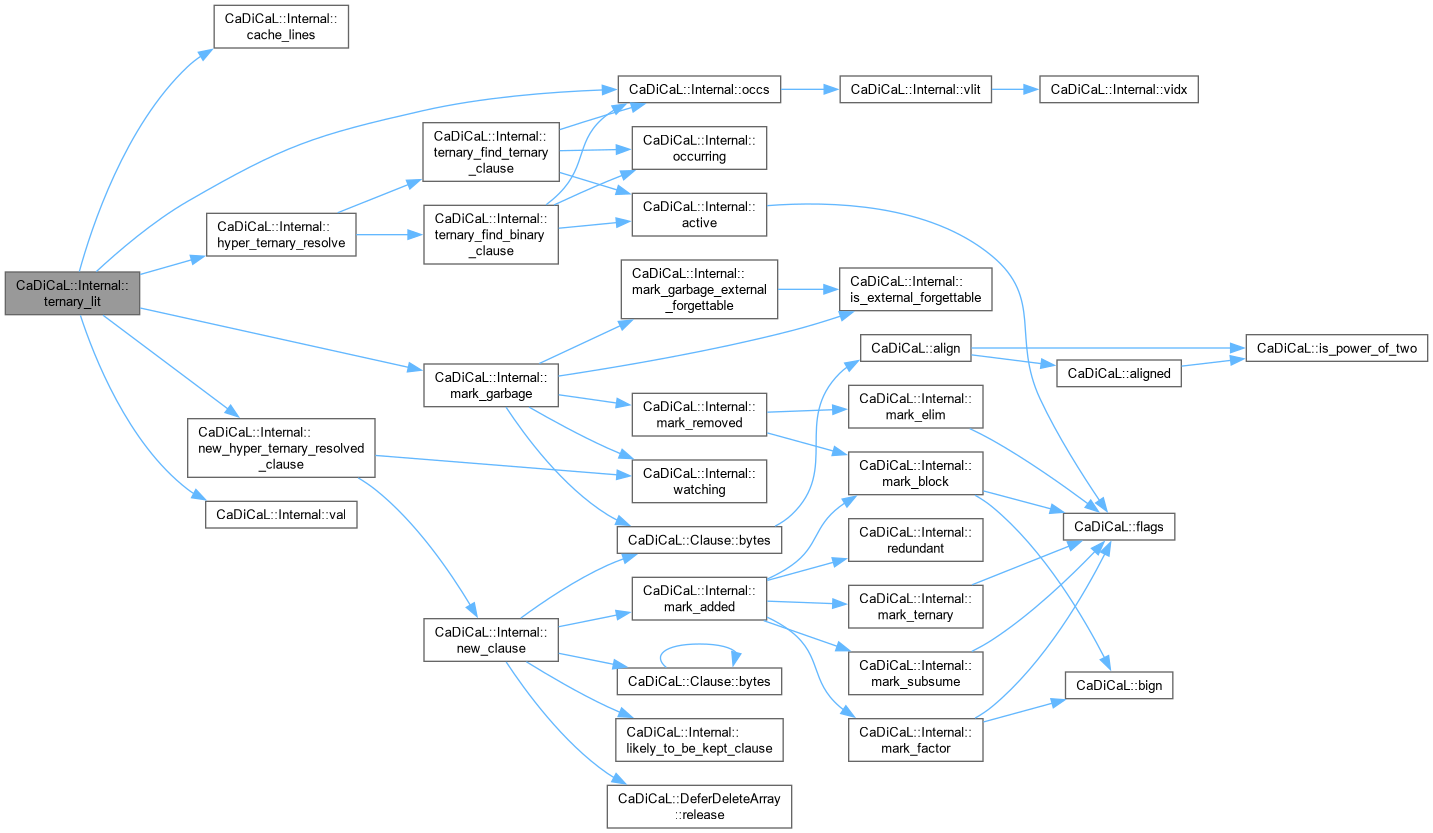
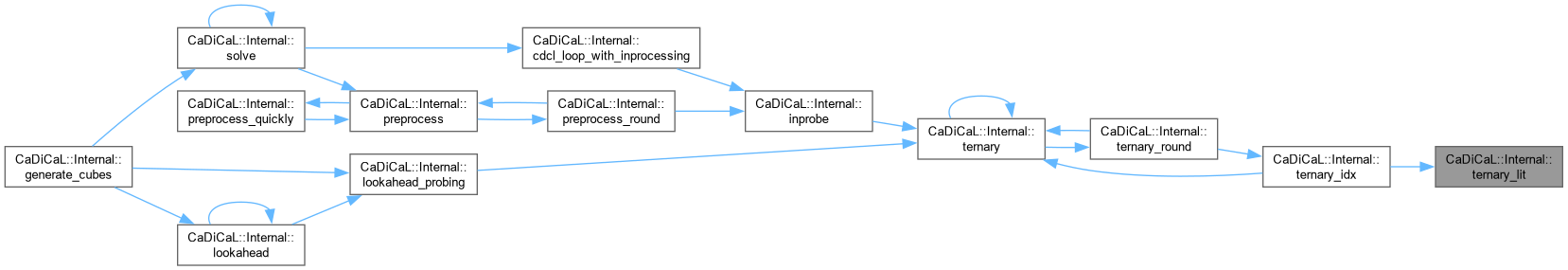
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::ternary_lit | ( | int | pivot, |
| int64_t & | steps, | ||
| int64_t & | htrs ) |
Definition at line 156 of file cadical_ternary.cpp.
| bool CaDiCaL::Internal::ternary_round | ( | int64_t & | steps, |
| int64_t & | htrs ) |
Definition at line 271 of file cadical_ternary.cpp.
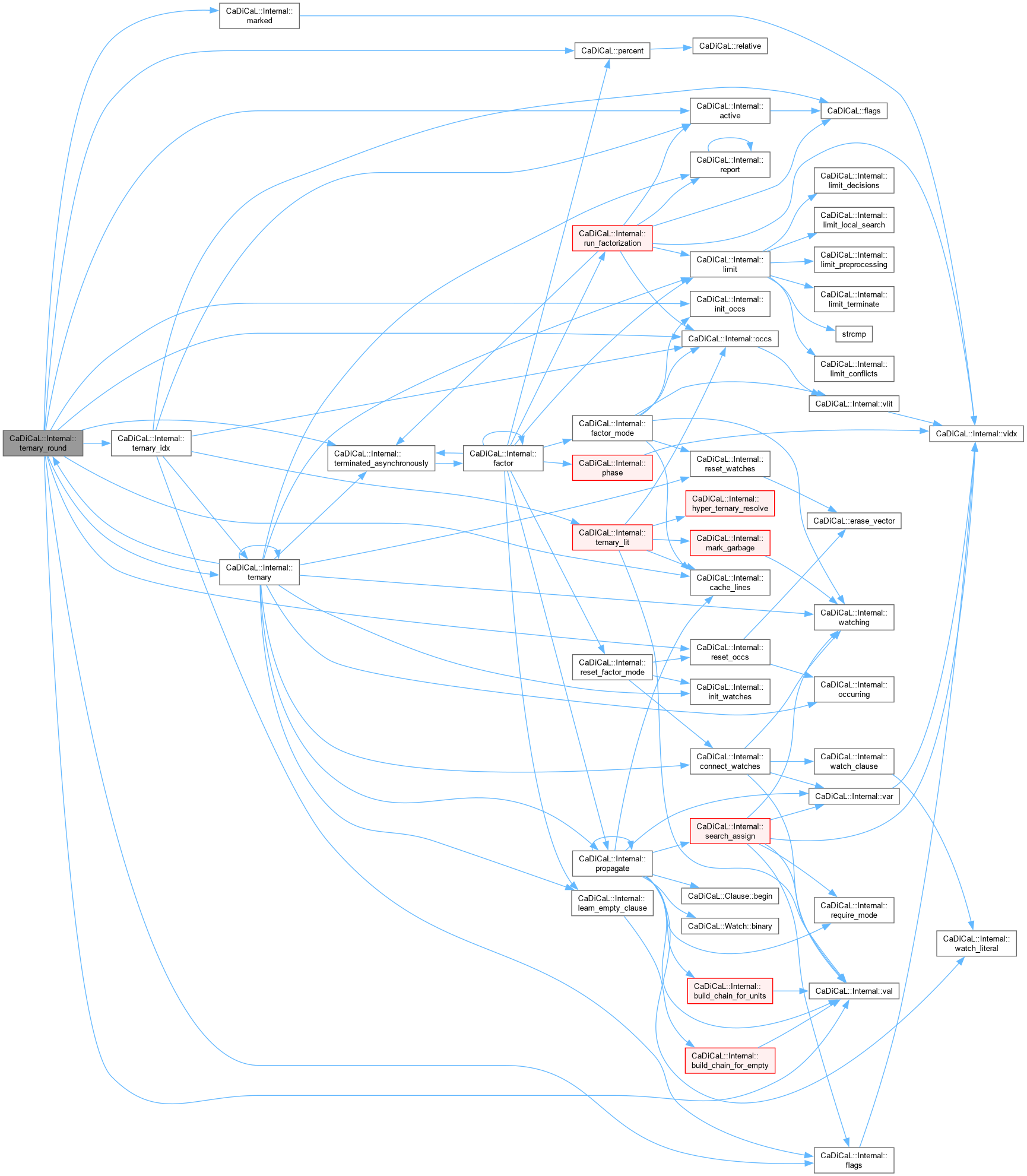
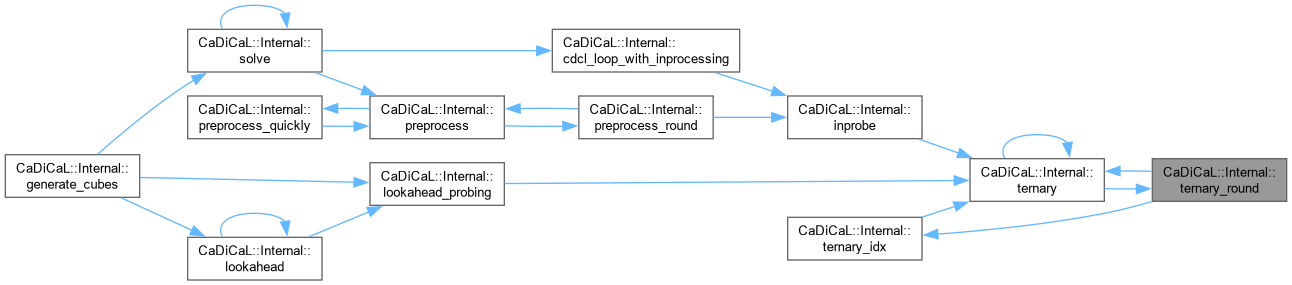
| double CaDiCaL::Internal::tied_next_factor_score | ( | int | lit | ) |
|
inline |
Definition at line 1660 of file internal.hpp.
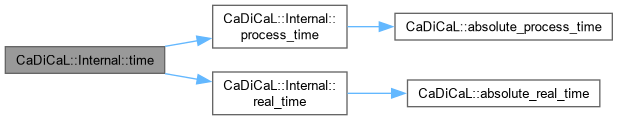

| void CaDiCaL::Internal::trace | ( | File * | file | ) |
Definition at line 126 of file cadical_proof.cpp.
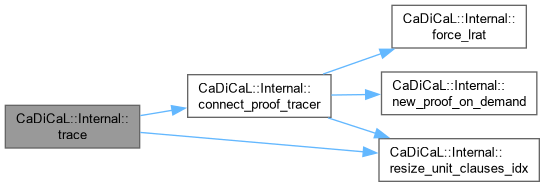
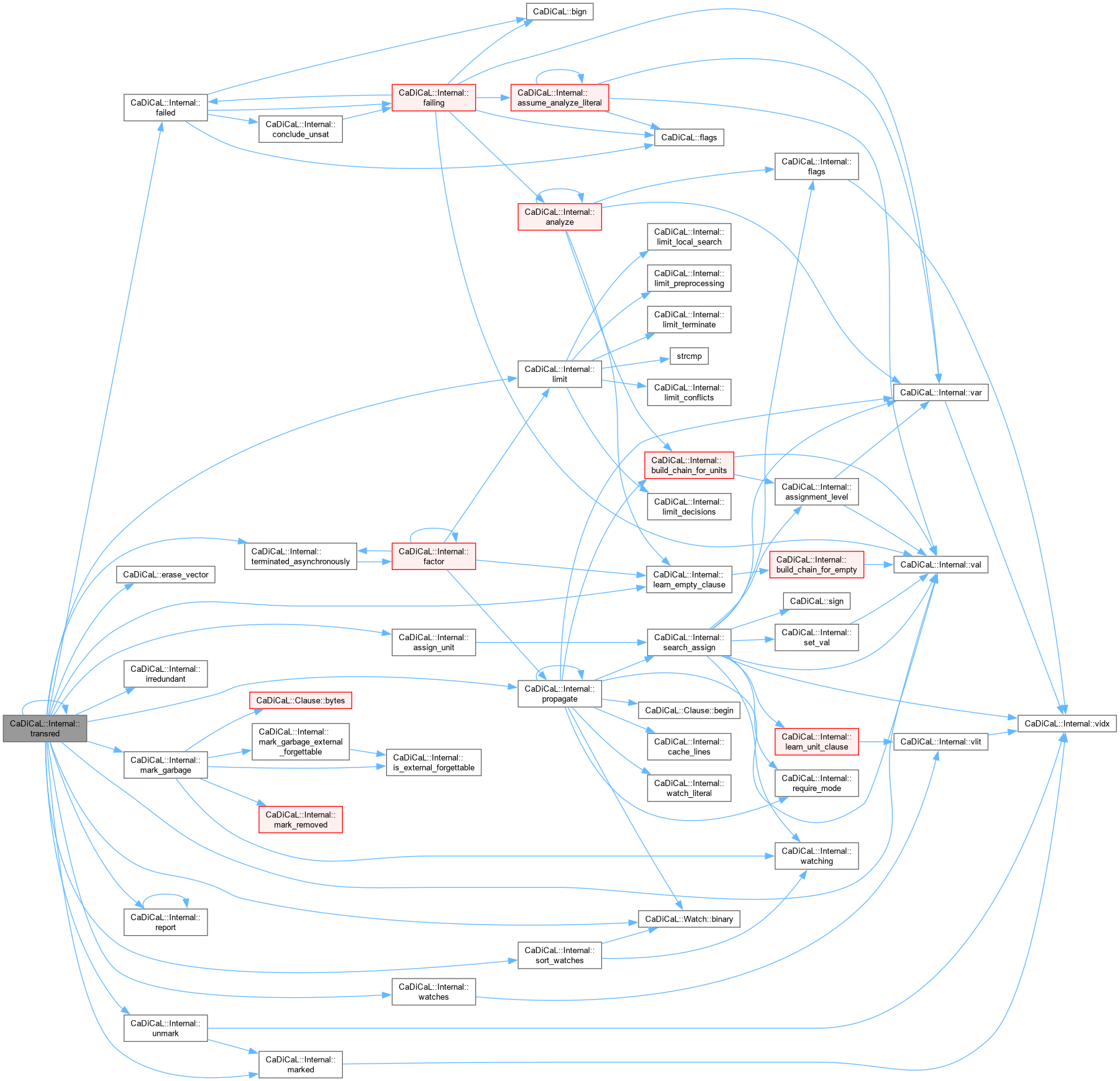
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::transred | ( | ) |
Definition at line 15 of file cadical_transred.cpp.
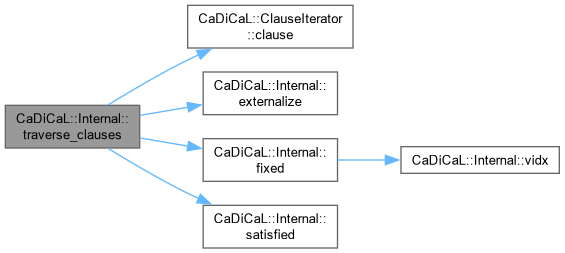
| bool CaDiCaL::Internal::traverse_clauses | ( | ClauseIterator & | it | ) |
Definition at line 1166 of file cadical_internal.cpp.
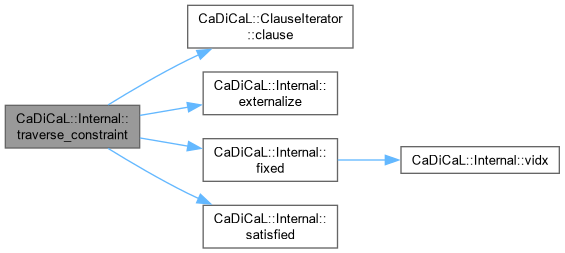
| bool CaDiCaL::Internal::traverse_constraint | ( | ClauseIterator & | it | ) |
Definition at line 1138 of file cadical_internal.cpp.
| int CaDiCaL::Internal::trivially_false_satisfiable | ( | ) |
Definition at line 34 of file cadical_lucky.cpp.
| int CaDiCaL::Internal::trivially_true_satisfiable | ( | ) |
Definition at line 81 of file cadical_lucky.cpp.
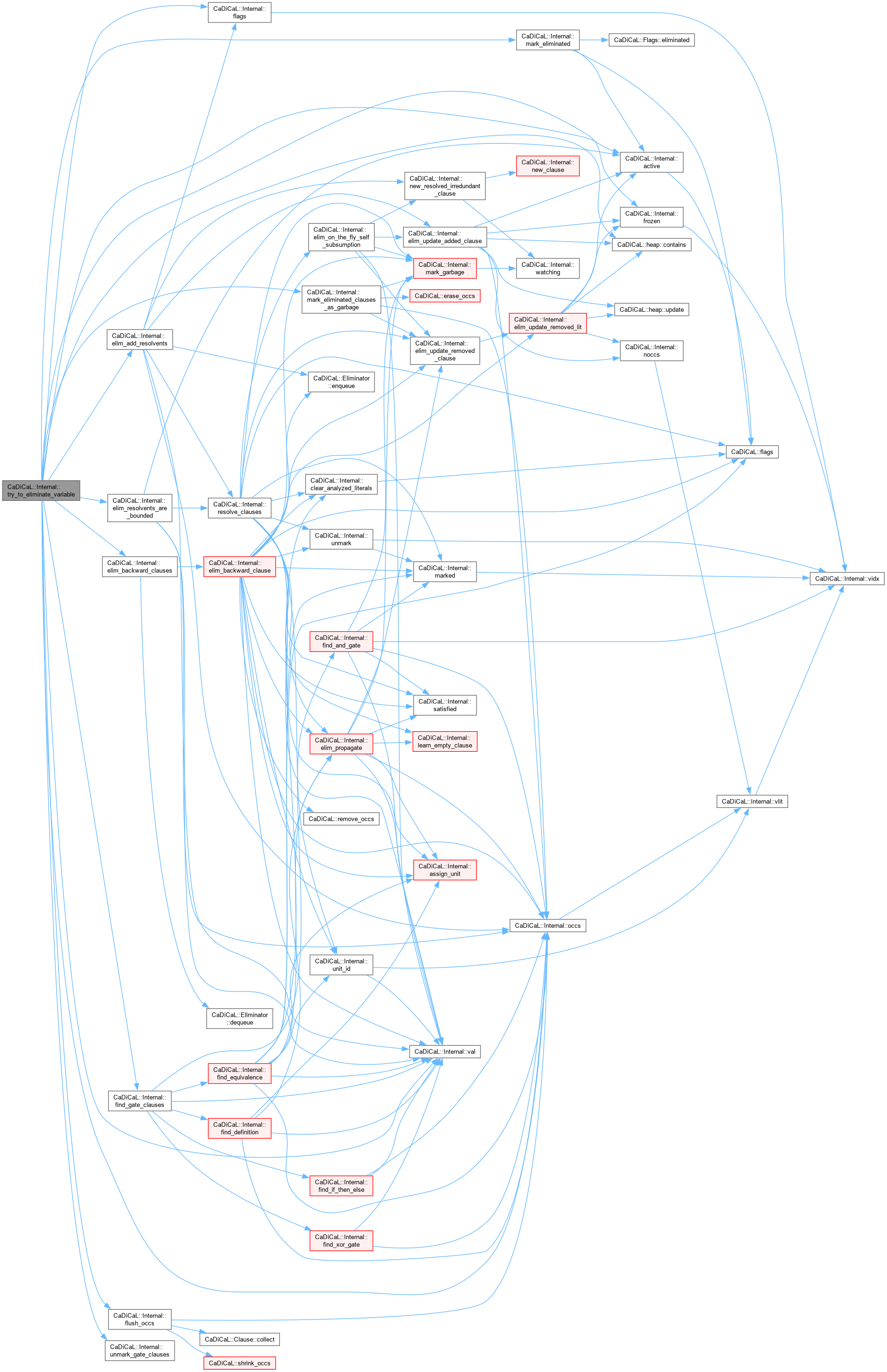
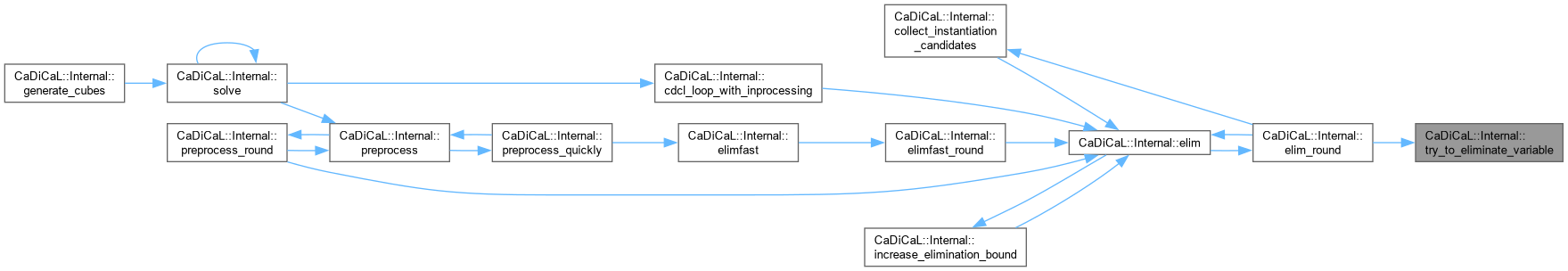
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::try_to_eliminate_variable | ( | Eliminator & | eliminator, |
| int | pivot, | ||
| bool & | deleted_binary_clause ) |
Definition at line 681 of file cadical_elim.cpp.
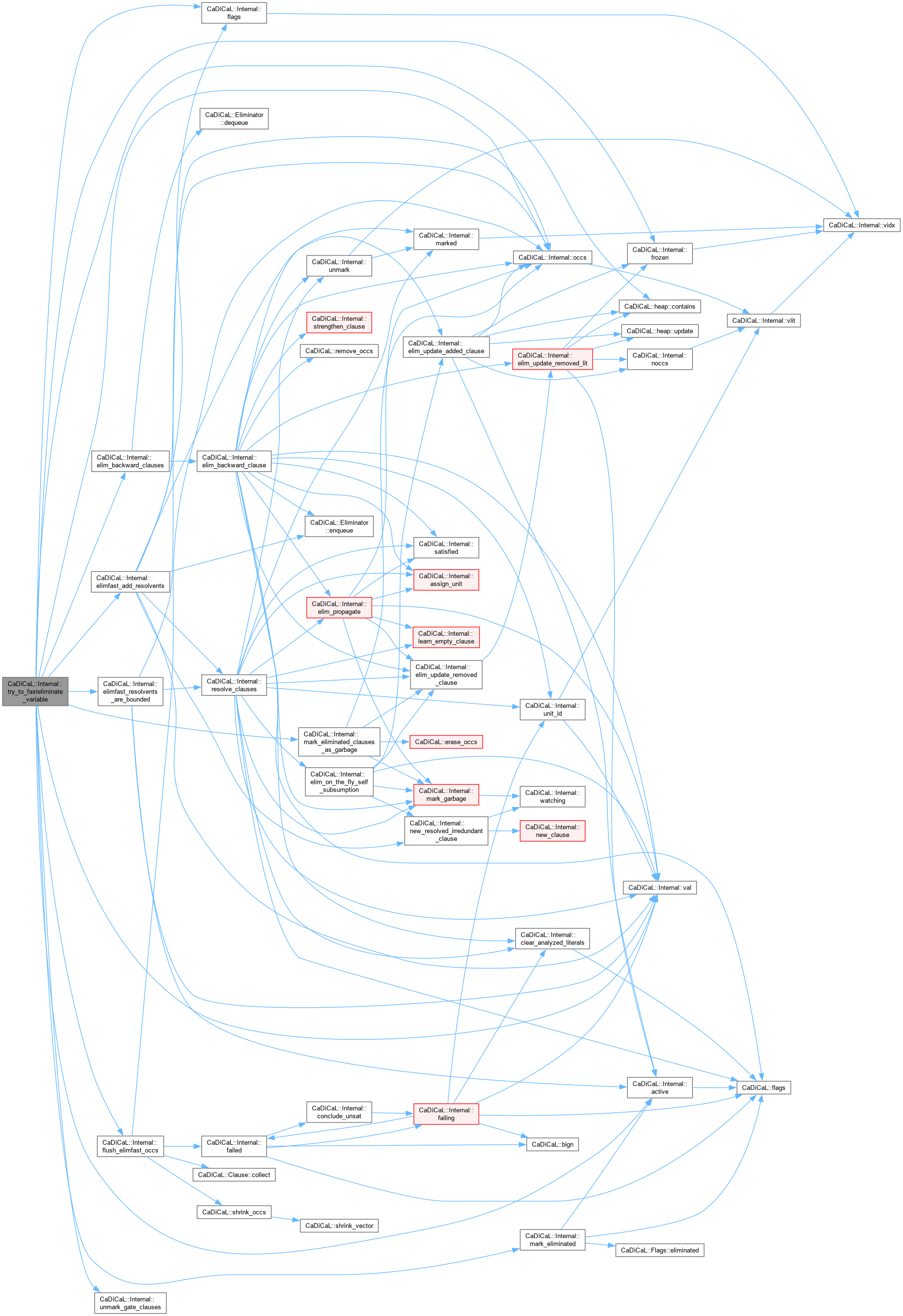
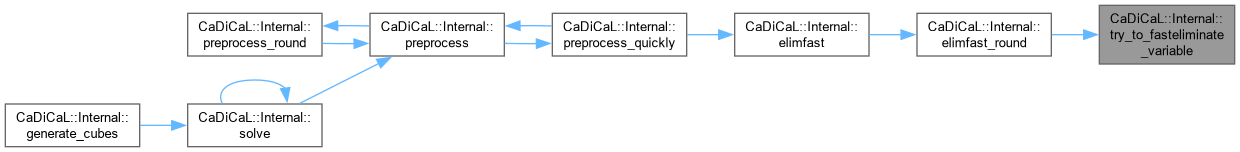
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::try_to_fasteliminate_variable | ( | Eliminator & | eliminator, |
| int | pivot, | ||
| bool & | deleted_binary_clause ) |
Definition at line 189 of file cadical_elimfast.cpp.
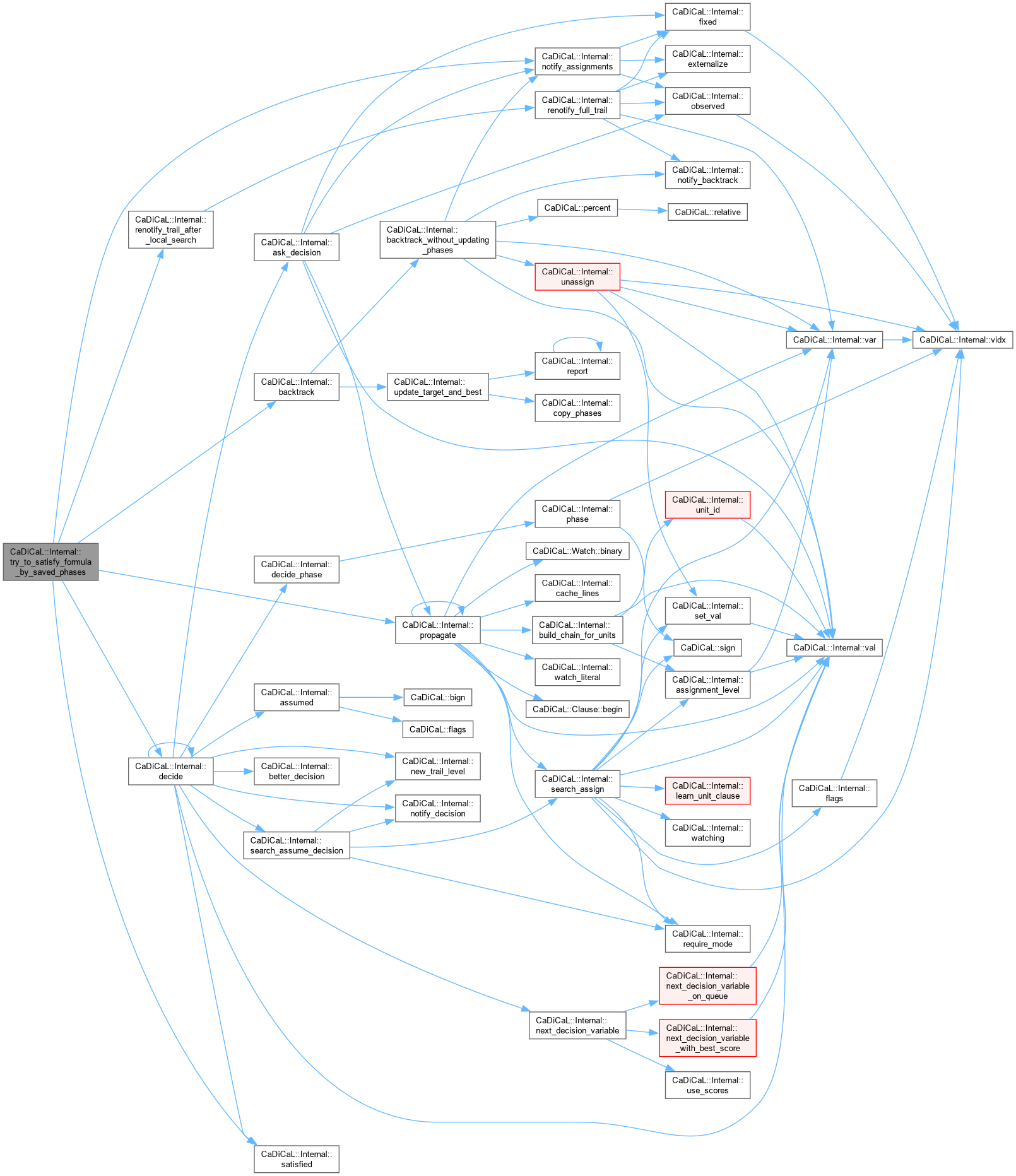
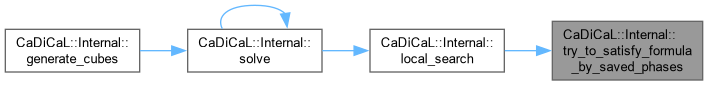
| int CaDiCaL::Internal::try_to_satisfy_formula_by_saved_phases | ( | ) |
Definition at line 752 of file cadical_internal.cpp.
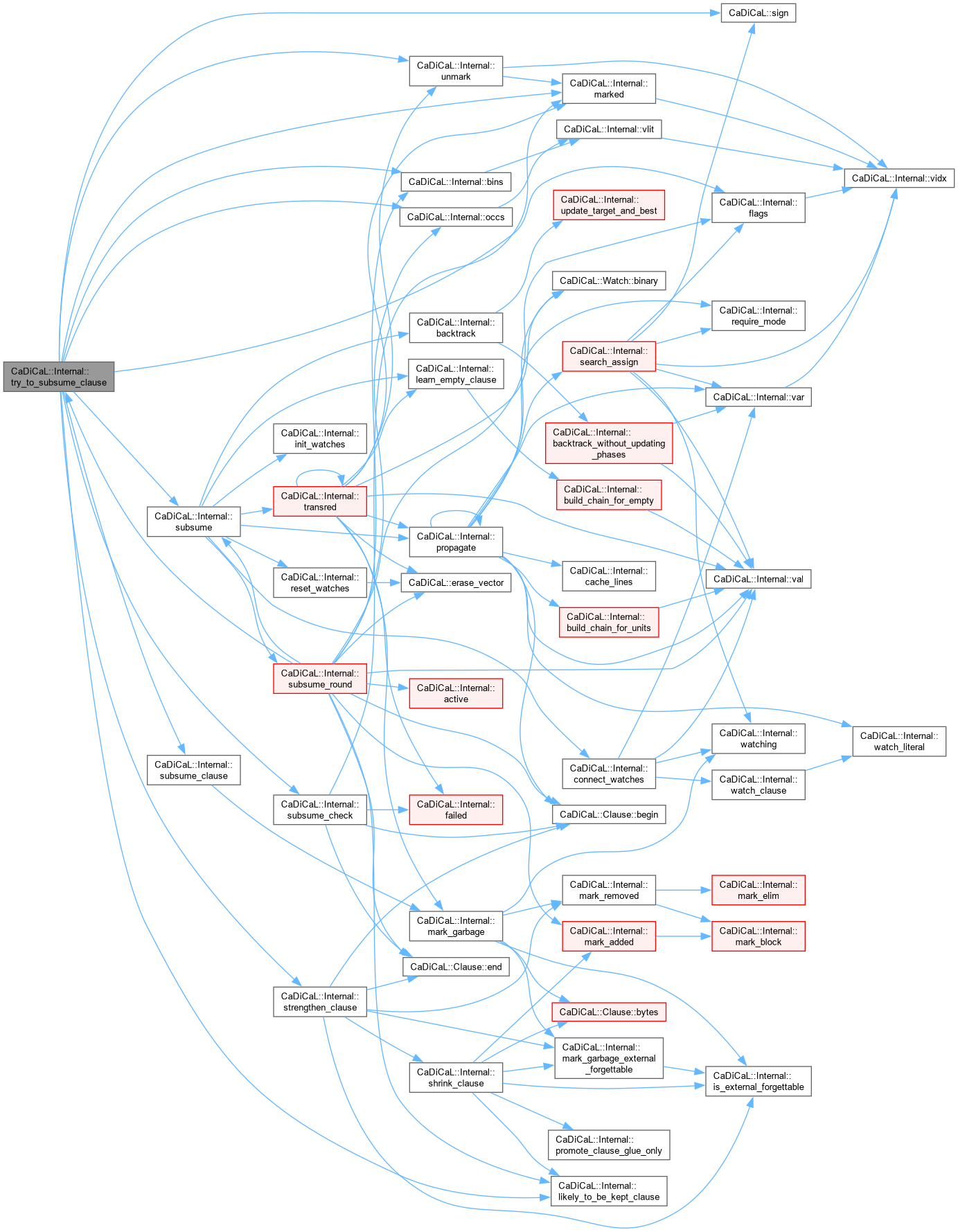
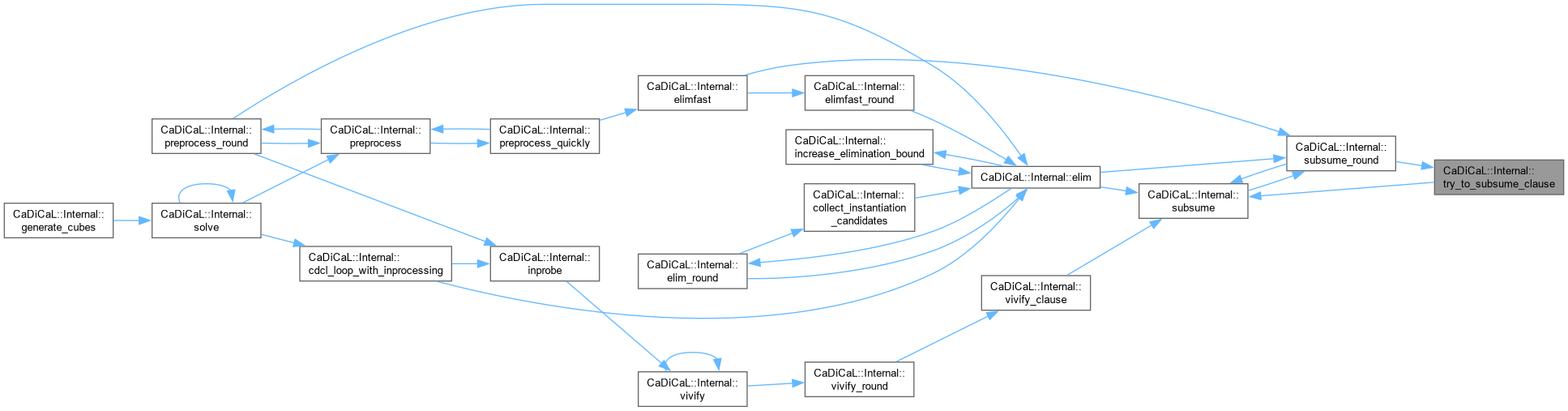
Definition at line 188 of file cadical_subsume.cpp.
|
inline |
Definition at line 412 of file internal.hpp.
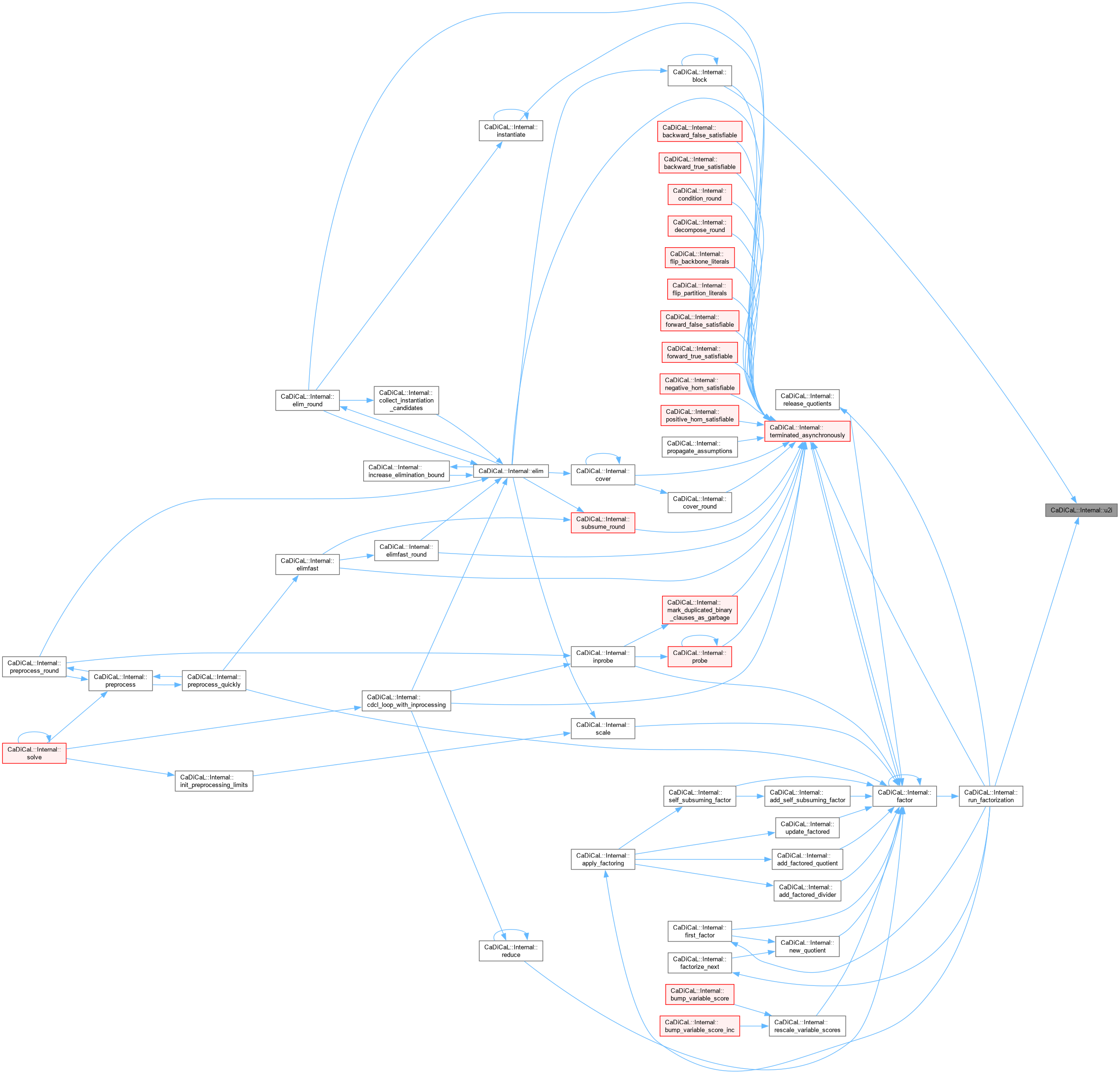
|
inline |
Definition at line 14 of file cadical_backtrack.cpp.
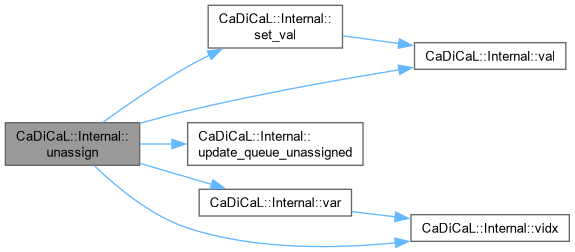
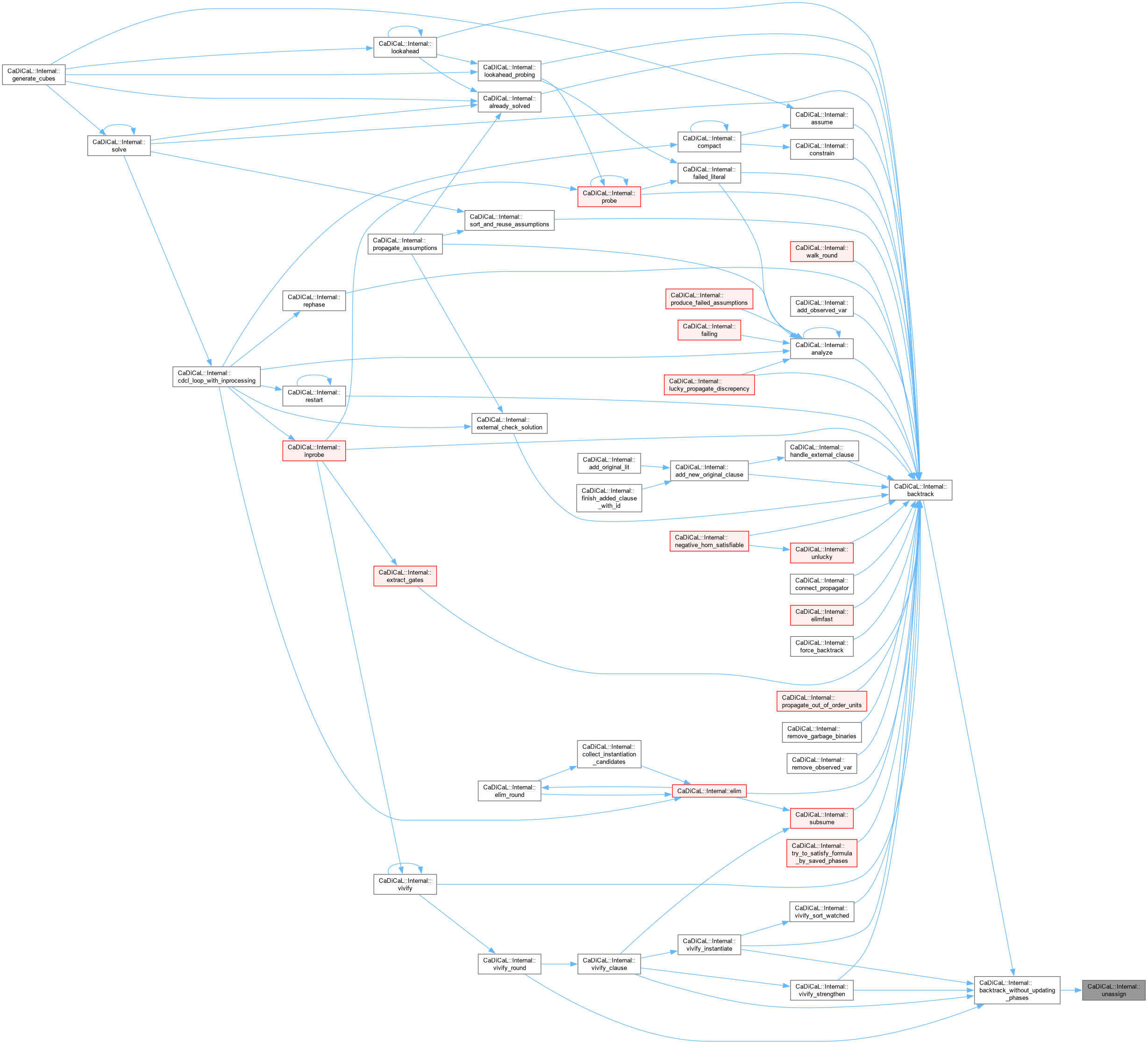
|
inline |
Definition at line 443 of file internal.hpp.
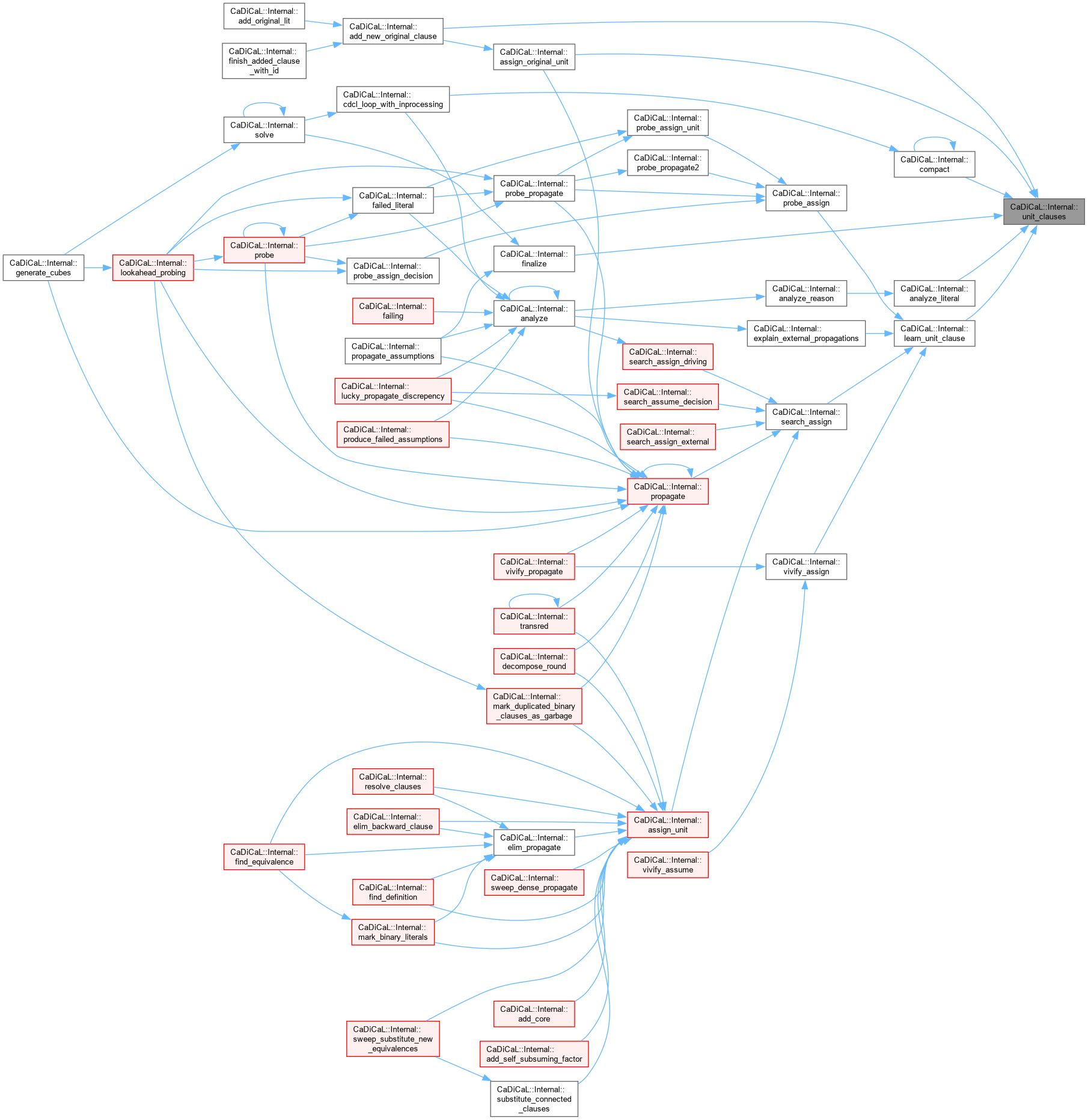
|
inline |
Definition at line 434 of file internal.hpp.

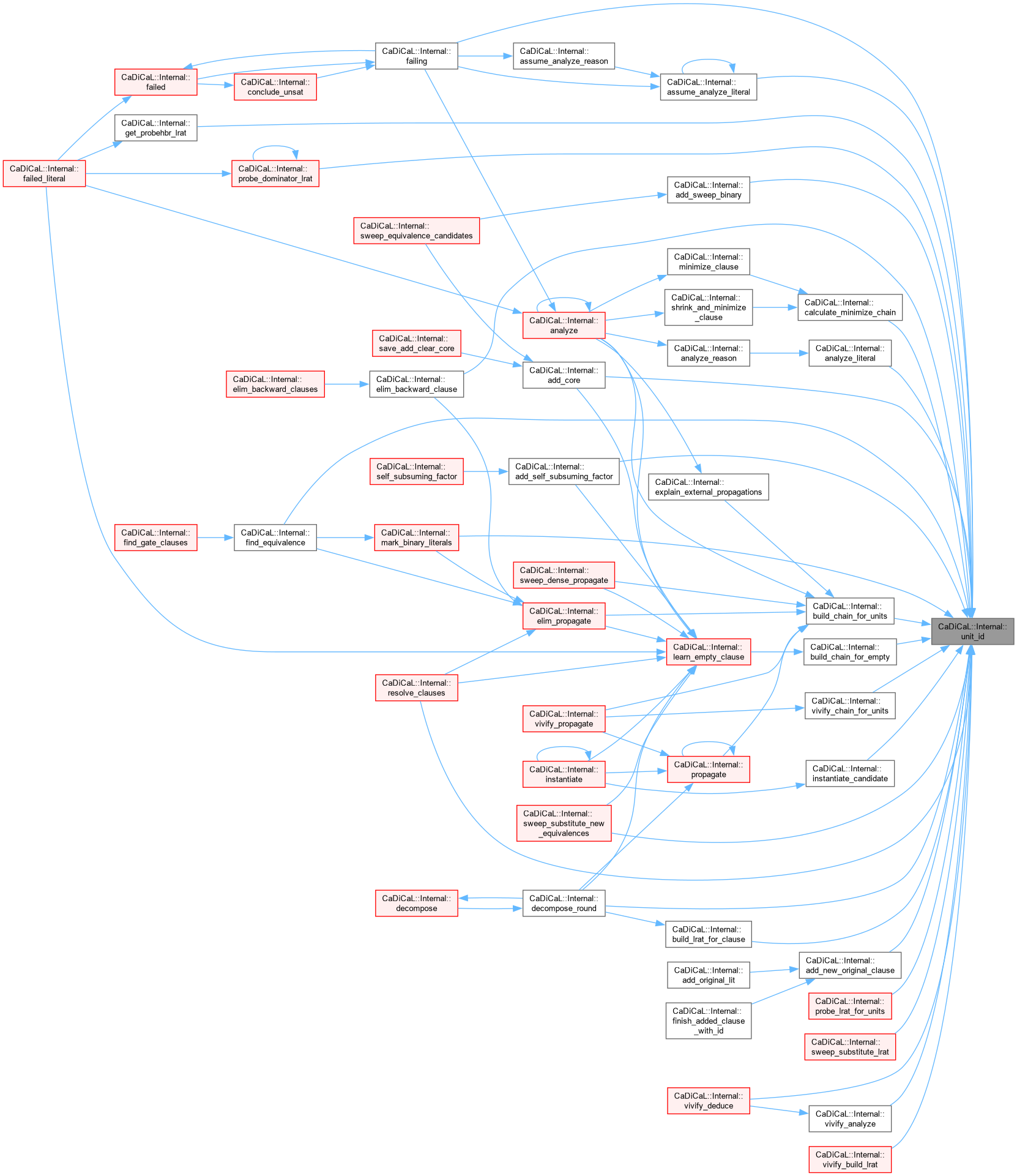
| int CaDiCaL::Internal::unlucky | ( | int | res | ) |
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::unmark | ( | Clause * | c | ) |
|
inline |
Definition at line 490 of file internal.hpp.


|
inline |
|
inline |
Definition at line 517 of file internal.hpp.

|
inline |
Definition at line 117 of file cadical_condition.cpp.
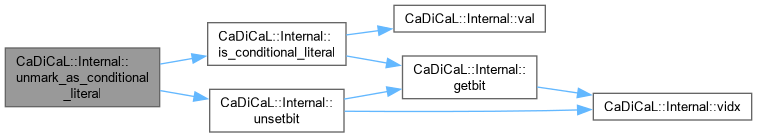
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::unmark_binary_literals | ( | Eliminator & | eliminator | ) |
Definition at line 192 of file cadical_gates.cpp.
|
inline |
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::unmark_clause | ( | ) |
|
inline |
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::unmark_gate_clauses | ( | Eliminator & | eliminator | ) |
Definition at line 758 of file cadical_gates.cpp.
|
inline |
Definition at line 141 of file cadical_condition.cpp.
|
inline |
Definition at line 599 of file internal.hpp.

| void CaDiCaL::Internal::unphase | ( | int | lit | ) |
Definition at line 37 of file cadical_phases.cpp.
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::unprotect_reasons | ( | ) |
Definition at line 140 of file cadical_collect.cpp.
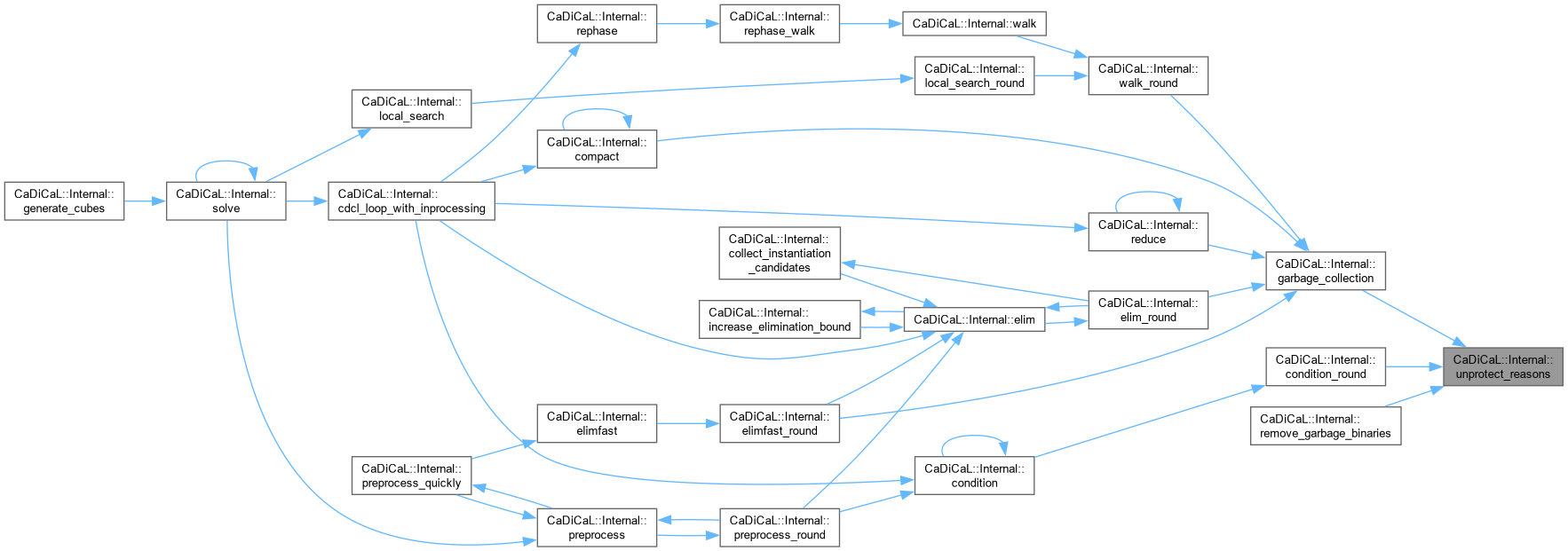
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::unschedule_sweeping | ( | Sweeper & | sweeper, |
| unsigned | swept, | ||
| unsigned | scheduled ) |
Definition at line 1845 of file cadical_sweep.cpp.
|
inline |
Definition at line 546 of file internal.hpp.


|
inline |
Definition at line 640 of file internal.hpp.
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::update_decision_rate_average | ( | ) |
Definition at line 927 of file cadical_analyze.cpp.
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::update_factor_candidate | ( | Factoring & | factoring, |
| int | lit ) |
Definition at line 742 of file cadical_factor.cpp.
Definition at line 701 of file cadical_factor.cpp.
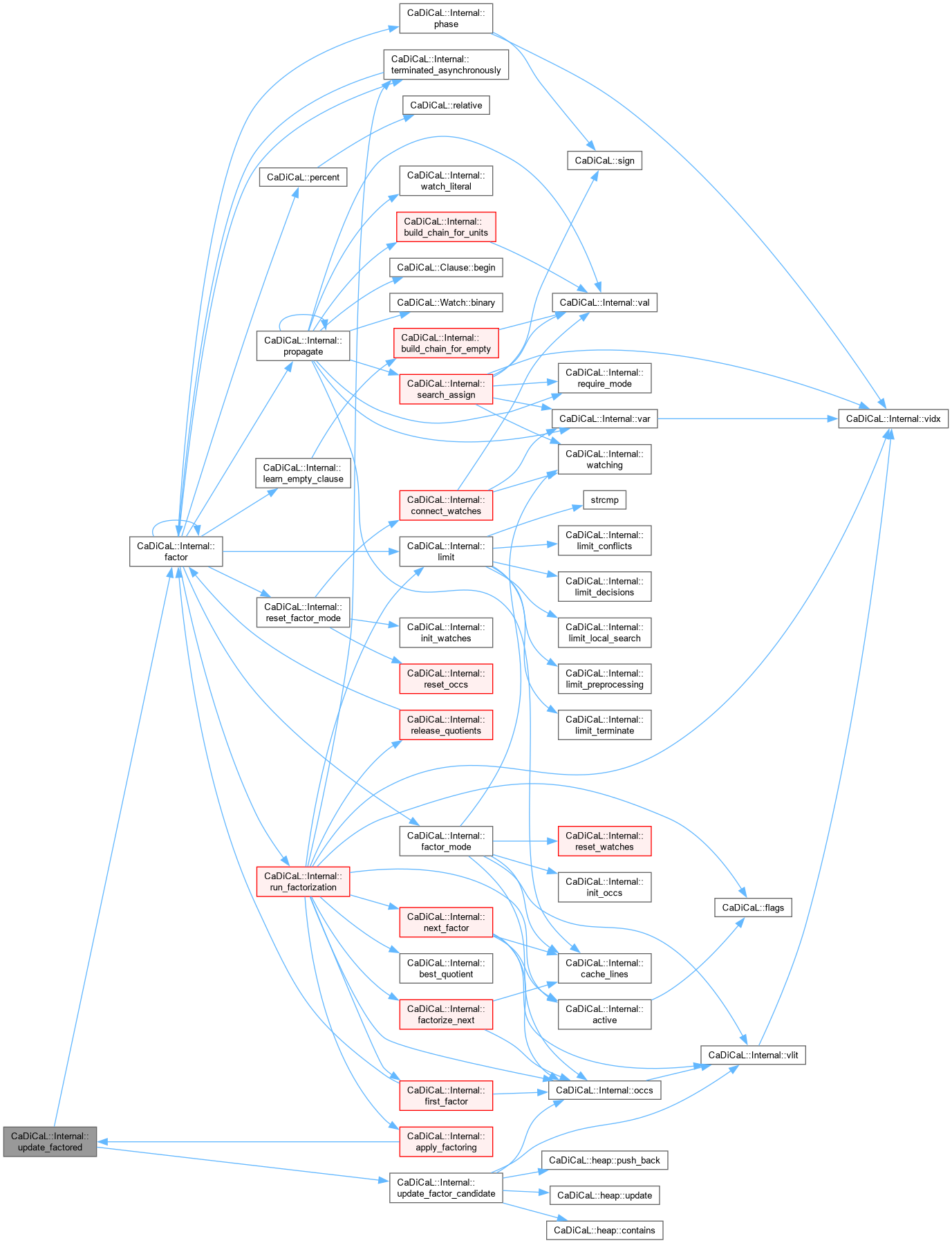
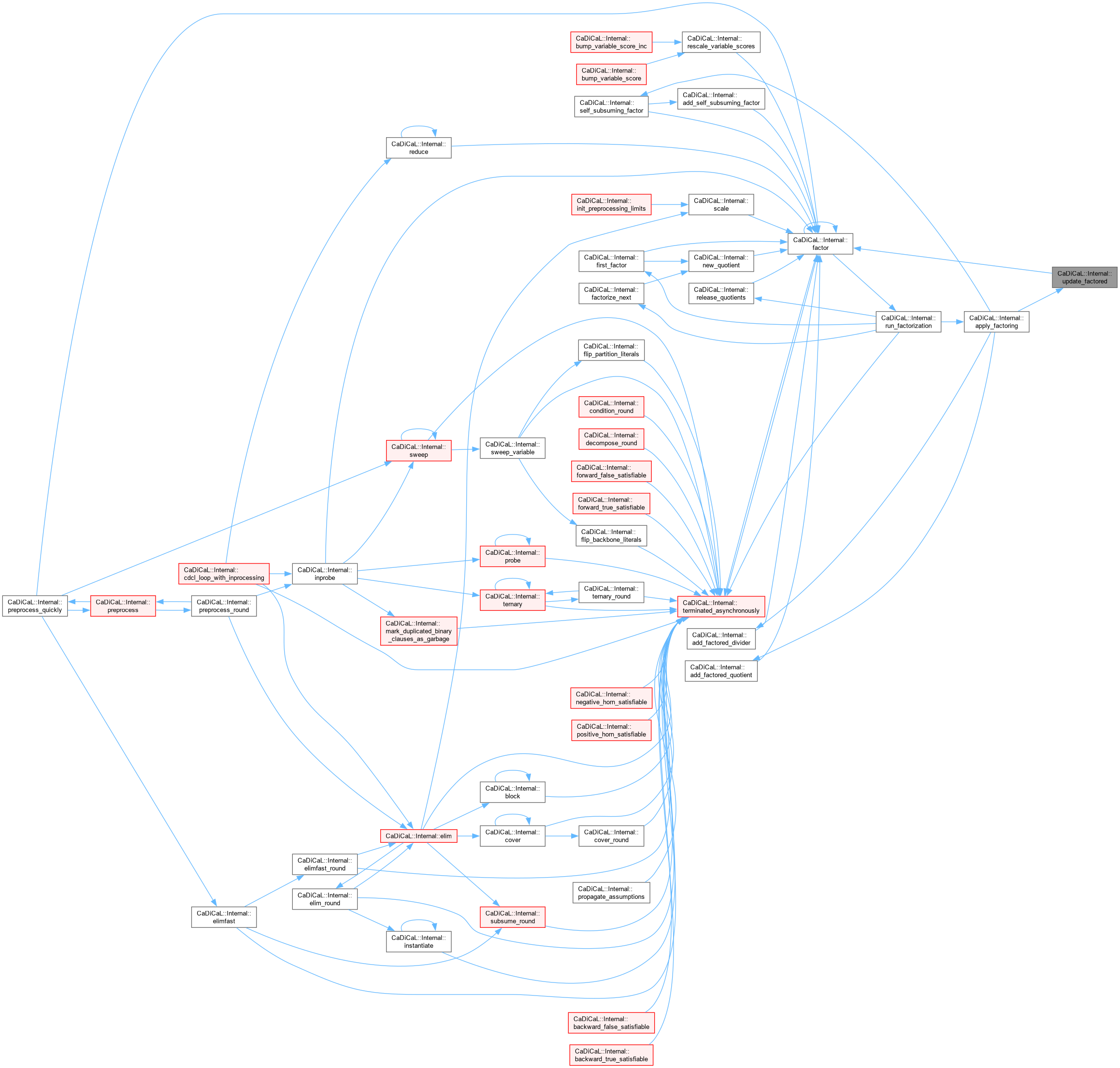
|
inline |
Definition at line 652 of file internal.hpp.
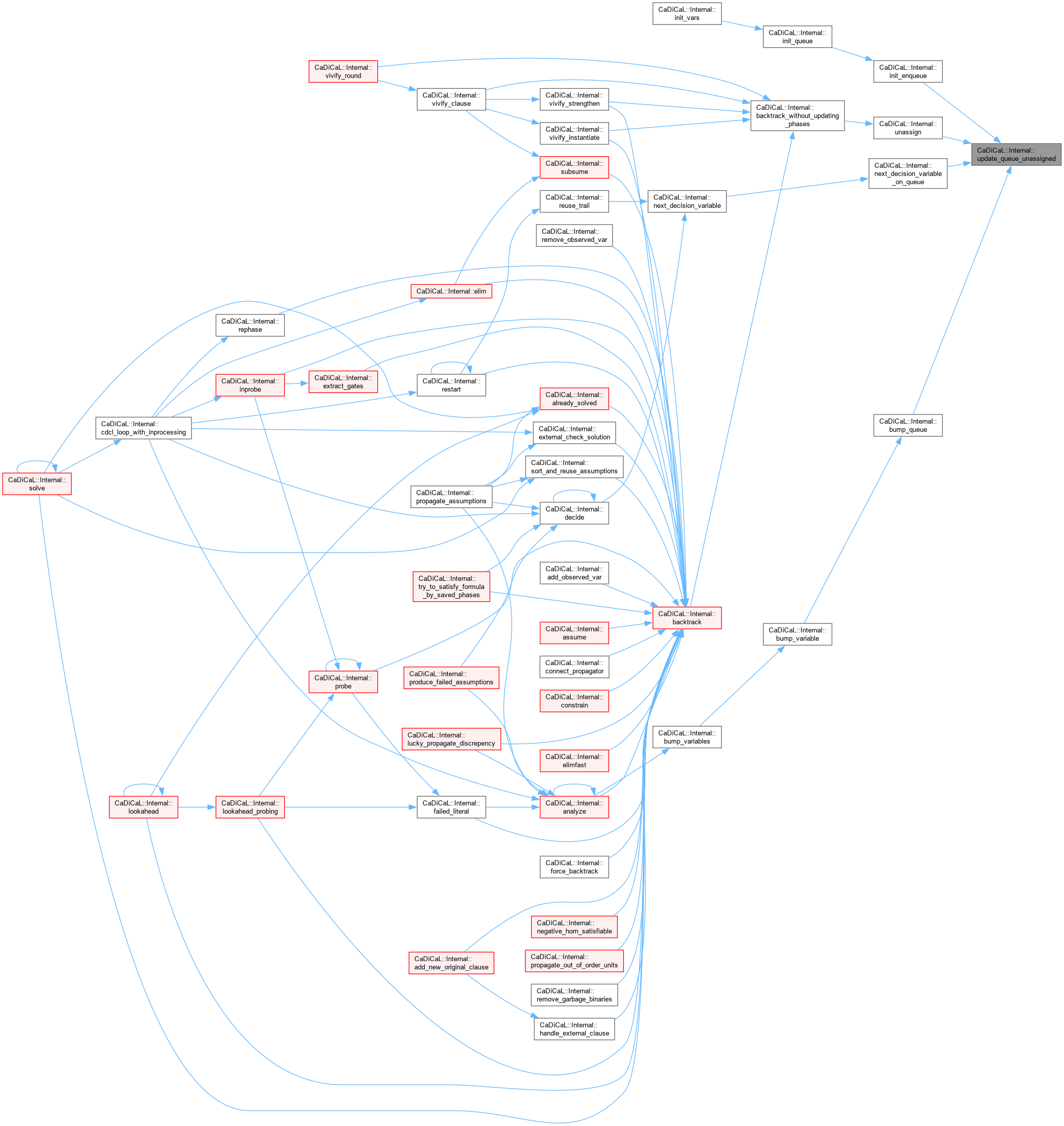
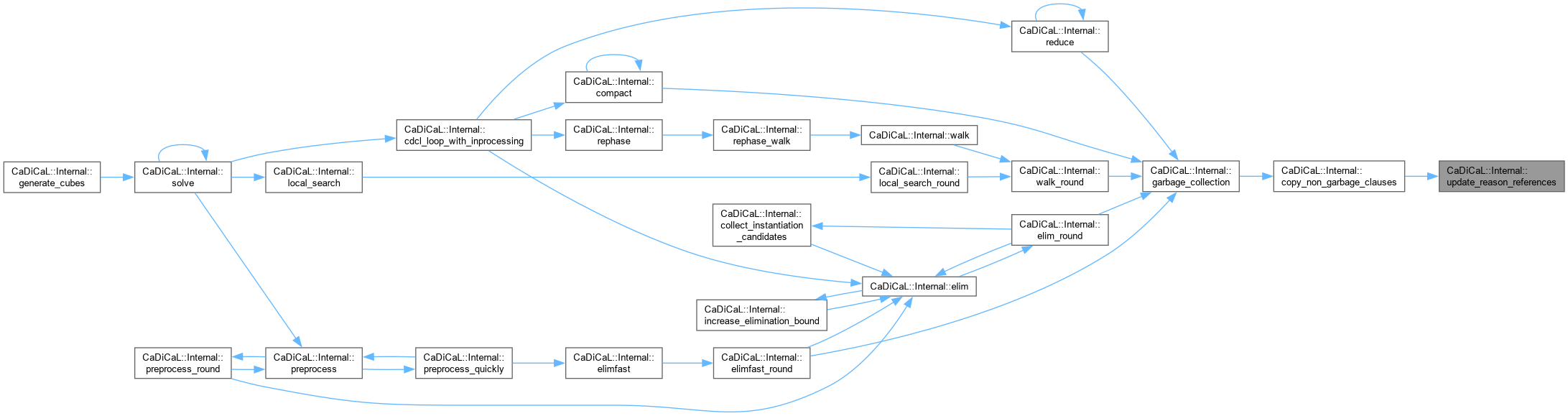
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::update_reason_references | ( | ) |
Definition at line 246 of file cadical_collect.cpp.

| void CaDiCaL::Internal::update_target_and_best | ( | ) |
Definition at line 50 of file cadical_backtrack.cpp.
|
inline |
|
inline |
Definition at line 1518 of file internal.hpp.
|
inline |
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::verror | ( | const char * | fmt, |
| va_list & | ap ) |
Definition at line 175 of file cadical_message.cpp.
|
inline |
Definition at line 395 of file internal.hpp.
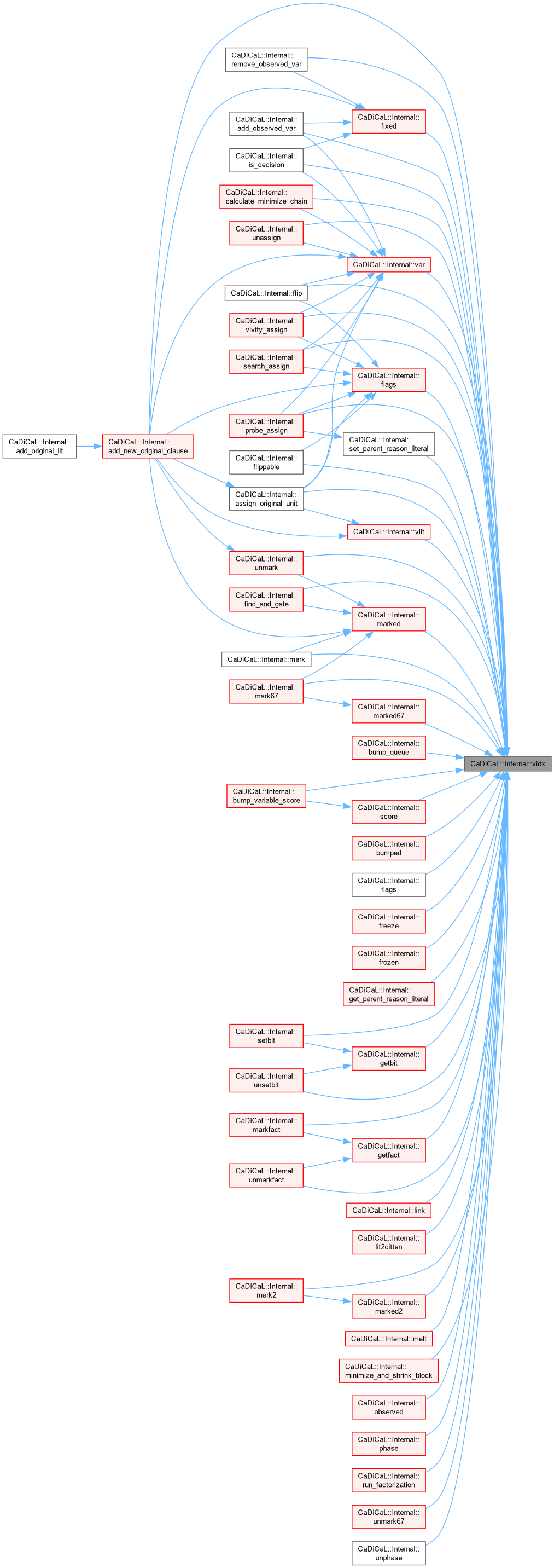
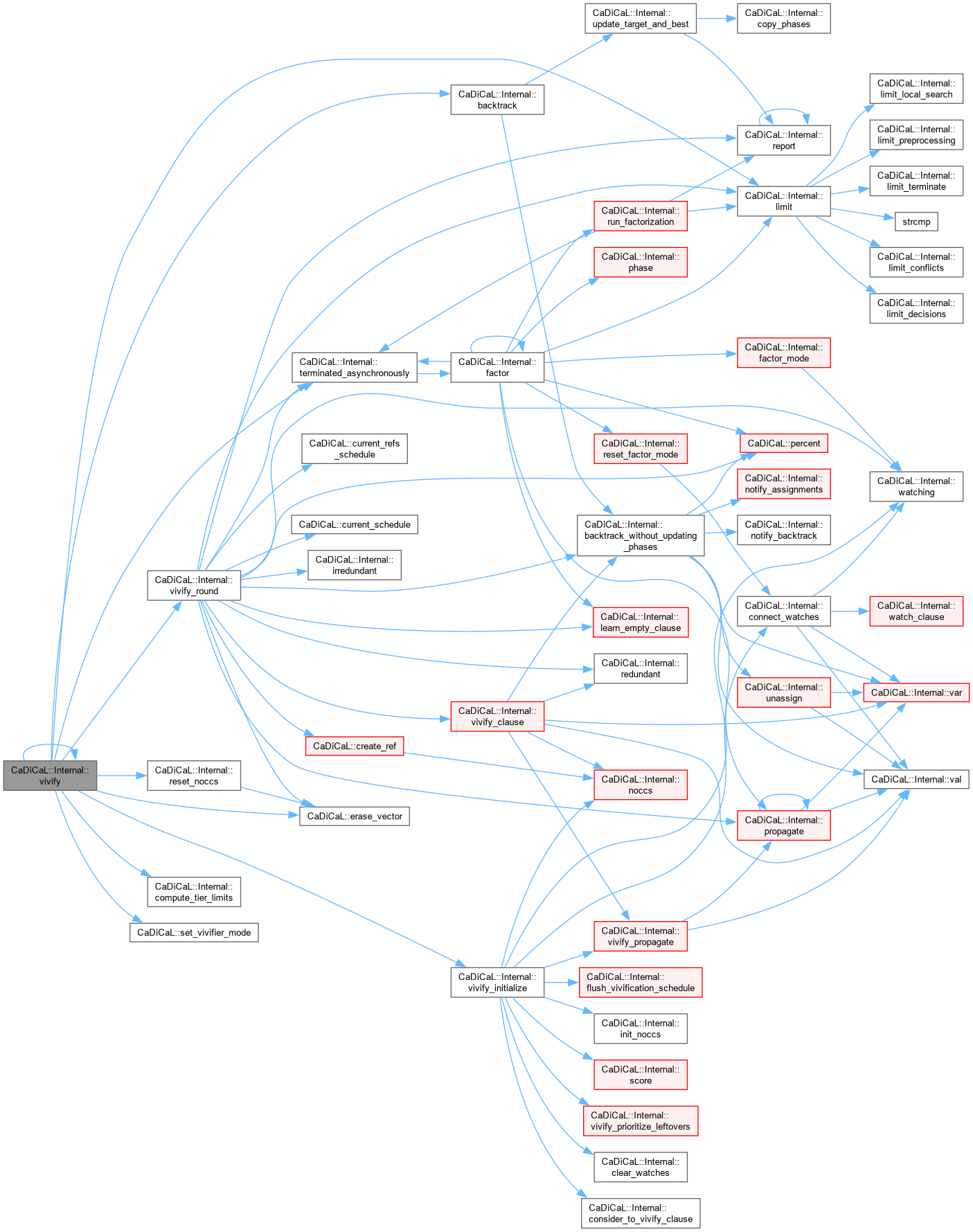
| bool CaDiCaL::Internal::vivify | ( | ) |
Definition at line 1804 of file cadical_vivify.cpp.
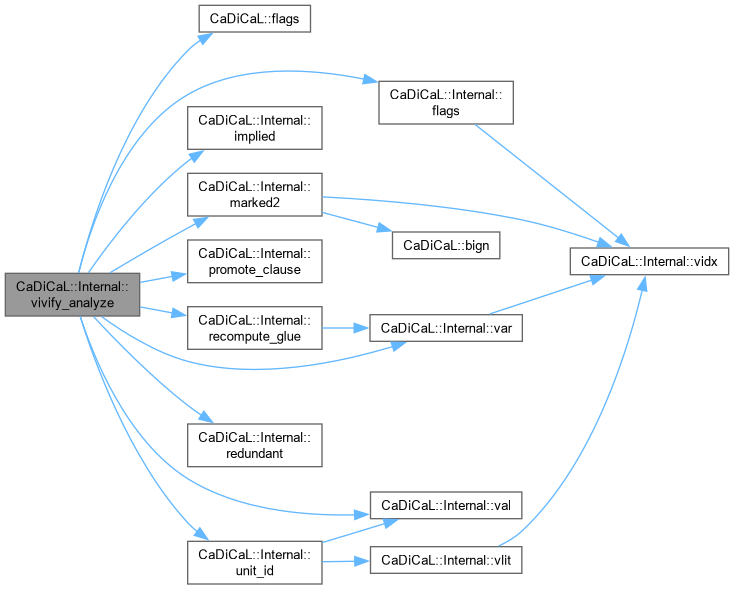
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::vivify_analyze | ( | Clause * | start, |
| bool & | subsumes, | ||
| Clause ** | subsuming, | ||
| const Clause * const | candidate, | ||
| int | implied, | ||
| bool & | redundant ) |
Definition at line 652 of file cadical_vivify.cpp.

|
inline |
Definition at line 146 of file cadical_vivify.cpp.

| void CaDiCaL::Internal::vivify_assume | ( | int | lit | ) |
Definition at line 170 of file cadical_vivify.cpp.

| void CaDiCaL::Internal::vivify_build_lrat | ( | int | lit, |
| Clause * | reason, | ||
| std::vector< std::tuple< int, Clause *, bool > > & | stack ) |
Definition at line 1257 of file cadical_vivify.cpp.

|
inline |
Definition at line 1309 of file cadical_vivify.cpp.

Definition at line 947 of file cadical_vivify.cpp.

| void CaDiCaL::Internal::vivify_deduce | ( | Clause * | candidate, |
| Clause * | conflct, | ||
| int | implied, | ||
| Clause ** | subsuming, | ||
| bool & | redundant ) |
Definition at line 743 of file cadical_vivify.cpp.

| void CaDiCaL::Internal::vivify_initialize | ( | Vivifier & | vivifier, |
| int64_t & | ticks ) |
Definition at line 1397 of file cadical_vivify.cpp.
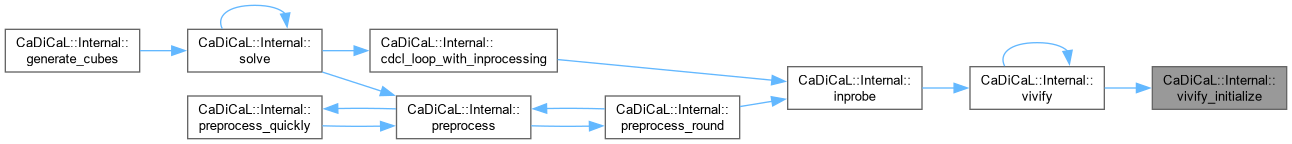
| bool CaDiCaL::Internal::vivify_instantiate | ( | const std::vector< int > & | sorted, |
| Clause * | c, | ||
| std::vector< std::tuple< int, Clause *, bool > > & | lrat_stack, | ||
| int64_t & | ticks ) |
Definition at line 901 of file cadical_vivify.cpp.

|
inline |
Definition at line 1373 of file cadical_vivify.cpp.
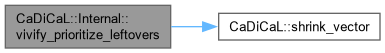

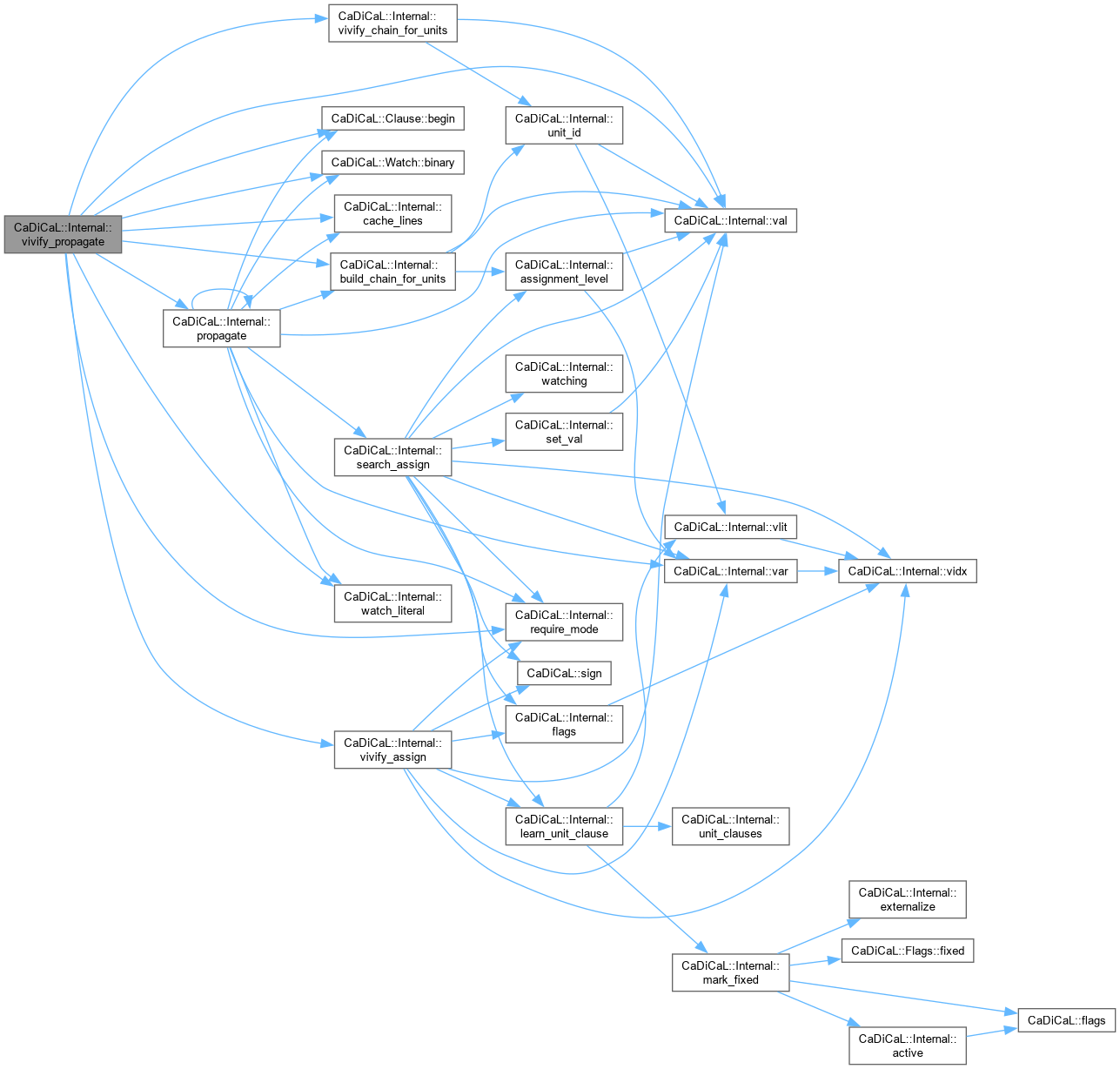
| bool CaDiCaL::Internal::vivify_propagate | ( | int64_t & | ticks | ) |
Definition at line 184 of file cadical_vivify.cpp.

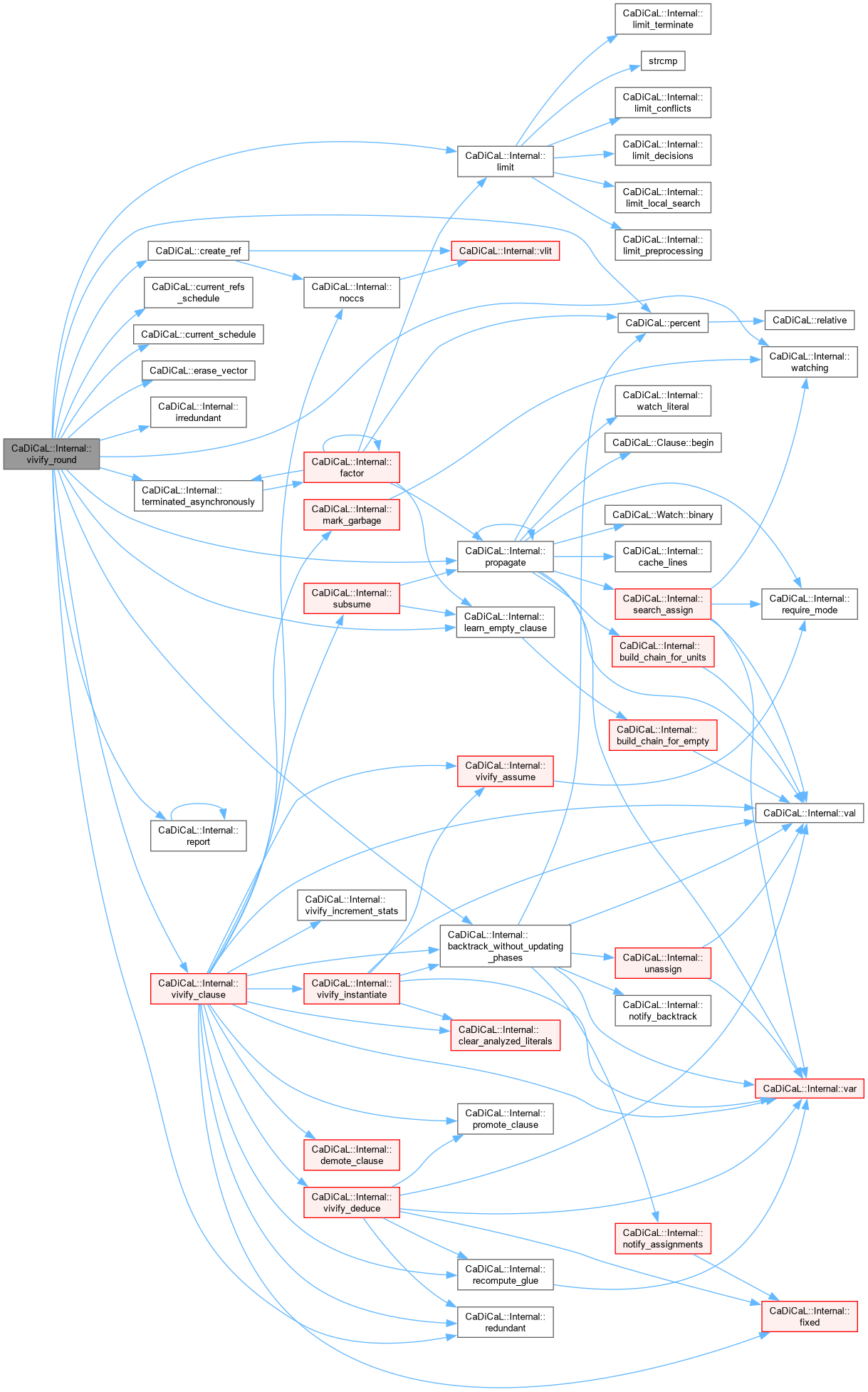
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::vivify_round | ( | Vivifier & | vivifier, |
| int64_t | delta ) |
Definition at line 1576 of file cadical_vivify.cpp.
Definition at line 842 of file cadical_vivify.cpp.


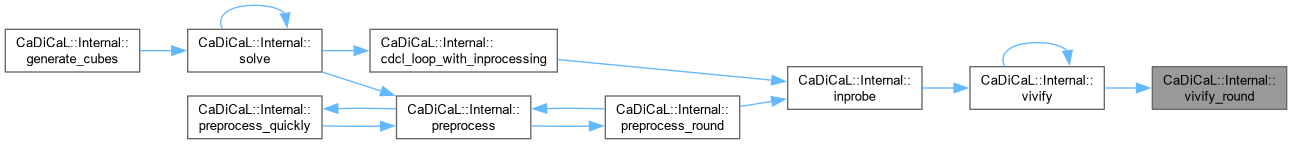
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::vivify_sort_watched | ( | Clause * | c | ) |
Definition at line 616 of file cadical_vivify.cpp.
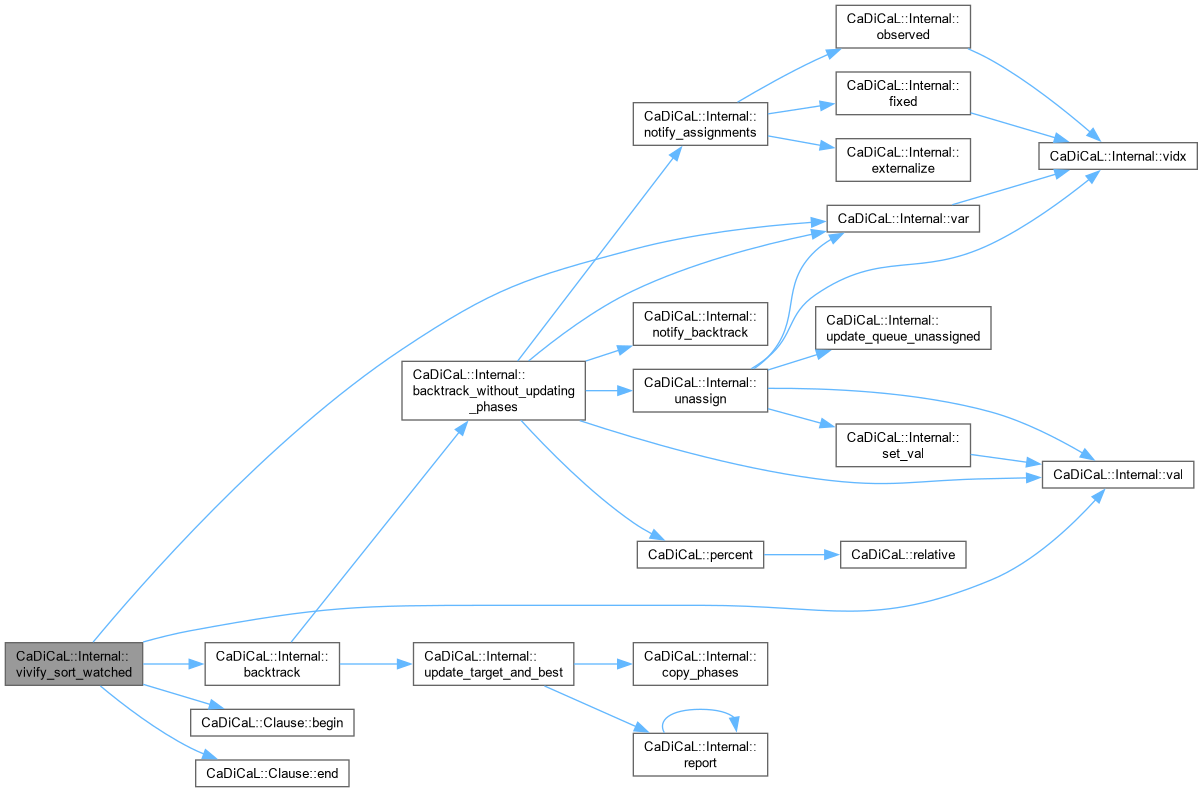

| void CaDiCaL::Internal::vivify_strengthen | ( | Clause * | candidate | ) |
Definition at line 555 of file cadical_vivify.cpp.
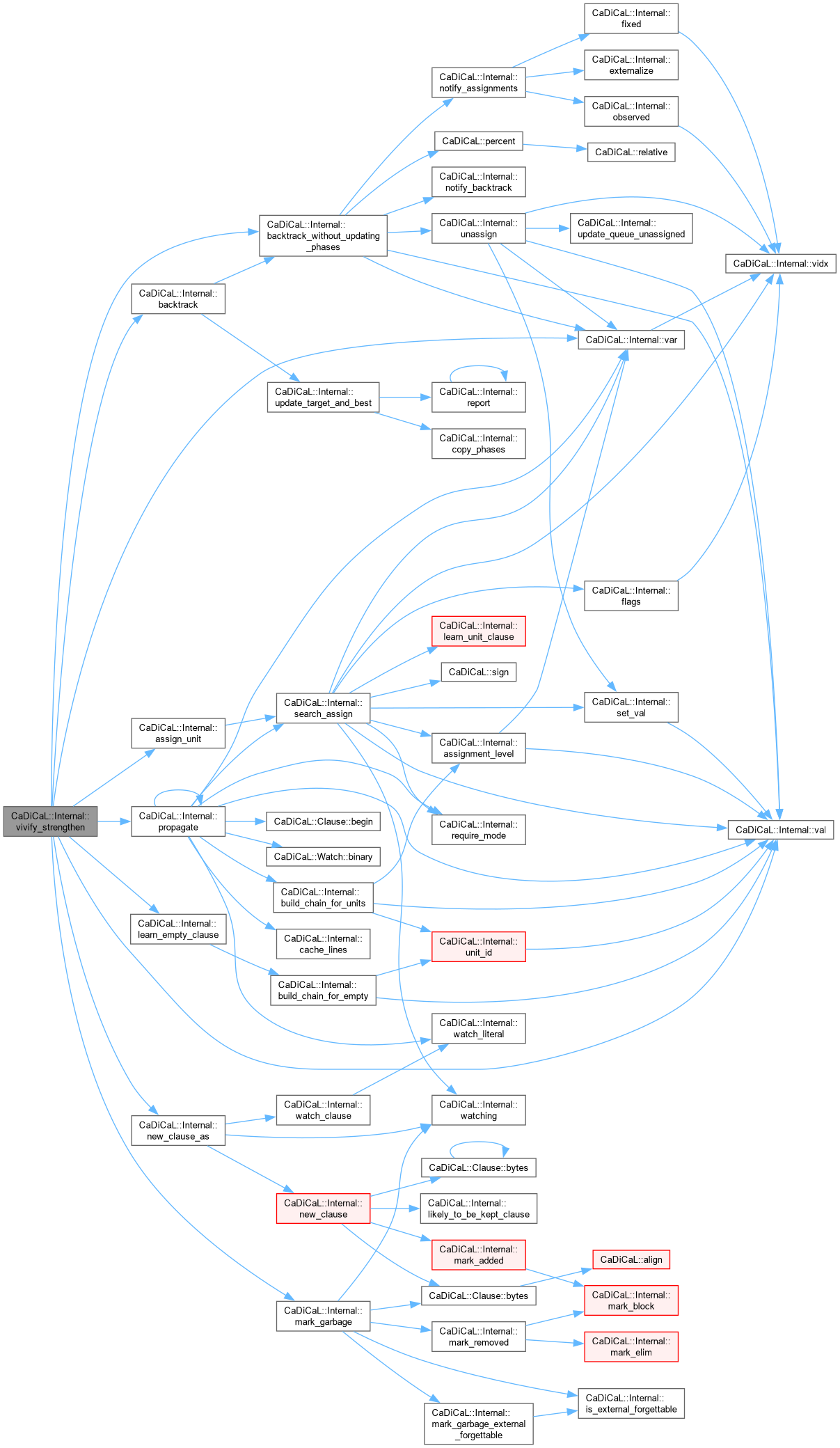

Definition at line 53 of file cadical_vivify.cpp.

|
inline |
Definition at line 408 of file internal.hpp.
| void CaDiCaL::Internal::walk | ( | ) |
Definition at line 696 of file cadical_walk.cpp.

| unsigned CaDiCaL::Internal::walk_break_value | ( | int | lit | ) |
Definition at line 117 of file cadical_walk.cpp.

| void CaDiCaL::Internal::walk_flip_lit | ( | Walker & | walker, |
| int | lit ) |
Definition at line 244 of file cadical_walk.cpp.

Definition at line 100 of file cadical_walk.cpp.

Definition at line 191 of file cadical_walk.cpp.

| int CaDiCaL::Internal::walk_round | ( | int64_t | limit, |
| bool | prev ) |
Definition at line 411 of file cadical_walk.cpp.
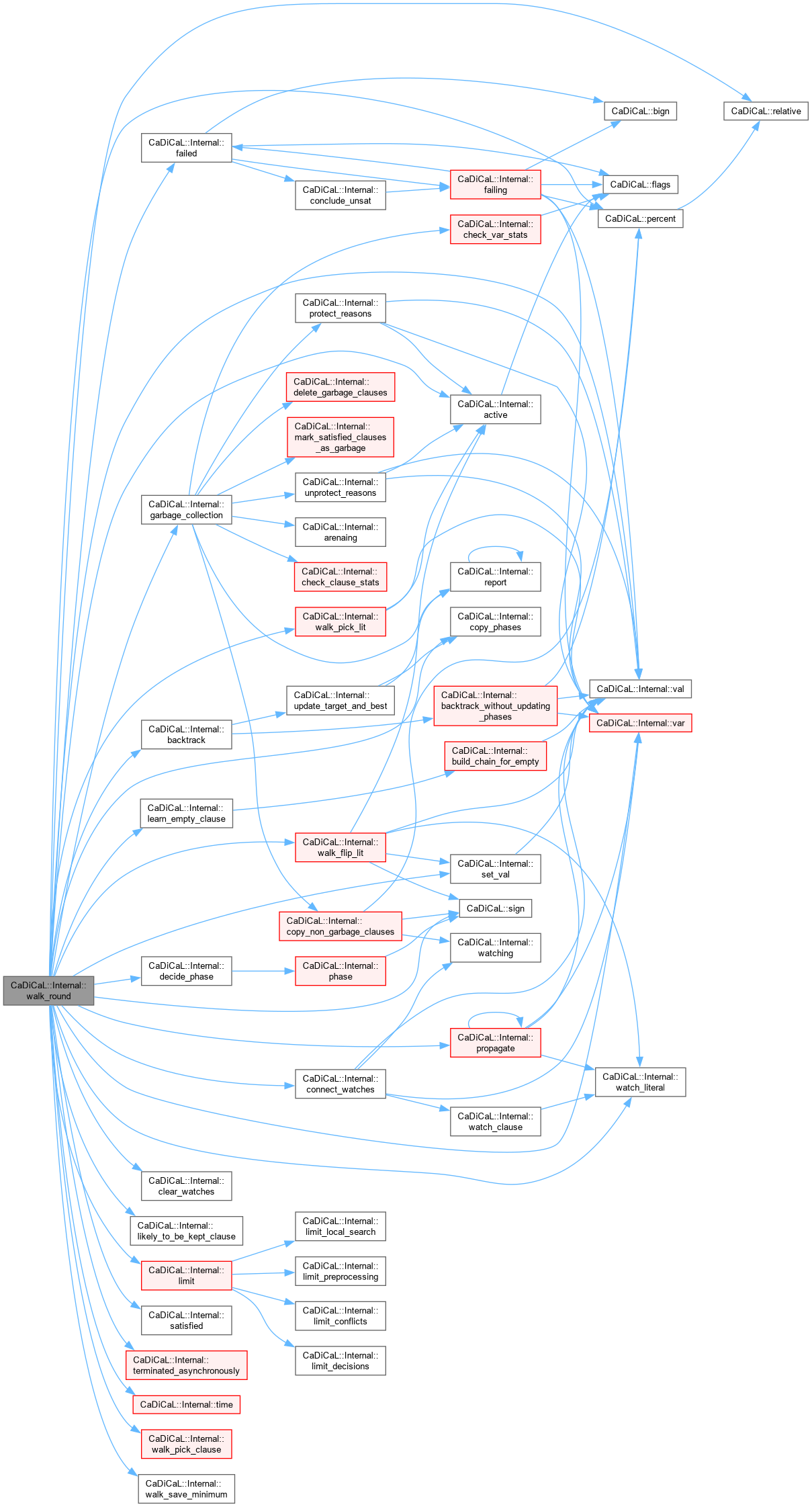

|
inline |
Definition at line 396 of file cadical_walk.cpp.

| void CaDiCaL::Internal::warning | ( | const char * | fmt, |
| ... ) |
Definition at line 140 of file cadical_message.cpp.
|
inline |
Definition at line 633 of file internal.hpp.
|
inline |
Definition at line 623 of file internal.hpp.
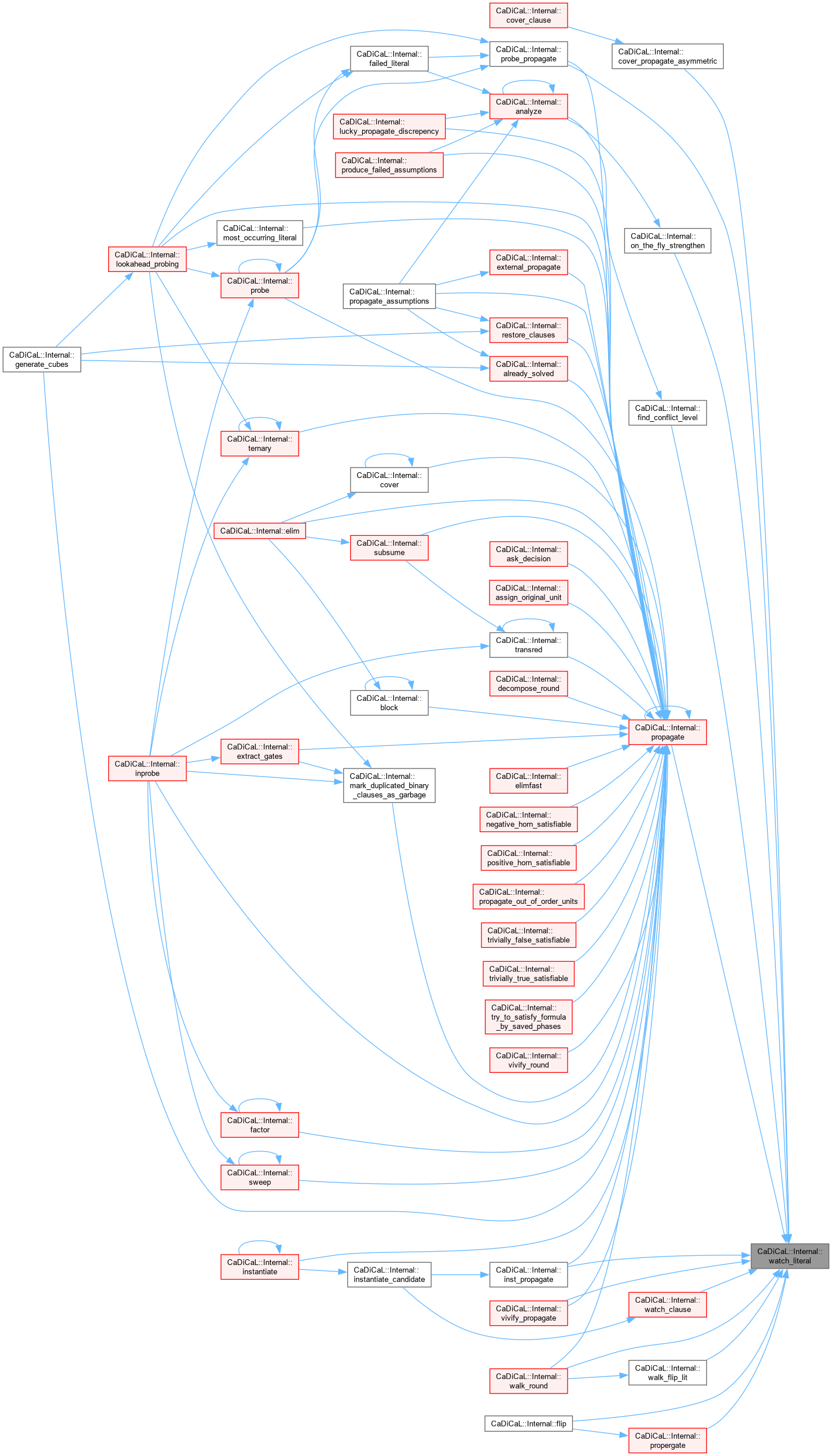
|
inline |
Definition at line 467 of file internal.hpp.

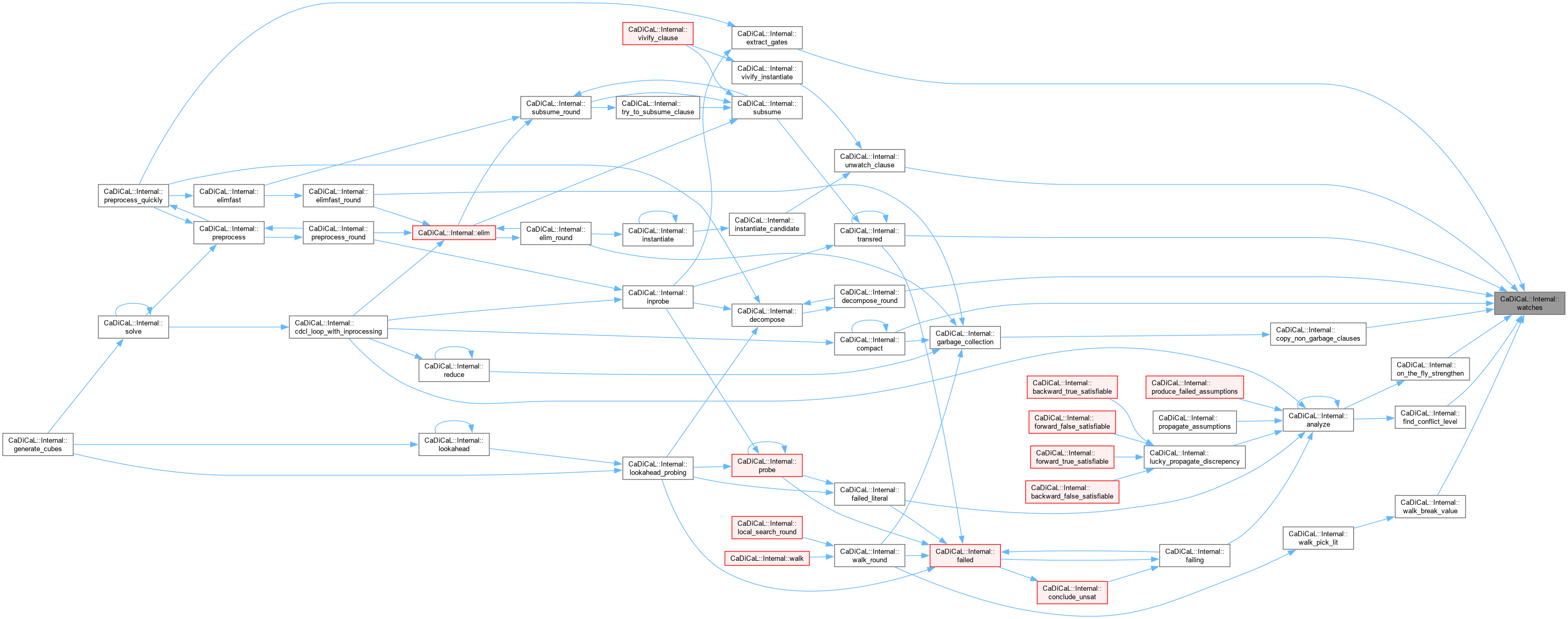
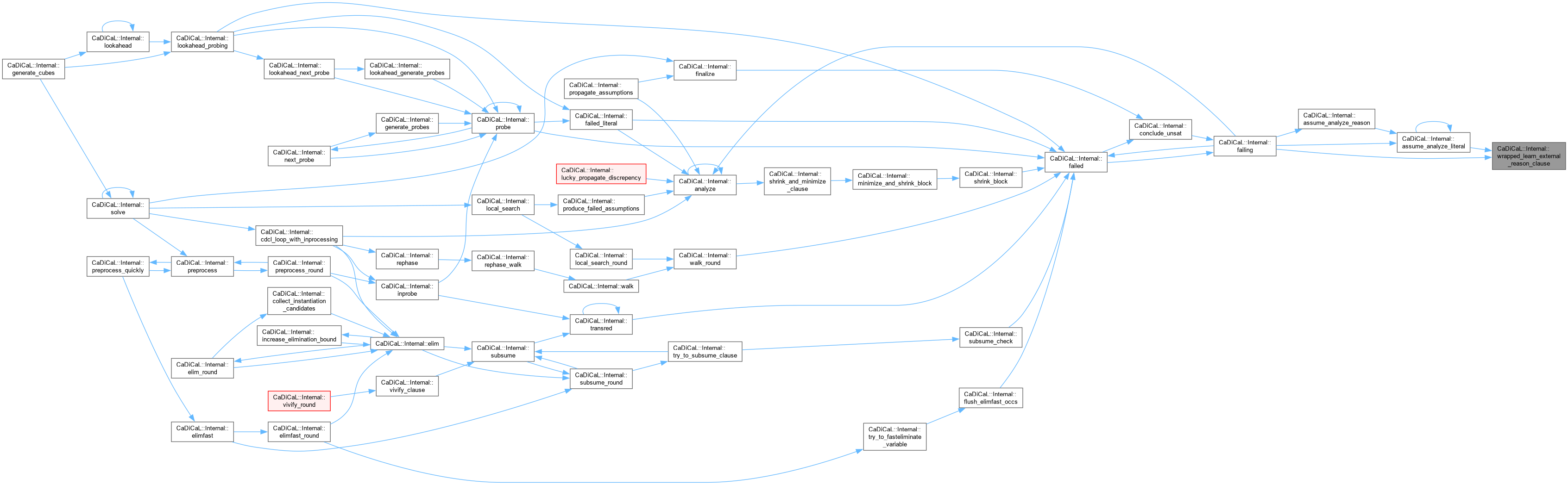
|
inline |
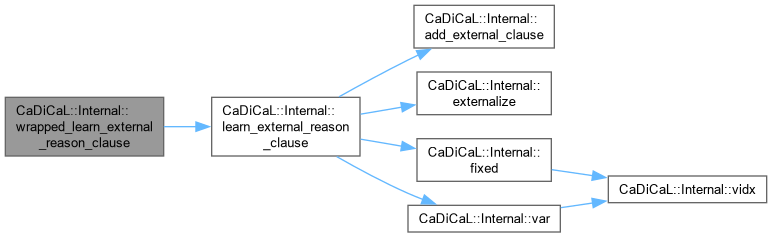
| Clause * CaDiCaL::Internal::wrapped_learn_external_reason_clause | ( | int | lit | ) |
Definition at line 715 of file cadical_external_propagate.cpp.
| vector<int> CaDiCaL::Internal::analyzed |
Definition at line 267 of file internal.hpp.
| Arena CaDiCaL::Internal::arena |
Definition at line 307 of file internal.hpp.
| vector<int> CaDiCaL::Internal::assumptions |
Definition at line 261 of file internal.hpp.
| Averages CaDiCaL::Internal::averages |
Definition at line 284 of file internal.hpp.
| size_t CaDiCaL::Internal::best_assigned |
Definition at line 256 of file internal.hpp.
Definition at line 240 of file internal.hpp.
| vector<int64_t> CaDiCaL::Internal::btab |
Definition at line 234 of file internal.hpp.
| cadical_kitten* CaDiCaL::Internal::citten |
Definition at line 277 of file internal.hpp.
| vector<int> CaDiCaL::Internal::clause |
Definition at line 260 of file internal.hpp.
| int64_t CaDiCaL::Internal::clause_id |
Definition at line 201 of file internal.hpp.
Definition at line 283 of file internal.hpp.
| bool CaDiCaL::Internal::concluded |
Definition at line 206 of file internal.hpp.
| vector<int64_t> CaDiCaL::Internal::conclusion |
Definition at line 207 of file internal.hpp.
| Clause* CaDiCaL::Internal::conflict |
Definition at line 242 of file internal.hpp.
| int64_t CaDiCaL::Internal::conflict_id |
Definition at line 204 of file internal.hpp.
| Delay CaDiCaL::Internal::congruence_delay |
Definition at line 286 of file internal.hpp.
| vector<int> CaDiCaL::Internal::constraint |
Definition at line 262 of file internal.hpp.
Definition at line 282 of file internal.hpp.
| Delay CaDiCaL::Internal::delay[2] |
Definition at line 285 of file internal.hpp.
| Delay CaDiCaL::Internal::delaying_sweep |
Definition at line 292 of file internal.hpp.
| Delay CaDiCaL::Internal::delaying_vivify_irredundant |
Definition at line 291 of file internal.hpp.
| bool CaDiCaL::Internal::did_external_prop |
Definition at line 193 of file internal.hpp.
| Clause* CaDiCaL::Internal::dummy_binary |
Definition at line 244 of file internal.hpp.
| Format CaDiCaL::Internal::error_message |
Definition at line 308 of file internal.hpp.
| bool CaDiCaL::Internal::ext_clause_forgettable |
Definition at line 249 of file internal.hpp.
| External* CaDiCaL::Internal::external |
Definition at line 312 of file internal.hpp.
| bool CaDiCaL::Internal::external_prop |
Definition at line 192 of file internal.hpp.
| bool CaDiCaL::Internal::external_prop_is_lazy |
Definition at line 194 of file internal.hpp.
| Clause* CaDiCaL::Internal::external_reason |
Definition at line 245 of file internal.hpp.
| vector<FileTracer *> CaDiCaL::Internal::file_tracers |
Definition at line 298 of file internal.hpp.
| bool CaDiCaL::Internal::force_no_backtrack |
Definition at line 247 of file internal.hpp.
| bool CaDiCaL::Internal::force_saved_phase |
Definition at line 188 of file internal.hpp.
| bool CaDiCaL::Internal::forced_backt_allowed |
Definition at line 195 of file internal.hpp.
| bool CaDiCaL::Internal::frat |
Definition at line 218 of file internal.hpp.
| bool CaDiCaL::Internal::from_propagator |
Definition at line 248 of file internal.hpp.
| vector<unsigned> CaDiCaL::Internal::frozentab |
Definition at line 223 of file internal.hpp.
Definition at line 233 of file internal.hpp.
| vector<int64_t> CaDiCaL::Internal::gtab |
Definition at line 235 of file internal.hpp.
| vector<int> CaDiCaL::Internal::i2e |
Definition at line 224 of file internal.hpp.
| Clause* CaDiCaL::Internal::ignore |
Definition at line 243 of file internal.hpp.
| Inc CaDiCaL::Internal::inc |
Definition at line 289 of file internal.hpp.
Definition at line 214 of file internal.hpp.
| Internal* CaDiCaL::Internal::internal |
Definition at line 311 of file internal.hpp.
| bool CaDiCaL::Internal::iterating |
Definition at line 183 of file internal.hpp.
| Last CaDiCaL::Internal::last |
Definition at line 288 of file internal.hpp.
| int CaDiCaL::Internal::level |
Definition at line 219 of file internal.hpp.
| vector<int> CaDiCaL::Internal::levels |
Definition at line 266 of file internal.hpp.
| Limit CaDiCaL::Internal::lim |
Definition at line 287 of file internal.hpp.
| Links CaDiCaL::Internal::links |
Definition at line 227 of file internal.hpp.
Definition at line 325 of file internal.hpp.
| bool CaDiCaL::Internal::localsearching |
Definition at line 184 of file internal.hpp.
| bool CaDiCaL::Internal::lookingahead |
Definition at line 185 of file internal.hpp.
| bool CaDiCaL::Internal::lrat |
Definition at line 217 of file internal.hpp.
| vector<int64_t> CaDiCaL::Internal::lrat_chain |
Definition at line 210 of file internal.hpp.
| bool CaDiCaL::Internal::marked_failed |
Definition at line 264 of file internal.hpp.
| vector<signed char> CaDiCaL::Internal::marks |
Definition at line 222 of file internal.hpp.
| const unsigned CaDiCaL::Internal::max_used = 255 |
Definition at line 314 of file internal.hpp.
| int CaDiCaL::Internal::max_var |
Definition at line 200 of file internal.hpp.
| vector<int64_t> CaDiCaL::Internal::mini_chain |
Definition at line 211 of file internal.hpp.
| vector<int64_t> CaDiCaL::Internal::minimize_chain |
Definition at line 212 of file internal.hpp.
| vector<int> CaDiCaL::Internal::minimized |
Definition at line 270 of file internal.hpp.
| int CaDiCaL::Internal::mode |
Definition at line 177 of file internal.hpp.
| Clause* CaDiCaL::Internal::newest_clause |
Definition at line 246 of file internal.hpp.
| size_t CaDiCaL::Internal::no_conflict_until |
Definition at line 258 of file internal.hpp.
| size_t CaDiCaL::Internal::notified |
Definition at line 251 of file internal.hpp.
| vector<int64_t> CaDiCaL::Internal::ntab |
Definition at line 239 of file internal.hpp.
| size_t CaDiCaL::Internal::num_assigned |
Definition at line 279 of file internal.hpp.
| Options CaDiCaL::Internal::opts |
Definition at line 301 of file internal.hpp.
| vector<int> CaDiCaL::Internal::original |
Definition at line 265 of file internal.hpp.
| int64_t CaDiCaL::Internal::original_id |
Definition at line 202 of file internal.hpp.
Definition at line 236 of file internal.hpp.
| vector<int> CaDiCaL::Internal::parents |
Definition at line 232 of file internal.hpp.
| Phases CaDiCaL::Internal::phases |
Definition at line 220 of file internal.hpp.
| string CaDiCaL::Internal::prefix |
Definition at line 309 of file internal.hpp.
| bool CaDiCaL::Internal::preprocessing |
Definition at line 186 of file internal.hpp.
| bool CaDiCaL::Internal::private_steps |
Definition at line 196 of file internal.hpp.
| Clause* CaDiCaL::Internal::probe_reason |
Definition at line 252 of file internal.hpp.
Definition at line 216 of file internal.hpp.
| vector<int> CaDiCaL::Internal::probes |
Definition at line 281 of file internal.hpp.
| Proof* CaDiCaL::Internal::proof |
Definition at line 294 of file internal.hpp.
| size_t CaDiCaL::Internal::propagated |
Definition at line 253 of file internal.hpp.
| size_t CaDiCaL::Internal::propagated2 |
Definition at line 254 of file internal.hpp.
| size_t CaDiCaL::Internal::propergated |
Definition at line 255 of file internal.hpp.
| bool CaDiCaL::Internal::protected_reasons |
Definition at line 187 of file internal.hpp.
| vector<int> CaDiCaL::Internal::ptab |
Definition at line 238 of file internal.hpp.
| Queue CaDiCaL::Internal::queue |
Definition at line 226 of file internal.hpp.
| Reap CaDiCaL::Internal::reap |
Definition at line 272 of file internal.hpp.
| vector<unsigned> CaDiCaL::Internal::relevanttab |
Definition at line 225 of file internal.hpp.
| Reluctant CaDiCaL::Internal::reluctant |
Definition at line 198 of file internal.hpp.
| char CaDiCaL::Internal::rephased |
Definition at line 197 of file internal.hpp.
| bool CaDiCaL::Internal::reported |
Definition at line 191 of file internal.hpp.
| int64_t CaDiCaL::Internal::reserved_ids |
Definition at line 203 of file internal.hpp.
Definition at line 237 of file internal.hpp.
| int64_t CaDiCaL::Internal::saved_decisions |
Definition at line 205 of file internal.hpp.
| double CaDiCaL::Internal::score_inc |
Definition at line 228 of file internal.hpp.
| ScoreSchedule CaDiCaL::Internal::scores |
Definition at line 229 of file internal.hpp.
| bool CaDiCaL::Internal::searching_lucky_phases |
Definition at line 189 of file internal.hpp.
| vector<int> CaDiCaL::Internal::shrinkable |
Definition at line 271 of file internal.hpp.
| vector<int> CaDiCaL::Internal::sign_marked |
Definition at line 269 of file internal.hpp.
| vector<double> CaDiCaL::Internal::stab |
Definition at line 230 of file internal.hpp.
| bool CaDiCaL::Internal::stable |
Definition at line 190 of file internal.hpp.
| vector<StatTracer *> CaDiCaL::Internal::stat_tracers |
Definition at line 299 of file internal.hpp.
| Stats CaDiCaL::Internal::stats |
Definition at line 302 of file internal.hpp.
| bool CaDiCaL::Internal::sweep_incomplete |
Definition at line 275 of file internal.hpp.
| vector<int> CaDiCaL::Internal::sweep_schedule |
Definition at line 274 of file internal.hpp.
| int CaDiCaL::Internal::tainted_literal |
Definition at line 250 of file internal.hpp.
| size_t CaDiCaL::Internal::target_assigned |
Definition at line 257 of file internal.hpp.
| volatile bool CaDiCaL::Internal::termination_forced |
Definition at line 320 of file internal.hpp.
| int CaDiCaL::Internal::tier1[2] |
Definition at line 178 of file internal.hpp.
| int CaDiCaL::Internal::tier2[2] |
Definition at line 180 of file internal.hpp.
Definition at line 296 of file internal.hpp.
| vector<int> CaDiCaL::Internal::trail |
Definition at line 259 of file internal.hpp.
| vector<int> CaDiCaL::Internal::unit_analyzed |
Definition at line 268 of file internal.hpp.
| vector<int64_t> CaDiCaL::Internal::unit_chain |
Definition at line 213 of file internal.hpp.
| vector<int64_t> CaDiCaL::Internal::unit_clauses_idx |
Definition at line 209 of file internal.hpp.
| bool CaDiCaL::Internal::unsat |
Definition at line 182 of file internal.hpp.
| bool CaDiCaL::Internal::unsat_constraint |
Definition at line 263 of file internal.hpp.
| signed char* CaDiCaL::Internal::vals |
Definition at line 221 of file internal.hpp.
Definition at line 324 of file internal.hpp.
| size_t CaDiCaL::Internal::vsize |
Definition at line 199 of file internal.hpp.
Definition at line 231 of file internal.hpp.
Definition at line 241 of file internal.hpp.