#include "fraigInt.h"
Go to the source code of this file.
Macros | |
| #define | Fraig_NodeIsSimComplement(p) |
| DECLARATIONS ///. | |
Functions | |
| Fraig_Node_t * | Fraig_NodeCreateConst (Fraig_Man_t *p) |
| FUNCTION DEFINITIONS ///. | |
| Fraig_Node_t * | Fraig_NodeCreatePi (Fraig_Man_t *p) |
| Fraig_Node_t * | Fraig_NodeCreate (Fraig_Man_t *p, Fraig_Node_t *p1, Fraig_Node_t *p2) |
| void | Fraig_NodeSimulate (Fraig_Node_t *pNode, int iWordStart, int iWordStop, int fUseRand) |
| #define Fraig_NodeIsSimComplement | ( | p | ) |
DECLARATIONS ///.
CFile****************************************************************
FileName [fraigNode.c]
PackageName [FRAIG: Functionally reduced AND-INV graphs.]
Synopsis [Implementation of the FRAIG node.]
Author [Alan Mishchenko alanm.nosp@m.i@ee.nosp@m.cs.be.nosp@m.rkel.nosp@m.ey.ed.nosp@m.u]
Affiliation [UC Berkeley]
Date [Ver. 2.0. Started - October 1, 2004]
Revision [
]
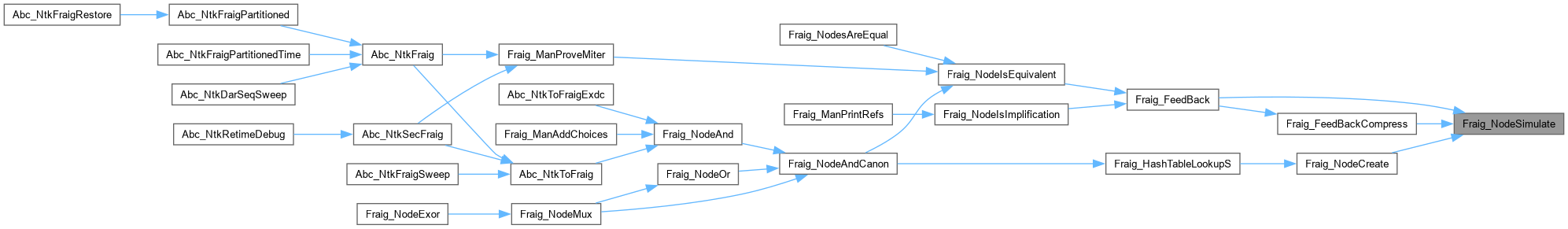
Definition at line 29 of file fraigNode.c.
| Fraig_Node_t * Fraig_NodeCreate | ( | Fraig_Man_t * | p, |
| Fraig_Node_t * | p1, | ||
| Fraig_Node_t * | p2 ) |
Function*************************************************************
Synopsis [Creates a new node.]
Description [This procedure should be called to create the constant node and the PI nodes first.]
SideEffects []
SeeAlso []
Definition at line 160 of file fraigNode.c.
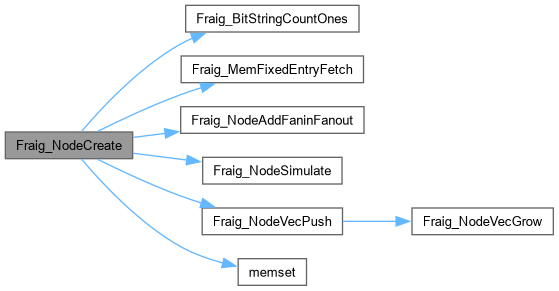
| Fraig_Node_t * Fraig_NodeCreateConst | ( | Fraig_Man_t * | p | ) |
FUNCTION DEFINITIONS ///.
Function*************************************************************
Synopsis [Creates the constant 1 node.]
Description []
SideEffects []
SeeAlso []
Definition at line 46 of file fraigNode.c.
| Fraig_Node_t * Fraig_NodeCreatePi | ( | Fraig_Man_t * | p | ) |
Function*************************************************************
Synopsis [Creates a primary input node.]
Description []
SideEffects []
SeeAlso []
Definition at line 87 of file fraigNode.c.
| void Fraig_NodeSimulate | ( | Fraig_Node_t * | pNode, |
| int | iWordStart, | ||
| int | iWordStop, | ||
| int | fUseRand ) |
Function*************************************************************
Synopsis [Simulates the node.]
Description [Simulates the random or dynamic simulation info through the node. Uses phases of the children to determine their real simulation info. Uses phase of the node to determine the way its simulation info is stored. The resulting info is guaranteed to be 0 for the first pattern.]
SideEffects [This procedure modified the hash value of the simulation info.]
SeeAlso []
Definition at line 226 of file fraigNode.c.